Abstract
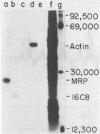
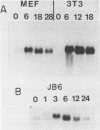
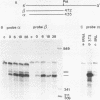
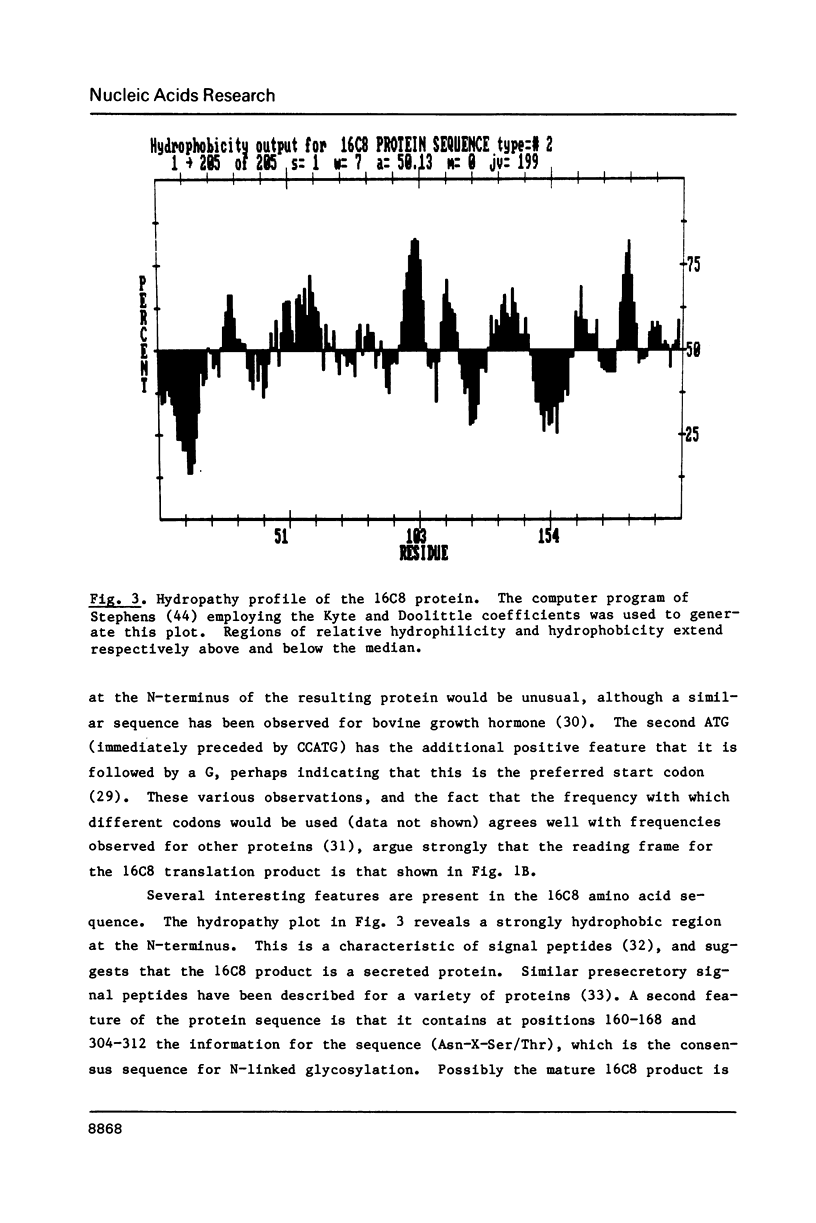
We present the DNA sequence of an essentially full-length cDNA clone of 16C8, a growth factor-inducible gene isolated from a mouse embryo fibroblast cDNA library. The 0.9-kb mRNA encodes an Mr 22,500 protein that has substantial homology to a human protein with the reported abilities to potentiate erythroid differentiation and to inhibit collagenases and other tissue metalloproteinases. The N-terminus of the predicted protein has a hydrophobic nature characteristic of secreted proteins, and two potential sites for N-linked glycosylation are present. The cytoplasmic concentration of 16C8 mRNA is maximal in mid G1 at about 6 h after serum stimulation of quiescent fibroblasts. Northern blot analysis showed a progressive reduction in the size of the induced 16C8 transcripts with increasing time after serum stimulation. This was shown to be due to the reduction in length of the poly(A) tails. S1 analysis of the 5' portion of the mRNA revealed the presence of three different species of transcript, only one of which was inducible.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Battey J., Moulding C., Taub R., Murphy W., Stewart T., Potter H., Lenoir G., Leder P. The human c-myc oncogene: structural consequences of translocation into the IgH locus in Burkitt lymphoma. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):779–787. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90534-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bialkowska-Hobrzanska H., Gilchrist C. A., Denhardt D. T. Escherichia coli rep gene: identification of the promoter and N terminus of the rep protein. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1004–1010. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1004-1010.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campisi J., Gray H. E., Pardee A. B., Dean M., Sonenshein G. E. Cell-cycle control of c-myc but not c-ras expression is lost following chemical transformation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90217-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael D. F., Sommer A., Thompson R. C., Anderson D. C., Smith C. G., Welgus H. G., Stricklin G. P. Primary structure and cDNA cloning of human fibroblast collagenase inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2407–2411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran B. H., Reffel A. C., Stiles C. D. Molecular cloning of gene sequences regulated by platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):939–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran B. H., Zullo J., Verma I. M., Stiles C. D. Expression of the c-fos gene and of an fos-related gene is stimulated by platelet-derived growth factor. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1080–1082. doi: 10.1126/science.6093261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colburn N. H., Wendel E. J., Abruzzo G. Dissociation of mitogenesis and late-stage promotion of tumor cell phenotype by phorbol esters: mitogen-resistant variants are sensitive to promotion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6912–6916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D. R., Denhardt D. T. A study of mitochondrial and nuclear transcription with cloned cDNA probes. Changes in the relative abundance of mitochondrial transcripts after stimulation of quiescent mouse fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Mar;157(1):127–143. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D. R., Parfett C. L., Denhardt D. T. Transcriptional regulation of two serum-induced RNAs in mouse fibroblasts: equivalence of one species to B2 repetitive elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3280–3288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnham P. J., Schimke R. T. Transcriptional regulation of mouse dihydrofolate reductase in the cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7675–7680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. N., Schmidt L. J., Hodgson C. P., Moses H. L., Getz M. J. Polyadenylylated RNA complementary to a mouse retrovirus-like multigene family is rapidly and specifically induced by epidermal growth factor stimulation of quiescent cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7317–7321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson J. C., Golde D. W., Kaufman S. E., Westbrook C. A., Hewick R. M., Kaufman R. J., Wong G. G., Temple P. A., Leary A. C., Brown E. L. Molecular characterization and expression of the gene encoding human erythroid-potentiating activity. 1985 Jun 27-Jul 3Nature. 315(6022):768–771. doi: 10.1038/315768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn R. R., Aller P., Yuan Z. A., Gibson C. W., Baserga R. Cell-cycle-specific cDNAs from mammalian cells temperature sensitive for growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6004–6008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek L., Calabretta B., Baserga R. Expression of cell-cycle-dependent genes in phytohemagglutinin-stimulated human lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5375–5379. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R. Synthetic oligonucleotide probes deduced from amino acid sequence data. Theoretical and practical considerations. