Abstract
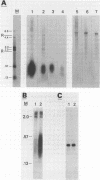
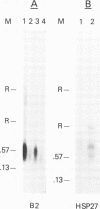
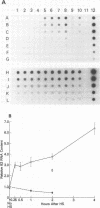
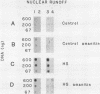
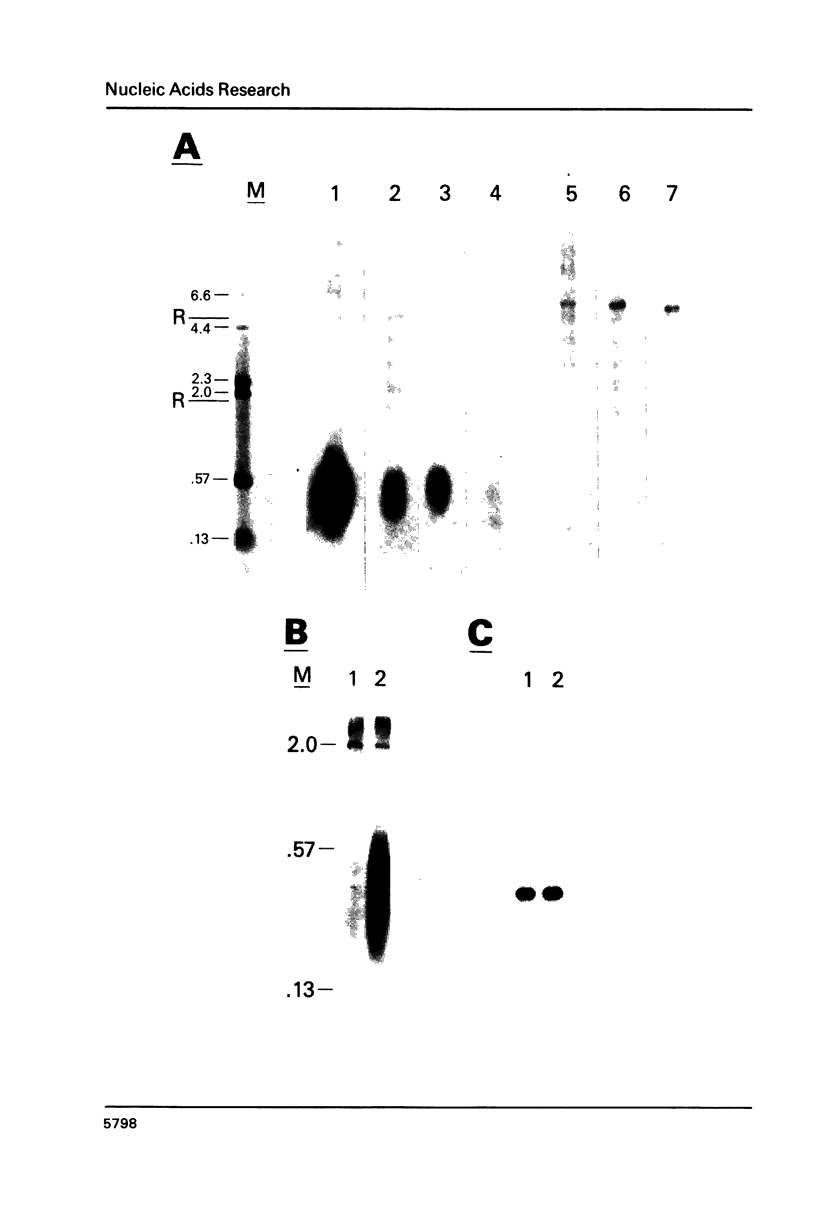
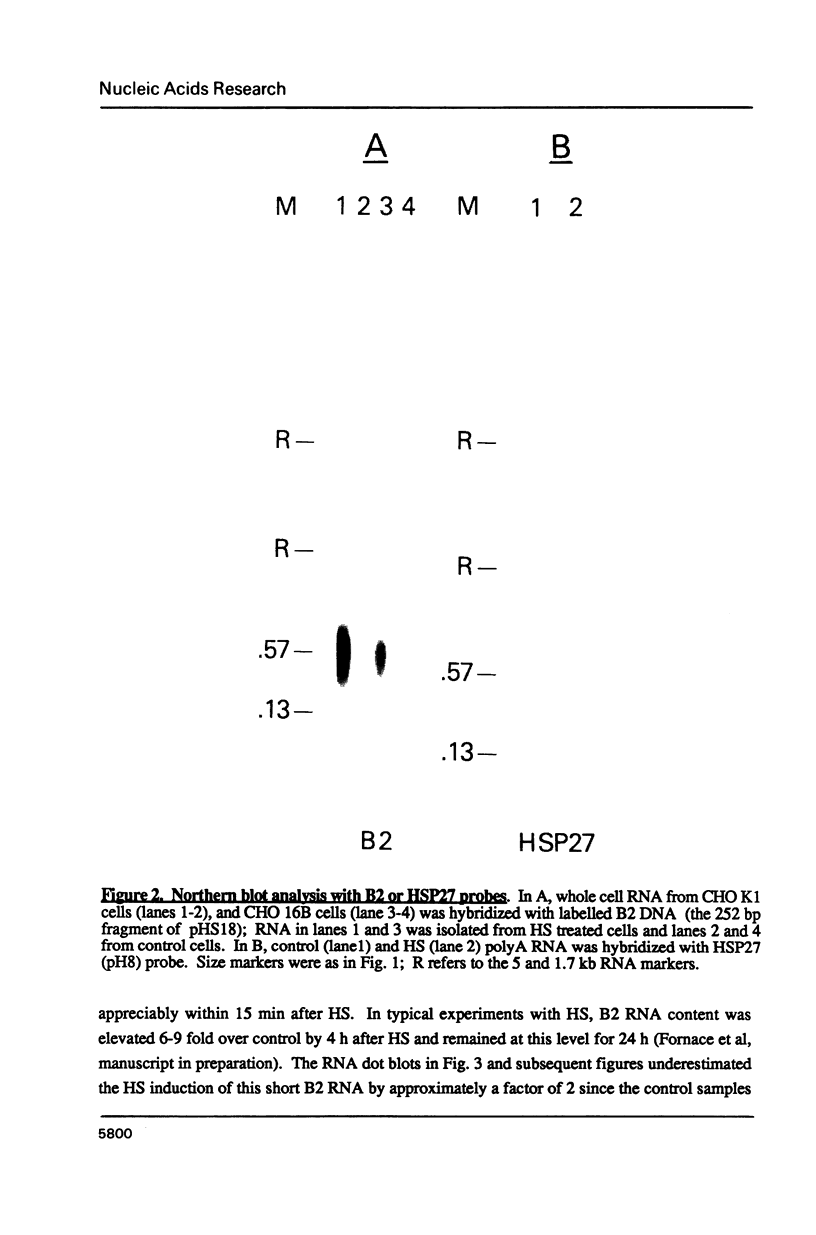
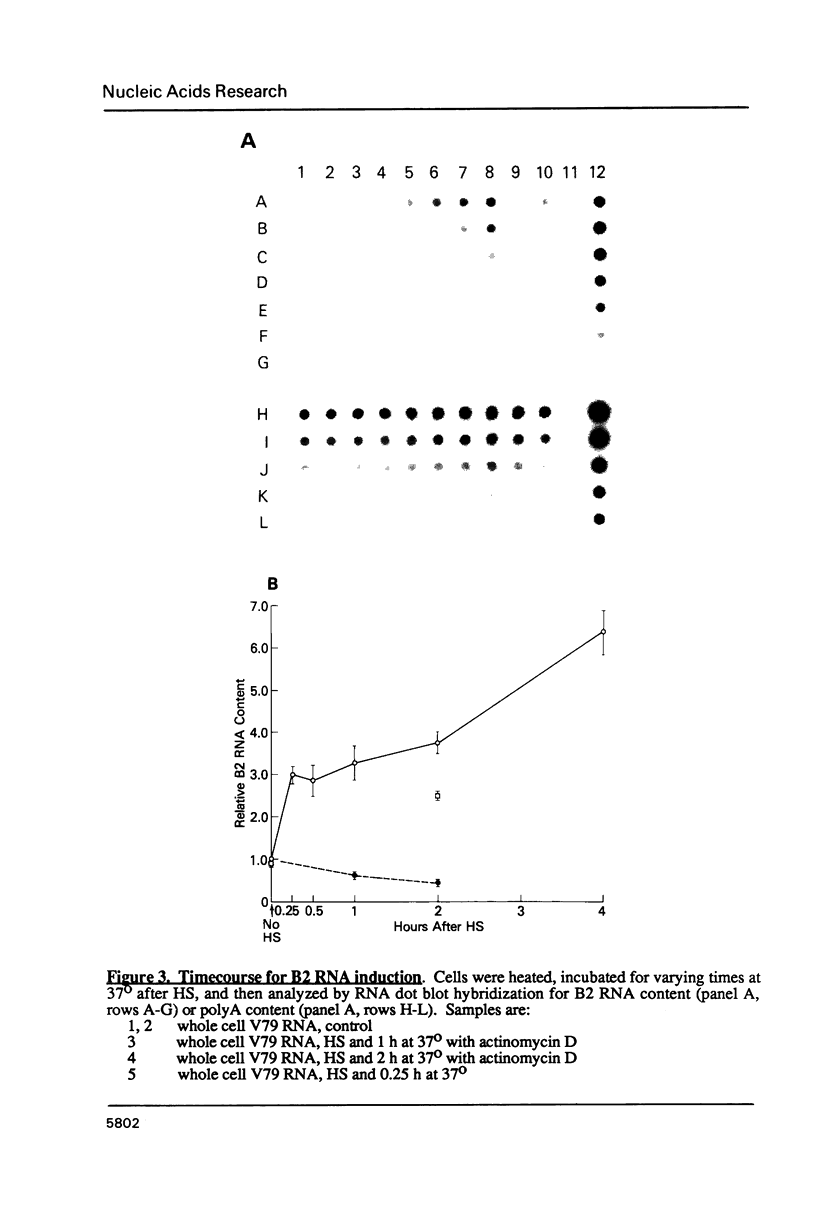
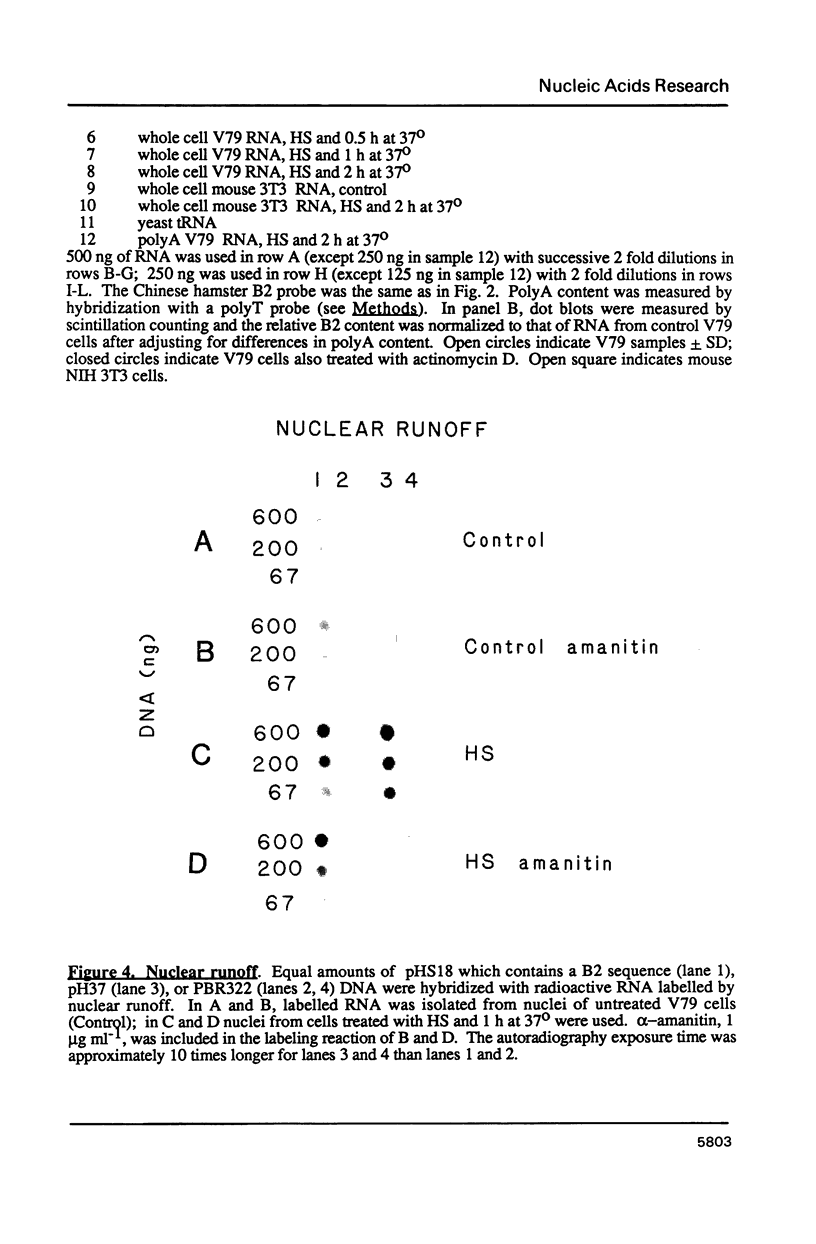
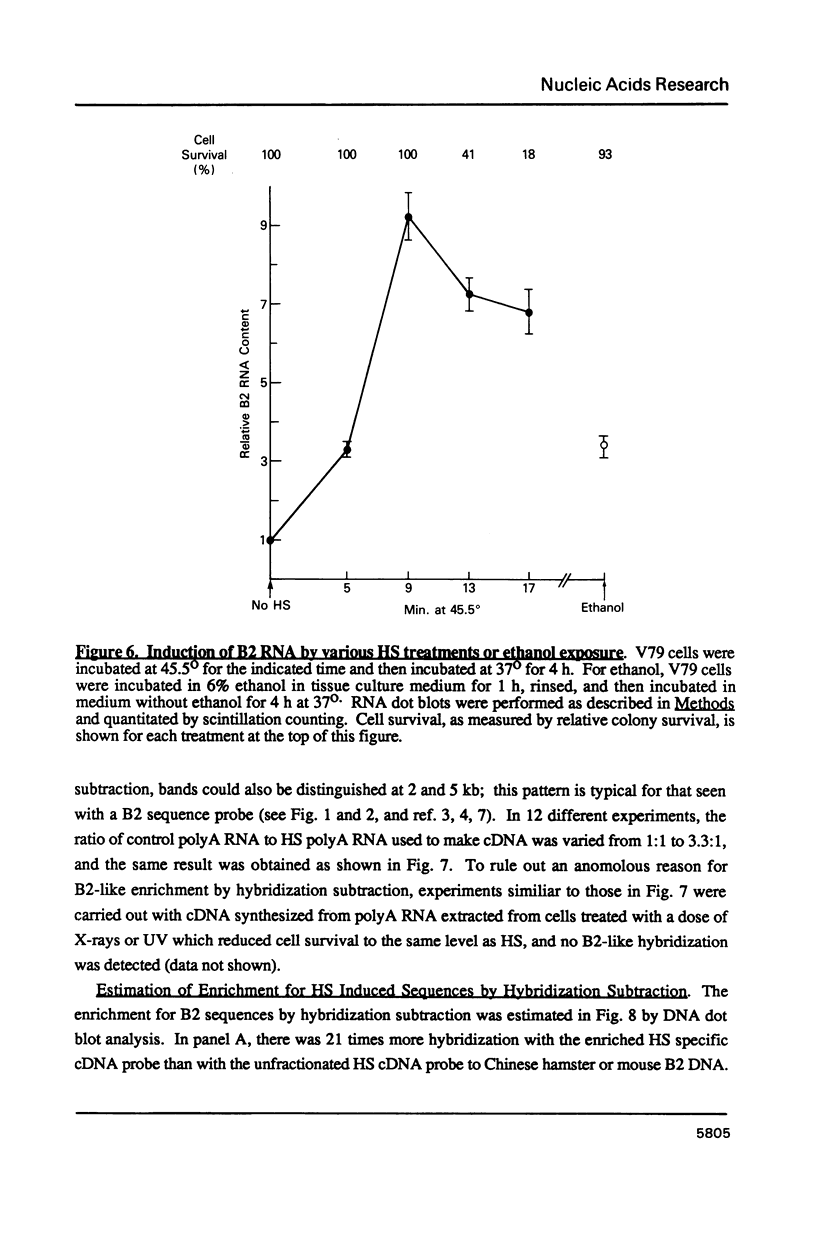
When hybridization subtraction was used to enrich for sequences induced by heat shock in Chinese hamster cells, B2 sequences were found to be one of the major sequences enriched. With cloned B2 probes, we found that the level of the short, 0.1 to 0.6 kb, polyadenylated RNA polymerase III transcripts of this repetitive genetic element increased approximately 10 to 20 fold after heat shock. Transcription of B2 RNA by RNA polymerase III was rapidly induced after heat shock based on time course studies and nuclear runoff experiments. The induction of B2 RNA was not a nonspecific response to lethality or cellular injury because maximum B2 RNA induction was observed with even nontoxic heating while no induction occurred with