Abstract
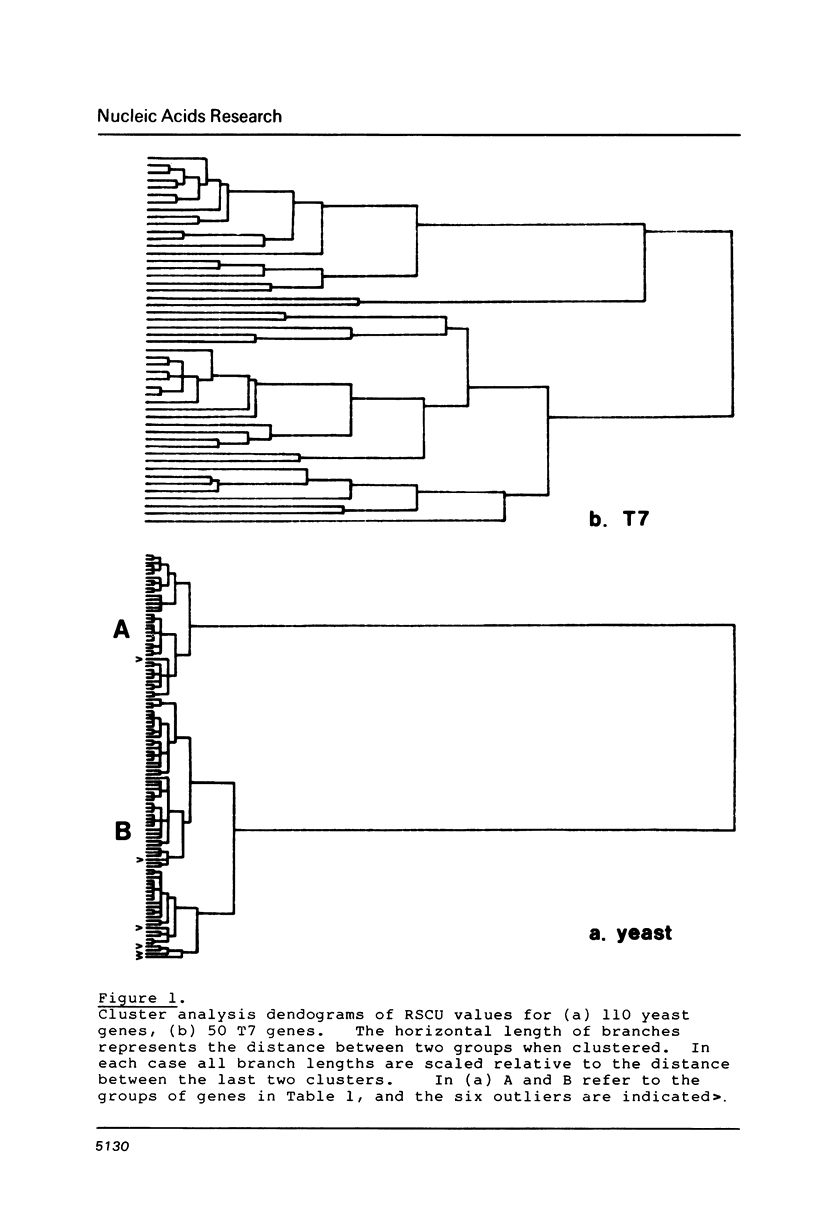
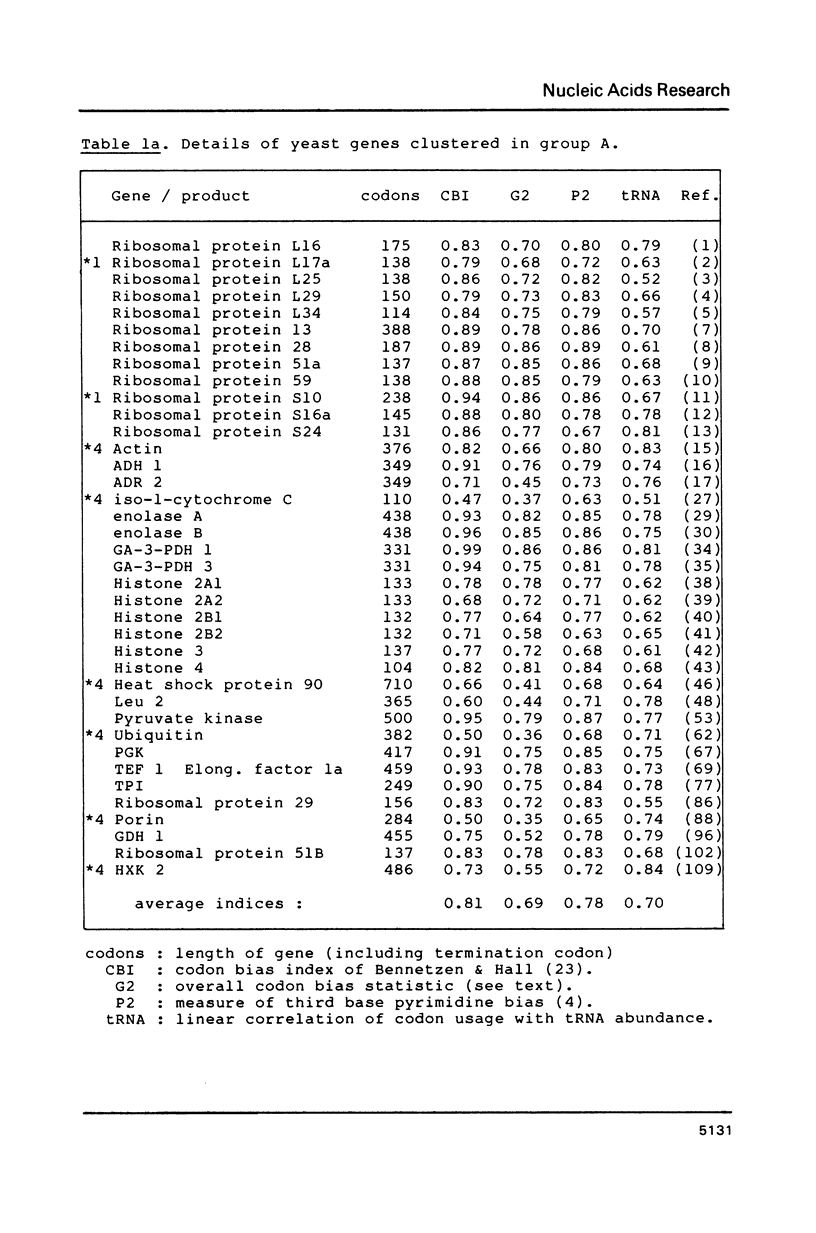
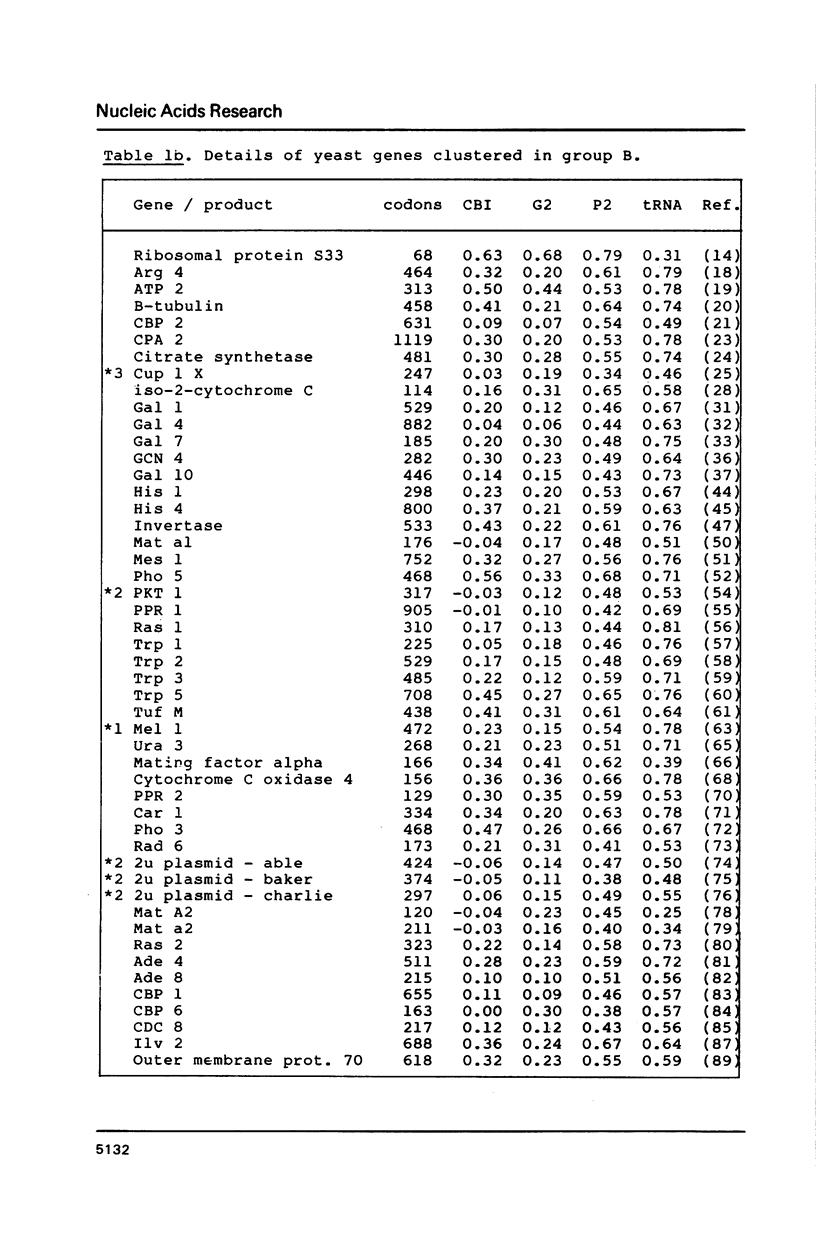
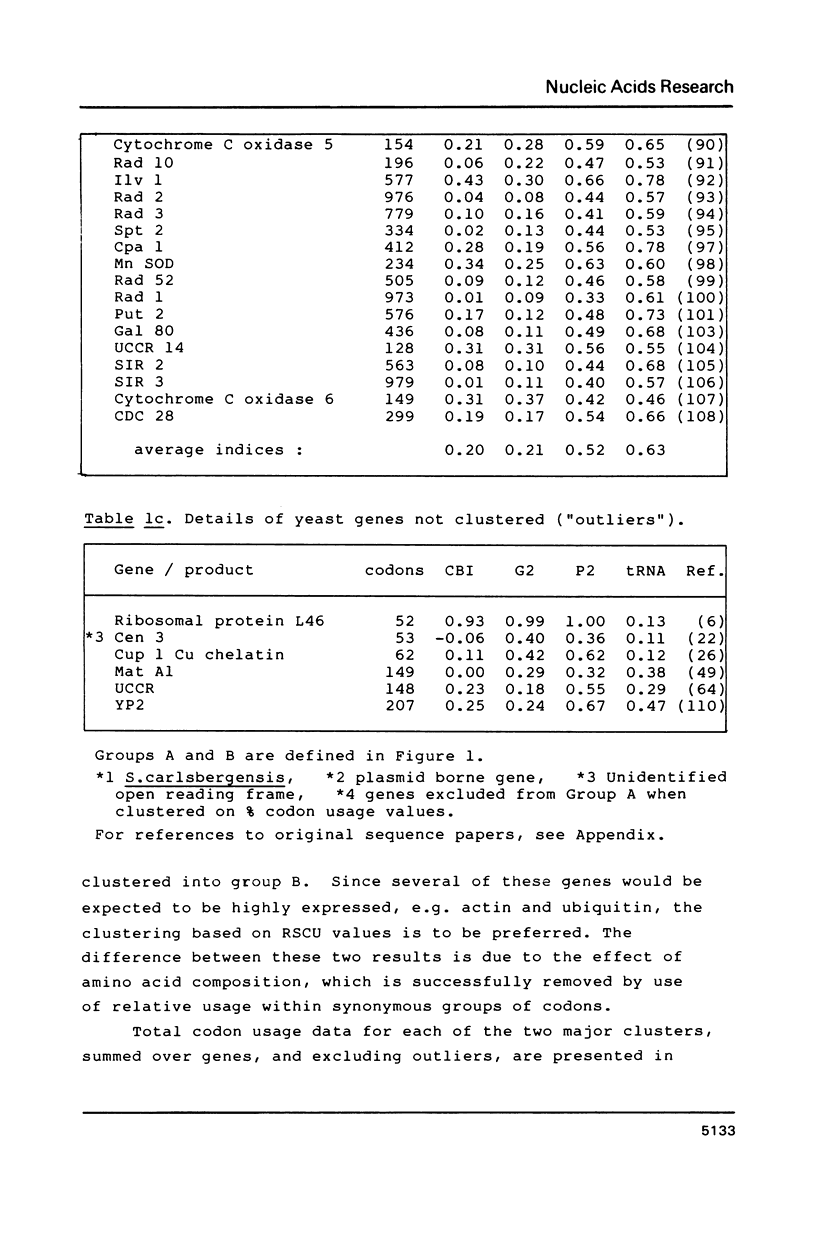
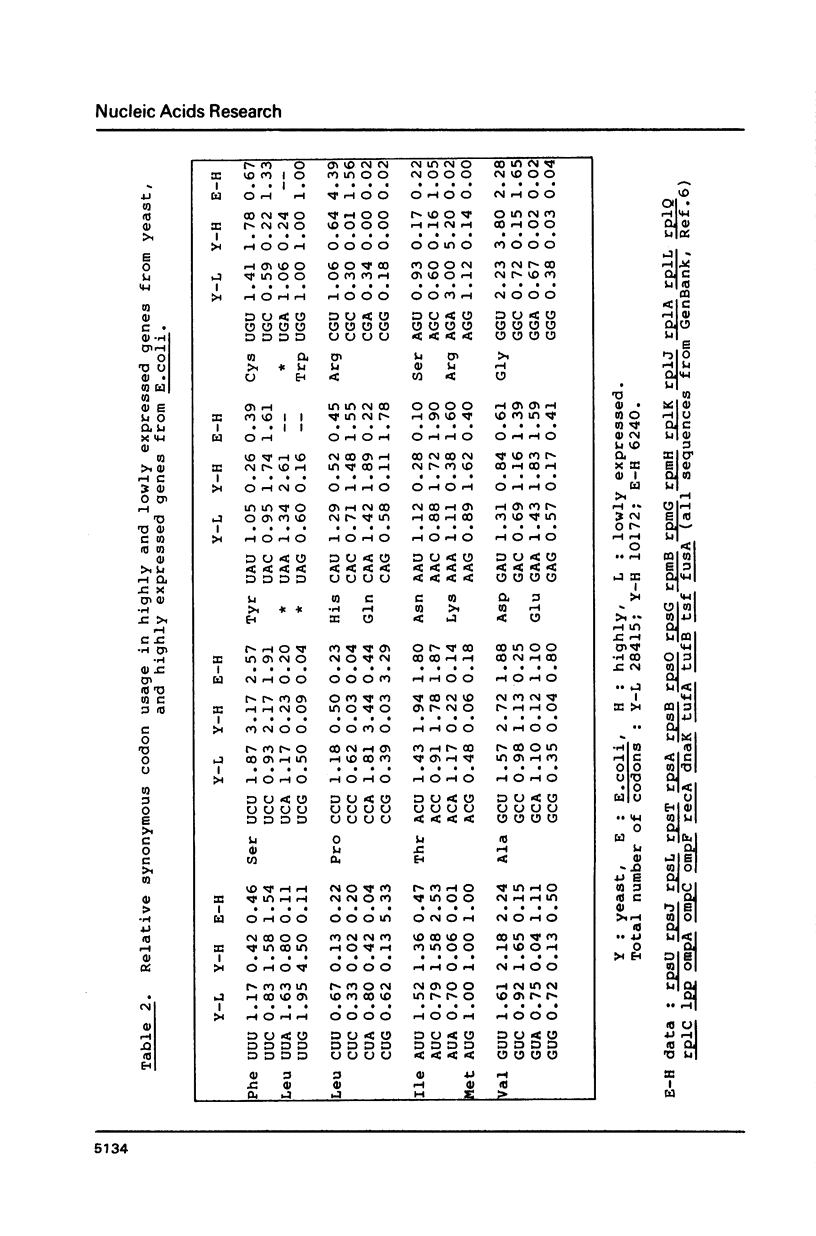
Codon usage data has been compiled for 110 yeast genes. Cluster analysis on relative synonymous codon usage revealed two distinct groups of genes. One group corresponds to highly expressed genes, and has much more extreme synonymous codon preference. The pattern of codon usage observed is consistent with that expected if a need to match abundant tRNAs, and intermediacy of tRNA-mRNA interaction energies are important selective constraints. Thus codon usage in the highly expressed group shows a higher correlation with tRNA abundance, a greater degree of third base pyrimidine bias, and a lesser tendency to the A+T richness which is characteristic of the yeast genome. The cluster analysis can be used to predict the likely level of gene expression of any gene, and identifies the pattern of codon usage likely to yield optimal gene expression in yeast.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abovich N., Rosbash M. Two genes for ribosomal protein 51 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae complement and contribute to the ribosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1871–1879. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adzuma K., Ogawa T., Ogawa H. Primary structure of the RAD52 gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2735–2744. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alber T., Kawasaki G. Nucleotide sequence of the triose phosphate isomerase gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(5):419–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson S. G., Buckingham R. H., Kurland C. G. Does codon composition influence ribosome function? EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):91–94. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01766.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreadis A., Hsu Y. P., Hermodson M., Kohlhaw G., Schimmel P. Yeast LEU2. Repression of mRNA levels by leucine and primary structure of the gene product. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8059–8062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arima K., Oshima T., Kubota I., Nakamura N., Mizunaga T., Toh-e A. The nucleotide sequence of the yeast PHO5 gene: a putative precursor of repressible acid phosphatase contains a signal peptide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1657–1672. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astell C. R., Ahlstrom-Jonasson L., Smith M., Tatchell K., Nasmyth K. A., Hall B. D. The sequence of the DNAs coding for the mating-type loci of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90356-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajwa W., Meyhack B., Rudolph H., Schweingruber A. M., Hinnen A. Structural analysis of the two tandemly repeated acid phosphatase genes in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7721–7739. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beacham I. R., Schweitzer B. W., Warrick H. M., Carbon J. The nucleotide sequence of the yeast ARG4 gene. Gene. 1984 Sep;29(3):271–279. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. Codon selection in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3026–3031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. The primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene for alcohol dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3018–3025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Findlay P. R., Johnson M. W. The relationship between base composition and codon usage in bacterial genes and its use for the simple and reliable identification of protein-coding sequences. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeyer L. G., Hill J. C., Dumas L. B. Saccharomyces cerevisiae CDC8 gene and its product. