Abstract
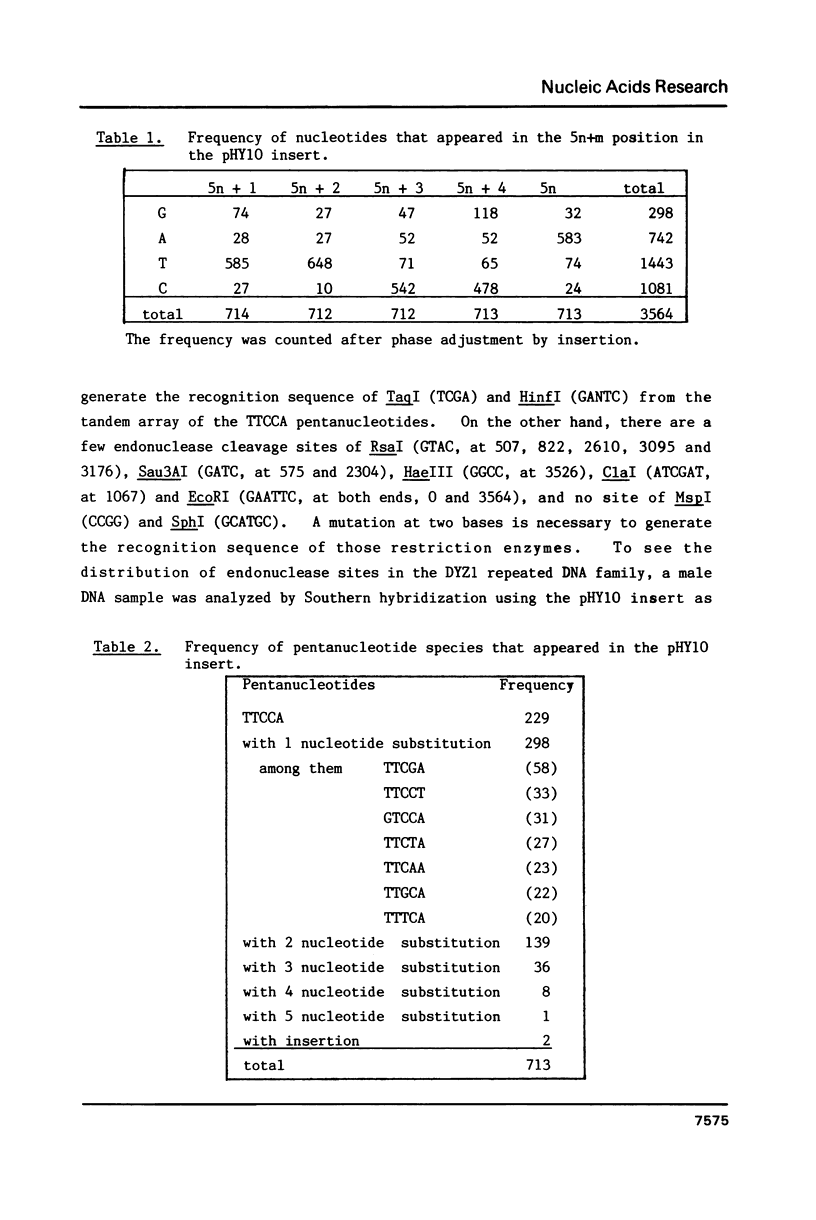
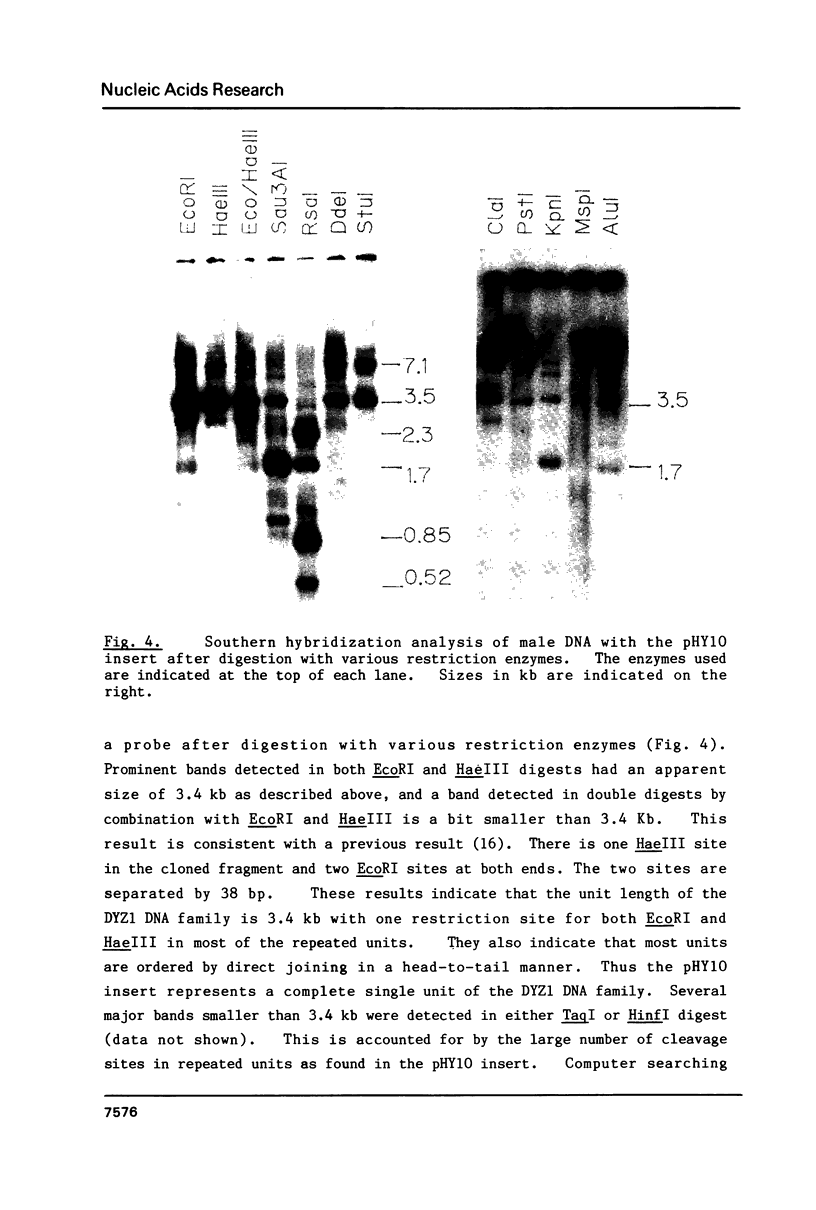
We have determined the complete nucleotide sequence of a 3564 bp EcoRI fragment which represents a major component of the human Y-chromosome specific repeated DNA family (DYZ1). Sequencing result showed a tandem array of pentanucleotides after five nucleotides were inserted or deleted at four positions. 229 out of the 713 pentanucleotides were TTCCA, and 297 were its single-base substituents. Southern hybridization analyses of male genomic DNAs showed that several endonuclease cleavage sites were located at intervals of 3.56kb in the DYZ1 locus. This indicates that the DYZ1 repeated DNA family evolved and expanded by unequal crossovers which occurred at distances of 3.56kb. As there is a uniformly distributed array of pentanucleotides on this locus, it is not a sequence homology that determines the distance of unequal crossovers. A higher order of chromatin structure may be involved in the determination of distance in unequal crossovers.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bostock C. J., Gosden J. R., Mitchell A. R. Localisation of a male-specific DNA fragment to a sub-region of the human Y chromosome. Nature. 1978 Mar 23;272(5651):324–328. doi: 10.1038/272324a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brutlag D. L. Molecular arrangement and evolution of heterochromatic DNA. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:121–144. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke H. J., Hindley J. Cloning of human satellite III DNA: different components are on different chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 25;6(10):3177–3197. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.10.3177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke H. J., McKay R. D. Evolution of a human Y chromosome-specific repeated sequence. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):453–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90319-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke H. Repeated sequence specific to human males. Nature. 1976 Jul 15;262(5565):182–186. doi: 10.1038/262182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corneo G., Ginelli E., Polli E. Renaturation properties and localization in heterochromatin of human satellite DNA's. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Nov 19;247(4):528–534. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90689-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L., Jolly D. J., Rubin C. M., Friedmann T., Schmid C. W. Base sequence studies of 300 nucleotide renatured repeated human DNA clones. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 5;151(1):17–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donehower L., Furlong C., Gillespie D., Kurnit D. DNA sequence of baboon highly repeated DNA: evidence for evolution by nonrandom unequal crossovers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2129–2133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle W. F., Sapienza C. Selfish genes, the phenotype paradigm and genome evolution. Nature. 