Abstract
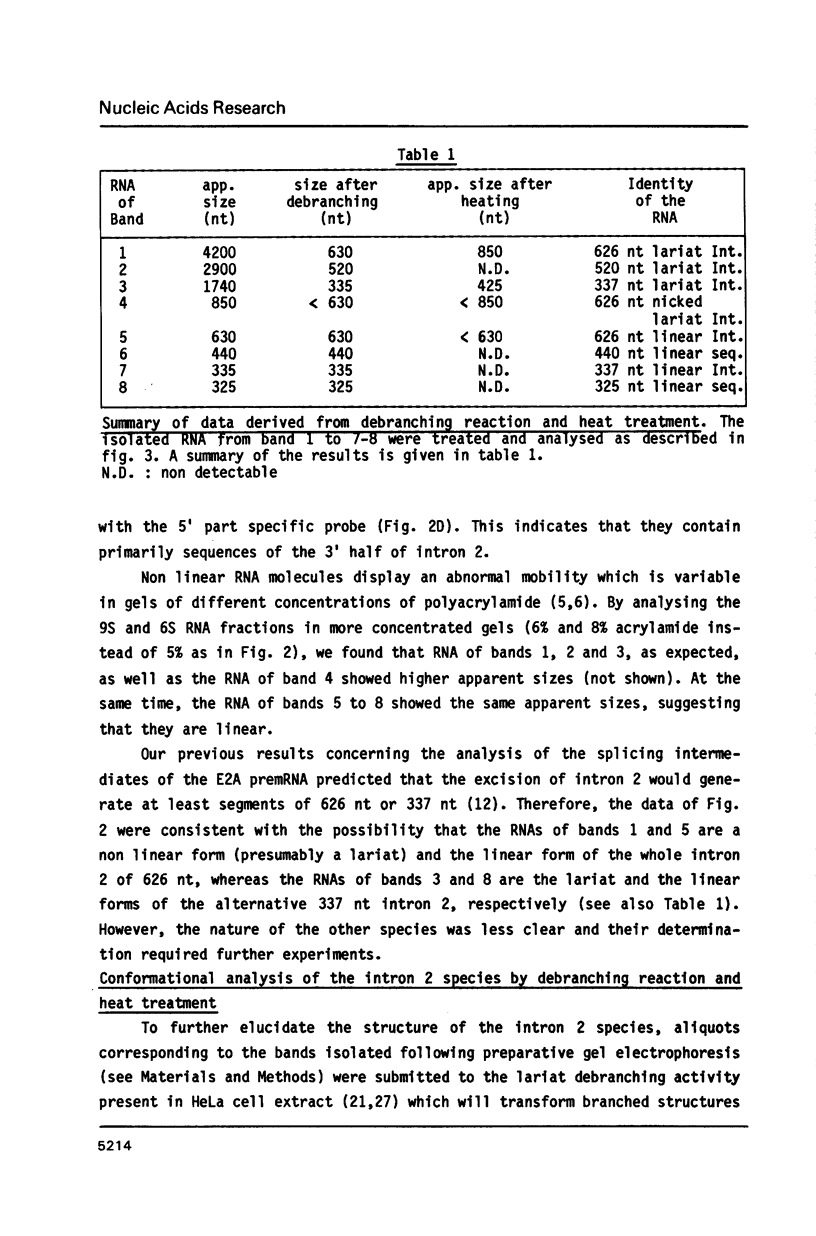
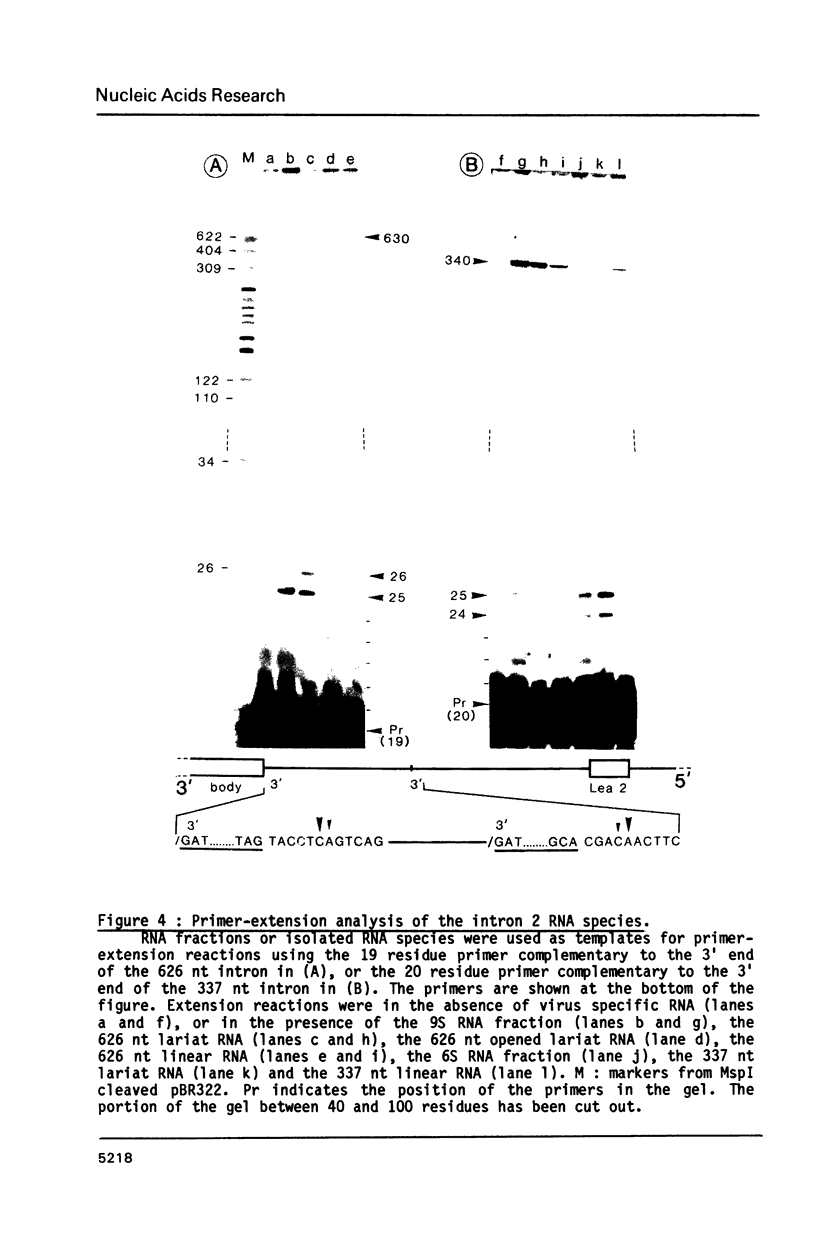
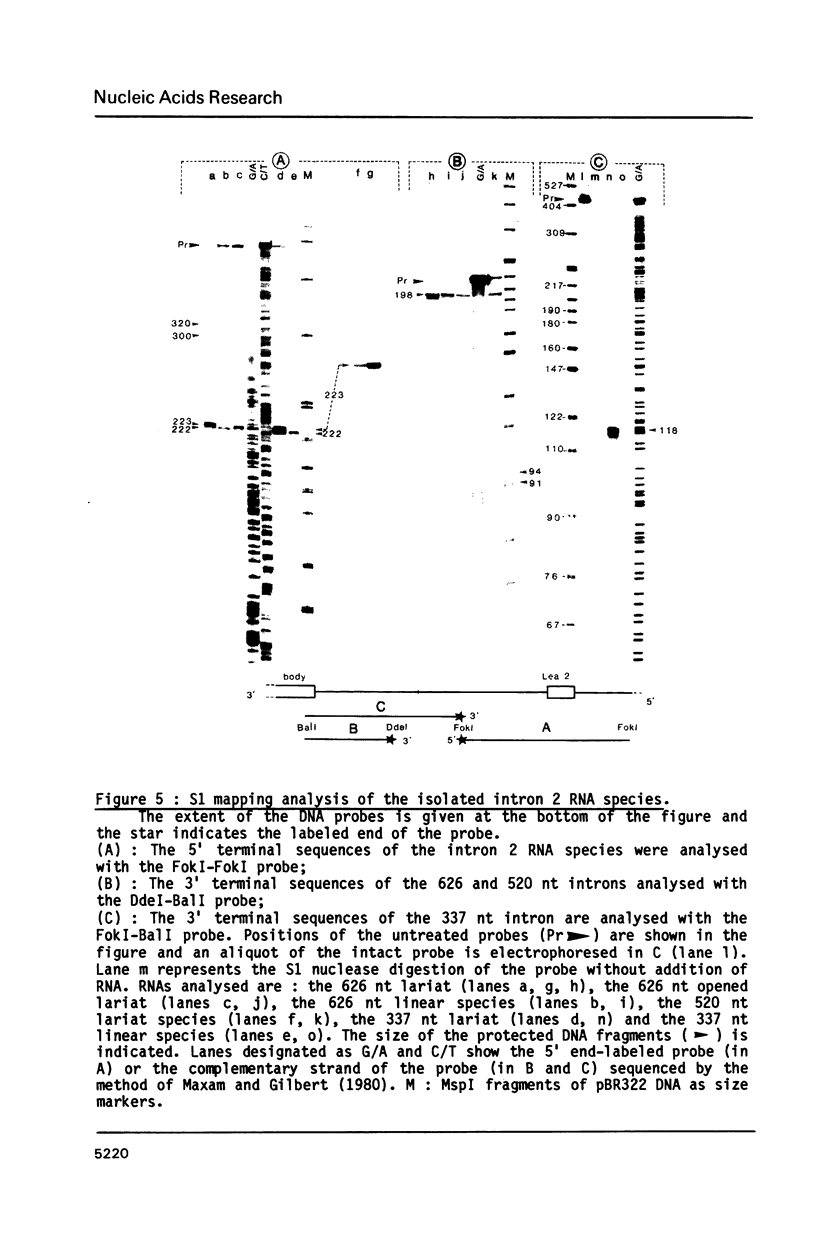
In the early period of cellular infection by adenovirus 2, the E2A region gives rise to 2 major mRNA species of 2.0 and 2.3 kilobases, formed by alternative excisions of intron 2 (Gattoni et al., 1986, J. Mol. Biol. 187, 379-307). We have analysed the excision pathways of this intron. Two major intron species of 626 and 337 nucleotides, generated by the use of 2 consensus 3' splicing sites and a minor intron species of 520 nucleotides, generated by the use of another weaker 3' splicing site, are identified, the 3 species sharing a common 5' splicing site. They are detected predominantly in the lariat form. For the 2 major species we analyzed, the branched nucleotides are localized at consensus branching sequences, 26 or 25 nucleotides upstream from the 3' terminal AG. Our results confirm that the first reactions of cleavage at the 5' end of introns and branching occur in vivo as described in in vitro systems. The second predominant form of intron 2 is the linear segment, whereas the nicked lariat form which is very minor, might not be a genuine product of in vivo splicing. All intron 2 molecules show practically intact 5' and 3' terminal sequences, indicating that they are well protected against nuclease attack throughout their life. Therefore, these results indicate that the primary reaction following the excision of the lariat intron is debranching. In addition, the existence of a potential 5' splicing site contiguous to the major internal 3' splicing site raised the possibility of an elimination of the major 626 nucleotide intron in 2 cycles of excision. However, we demonstrate that intron 2 is systematically excised by a one cycle process, which is likely to represent the general rule for the production of correctly spliced mRNA.