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):583–590. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostian K. A., Elliott Q., Bussey H., Burn V., Smith A., Tipper D. J. Sequence of the preprotoxin dsRNA gene of type I killer yeast: multiple processing events produce a two-component toxin. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):741–751. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90354-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. L., Tekamp-Olson P., Najarian R. The isolation, characterization, and sequence of the pyruvate kinase gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2193–2201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Taussig R., Kustu S., Botstein D. The secreted form of invertase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is synthesized from mRNA encoding a signal sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;3(3):439–447. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.3.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choe J., Kolodrubetz D., Grunstein M. The two yeast histone H2A genes encode similar protein subtypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1484–1487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citron B. A., Donelson J. E. Sequence of the Saccharomyces GAL region and its transcription in vivo. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):269–278. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.269-278.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Haan M., van Loon A. P., Kreike J., Vaessen R. T., Grivell L. A. The biosynthesis of the ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase complex in yeast. DNA sequence analysis of the nuclear gene coding for the 14-kDa subunit. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 2;138(1):169–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07896.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar R., Nieto A., Koller R., DeFeo-Jones D., Scolnick E. M. Nucleotide sequence of two rasH related-genes isolated from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 25;12(8):3611–3618. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.8.3611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieckmann C. L., Homison G., Tzagoloff A. Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system. Nucleotide sequence of a yeast nuclear gene (CBP1) involved in 5' end processing of cytochrome b pre-mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):4732–4738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieckmann C. L., Tzagoloff A. Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system. CBP6, a yeast nuclear gene necessary for synthesis of cytochrome b. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1513–1520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue T. F., Farabaugh P. J., Fink G. R. The nucleotide sequence of the HIS4 region of yeast. Gene. 1982 Apr;18(1):47–59. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90055-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falco S. C., Dumas K. S., Livak K. J. Nucleotide sequence of the yeast ILV2 gene which encodes acetolactate synthase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 11;13(11):4011–4027. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.11.4011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrelly F. W., Finkelstein D. B. Complete sequence of the heat shock-inducible HSP90 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5745–5751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald-Hayes M., Clarke L., Carbon J. Nucleotide sequence comparisons and functional analysis of yeast centromere DNAs. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):235–244. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90108-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fröhlich K. U., Entian K. D., Mecke D. The primary structure of the yeast hexokinase PII gene (HXK2) which is responsible for glucose repression. Gene. 1985;36(1-2):105–111. