Abstract
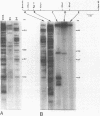
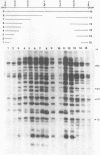
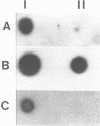
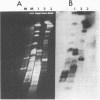
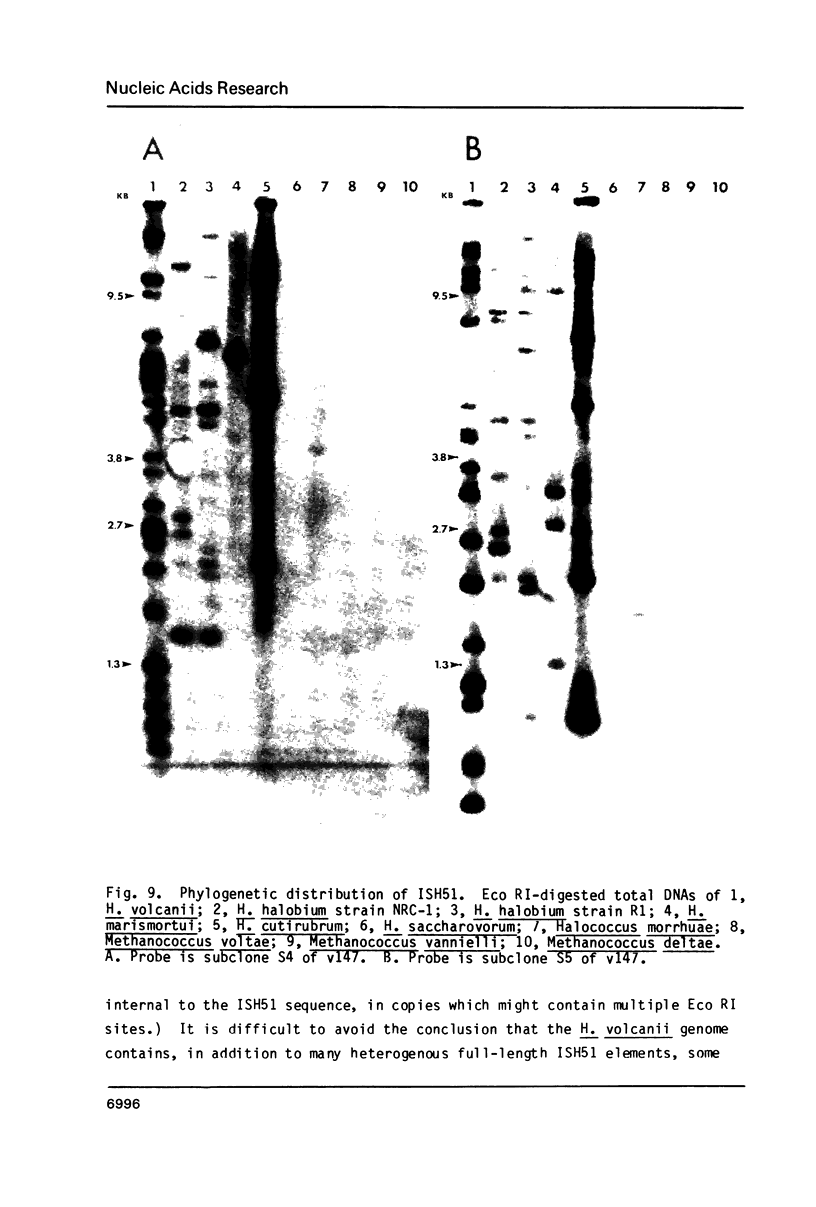
We describe a new family of repetitive elements in the genome of the archaebacterium Halobacterium volcanii. There are some 20-30 copies of this element, which we designate ISH51. Sequenced copies show typical insertion sequence characteristics (terminal inverted repeats, direct flanking repeats of "target site" DNA). However, members of the ISH51 family are highly heterogeneous, showing on average only 85% primary sequence homology; and some genomic copies appear to be severely truncated. Some ISH51 elements are clustered together in regions of relatively AT-rich DNA. There are at least five such AT-rich "islands" in the H. volcanii genome. Repetitive sequences homologous to ISH51 are found in the genomes of most Halobacterium and Halococcus species.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Betlach M., Pfeifer F., Friedman J., Boyer H. W. Bacterio-opsin mutants of Halobacterium halobium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1416–1420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betlach M., Pfeifer F., Friedman J., Boyer H. W. Bacterio-opsin mutants of Halobacterium halobium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1416–1420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bünemann H., Müller W. Base specific fractionation of double stranded DNA: affinity chromatography on a novel type of adsorbant. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Mar;5(3):1059–1074. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Separation of chromosomal DNA molecules from yeast by orthogonal-field-alternation gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5647–5664. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., McClure B. A., Houchins J. P. A rapid single-stranded cloning strategy for producing a sequential series of overlapping clones for use in DNA sequencing: application to sequencing the corn mitochondrial 18 S rDNA. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels C. J., Hofman J. D., MacWilliam J. G., Doolittle W. F., Woese C. R., Luehrsen K. R., Fox G. E. Sequence of 5S ribosomal RNA gene regions and their products in the archaebacterium Halobacterium volcanii. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;198(2):270–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00383005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Brenner S., Barnett L., Cesareni G. Novel bacteriophage lambda cloning vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5172–5176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. L., McCarthy B. J. Characterization of the deoxyribonucleic acid of various strains of halophilic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):248–254. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.248-254.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer F., Betlach M. Genome organization in Halobacterium halobium: a 70 kb island of more (AT) rich DNA in the chromosome. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;198(3):449–455. doi: 10.1007/BF00332938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer F., Friedman J., Boyer H. W., Betlach M. Characterization of insertions affecting the expression of the bacterio-opsin gene in Halobacterium halobium. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 12;12(5):2489–2497. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.5.2489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer F., Weidinger G., Goebel W. Characterization of plasmids in halobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):369–374. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.369-374.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer F., Weidinger G., Goebel W. Genetic variability in Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):375–381. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.375-381.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapienza C., Doolittle W. F. Unusual physical organization of the Halobacterium genome. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):384–389. doi: 10.1038/295384a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapienza C., Rose M. R., Doolittle W. F. High-frequency genomic rearrangements involving archaebacterial repeat sequence elements. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):182–185. doi: 10.1038/299182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnabel H., Palm P., Dick K., Grampp B. Sequence analysis of the insertion element ISH1.8 and of associated structural changes in the genome of phage PhiH of the archaebacterium Halobacterium halobium. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1717–1722. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02037.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Fox G. E. Phylogenetic structure of the prokaryotic domain: the primary kingdoms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5088–5090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Magrum L. J., Fox G. E. Archaebacteria. J Mol Evol. 1978 Aug 2;11(3):245–251. doi: 10.1007/BF01734485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu W. L., Doolittle W. F. Structure of the archaebacterial transposable element ISH50. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):4195–4199. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.4195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]