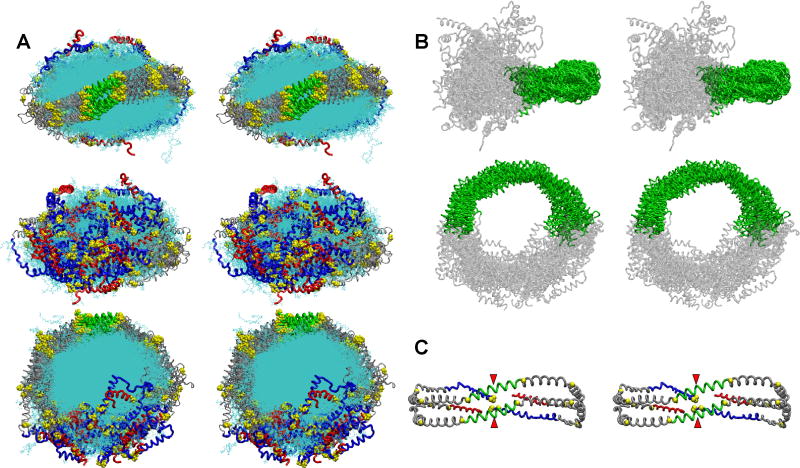
FIGURE 6. Detailed stereo images of the double belt structure of FL-apoA-I in the R2-216 ensemble after MDSA.
The protein chains of the final structures of the sixteen member ensemble were aligned between residues 77-188, the domain containing the interhelical solvent-inaccessible salt bridges. A. Cross-eyed stereo images of the aligned structures viewed from three different directions. Upper panel, view from helix 5 side; middle panel, view from terminal domain side; lower panel, view from disc top. C-terminal helix 10 domains, residues 220-243 (red licorice), N-terminal domains, residues 1-43 (blue licorice), helix 5 domain (green licorice), remainder of protein (gray licorice), and lipid (cyan line). B. Cross-eyed stereo image of the aligned structures showing the relative immobility of the central domain (green licorice) and mobility of the terminal domains (gray licorice). C. Cross-eyed stereo image of an average final structure created from calculated average coordinates. The apoA-I double belt is viewed from the helix 5 domain. The protein is represented as a Cα backbone licorice model except Cα proline (spacefilling yellow). Helix 5 (green), C-terminal helix 10 domains, residues 220-243 (red), N-terminal domains, residues 1-43 (blue), and remainder of protein (gray). The N-terminal proline-rich domains are indicated by red arrowheads.