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Donath C., Sander C. A yeast gene encoding a protein homologous to the human c-has/bas proto-oncogene product. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):704–707. doi: 10.1038/306704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Sures I. Structure of a split yeast gene: complete nucleotide sequence of the actin gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2546–2550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouy M., Gautier C. Codon usage in bacteria: correlation with gene expressivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7055–7074. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham R., Gautier C., Gouy M., Jacobzone M., Mercier R. Codon catalog usage is a genome strategy modulated for gene expressivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):r43–r74. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.213-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham R., Gautier C., Gouy M., Mercier R., Pavé A. Codon catalog usage and the genome hypothesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):r49–r62. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.197-c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosjean H., Fiers W. Preferential codon usage in prokaryotic genes: the optimal codon-anticodon interaction energy and the selective codon usage in efficiently expressed genes. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90157-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. L., Donelson J. E. Nucleotide sequence of the yeast plasmid. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):860–865. doi: 10.1038/286860a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hase T., Riezman H., Suda K., Schatz G. Import of proteins into mitochondria: nucleotide sequence of the gene for a 70-kd protein of the yeast mitochondrial outer membrane. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2169–2172. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01718.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G. Evidence for translational regulation of the activator of general amino acid control in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6442–6446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G., Fink G. R. Repeated DNA sequences upstream from HIS1 also occur at several other co-regulated genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5238–5247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitzeman R. A., Hagie F. E., Hayflick J. S., Chen C. Y., Seeburg P. H., Derynck R. The primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene for 3-phosphoglycerate kinase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7791–7808. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. P., Holland M. J. The primary structure of a glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9839–9845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. P., Labieniec L., Swimmer C., Holland M. J. Homologous nucleotide sequences at the 5' termini of messenger RNAs synthesized from the yeast enolase and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene families. The primary structure of a third yeast glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5291–5299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland M. J., Holland J. P., Thill G. P., Jackson K. A. The primary structures of two yeast enolase genes. Homology between the 5' noncoding flanking regions of yeast enolase and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 10;256(3):1385–1395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubert J. C., Guyonvarch A., Kammerer B., Exinger F., Liljelund P., Lacroute F. Complete sequence of a eukaryotic regulatory gene. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):2071–2073. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01702.