Abstract
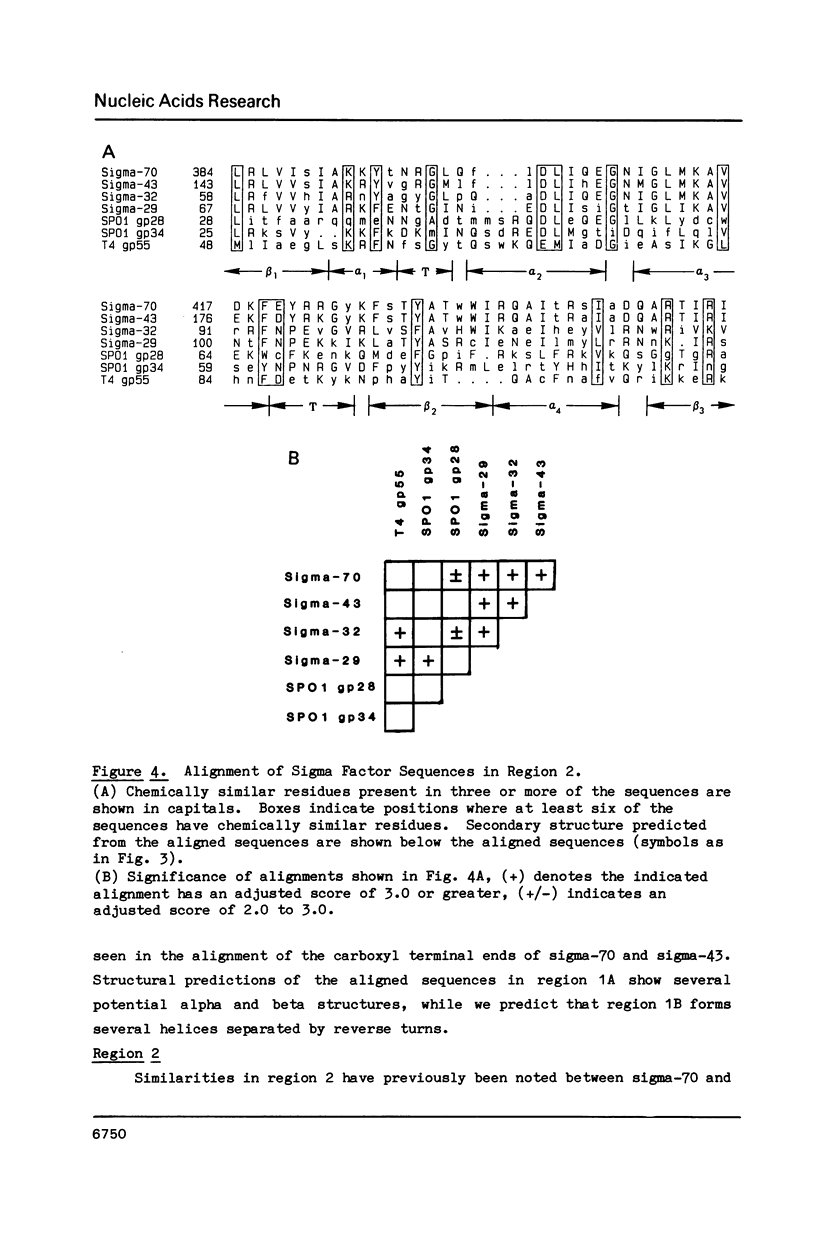
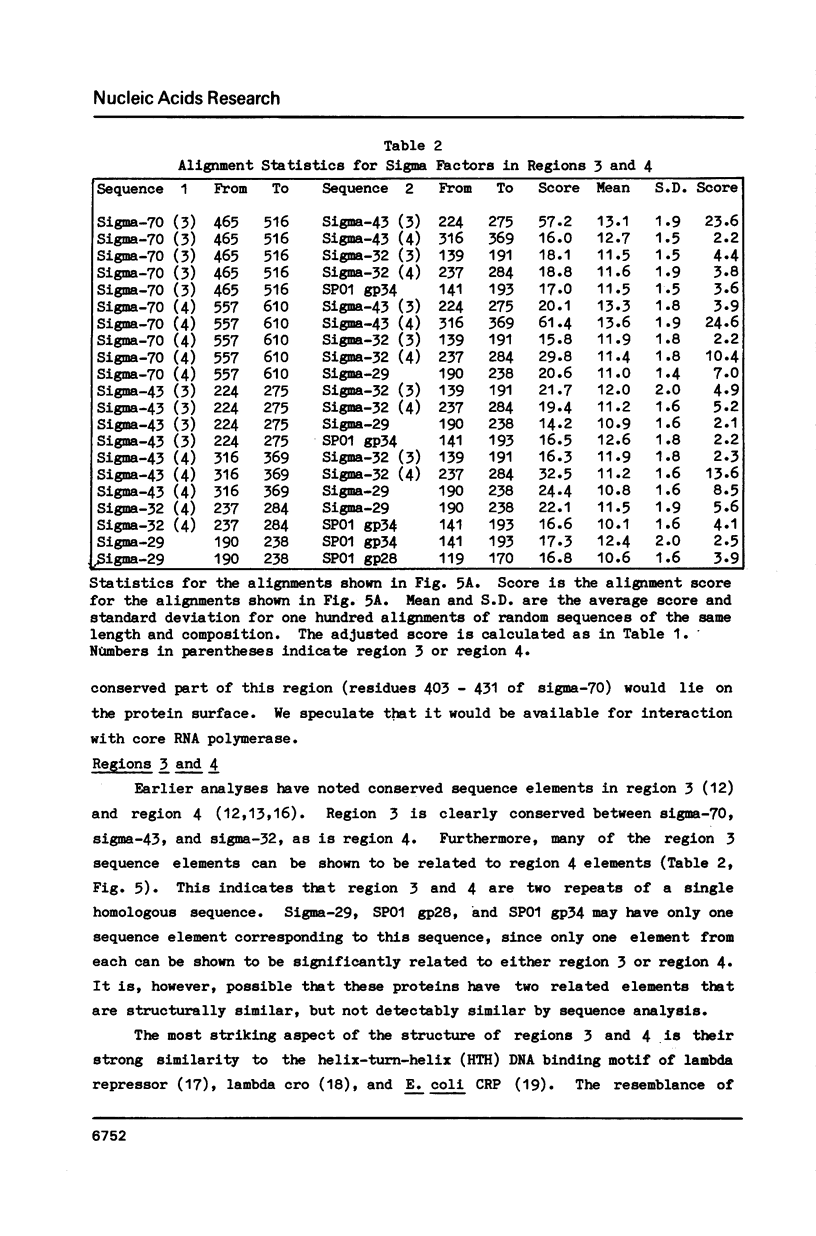
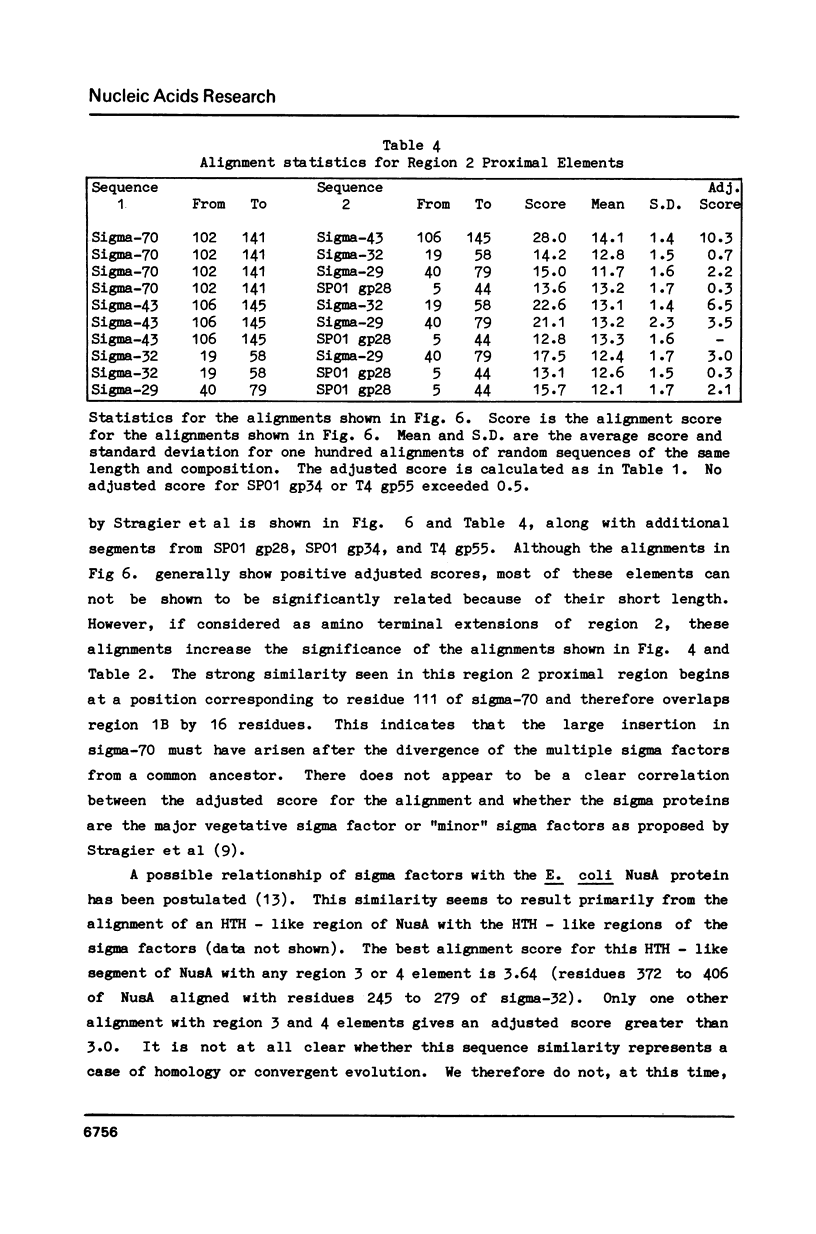
We show, using dot matrix comparisons and statistical analysis of sequence alignments, that seven sequenced sigma factors, E. coli sigma-70 and sigma-32, B. subtilis sigma-43 and sigma-29, phage SP01 gene products 28 and 34, and phage T4 gene product 55, comprise a homologous family of proteins. Sigma-70, sigma-32, and sigma-43 each have two copies of a sequence similar to the helix-turn-helix DNA binding motif seen in CRP, and lambda repressor and cro proteins. B. subtilis sigma-29, SP01 gp28, and SP01 gp34 have at least one copy similar to this sequence. We propose that a second sequence, conserved in all seven proteins is the core RNA polymerase binding site. A third region, present only in sigma-70 and sigma-43, may also be involved in interaction with core. Available mutational evidence supports our model for sigma factor structure.