Full text
PDF




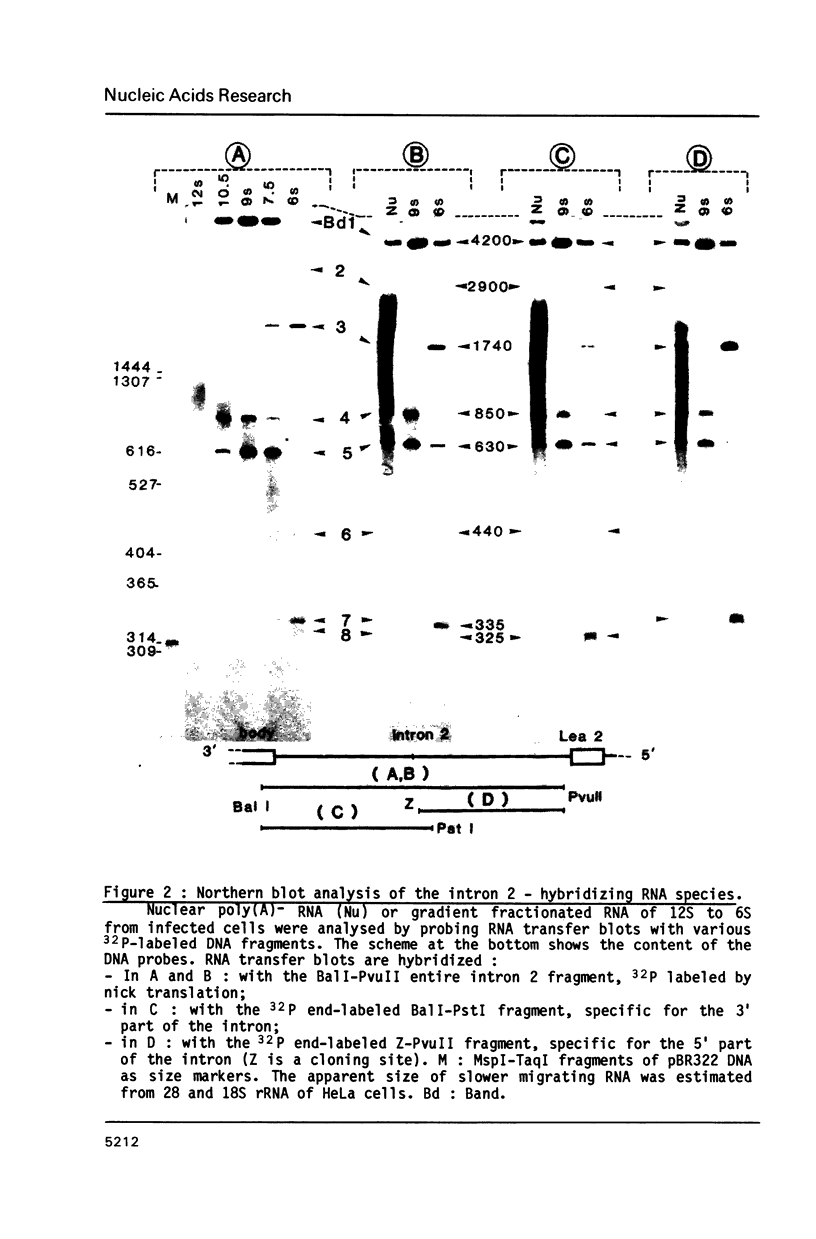












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avvedimento V. E., Vogeli G., Yamada Y., Maizel J. V., Jr, Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. Correlation between splicing sites within an intron and their sequence complementarity with U1 RNA. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):689–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90432-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholeyns J., Baudhuin P. Purification of rat liver particulate neutral ribonuclease and comparison of properties with pancreas and serum ribonucleases. Biochem J. 1977 Jun 15;164(3):675–683. doi: 10.1042/bj1640675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berget S. M., Sharp P. A. Structure of late adenovirus 2 heterogeneous nuclear RNA. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 25;129(4):547–565. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90468-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J., Davidson N. Rates of formation and thermal stabilities of RNA:DNA and DNA:DNA duplexes at high concentrations of formamide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1539–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleclough C., Wood D. Introns excised from immunoglobulin pre-mRNAs exist as discrete species. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2017–2022. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras R., Gheysen D., Knowland J., van de Voorde A., Fiers W. Evidence for the direct involvement of DNA replication origin in synthesis of late SV40 RNA. Nature. 1982 Dec 9;300(5892):500–505. doi: 10.1038/300500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Cycloheximide stimulates early adenovirus transcription if early gene expression is allowed before treatment. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):683–692. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.683-692.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domdey H., Apostol B., Lin R. J., Newman A., Brody E., Abelson J. Lariat structures are in vivo intermediates in yeast pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):611–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90468-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frendewey D., Keller W. Stepwise assembly of a pre-mRNA splicing complex requires U-snRNPs and specific intron sequences. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):355–367. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gattoni R., Keohavong P., Stévenin J. Splicing of the E2A premessenger RNA of adenovirus serotype 2. Multiple pathways in spite of excision of the entire large intron. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 5;187(3):379–397. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90440-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman H. M. Repair of overlapping DNA termini. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):63–64. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski P. J., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Messenger RNA splicing in vitro: an excised intervening sequence and a potential intermediate. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):415–427. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90372-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski P. J., Seiler S. R., Sharp P. A. A multicomponent complex is involved in the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):345–353. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Maniatis T., Melton D. A. Human beta-globin pre-mRNA synthesized in vitro is accurately spliced in Xenopus oocyte nuclei. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):681–694. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld G. C., Koster A., Flavell R. A. A transcription map for the rabbit beta-globin gene. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):573–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N., Keller W. Splicing of in vitro synthesized messenger RNA precursors in HeLa cell extracts. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):89–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90211-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith G., Pixa G., Fix C., Dirheimer G. Primary structure of three tRNAs from brewer's yeast: tRNAPro2, tRNAHis1 and tRNAHis2. Biochimie. 