Abstract
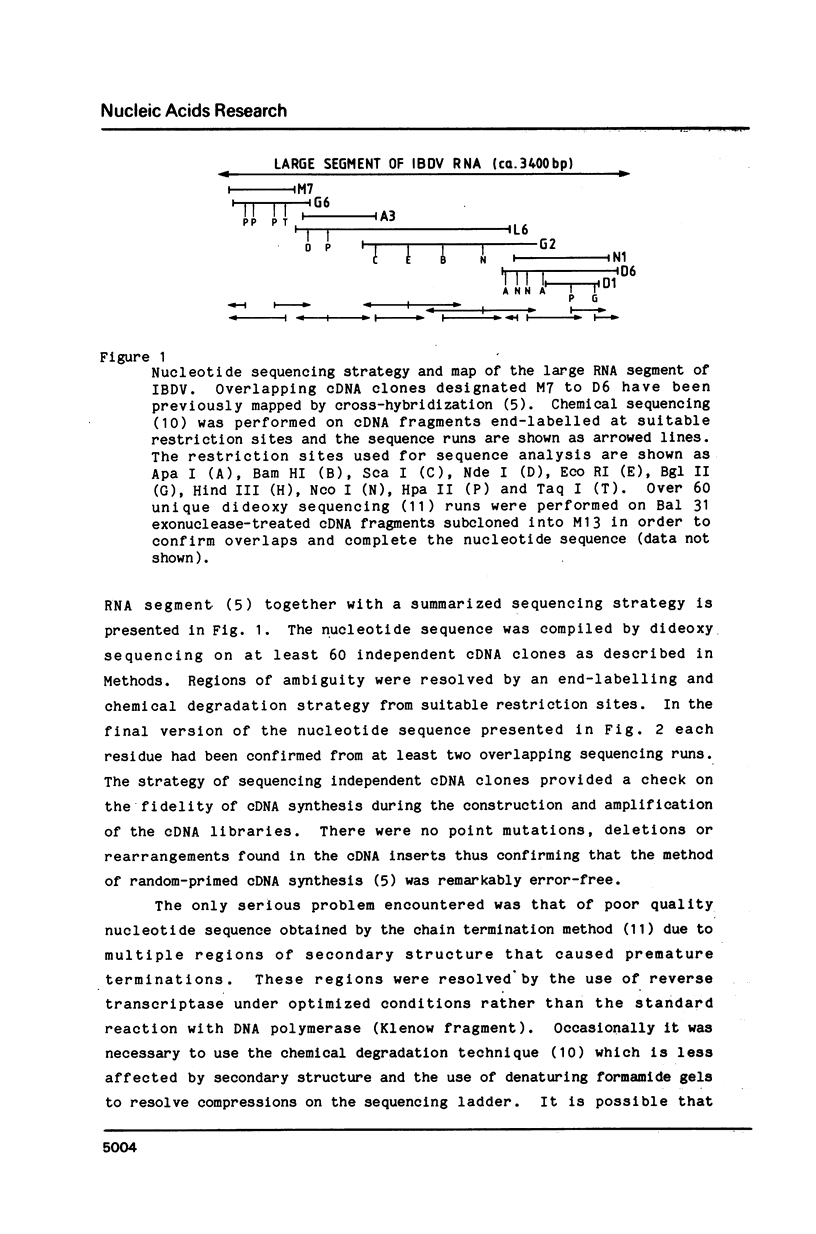
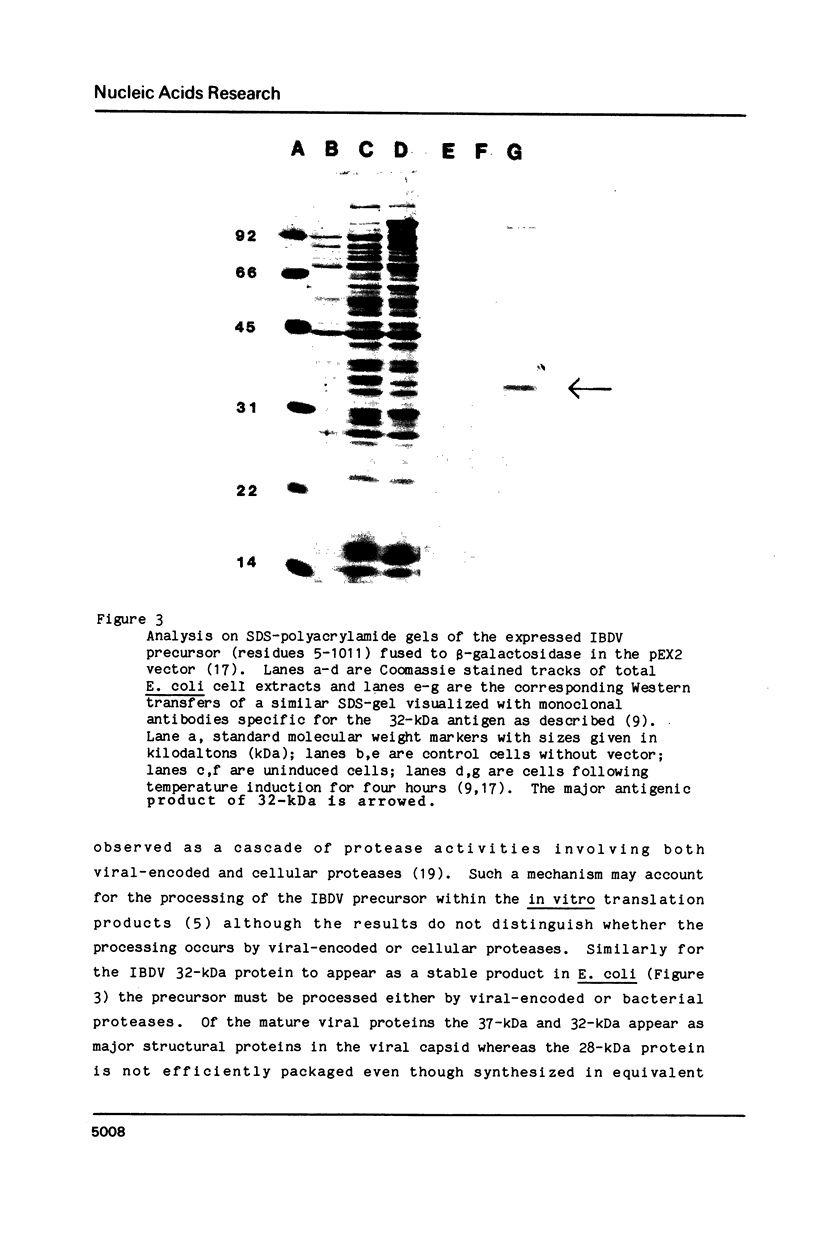
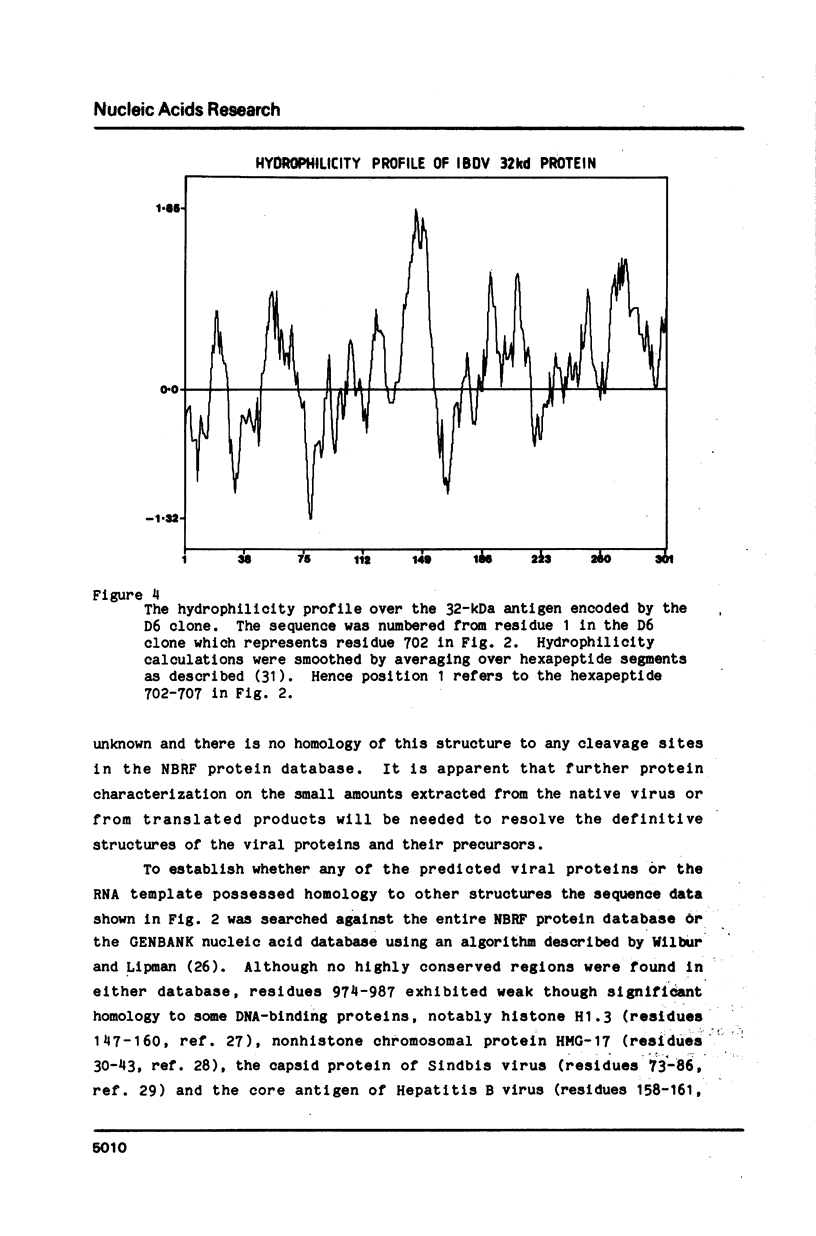
The larger RNA segment of infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV: Australian strain 002-73) has been characterized by cDNA cloning and nucleotide sequence analysis. We believe IBDV is the first birnavirus to be sequenced and so have confirmed the coding region by N-terminal amino acid sequence analysis of intact viral proteins and several tryptic peptide fragments. The large RNA segment encodes in order the 37-kDa, 28-kDa and 32-kDa proteins within a continuous open reading frame and the primary translation product appears to be subsequently processed into the mature viral proteins. The large protein precursor is still processed into the 32-kDa host protective immunogen when expressed as a fusion protein in E. coli. These results are in marked contrast to the predictions from in vitro translation data that birnavirus genomes are expressed as polycistronic templates. We can now propose that birnaviruses, in particular IBDV, possess monocistronic segments and that the precursor is proteolytically processed in vivo. The sequence data presented for the 32-kDa host protective immunogen may provide the basic information needed for the production of an effective subunit vaccine against this commercially important virus.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azad A. A., Barrett S. A., Fahey K. J. The characterization and molecular cloning of the double-stranded RNA genome of an Australian strain of infectious bursal disease virus. Virology. 1985 May;143(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azad A. A., Fahey K. J., Barrett S. A., Erny K. M., Hudson P. J. Expression in Escherichia coli of cDNA fragments encoding the gene for the host-protective antigen of infectious bursal disease virus. Virology. 1986 Mar;149(2):190–198. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90120-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobos P., Hill B. J., Hallett R., Kells D. T., Becht H., Teninges D. Biophysical and biochemical characterization of five animal viruses with bisegmented double-stranded RNA genomes. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):593–605. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.593-605.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey K. J., O'Donnell I. J., Azad A. A. Characterization by Western blotting of the immunogens of infectious bursal disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1985 Jul;66(Pt 7):1479–1488. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-7-1479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey K. J., O'Donnell I. J., Bagust T. J. Antibody to the 32K structural protein of infectious bursal disease virus neutralizes viral infectivity in vitro and confers protection on young chickens. J Gen Virol. 1985 Dec;66(Pt 12):2693–2702. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-12-2693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubman M. J., Baxt B. Translation of foot-and-mouth disease virion RNA and processing of the primary cleavage products in a rabbit reticulocyte lysate. Virology. 1982 Jan 15;116(1):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90399-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanecak R., Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Proteolytic processing of poliovirus polypeptides: antibodies to polypeptide P3-7c inhibit cleavage at glutamine-glycine pairs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3973–3977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Sowder R., Copeland T. D., Smythers G., Oroszlan S. Quantitative separation of murine leukemia virus proteins by reversed-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography reveals newly described gag and env cleavage products. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):492–500. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.492-500.