Full text
PDF















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson W. F., Ohlendorf D. H., Takeda Y., Matthews B. W. Structure of the cro repressor from bacteriophage lambda and its interaction with DNA. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):754–758. doi: 10.1038/290754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyreuther K., Adler K., Geisler N., Klemm A. The amino-acid sequence of lac repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3576–3580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Travers A. A., Dunn J. J., Bautz E. K. Factor stimulating transcription by RNA polymerase. Nature. 1969 Jan 4;221(5175):43–46. doi: 10.1038/221043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton Z., Burgess R. R., Lin J., Moore D., Holder S., Gross C. A. The nucleotide sequence of the cloned rpoD gene for the RNA polymerase sigma subunit from E coli K12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2889–2903. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelm B. K., Beard C., Geiduschek E. P. Changes in the association between Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase core and two specificity-determining subunits during transcription. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 10;20(23):6564–6569. doi: 10.1021/bi00526a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen A. C., Young E. T. T4 late transcripts are initiated near a conserved DNA sequence. Nature. 1982 Sep 23;299(5881):369–371. doi: 10.1038/299369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossart P., Gicquel-Sanzey B. Cloning and sequence of the crp gene of Escherichia coli K 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 25;10(4):1363–1378. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.4.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo M., Brzustowicz L., Hannett N., Pero J. Bacteriophage SPO1 genes 33 and 34. Location and primary structure of genes encoding regulatory subunits of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):533–547. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo M., Pero J. Overproduction and purification of a bacteriophage SPO1-encoded RNA polymerase sigma factor. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6681–6685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo M., Pero J. Structure of a Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage SPO1 gene encoding RNA polymerase sigma factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1236–1240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi R. H. Multiple RNA polymerase holoenzymes exert transcriptional specificity in Bacillus subtilis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Apr 1;214(2):772–781. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90084-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F. Similar amino acid sequences: chance or common ancestry? Science. 1981 Oct 9;214(4517):149–159. doi: 10.1126/science.7280687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T., Geiduschek E. P. Defining a bacteriophage T4 late promoter: absence of a "-35" region. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson B. D., Burton Z. F., Watanabe K. K., Burgess R. R. Nucleotide sequence of the rpsU-dnaG-rpoD operon from Salmonella typhimurium and a comparison of this sequence with the homologous operon of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1985;40(1):67–78. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90025-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitt M. A., Wang L. F., Doi R. H. A strong sequence homology exists between the major RNA polymerase sigma factors of Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7178–7185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gram H., Rüger W. Genes 55, alpha gt, 47 and 46 of bacteriophage T4: the genomic organization as deduced by sequence analysis. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):257–264. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02344.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribskov M., Burgess R. R., Devereux J. PEPPLOT, a protein secondary structure analysis program for the UWGCG sequence analysis software package. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):327–334. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. D., Erickson J. W., Gross C. A. The htpR gene product of E. coli is a sigma factor for heat-shock promoters. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90493-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffron F., McCarthy B. J., Ohtsubo H., Ohtsubo E. DNA sequence analysis of the transposon Tn3: three genes and three sites involved in transposition of Tn3. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1153–1163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochschild A., Irwin N., Ptashne M. Repressor structure and the mechanism of positive control. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):319–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90451-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horii T., Ogawa T., Ogawa H. Nucleotide sequence of the lexA gene of E. coli. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):689–697. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90432-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiang M. W., Cole R. D., Takeda Y., Echols H. Amino acid sequence of Cro regulatory protein of bacteriophage lambda. Nature. 1977 Nov 17;270(5634):275–277. doi: 10.1038/270275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu J. C., Gross C. A. Marker rescue with plasmids bearing deletions in rpoD identifies a dispensable part of E. coli sigma factor. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(3):492–498. doi: 10.1007/BF00425768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu J. C., Gross C. A. Mutations in the sigma subunit of E. coli RNA polymerase which affect positive control of transcription. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;199(1):7–13. doi: 10.1007/BF00327502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. Defining a bacteriophage T4 late promoter: bacteriophage T4 gene 55 protein suffices for directing late promoter recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5101–5105. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landick R., Vaughn V., Lau E. T., VanBogelen R. A., Erickson J. W., Neidhardt F. C. Nucleotide sequence of the heat shock regulatory gene of E. coli suggests its protein product may be a transcription factor. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90538-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R., Pero J. Cascades of Sigma factors. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):582–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90164-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe P. A., Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Purification and properties of the sigma subunit of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 3;18(7):1344–1352. doi: 10.1021/bi00574a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizel J. V., Jr, Lenk R. P. Enhanced graphic matrix analysis of nucleic acid and protein sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7665–7669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markham B. E., Little J. W., Mount D. W. Nucleotide sequence of the lexA gene of Escherichia coli K-12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):4149–4161. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.4149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. B., Steitz T. A. Structure of catabolite gene activator protein at 2.9 A resolution suggests binding to left-handed B-DNA. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):744–749. doi: 10.1038/290744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov Y. A., Guryev S. O., Krayev A. S., Monastyrskaya G. S., Skryabin K. G., Sverdlov E. D., Zakharyev V. M., Bayev A. A. Primary structure of an EcoRI fragment of lambda imm434 DNA containing regions cI-cro of phage 434 and cII-o of phage lambda. Gene. 1979 Jul;6(3):235–249. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Lewis M. The operator-binding domain of lambda repressor: structure and DNA recognition. Nature. 1982 Jul 29;298(5873):443–447. doi: 10.1038/298443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R., Shibuya G. I., Steitz J. A. Nucleotide sequence of gamma delta resolvase gene and demonstration that its gene product acts as a repressor of transcription. Nature. 1982 Nov 25;300(5890):381–383. doi: 10.1038/300381a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer R. T. DNA sequence of the bacteriophage gama cI gene. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):301–302. doi: 10.1038/276301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer R. T., Pan J., Hopper P., Hehir K., Brown J., Poteete A. R. Primary structure of the phage P22 repressor and its gene c2. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 9;20(12):3591–3598. doi: 10.1021/bi00515a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz E., Scherer G., Hobom G., Kössel H. Nucleotide sequence of cro, cII and part of the O gene in phage lambda DNA. Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):410–414. doi: 10.1038/272410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. J., Guest J. R. Nucleotide sequence of the fnr gene and primary structure of the Enr protein of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):6119–6130. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.6119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shorenstein R. G., Losick R. Comparative size and properties of the sigma subunits of ribonucleic acid polymerase from Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):6170–6173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Zieg J., Mandel G., Simon M. Analysis of the functional components of the phase variation system. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):17–26. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstone A. E., Goman M., Scaife J. G. ALT: a new factor involved in the synthesis of RNA by Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;118(3):223–234. doi: 10.1007/BF00333459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner C. M., Schleif R. Is the amino acid but not the nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli araC gene conserved? J Mol Biol. 1982 Feb 5;154(4):649–652. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(82)80020-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stragier P., Bouvier J., Bonamy C., Szulmajster J. A developmental gene product of Bacillus subtilis homologous to the sigma factor of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):376–378. doi: 10.1038/312376a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stragier P., Parsot C., Bouvier J. Two functional domains conserved in major and alternate bacterial sigma factors. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 22;187(1):11–15. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81203-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tijan R., Pero J. Bacteriophage SP01 regulatory proteins directing late gene transcription in vitro. Nature. 1976 Aug 26;262(5571):753–757. doi: 10.1038/262753a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trempy J. E., Bonamy C., Szulmajster J., Haldenwang W. G. Bacillus subtilis sigma factor sigma 29 is the product of the sporulation-essential gene spoIIG. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4189–4192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yura T., Tobe T., Ito K., Osawa T. Heat shock regulatory gene (htpR) of Escherichia coli is required for growth at high temperature but is dispensable at low temperature. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6803–6807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- deHaseth P. L., Lohman T. M., Burgess R. R., Record M. T., Jr Nonspecific interactions of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase with native and denatured DNA: differences in the binding behavior of core and holoenzyme. Biochemistry. 1978 May 2;17(9):1612–1622. doi: 10.1021/bi00602a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. Sequence of galR gene indicates a common evolutionary origin of lac and gal repressor in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2427–2431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


