Abstract
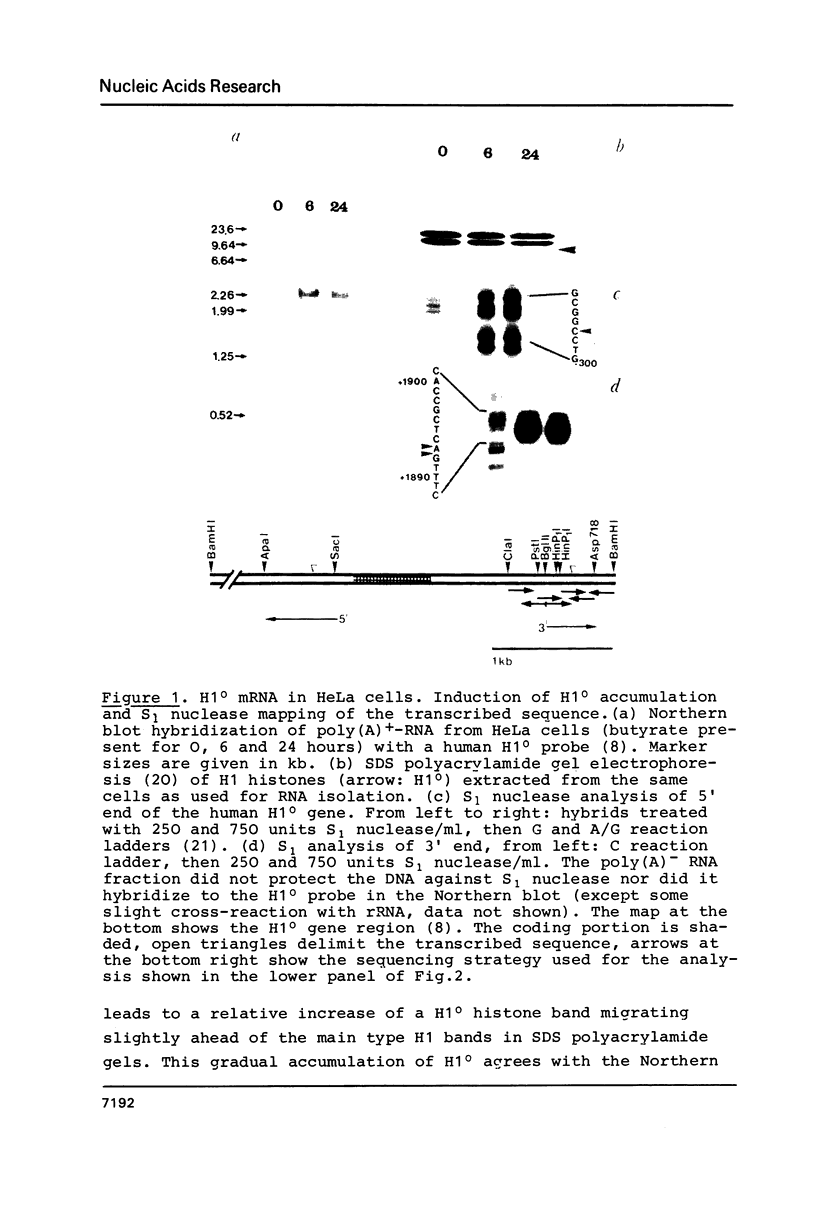
Sodium butyrate was used to induce the accumulation of human H1(0) mRNA in HeLa cells. The length of this mRNA (2,300 nucleotides) was determined by Northern blot hybridization and S1 nuclease analysis using a human H1(0) gene probe. The mRNA shows long 5' and 3' non coding segments and it is polyadenylated. The signal for this step of mRNA maturation (cleavage and polyadenylation) appears to be the hexanucleotide AAUAAA in analogy to most (other than histone) mRNA species. Thus, the mode of maturation of H1(0) mRNA differs, on one hand, from that of the cell cycle dependent mRNA species, where it is based on a specific stem-and-loop structure. On the other hand, the 3' end of H1(0) mRNA varies from H5 mRNA, which is characterized by two unique dyad symmetry structures at its 3' end.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan J., Smith B. J., Dunn B., Bustin M. Antibodies against the folding domain of histone H5 cross-react with H1(0) but not with H1. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10533–10535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Candido E. P., Reeves R., Davie J. R. Sodium butyrate inhibits histone deacetylation in cultured cells. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90305-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabanas A., Khoury E., Goeltz P., Froussard P., Gjerset R., Dod B., Eisen H., Lawrence J. J. Effects of butyric acid on cell cycle regulation and induction of histone H1(0) in mouse cells and tissue culture. Inducibility of H1 (0)in the late S-G2 phase of the cell cycle. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 25;183(2):141–151. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90208-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Anna J. A., Gurley L. R., Tobey R. A. Syntheses and modulations in the chromatin contents of histones H1 degrees and H1 during G1 and S phases in Chinese hamster cells. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 17;21(17):3991–4001. doi: 10.1021/bi00260a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doenecke D., Tönjes R. Conserved dyad symmetry structures at the 3' end of H5 histone genes. Analysis of the duck H5 gene. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 15;178(2):121–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doenecke D., Tönjes R. Differential distribution of lysine and arginine residues in the closely related histones H1 and H5. Analysis of a human H1 gene. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 5;187(3):461–464. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90446-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Bos E., Stahl H. Translation of HeLa cell histone messenger RNAs in cell-free protein synthesizing systems from rabbit reticulocytes, HeLa cells, and wheat germ. Methods Cell Biol. 1978;19:197–213. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gjerset R., Gorka C., Hasthorpe S., Lawrence J. J., Eisen H. Developmental and hormonal regulation of protein H1 degrees in rodents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2333–2337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. M., Davis C., Cole R. D. Induction of histone H1(0) differs with different treatments among different cell lines. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 9;189(1):92–96. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80849-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C., Birnstiel M. L. The organization and expression of histone gene families. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppel F., Allet B., Eisen H. Appearance of a chromatin protein during the erythroid differentiation of Friend virus-transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):653–656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Robins A. J., Colman A., Wells J. R. Chicken histone H5 mRNA: the polyadenylated RNA lacks the conserved histone 3' terminator sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6777–6785. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder A., Leder P. Butyric acid, a potent inducer of erythroid differentiation in cultured erythroleukemic cells. Cell. 1975 Jul;5(3):319–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks P. A., Chen Z., Banks J., Rifkind R. A. Erythroleukemia cells: variants inducible for hemoglobin synthesis without commitment to terminal cell division. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2281–2284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson E., Bustin M. Monoclonal antibodies against distinct determinants of histone H5 bind to chromatin. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 17;23(15):3459–3466. doi: 10.1021/bi00310a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molgaard H. V., Perucho M., Ruiz-Carrillo A. Histone H5 messenger RNA is polyadenylated. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):502–504. doi: 10.1038/283502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Fisher E. F., Caruthers M. H., Berk A. J. Inhibition of RNA cleavage but not polyadenylation by a point mutation in mRNA 3' consensus sequence AAUAAA. Nature. 1983 Oct 13;305(5935):600–605. doi: 10.1038/305600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mura C. V., Stollar B. D. Serological detection of homologies of H1o with H5 and H1 histones. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):9767–9769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Chalkley R. A new histone found only in mammalian tissues with little cell division. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Dec 4;37(6):1042–1049. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90237-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pehrson J. R., Cole R. D. Bovine H10 histone subfractions contain an invariant sequence which matches histones H5 rather than H1. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 14;20(8):2298–2301. doi: 10.1021/bi00511a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pehrson J., Cole R. D. Histone H10 accumulates in growth-inhibited cultured cells. Nature. 1980 May 1;285(5759):43–44. doi: 10.1038/285043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieler C., Adolf G. R., Swetly P. Accumulation of histone H1(0) during chemically induced differentiation of murine neuroblastoma cells. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(2):329–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05242.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Carrillo A., Affolter M., Renaud J. Genomic organization of the genes coding for the six main histones of the chicken: complete sequence of the H5 gene. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):843–859. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80191-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. J., Harris M. R., Sigournay C. M., Mayes E. L., Bustin M. A survey of H1o-and H5-like protein structure and distribution in higher and lower eukaryotes. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 16;138(2):309–317. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07916.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. J., Walker J. M., Johns E. W. Structural homology between a mammalian H1(0) subfraction and avian erythrocyte-specific histone H5. FEBS Lett. 1980 Mar 24;112(1):42–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80122-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda H., Logan K. A., Bradbury E. M. Antibody against globular domain of H10 histone. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jan 30;166(2):263–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80092-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]