other agents such as UV or X-radiation. Since B2 RNA increased after heat shock in several different Chinese hamster and mouse cell lines, induction of B2 RNA by heat shock is probably common in rodent cells. B2 RNA may also be the most abundant transcript induced by heat shock because the level of B2 RNA was substantially higher than several other abundant transcripts induced by heat shock including a rodent HSP70. Our finding of the induction of high levels of RNA polymerase III B2 transcripts in different rodent cells raise the possibility of a role in the heat shock response.
Full text
PDF







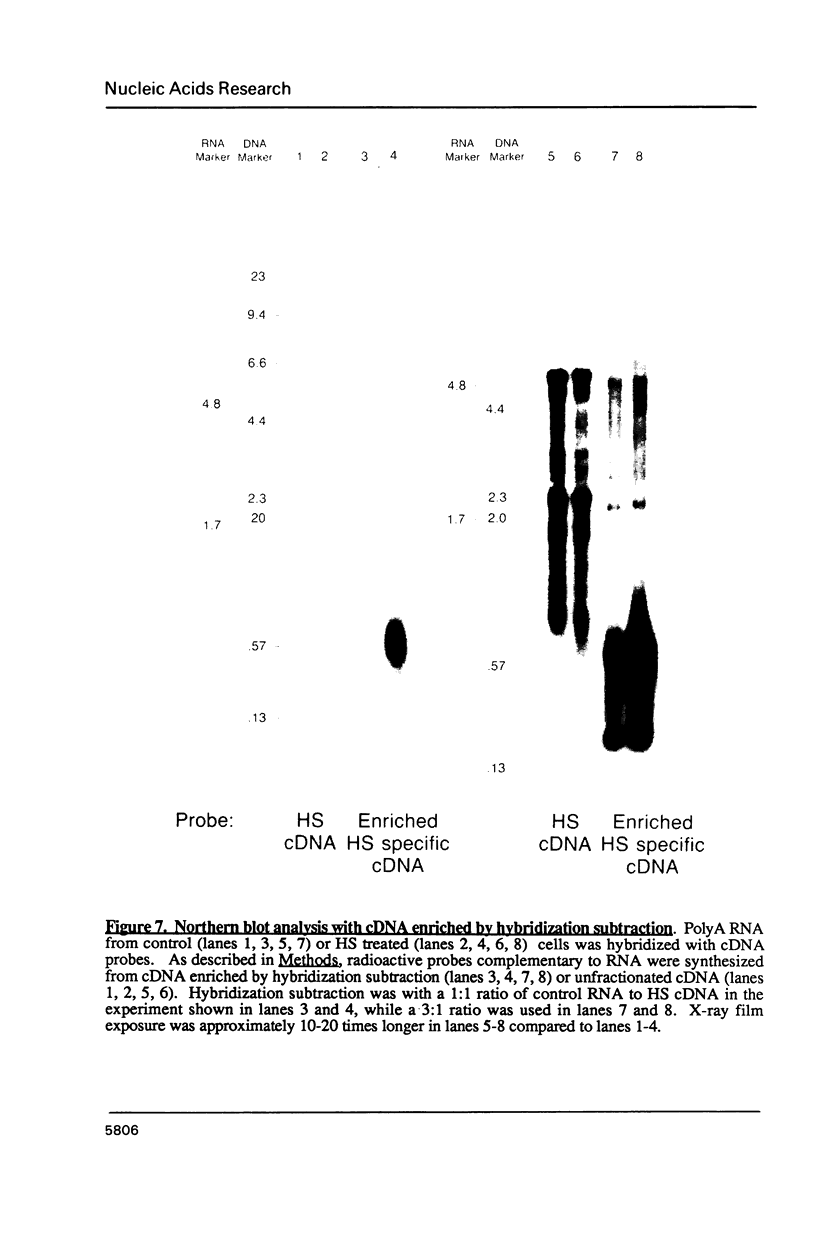
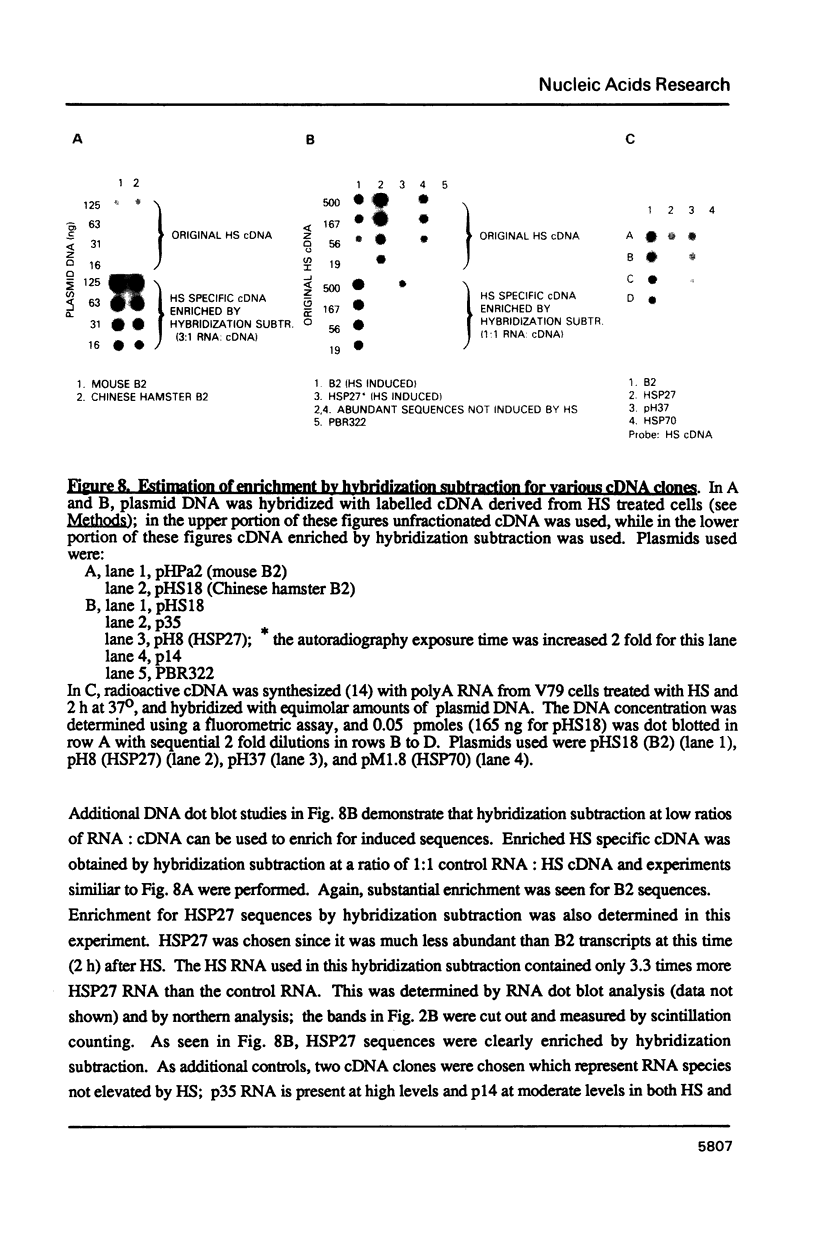




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett K. L., Hill R. E., Pietras D. F., Woodworth-Gutai M., Kane-Haas C., Houston J. M., Heath J. K., Hastie N. D. Most highly repeated dispersed DNA families in the mouse genome. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1561–1571. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree G. R., Kant J. A. Molecular cloning of cDNA for the alpha, beta, and gamma chains of rat fibrinogen. A family of coordinately regulated genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9718–9723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dony C., Kessel M., Gruss P. Post-transcriptional control of myc and p53 expression during differentiation of the embryonal carcinoma cell line F9. Nature. 1985 Oct 17;317(6038):636–639. doi: 10.1038/317636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornace A. J., Jr, Cummings D. E., Comeau C. M., Kant J. A., Crabtree G. R. Structure of the human gamma-fibrinogen gene. Alternate mRNA splicing near the 3' end of the gene produces gamma A and gamma B forms of gamma-fibrinogen. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12826–12830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeffler W. K., Roeder R. G. Enhancement of RNA polymerase III transcription by the E1A gene product of adenovirus. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):955–963. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80076-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Kao H. T., Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R., Strickland S. Common control of the heat shock gene and early adenovirus genes: evidence for a cellular E1A-like activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):867–874. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramerov D. A., Lekakh I. V., Samarina O. P., Ryskov A. P. The sequences homologous to major interspersed repeats B1 and B2 of mouse genome are present in mRNA and small cytoplasmic poly(A) + RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7477–7491. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramerov D. A., Tillib S. V., Lekakh I. V., Ryskov A. P., Georgiev G. P. Biosynthesis and cytoplasmic distribution of small poly(A)-containing B2 RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Feb 20;824(2):85–98. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(85)90084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramerov D. A., Tillib S. V., Ryskov A. P., Georgiev G. P. Nucleotide sequence of small polyadenylated B2 RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 25;13(18):6423–6437. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.18.6423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krayev A. S., Markusheva T. V., Kramerov D. A., Ryskov A. P., Skryabin K. G., Bayev A. A., Georgiev G. P. Ubiquitous transposon-like repeats B1 and B2 of the mouse genome: B2 sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7461–7475. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Induction of the synthesis of a 70,000 dalton mammalian heat shock protein by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):913–919. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90453-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens G. P., Chaudhari N., Hahn W. E. Brain "identifier sequence" is not restricted to brain: similar abundance in nuclear RNA of other organs. Science. 1985 Sep 20;229(4719):1263–1265. doi: 10.1126/science.2412293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo A., Mitchell J. B., McPherson S. The effects of glutathione depletion on thermotolerance and heat stress protein synthesis. Br J Cancer. 1984 Jun;49(6):753–758. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1984.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryskov A. P., Ivanov P. L., Kramerov D. A., Georgiev G. P. Mouse ubiquitous B2 repeat in polysomal and cytoplasmic poly(A)+RNAs: uniderectional orientation and 3'-end localization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6541–6558. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryskov A. P., Ivanov P. L., Tokarskaya O. N., Kramerov D. A., Grigoryan M. S., Georgiev G. P. Major transcripts containing B1 and B2 repetitive sequences in cytoplasmic poly(A)+RNA from mouse tissues. FEBS Lett. 1985 Mar 11;182(1):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81156-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapienza C., St-Jacques B. 'Brain-specific' transcription and evolution of the identifier sequence. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):418–420. doi: 10.1038/319418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent T. D., Dawid I. B. Differential gene expression in the gastrula of Xenopus laevis. Science. 1983 Oct 14;222(4620):135–139. doi: 10.1126/science.6688681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh K., Carey M., Saragosti S., Botchan M. Expression of enhanced levels of small RNA polymerase III transcripts encoded by the B2 repeats in simian virus 40-transformed mouse cells. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):553–556. doi: 10.1038/314553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand D. J., McDonald J. F. Copia is transcriptionally responsive to environmental stress. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4401–4410. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G., Milner R. J., Gottesfeld J. M., Reynolds W. Control of neuronal gene expression. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1308–1315. doi: 10.1126/science.6474179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker C., Cappello J., Lodish H. F., George P., Chung S. Dictyostelium transposable element DIRS-1 has 350-base-pair inverted terminal repeats that contain a heat shock promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2660–2664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]