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Codon usage and tRNA content in unicellular and multicellular organisms. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Jan;2(1):13–34. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes: a proposal for a synonymous codon choice that is optimal for the E. coli translational system. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):389–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Correlation between the abundance of yeast transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in protein genes. Differences in synonymous codon choice patterns of yeast and Escherichia coli with reference to the abundance of isoaccepting transfer RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 15;158(4):573–597. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90250-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston T. C., Borgia P. T., Parker J. Codon specificity of starvation induced misreading. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(3):459–465. doi: 10.1007/BF00341447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammerer B., Guyonvarch A., Hubert J. C. Yeast regulatory gene PPR1. I. Nucleotide sequence, restriction map and codon usage. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 5;180(2):239–250. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammerer B., Guyonvarch A., Hubert J. C. Yeast regulatory gene PPR1. I. Nucleotide sequence, restriction map and codon usage. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 5;180(2):239–250. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Najarian R., Haslinger A., Valenzuela P., Welch J., Fogel S. Primary structure and transcription of an amplified genetic locus: the CUP1 locus of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):337–341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krzywicki K. A., Brandriss M. C. Primary structure of the nuclear PUT2 gene involved in the mitochondrial pathway for proline utilization in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2837–2842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurjan J., Herskowitz I. Structure of a yeast pheromone gene (MF alpha): a putative alpha-factor precursor contains four tandem copies of mature alpha-factor. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):933–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90298-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käufer N. F., Fried H. M., Schwindinger W. F., Jasin M., Warner J. R. Cycloheximide resistance in yeast: the gene and its protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 25;11(10):3123–3135. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.10.3123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R. Synthetic oligonucleotide probes deduced from amino acid sequence data. Theoretical and practical considerations. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 5;183(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon A., Gesteland R. F. Primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL4 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):260–267. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leer R. J., van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Hagendoorn M. J., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. Structural comparison of yeast ribosomal protein genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 11;12(17):6685–6700. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.17.6685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leer R. J., van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Kraakman P., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. The genes for yeast ribosomal proteins S24 and L46 are adjacent and divergently transcribed. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):701–709. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leer R. J., van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Molenaar C. M., Cohen L. H., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. The structure of the gene coding for the phosphorylated ribosomal protein S10 in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5869–5878. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leer R. J., van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Schoppink P. J., Cornelissen M. T., Cohen L. H., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. Yeast ribosomal protein S33 is encoded by an unsplit gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7759–7768. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. H., Gojobori T., Nei M. Pseudogenes as a paradigm of neutral evolution. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):237–239. doi: 10.1038/292237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. H., Wu C. I., Luo C. C. A new method for estimating synonymous and nonsynonymous rates of nucleotide substitution considering the relative likelihood of nucleotide and codon changes. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Mar;2(2):150–174. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusty C. J., Widgren E. E., Broglie K. E., Nyunoya H. Yeast carbamyl phosphate synthetase. Structure of the yeast gene and homology to Escherichia coli carbamyl phosphate synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14466–14477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lörincz A. T., Reed S. I. Primary structure homology between the product of yeast cell division control gene CDC28 and vertebrate oncogenes. Nature. 1984 Jan 12;307(5947):183–185. doi: 10.1038/307183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maarse A. C., Van Loon A. P., Riezman H., Gregor I., Schatz G., Grivell L. A. Subunit IV of yeast cytochrome c oxidase: cloning and nucleotide sequencing of the gene and partial amino acid sequencing of the mature protein. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2831–2837. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02216.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marres C. A., Van Loon A. P., Oudshoorn P., Van Steeg H., Grivell L. A., Slater E. C. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the nuclear gene coding for manganese superoxide dismutase of yeast mitochondria, a gene previously assumed to code for the Rieske iron-sulphur protein. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Feb 15;147(1):153–161. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08731.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGraw P., Tzagoloff A. Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system. Characterization of a yeast nuclear gene involved in the processing of the cytochrome b pre-mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9459–9468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor J., Dobson M. J., Roberts N. A., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. Factors affecting heterologous gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1985;33(2):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90096-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara K., Sato R. Molecular cloning and sequencing of cDNA for yeast porin, an outer mitochondrial membrane protein: a search for targeting signal in the primary structure. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):769–774. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03695.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra G., Warner J. R. A yeast ribosomal protein gene whose intron is in the 5' leader. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9218–9224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata T., Hayashida H. Extraordinarily high evolutionary rate of pseudogenes: evidence for the presence of selective pressure against changes between synonymous codons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5739–5743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molenaar C. M., Woudt L. P., Jansen A. E., Mager W. H., Planta R. J., Donovan D. M., Pearson N. J. Structure and organization of two linked ribosomal protein genes in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 11;12(19):7345–7358. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.19.7345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery D. L., Leung D. W., Smith M., Shalit P., Faye G., Hall B. D. Isolation and sequence of the gene for iso-2-cytochrome c in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):541–545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moye W. S., Amuro N., Rao J. K., Zalkin H. Nucleotide sequence of yeast GDH1 encoding nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-dependent glutamate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8502–8508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäntsälä P., Zalkin H. Glutamine nucleotide sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae ADE4 encoding phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8478–8484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata S., Nagashima K., Tsunetsugu-Yokota Y., Fujimura K., Miyazaki M., Kaziro Y. Polypeptide chain elongation factor 1 alpha (EF-1 alpha) from yeast: nucleotide sequence of one of the two genes for EF-1 alpha from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1825–1830. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02053.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata S., Tsunetsugu-Yokota Y., Naito A., Kaziro Y. Molecular cloning and sequence determination of the nuclear gene coding for mitochondrial elongation factor Tu of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6192–6196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumovski L., Chu G., Berg P., Friedberg E. C. RAD3 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: nucleotide sequence of wild-type and mutant alleles, transcript mapping, and aspects of gene regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):17–26. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neff N. F., Thomas J. H., Grisafi P., Botstein D. Isolation of the beta-tubulin gene from yeast and demonstration of its essential function in vivo. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90350-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolet C. M., Chenevert J. M., Friedberg E. C. The RAD2 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: nucleotide sequence and transcript mapping. Gene. 1985;36(3):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogi Y., Fukasawa T. Nucleotide sequence of the yeast regulatory gene GAL80. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9287–9298. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussinov R. Doublet frequencies in evolutionary distinct groups. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1749–1763. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyunoya H., Lusty C. J. Sequence of the small subunit of yeast carbamyl phosphate synthetase and identification of its catalytic domain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9790–9798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogasawara N. Markedly unbiased codon usage in Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1985;40(1):145–150. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozkaynak E., Finley D., Varshavsky A. The yeast ubiquitin gene: head-to-tail repeats encoding a polyubiquitin precursor protein. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):663–666. doi: 10.1038/312663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S. Escherichia coli ribosomes translate in vivo with variable rate. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2895–2898. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02227.