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 5;183(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau L. F., Nathans D. Identification of a set of genes expressed during the G0/G1 transition of cultured mouse cells. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3145–3151. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04057.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ley T. J., Anagnou N. P., Pepe G., Nienhuis A. W. RNA processing errors in patients with beta-thalassemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4775–4779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Nathans D. Growth-related changes in specific mRNAs of cultured mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4271–4275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Nathans D. Nucleotide sequence of a growth-related mRNA encoding a member of the prolactin-growth hormone family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4255–4259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu H. T., Baserga R., Mercer W. E. Adenovirus type 2 activates cell cycle-dependent genes that are a subset of those activated by serum. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2936–2942. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Leroy P., Ruhlmann C., Gesnel M. C., Breathnach R. Isolation of the oncogene and epidermal growth factor-induced transin gene: complex control in rat fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1679–1686. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Rautmann G., Magun B. E., Breathnach R. Epidermal growth factor or serum stimulation of rat fibroblasts induces an elevation in mRNA levels for lactate dehydrogenase and other glycolytic enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):711–726. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrogan M., Simonsen C. C., Smouse D. T., Farnham P. J., Schimke R. T. Heterogeneity at the 5' termini of mouse dihydrofolate reductase mRNAs. Evidence for multiple promoter regions. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2307–2314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer J. F., Wake S. A. An analysis of the rate of metallothionein mRNA poly(A)-shortening using RNA blot hybridization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):7929–7943. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.7929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. L., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. Molecular cloning of DNA complementary to bovine growth hormone mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7521–7524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Bravo R., Burckhardt J., Curran T. Induction of c-fos gene and protein by growth factors precedes activation of c-myc. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):716–720. doi: 10.1038/312716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parfett C. L., Hamilton R. T., Howell B. W., Edwards D. R., Nilsen-Hamilton M., Denhardt D. T. Characterization of a cDNA clone encoding murine mitogen-regulated protein: regulation of mRNA levels in mortal and immortal cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3289–3292. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnes J. R., Velan B., Felsenfeld A., Ramanathan L., Ferrini U., Appella E., Seidman J. G. Mouse beta 2-microglobulin cDNA clones: a screening procedure for cDNA clones corresponding to rare mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2253–2257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Halvorson H. O. A putative signal peptidase recognition site and sequence in eukaryotic and prokaryotic signal peptides. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 25;167(2):391–409. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin M. S., Doherty P. J., Gottesman M. M. The tumor promoter phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate induces a program of altered gene expression similar to that induced by platelet-derived growth factor and transforming oncogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):357–360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skup D., Windass J. D., Sor F., George H., Williams B. R., Fukuhara H., De Maeyer-Guignard J., De Maeyer E. Molecular cloning of partial cDNA copies of two distinct mouse IFN-beta mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3069–3084. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Challoner P. B., Neiman P. E., Groudine M. Expression of the c-myb proto-oncogene during cellular proliferation. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):374–380. doi: 10.1038/319374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Transient accumulation of c-fos RNA following serum stimulation requires a conserved 5' element and c-fos 3' sequences. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):889–902. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. S., Johnson L. F. Regulation of dihydrofolate reductase gene transcription in methotrexate-resistant mouse fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Feb;110(2):183–189. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041100212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Signal sequences. The limits of variation. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]