Abstract
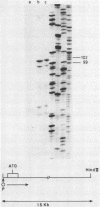
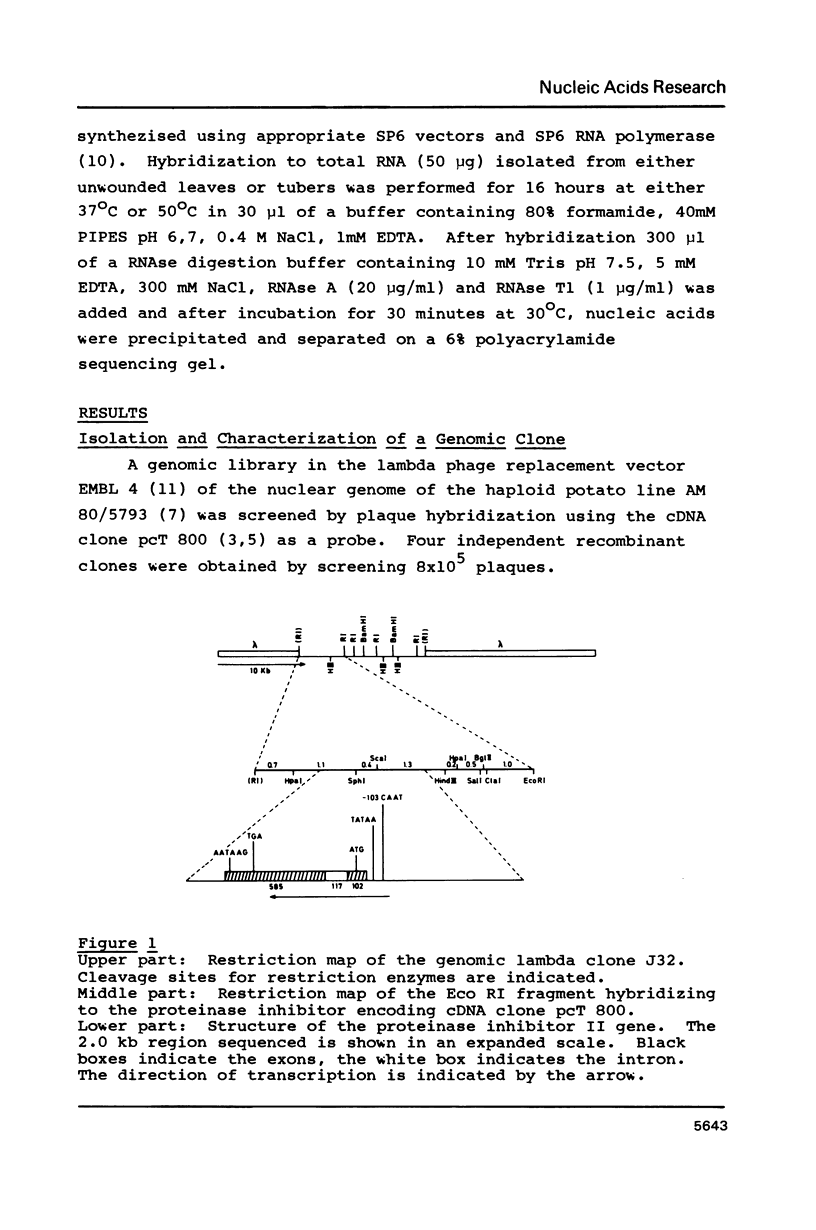
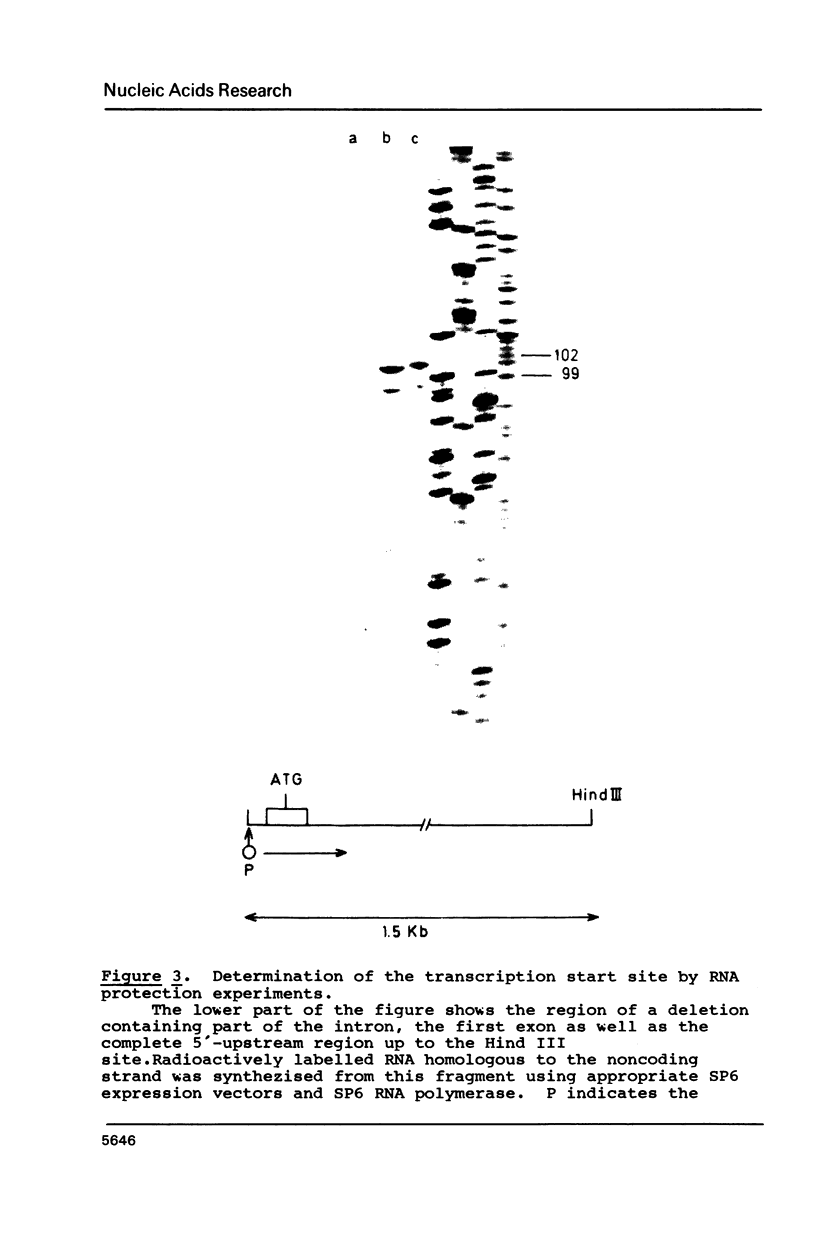
The isolation and characterization of a genomic clone encoding proteinase inhibitor II of potato (Solanum tuberosum) is described. The structure of this gene was determined by sequencing a genomic fragment of about 2 kb containing the entire RNA coding as well as about 900 nucleotides of the 5'-upstream and 250 nucleotides of the 3'-downstream region. The transcription start site was determined by RNase protection experiments. The comparison of the genomic sequence with cDNA sequences reveals the presence of one intron with a length of 117 nucleotides. The genomic clone contains an open reading frame of 462 nucleotides allowing for a protein of 154 amino acids. The proteinase inhibitor II gene displays typical features of eucaryotic genes. The sequence TATAAA is found 26 nucleotides upstream of the transcription initiation site and the sequence CAAAT at position--103. In the 3'-region the sequence AATAA is found 33 nucleotides in front of the poly-A addition site.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop P. D., Makus D. J., Pearce G., Ryan C. A. Proteinase inhibitor-inducing factor activity in tomato leaves resides in oligosaccharides enzymically released from cell walls. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3536–3540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean C., Tamaki S., Dunsmuir P., Favreau M., Katayama C., Dooner H., Bedbrook J. mRNA transcripts of several plant genes are polyadenylated at multiple sites in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 11;14(5):2229–2240. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.5.2229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slightom J. L., Sun S. M., Hall T. C. Complete nucleotide sequence of a French bean storage protein gene: Phaseolin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1897–1901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]