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Calnek B. W. In vitro replication of infectious bursal disease virus in established lymphoid cell lines and chicken B lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):964–970. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.964-970.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson P., Haley J., Cronk M., Shine J., Niall H. Molecular cloning and characterization of cDNA sequences coding for rat relaxin. Nature. 1981 May 14;291(5811):127–131. doi: 10.1038/291127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klump W., Marquardt O., Hofschneider P. H. Biologically active protease of foot and mouth disease virus is expressed from cloned viral cDNA in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3351–3355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A. Tapping the immunological repertoire to produce antibodies of predetermined specificity. Nature. 1982 Oct 14;299(5884):593–596. doi: 10.1038/299592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKern N. M., O'Donnell I. J., Stewart D. J., Clark B. L. Primary structure of pilin protein from Bacteroides nodosus strain 216: comparison with the corresponding protein from strain 198. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Jan;131(1):1–6. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens P. P., Dobos P. Messenger RNA of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus is polycistronic. Nature. 1982 May 20;297(5863):243–246. doi: 10.1038/297243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasek M., Goto T., Gilbert W., Zink B., Schaller H., MacKay P., Leadbetter G., Murray K. Hepatitis B virus genes and their expression in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):575–579. doi: 10.1038/282575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. D., Nehrlich S., Oyer P. E., Steiner D. F. Determination of the amino acid sequence of the monkey, sheep, and dog proinsulin C-peptides by a semi-micro Edman degradation procedure. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 10;247(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. M., Strauss J. H. Nucleotide sequence of the 26S mRNA of Sindbis virus and deduced sequence of the encoded virus structural proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2062–2066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Müller-Hill B. Easy identification of cDNA clones. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1791–1794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Luzio J. P. Construction of a new family of high efficiency bacterial expression vectors: identification of cDNA clones coding for human liver proteins. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1429–1434. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Quinn P. S., Chan S. J., Marsh J., Tager H. S. Processing mechanisms in the biosynthesis of proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;343:1–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb47238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian Y. C., Shih D. S. Cleavage of a viral polyprotein by a cellular proteolytic activity. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):547–551. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.547-551.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. M., Stearn C., Johns E. W. The primary structure of non-histone chromosomal protein HMG17 from chicken erythrocyte nuclei. FEBS Lett. 1980 Apr 7;112(2):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80181-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur W. J., Lipman D. J. Rapid similarity searches of nucleic acid and protein data banks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyeth P. J., Cullen G. A. The use of an inactivated infectious bursal disease oil emulsion vaccine in commercial broiler parent chickens. Vet Rec. 1979 Mar 3;104(9):188–193. doi: 10.1136/vr.104.9.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]