1980 Apr 17;284(5757):601–603. doi: 10.1038/284601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosden J. R., Mitchell A. R., Buckland R. A., Clayton R. P., Evans H. J. The location of four human satellite DNAs on human chromosomes. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Apr;92(1):148–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90648-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper M. E., Ullrich A., Saunders G. F. Localization of the human insulin gene to the distal end of the short arm of chromosome 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4458–4460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Thein S. L. Hypervariable 'minisatellite' regions in human DNA. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):67–73. doi: 10.1038/314067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kost T. A., Theodorakis N., Hughes S. H. The nucleotide sequence of the chick cytoplasmic beta-actin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 10;11(23):8287–8301. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.23.8287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau Y. F. Detection of Y-specific repeat sequences in normal and variant human chromosomes using in situ hybridization with biotinylated probes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;39(3):184–187. doi: 10.1159/000132132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau Y. F., Huang J. C., Dozy A. M., Kan Y. W. A rapid screening test for antenatal sex determination. Lancet. 1984 Jan 7;1(8367):14–16. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orgel L. E., Crick F. H. Selfish DNA: the ultimate parasite. Nature. 1980 Apr 17;284(5757):604–607. doi: 10.1038/284604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poncz M., Solowiejczyk D., Ballantine M., Schwartz E., Surrey S. "Nonrandom" DNA sequence analysis in bacteriophage M13 by the dideoxy chain-termination method. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4298–4302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P. Evolution of repeated DNA sequences by unequal crossover. Science. 1976 Feb 13;191(4227):528–535. doi: 10.1126/science.1251186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada M., Lewis J. A., Grodzicker T. Overproduction of the protein product of a nonselected foreign gene carried by an adenovirus vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3567–3571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Chapelle A., Page D. C., Brown L., Kaski U., Parvinen T., Tippett P. A. The origin of 45,X males. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Mar;38(3):330–340. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]