Abstract
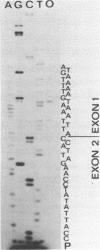
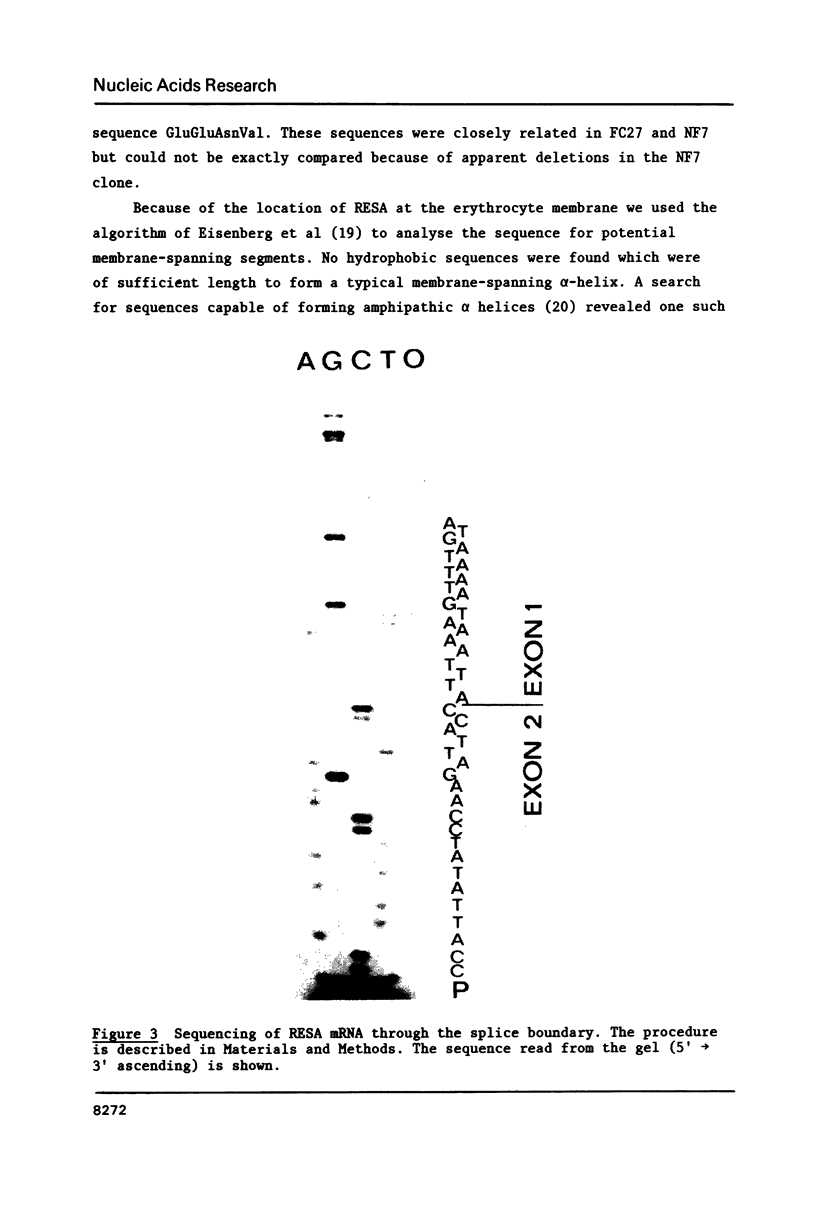
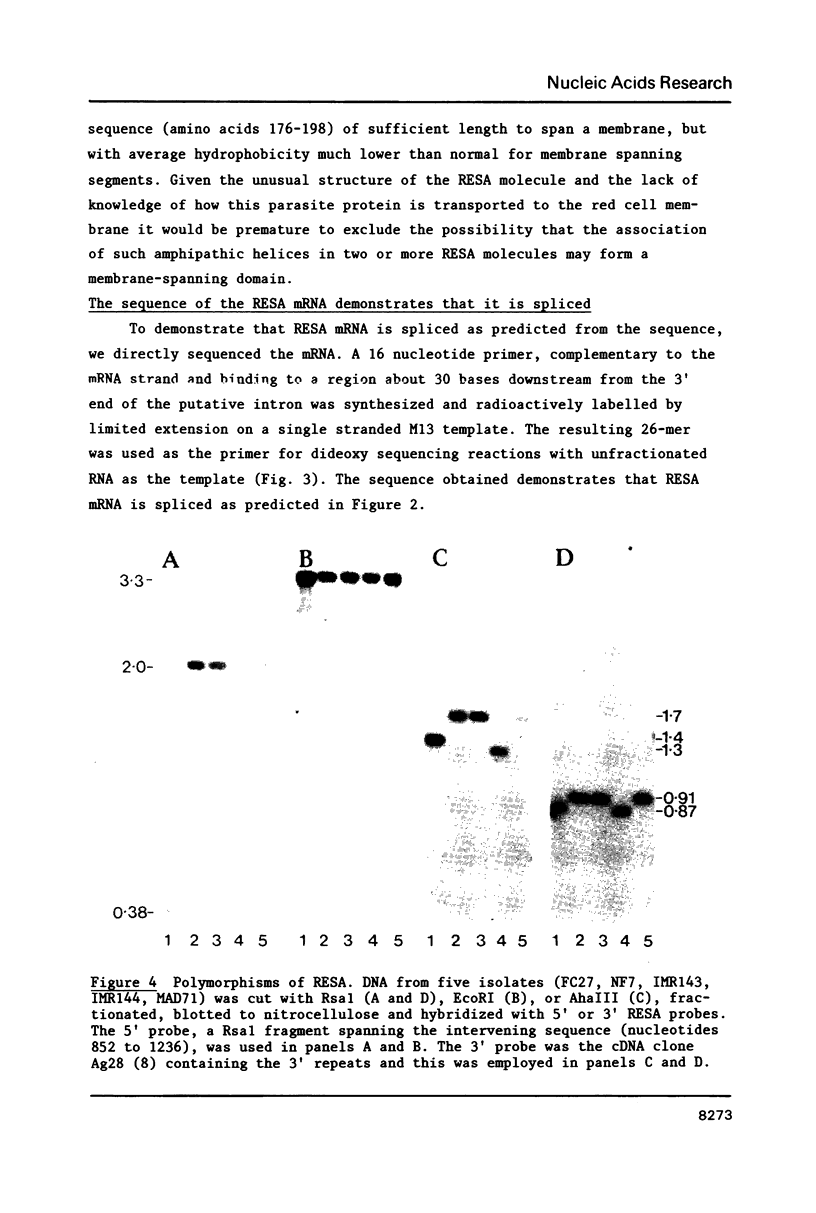
We have determined the nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the ring-infected erythrocyte surface antigen (RESA) of Plasmodium falciparum, an antigen that has been shown to confer protective immunity on monkeys. The sequence has enabled us to predict the structure of the RESA gene and the amino acid sequence of its protein product. The gene consists of two exons with a short intron located near the 5' end of the coding region. A hydrophobic amino acid segment predicted for the 3' end of exon 1 is consistent with the possibility that exon 1 encodes trafficking signal sequences. We show that restriction fragment length polymorphisms can be used to define two different alleles of RESA, represented by isolates FC27 and NF7, and compare the FC27 sequence with that of a long cDNA clone from NF7 described previously.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anders R. F., Shi P. T., Scanlon D. B., Leach S. J., Coppel R. L., Brown G. V., Stahl H. D., Kemp D. J. Antigenic repeat structures in proteins of Plasmodium falciparum. Ciba Found Symp. 1986;119:164–183. doi: 10.1002/9780470513286.ch10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V. The membrane skeleton of human erythrocytes and its implications for more complex cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:273–304. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berzins K., Perlmann H., Wåhlin B., Carlsson J., Wahlgren M., Udomsangpetch R., Björkman A., Patarroyo M. E., Perlmann P. Rabbit and human antibodies to a repeated amino acid sequence of a Plasmodium falciparum antigen, Pf 155, react with the native protein and inhibit merozoite invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1065–1069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. V., Culvenor J. G., Crewther P. E., Bianco A. E., Coppel R. L., Saint R. B., Stahl H. D., Kemp D. J., Anders R. F. Localization of the ring-infected erythrocyte surface antigen (RESA) of Plasmodium falciparum in merozoites and ring-infected erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1985 Aug 1;162(2):774–779. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.2.774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppel R. L., Cowman A. F., Anders R. F., Bianco A. E., Saint R. B., Lingelbach K. R., Kemp D. J., Brown G. V. Immune sera recognize on erythrocytes Plasmodium falciparum antigen composed of repeated amino acid sequences. 1984 Aug 30-Sep 5Nature. 