Abstract
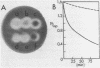
The nucleotide sequence of the portion of a Bacillus subtilis (strain PAP115) 3 kb Pst I fragment which contains an endo-beta-1, 4-glucanase gene has been determined. This gene encodes a protein of 499 amino acid residues (Mr = 55,234) with a typical B. subtilis signal peptide. Escherichia coli which has been transformed with this gene produces an extracellular endoglucanase with an amino-terminus corresponding to the thirtieth encoded amino acid residue. The gene is preceded by a cryptic reading frame with a rho-independent terminator structure, and itself has such a structure in the immediate 3'-flanking region. We have also identified, in the 5'-flanking region, nucleotide sequences which resemble promoter elements recognized by Bacillus RNA polymerase E sigma 43. Comparison of the encoded amino acid sequence to other known beta-glucanases reveals a small region of similarity to the encoded protein of the Clostridium thermocellum celB gene. These similar regions may contain substrate-binding and/or catalytic sites.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Band L., Henner D. J. Bacillus subtilis requires a "stringent" Shine-Dalgarno region for gene expression. DNA. 1984;3(1):17–21. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banner C. D., Moran C. P., Jr, Losick R. Deletion analysis of a complex promoter for a developmentally regulated gene from Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1983 Aug 5;168(2):351–365. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Béguin P., Cornet P., Aubert J. P. Sequence of a cellulase gene of the thermophilic bacterium Clostridium thermocellum. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):102–105. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.102-105.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierstein R., Wickner W. Requirements for substrate recognition by bacterial leader peptidase. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):427–431. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04228.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobinson K. F., Spiegelman G. B. Nucleotide sequence and transcription of a bacteriophage 29 early promoter. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):5950–5955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita Y., Fujita T. Identification and nucleotide sequence of the promoter region of the Bacillus subtilis gluconate operon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1237–1252. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitt M. A., Wang L. F., Doi R. H. A strong sequence homology exists between the major RNA polymerase sigma factors of Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7178–7185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grépinet O., Béguin P. Sequence of the cellulase gene of Clostridium thermocellum coding for endoglucanase B. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1791–1799. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogeweg P., Hesper B. The alignment of sets of sequences and the construction of phyletic trees: an integrated method. J Mol Evol. 1984;20(2):175–186. doi: 10.1007/BF02257378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes W. M., Platt T., Rosenberg M. Termination of transcription in E. coli. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1029–1032. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara H., Sasaki T., Tsuboi A., Yamagata H., Tsukagoshi N., Udaka S. Complete nucleotide sequence of a thermophilic alpha-amylase gene: homology between prokaryotic and eukaryotic alpha-amylases at the active sites. J Biochem. 1985 Jul;98(1):95–103. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. C., Moran C. P., Jr, Losick R. Two RNA polymerase sigma factors from Bacillus subtilis discriminate between overlapping promoters for a developmentally regulated gene. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):800–804. doi: 10.1038/302800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehtovaara P., Ulmanen I., Palva I. In vivo transcription initiation and termination sites of an alpha-amylase gene from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens cloned in Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):11–16. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90099-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay R. M., Baird S., Dove M. J., Erratt J. A., Gines M., Moranelli F., Nasim A., Willick G. E., Yaguchi M., Seligy V. L. Glucanase gene diversity in prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms. Biosystems. 1985;18(3-4):279–292. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(85)90028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mongkolsuk S., Duvall E. J., Lovett P. S. Transcription termination signal for the cat-86 indicator gene in a Bacillus subtilis promoter-cloning plasmid. Gene. 1985;37(1-3):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90260-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., LeGrice S. F., Lee G., Stephens M., Sonenshein A. L., Pero J., Losick R. Nucleotide sequences that signal the initiation of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00729452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. Protein secretion in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:615–648. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priest F. G. Extracellular enzyme synthesis in the genus Bacillus. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):711–753. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.711-753.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pétré D., Béguin P., Millet J., Aubert J. P. Heterologous hybridization of bacterial DNA to the endoglucanases A and B structural genes celA and celB of Clostridium thermocellum. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1985 Sep-Oct;136B(2):113–124. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(85)80038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson L. M., Chambliss G. H. Cloning of the Bacillus subtilis DLG beta-1,4-glucanase gene and its expression in Escherichia coli and B. subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):612–619. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.612-619.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. C. Conserved amino acid sequence domains in alpha-amylases from plants, mammals, and bacteria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 16;128(1):470–476. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91702-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salser W. Globin mRNA sequences: analysis of base pairing and evolutionary implications. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):985–1002. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sashihara N., Kudo T., Horikoshi K. Molecular cloning and expression of cellulase genes of alkalophilic Bacillus sp. strain N-4 in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):503–506. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.503-506.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Le Coq D., Aymerich S., Gonzy-Tréboul G., Gay P. The DNA sequence of the gene for the secreted Bacillus subtilis enzyme levansucrase and its genetic control sites. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;200(2):220–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00425427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takkinen K., Pettersson R. F., Kalkkinen N., Palva I., Söderlund H., Käriäinen L. Amino acid sequence of alpha-amylase from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens deduced from the nucleotide sequence of the cloned gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1007–1013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatti K. M., Kenney T. J., Hay R. E., Moran C. P., Jr Promoter specificity of a sporulation-induced form of RNA polymerase from Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1985;36(1-2):151–157. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90079-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatti K. M., Moran C. P., Jr Promoter recognition by sigma-37 RNA polymerase from Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1984 May 25;175(3):285–297. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90349-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasantha N., Thompson L. D., Rhodes C., Banner C., Nagle J., Filpula D. Genes for alkaline protease and neutral protease from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens contain a large open reading frame between the regions coding for signal sequence and mature protein. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):811–819. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.811-819.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang P. Z., Doi R. H. Overlapping promoters transcribed by bacillus subtilis sigma 55 and sigma 37 RNA polymerase holoenzymes during growth and stationary phases. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8619–8625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. L., Price C. W., Goldfarb D. S., Doi R. H. The subtilisin E gene of Bacillus subtilis is transcribed from a sigma 37 promoter in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaguchi M., Roy C., Rollin C. F., Paice M. G., Jurasek L. A fungal cellulase shows sequence homology with the active site of hen egg-white lysozyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Oct 31;116(2):408–411. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90537-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki H., Ohmura K., Nakayama A., Takeichi Y., Otozai K., Yamasaki M., Tamura G., Yamane K. Alpha-amylase genes (amyR2 and amyE+) from an alpha-amylase-hyperproducing Bacillus subtilis strain: molecular cloning and nucleotide sequences. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):327–337. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.327-337.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]