Abstract
We have constructed a plasmid (pRIF 309+) carrying the EcoRI restriction endonuclease gene and the f1 origin of replication. Upon transformation of this plasmid into E. coli and infection with bacteriophage f1 single stranded plasmids are produced which can be used for sequencing and site directed mutagenesis. Using this single stranded DNA and synthetic oligodeoxynucleotides we have introduced point mutations at defined positions of the EcoRI gene. Since in pRIF309+ the EcoRI gene is under the control of the pL-promoter, high level expression of the mutated EcoRI gene could be obtained upon induction. Mutant EcoRI enzymes were purified to homogeneity and characterized in structural and functional terms. Our results demonstrate that the Glu 111----Gln, Glu 144----Gln and Arg 145----Lys -mutants adopt a very similar conformation as the wild type enzyme, but have by two orders of magnitude smaller specific activities than the wild type enzyme, mainly due to a reduction of the Vmax-value.
Full text
PDF









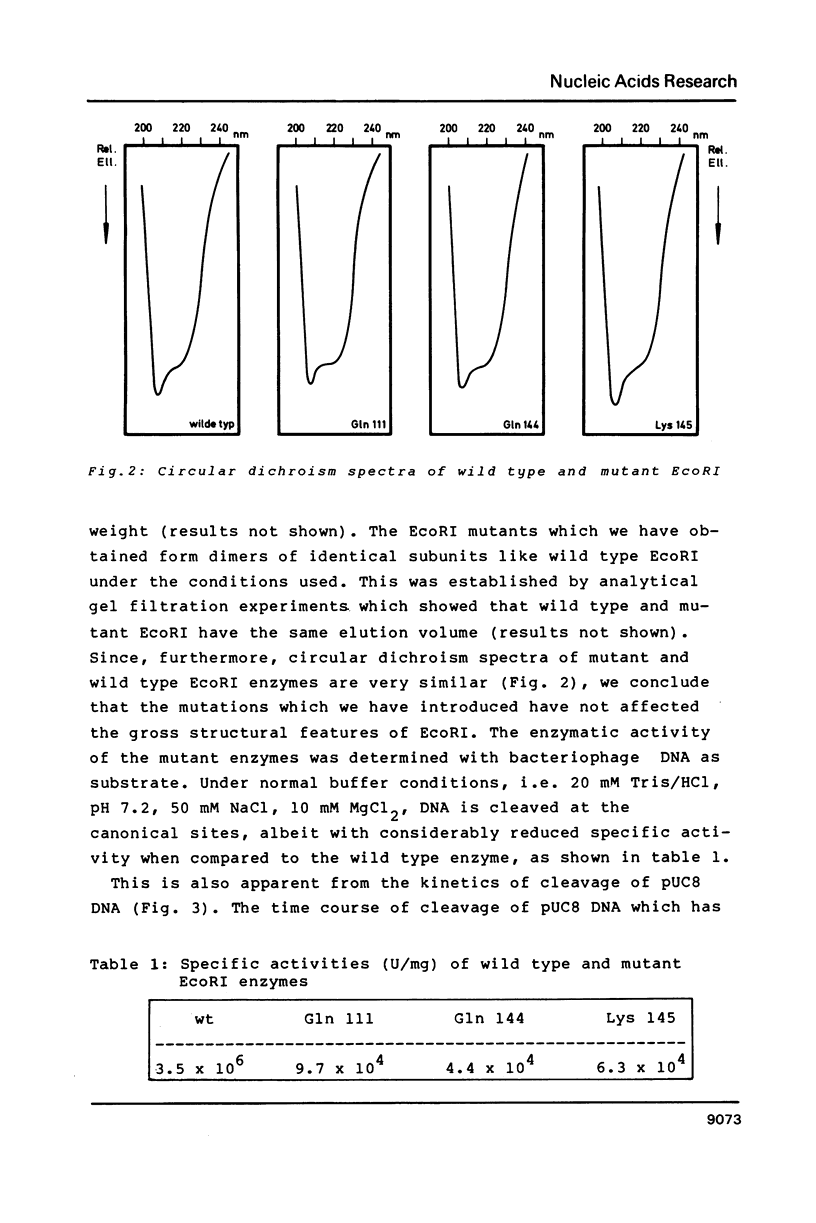
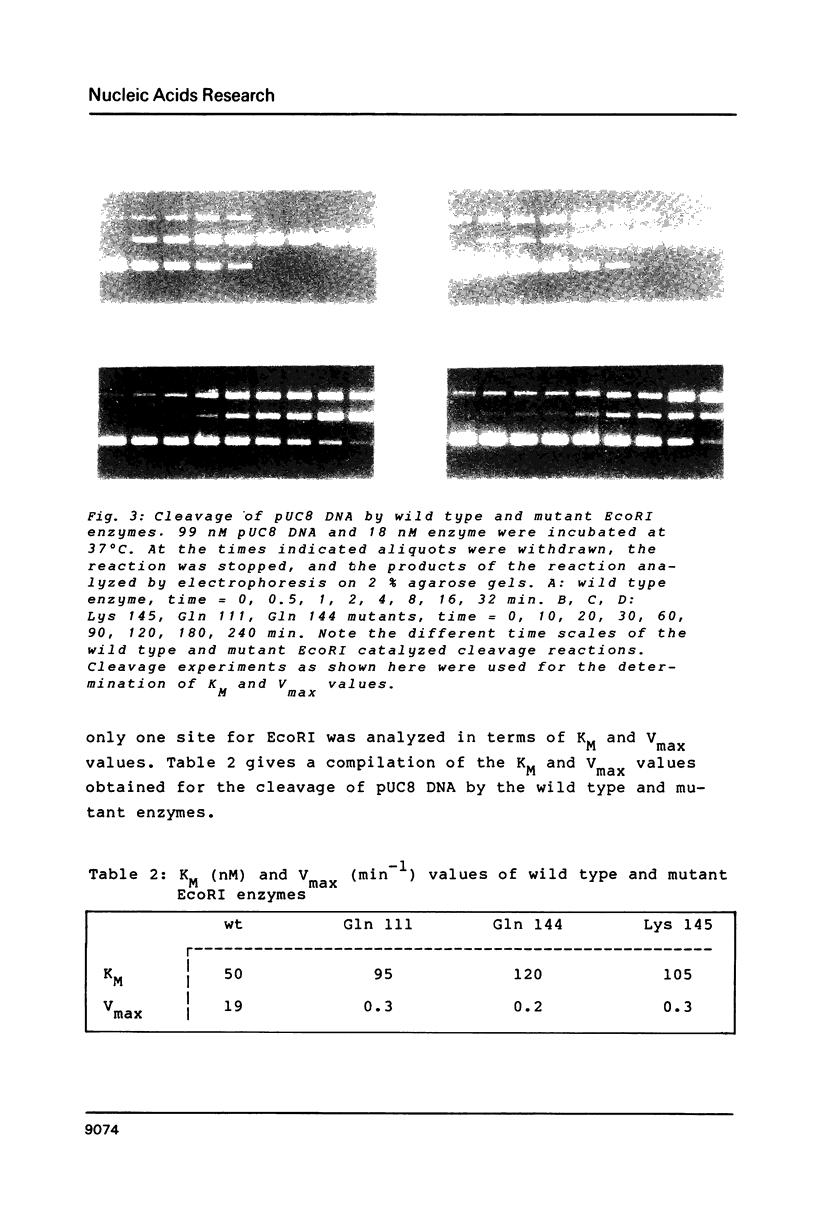






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bedouelle H., Winter G. A model of synthetase/transfer RNA interaction as deduced by protein engineering. 1986 Mar 27-Apr 2Nature. 320(6060):371–373. doi: 10.1038/320371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehbrecht H. J., Pingoud A., Urbanke C., Maass G., Gualerzi C. Linear diffusion of restriction endonucleases on DNA. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6160–6166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederick C. A., Grable J., Melia M., Samudzi C., Jen-Jacobson L., Wang B. C., Greene P., Boyer H. W., Rosenberg J. M. Kinked DNA in crystalline complex with EcoRI endonuclease. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):327–331. doi: 10.1038/309327a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goppelt M., Pingoud A., Maass G., Mayer H., Köster H., Frank R. The interaction of the EcoRI restriction endonuclease with its substrate. A physico-chemical study employing natural and synthetic oligonucleotides and polynucleotides. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Feb;104(1):101–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halford S. E., Johnson N. P. Single turnovers of the EcoRI restriction endonuclease. Biochem J. 1983 May 1;211(2):405–415. doi: 10.1042/bj2110405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halford S. E., Johnson N. P. The EcoRI restriction endonuclease with bacteriophage lambda DNA. Equilibrium binding studies. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 1;191(2):593–604. doi: 10.1042/bj1910593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu M., Berg P. Altering the specificity of restriction endonuclease: effect of replacing Mg2+ with Mn2+. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 10;17(1):131–138. doi: 10.1021/bi00594a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Phillips S., Edgell M. H., Gillam S., Jahnke P., Smith M. Mutagenesis at a specific position in a DNA sequence. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 25;253(18):6551–6560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Ike Y., Ikuta S., Itakura K. Solid phase synthesis of polynucleotides. VI. Further studies on polystyrene copolymers for the solid support. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1755–1769. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack W. E., Terry B. J., Modrich P. Involvement of outside DNA sequences in the major kinetic path by which EcoRI endonuclease locates and leaves its recognition sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4010–4014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jen-Jacobson L., Kurpiewski M., Lesser D., Grable J., Boyer H. W., Rosenberg J. M., Greene P. J. Coordinate ion pair formation between EcoRI endonuclease and DNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14638–14646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jen-Jacobson L., Lesser D., Kurpiewski M. The enfolding arms of EcoRI endonuclease: role in DNA binding and cleavage. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):619–629. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90294-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim R., Modrich P., Kim S. H. 'Interactive' recognition in EcoRI restriction enzyme-DNA complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 11;12(19):7285–7292. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.19.7285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langowski J., Alves J., Pingoud A., Maass G. Does the specific recognition of DNA by the restriction endonuclease EcoRI involve a linear diffusion step? Investigation of the processivity of the EcoRI endonuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):501–513. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langowski J., Pingoud A., Goppelt M., Maass G. Inhibition of Eco RI action by polynucleotides. A characterization of the non-specific binding of the enzyme to DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 24;8(20):4727–4736. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.20.4727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luke P. A., Halford S. E. Solubility of the EcoRI restriction endonuclease and its purification from an over-producing strain. Gene. 1985;37(1-3):241–246. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90278-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luke P. A., Halford S. E. Solubility of the EcoRI restriction endonuclease and its purification from an over-producing strain. Gene. 1985;37(1-3):241–246. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90278-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modrich P., Zabel D. EcoRI endonuclease. Physical and catalytic properties of the homogenous enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):5866–5874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A. K., Rubin R. A., Kim S. H., Modrich P. DNA sequences of structural genes for Eco RI DNA restriction and modification enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2131–2139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton C. R., Greene A. R., Heathcliffe G. R., Atkinson T. C., Holland D., Markham A. F., Edge M. D. Ion-exchange high-performance liquid chromatography of oligodeoxyribonucleotides using formamide. Anal Biochem. 1983 Feb 15;129(1):22–30. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg J. M., Greene P. Eco RI* specificity and hydrogen bonding. DNA. 1982;1(2):117–124. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1982.1.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek S., Pingoud A., Maass G., Zabeau M. Polypeptide sequences involved in the cleavage of DNA by the restriction endonuclease EcoRI. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2228–2234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suck D., Oefner C. Structure of DNase I at 2.0 A resolution suggests a mechanism for binding to and cutting DNA. Nature. 1986 Jun 5;321(6070):620–625. doi: 10.1038/321620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry B. J., Jack W. E., Modrich P. Facilitated diffusion during catalysis by EcoRI endonuclease. Nonspecific interactions in EcoRI catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13130–13137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry B. J., Jack W. E., Rubin R. A., Modrich P. Thermodynamic parameters governing interaction of EcoRI endonuclease with specific and nonspecific DNA sequences. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9820–9825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfes H., Fliess A., Pingoud A. A comparison of the structural requirements for DNA cleavage by the isoschizomers HaeIII, BspRI and BsuRI. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jul 1;150(1):105–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfes H., Fliess A., Winkler F., Pingoud A. Cross-linking of bromodeoxyuridine-substituted oligonucleotides to the EcoRI and EcoRV restriction endonucleases. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 1;159(2):267–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09863.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhead J. L., Bhave N., Malcolm A. D. Cation dependence of restriction endonuclease EcoRI activity. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(2):293–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhead J. L., Malcolm A. D. Non-specific binding of restriction endonuclease EcoR1 to DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 25;8(2):389–402. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.2.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhead J. L., Malcolm A. D. The essential carboxyl group in restriction endonuclease EcoRI. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(1):125–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05678.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