1983 Nov-Dec;65(11-12):661–672. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(84)80030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kole R., Weissman S. M. Accurate in vitro splicing of human beta-globin RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 25;10(18):5429–5445. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.18.5429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Grabowski P. J., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Characterization of the branch site in lariat RNAs produced by splicing of mRNA precursors. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):552–557. doi: 10.1038/313552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Ruskin B., Green M. R. Normal and mutant human beta-globin pre-mRNAs are faithfully and efficiently spliced in vitro. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):993–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer A., Keller W. Purification of a protein required for the splicing of pre-mRNA and its separation from the lariat debranching enzyme. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3571–3581. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04119.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühne T., Wieringa B., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Evidence against a scanning model of RNA splicing. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):727–733. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01492.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariman E. C., van Beek-Reinders R. J., van Venrooij W. J. Alternative splicing pathways exist in the formation of adenoviral late messenger RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jan 15;163(2):239–256. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munroe S. H. A large inverted repeat sequence overlaps two acceptor splice sites in adenovirus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8891–8900. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble J. C., Prives C., Manley J. L. In vitro splicing of simian virus 40 early pre mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1219–1235. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Hardy S. F., Sharp P. A. Splicing of adenovirus RNA in a cell-free transcription system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5230–5234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. Intron sequences involved in lariat formation during pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal R., Raskas H. J. Nuclei of adenovirus 2-infected cells contain an RNA species that corresponds to an intron excised intact from mRNA precursors. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1084–1092. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Green M. R. An RNA processing activity that debranches RNA lariats. Science. 1985 Jul 12;229(4709):135–140. doi: 10.1126/science.2990042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Greene J. M., Green M. R. Cryptic branch point activation allows accurate in vitro splicing of human beta-globin intron mutants. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):833–844. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sittler A., Gallinaro H., Jacob M. In vivo splicing of the premRNAs from early region 3 of adenovirus-2: the products of cleavage at the 5' splice site of the common intron. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1187–1207. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D. Alternative splicing caused by RNA secondary structure. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):667–676. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90239-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stévenin J., Gattoni R., Keohavong P., Jacob M. Mild nuclease treatment as a probe for a non-random distribution of adenovirus-specific RNA sequences and of cellular RNA in nuclear ribonucleoprotein fibrils. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 5;155(3):185–205. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeitlin S., Efstratiadis A. In vivo splicing products of the rabbit beta-globin pre-mRNA. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):589–602. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90466-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]