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds P., Weber S., Prakash L. RAD6 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a protein containing a tract of 13 consecutive aspartates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):168–172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M., Lilley R., Little S., Emtage J. S., Yarranton G., Stephens P., Millican A., Eaton M., Humphreys G. Codon usage can affect efficiency of translation of genes in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 11;12(17):6663–6671. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.17.6663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder G. S., Beard C., Smith M., Keranen S. Isolation and characterization of the SPT2 gene, a negative regulator of Ty-controlled yeast gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1543–1553. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M., Grisafi P., Botstein D. Structure and function of the yeast URA3 gene: expression in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1984 Jul-Aug;29(1-2):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90172-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. W., Smith M., Williamson V. M., Young E. T. Nucleotide sequence of the yeast alcohol dehydrogenase II gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2674–2682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltzgaber-Muller J., Kunapuli S. P., Douglas M. G. Nuclear genes coding the yeast mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase complex. Isolation of ATP2 coding the F1-ATPase beta subunit. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11465–11470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz L. D., Friesen J. D. Nucleotide sequence of the tcml gene (ribosomal protein L3) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):8–14. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.8-14.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Rogers M. S., McConnell D. J. Selection pressures on codon usage in the complete genome of bacteriophage T7. J Mol Evol. 1984;21(2):150–160. doi: 10.1007/BF02100089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Squire M., Nasmyth K. A. Characterization of two genes required for the position-effect control of yeast mating-type genes. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2817–2823. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02214.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. M., Andrésson O. S. DNA sequences of yeast H3 and H4 histone genes from two non-allelic gene sets encode identical H3 and H4 proteins. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 25;169(3):663–690. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M., Leung D. W., Gillam S., Astell C. R., Montgomery D. L., Hall B. D. Sequence of the gene for iso-1-cytochrome c in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):753–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Measurements of the effects that coding for a protein has on a DNA sequence and their use for finding genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):551–567. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suissa M., Suda K., Schatz G. Isolation of the nuclear yeast genes for citrate synthase and fifteen other mitochondrial proteins by a new screening method. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1773–1781. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02045.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner-Smith M., Bozzato R. P., Skipper N., Davies R. W., Hopper J. E. Analysis of the inducible MEL1 gene of Saccharomyces carlsbergensis and its secreted product, alpha-galactosidase (melibiase). Gene. 1985;36(3):333–340. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90188-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumrada R. A., Cooper T. G. Nucleotide sequence of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae arginase gene (CAR1) and its transcription under various physiological conditions. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):1078–1087. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.1078-1087.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séraphin B., Simon M., Faye G. Primary structure of a gene for subunit V of the cytochrome c oxidase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet. 1985;9(6):435–439. doi: 10.1007/BF00434047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teem J. L., Rosbash M. Expression of a beta-galactosidase gene containing the ribosomal protein 51 intron is sensitive to the rna2 mutation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4403–4407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thireos G., Penn M. D., Greer H. 5' untranslated sequences are required for the translational control of a yeast regulatory gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5096–5100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschumper G., Carbon J. Sequence of a yeast DNA fragment containing a chromosomal replicator and the TRP1 gene. Gene. 1980 Jul;10(2):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90133-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Loon A. P., De Groot R. J., De Haan M., Dekker A., Grivell L. A. The DNA sequence of the nuclear gene coding for the 17-kd subunit VI of the yeast ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase: a protein with an extremely high content of acidic amino acids. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1039–1043. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01924.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varenne S., Buc J., Lloubes R., Lazdunski C. Translation is a non-uniform process. Effect of tRNA availability on the rate of elongation of nascent polypeptide chains. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):549–576. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis J. W., Hereford L., Grunstein M. Histone H2B genes of yeast encode two different proteins. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):799–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90556-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Gangloff J., Bonnet J., Boulanger Y., Ebel J. P., Fasiolo F. Primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene for methionyl-tRNA synthetase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2437–2441. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss W. A., Friedberg E. C. Molecular cloning and characterization of the yeast RAD10 gene and expression of RAD10 protein in E. coli. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1575–1582. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03819.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. H., Lusnak K., Fogel S. Mismatch-specific post-meiotic segregation frequency in yeast suggests a heteroduplex recombination intermediate. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):350–352. doi: 10.1038/315350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright R. M., Ko C., Cumsky M. G., Poyton R. O. Isolation and sequence of the structural gene for cytochrome c oxidase subunit VI from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15401–15407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang E., Friedberg E. C. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence analysis of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAD1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2161–2169. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalkin H., Paluh J. L., van Cleemput M., Moye W. S., Yanofsky C. Nucleotide sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes TRP2 and TRP3 encoding bifunctional anthranilate synthase: indole-3-glycerol phosphate synthase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3985–3992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalkin H., Yanofsky C. Yeast gene TRP5: structure, function, regulation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1491–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