310(5980):789–792. doi: 10.1038/310789a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppel R. L., Cowman A. F., Lingelbach K. R., Brown G. V., Saint R. B., Kemp D. J., Anders R. F. Isolate-specific S-antigen of Plasmodium falciparum contains a repeated sequence of eleven amino acids. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):751–756. doi: 10.1038/306751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowman A. F., Coppel R. L., Saint R. B., Favaloro J., Crewther P. E., Stahl H. D., Bianco A. E., Brown G. V., Anders R. F., Kemp D. J. The ring-infected erythrocyte surface antigen (RESA) polypeptide of Plasmodium falciparum contains two separate blocks of tandem repeats encoding antigenic epitopes that are naturally immunogenic in man. Mol Biol Med. 1984 Jun;2(3):207–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowman A. F., Saint R. B., Coppel R. L., Brown G. V., Anders R. F., Kemp D. J. Conserved sequences flank variable tandem repeats in two S-antigen genes of Plasmodium falciparum. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):775–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90337-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dame J. B., Williams J. L., McCutchan T. F., Weber J. L., Wirtz R. A., Hockmeyer W. T., Maloy W. L., Haynes J. D., Schneider I., Roberts D. Structure of the gene encoding the immunodominant surface antigen on the sporozoite of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):593–599. doi: 10.1126/science.6204383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLisi C., Berzofsky J. A. T-cell antigenic sites tend to be amphipathic structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7048–7052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekowski S. A., Rybicki A., Drickamer K. A tyrosine kinase associated with the red cell membrane phosphorylates band 3. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2750–2753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., Schwarz E., Komaromy M., Wall R. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):125–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaul R. K., Murthy S. N., Reddy A. G., Steck T. L., Kohler H. Amino acid sequence of the N alpha-terminal 201 residues of human erythrocyte membrane band 3. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):7981–7990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Coppel R. L., Cowman A. F., Saint R. B., Brown G. V., Anders R. F. Expression of Plasmodium falciparum blood-stage antigens in Escherichia coli: detection with antibodies from immune humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3787–3791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Coppel R. L., Stahl H. D., Bianco A. E., Corcoran L. M., McIntyre P., Langford C. J., Favaloro J. M., Crewther P. E., Brown G. V. The Wellcome Trust lecture. Genes for antigens of Plasmodium falciparum. Parasitology. 1986;92 (Suppl):S83–108. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000085711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochan J., Perkins M., Ravetch J. V. A tandemly repeated sequence determines the binding domain for an erythrocyte receptor binding protein of P. falciparum. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):689–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90834-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenen M., Scherf A., Mercereau O., Langsley G., Sibilli L., Dubois P., Pereira da Silva L., Müller-Hill B. Human antisera detect a Plasmodium falciparum genomic clone encoding a nonapeptide repeat. 1984 Sep 27-Oct 3Nature. 311(5984):382–385. doi: 10.1038/311382a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann H., Berzins K., Wahlgren M., Carlsson J., Björkman A., Patarroyo M. E., Perlmann P. Antibodies in malarial sera to parasite antigens in the membrane of erythrocytes infected with early asexual stages of Plasmodium falciparum. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1686–1704. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Graphic methods to determine the function of nucleic acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):521–538. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H. D., Crewther P. E., Anders R. F., Brown G. V., Coppel R. L., Bianco A. E., Mitchell G. F., Kemp D. J. Interspersed blocks of repetitive and charged amino acids in a dominant immunogen of Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):543–547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H. D., Kemp D. J., Crewther P. E., Scanlon D. B., Woodrow G., Brown G. V., Bianco A. E., Anders R. F., Coppel R. L. Sequence of a cDNA encoding a small polymorphic histidine- and alanine-rich protein from Plasmodium falciparum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7837–7846. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wåhlin B., Wahlgren M., Perlmann H., Berzins K., Björkman A., Patarroyo M. E., Perlmann P. Human antibodies to a Mr 155,000 Plasmodium falciparum antigen efficiently inhibit merozoite invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7912–7916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]