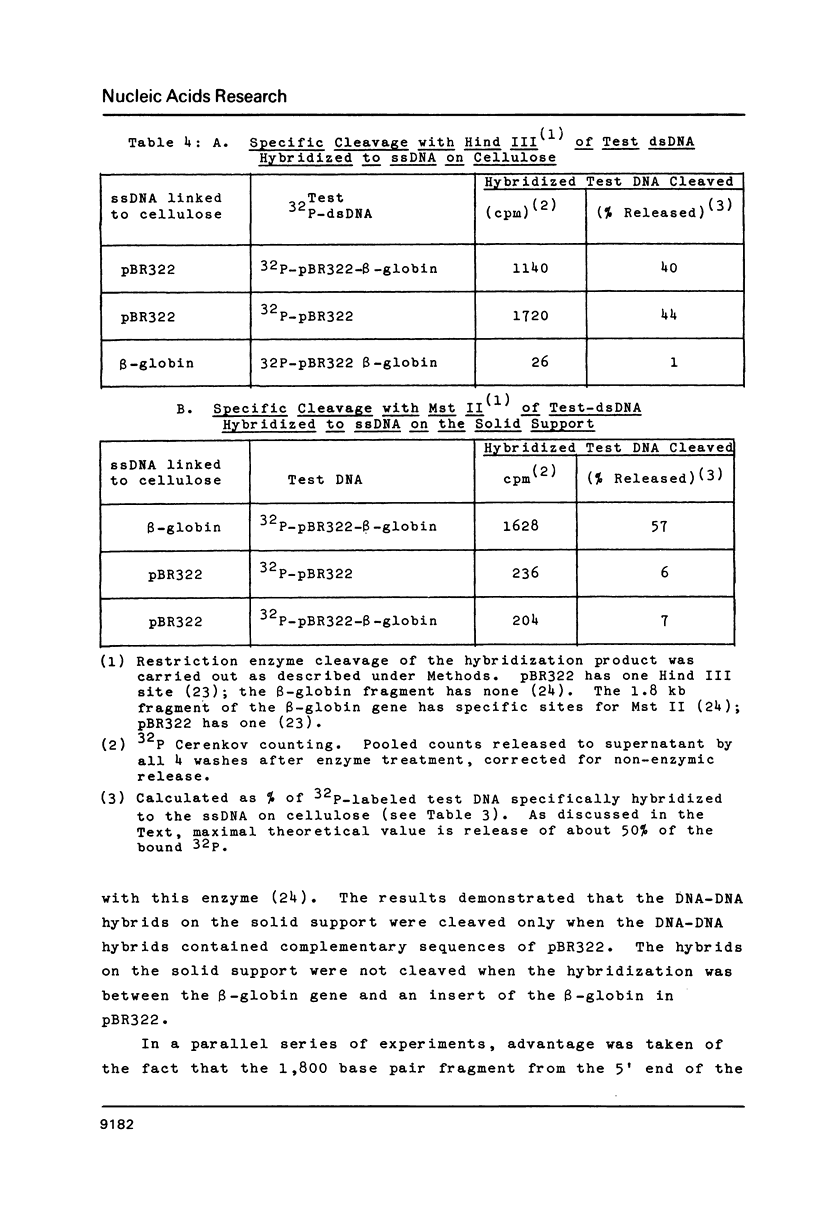
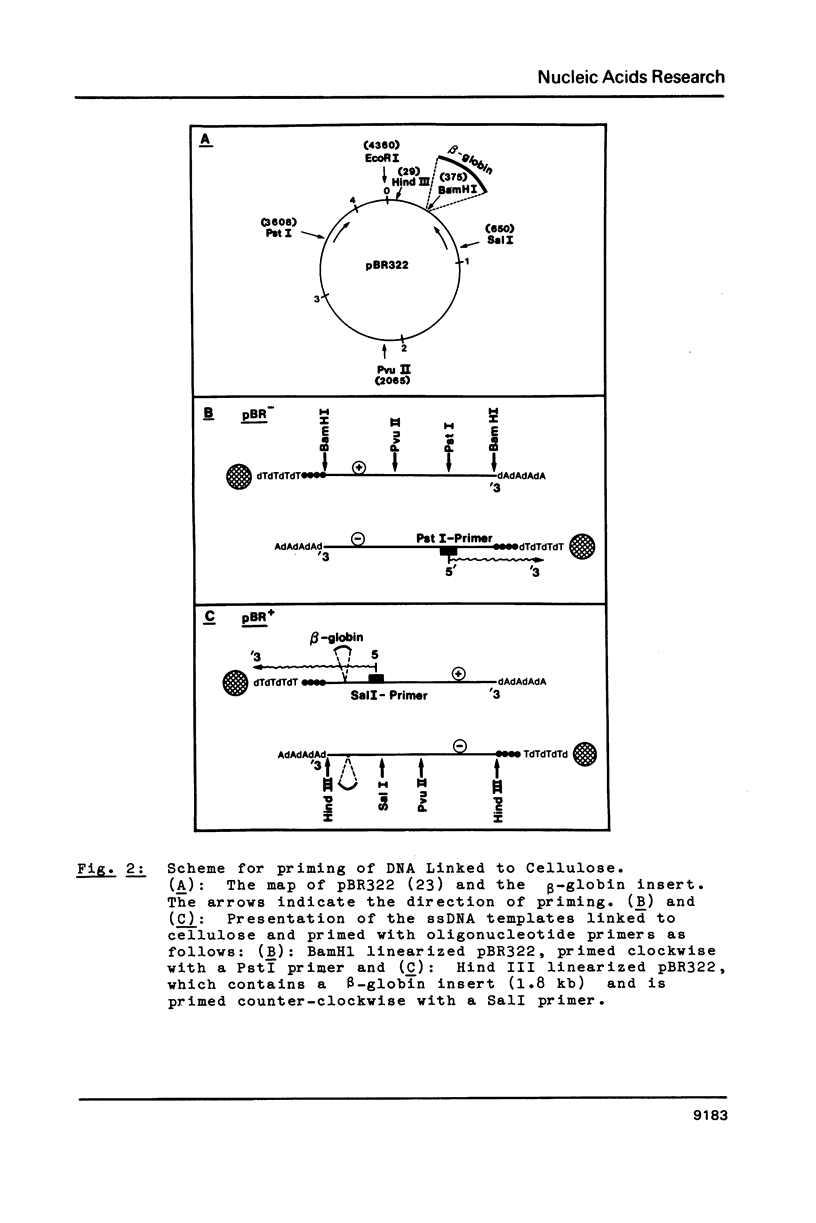
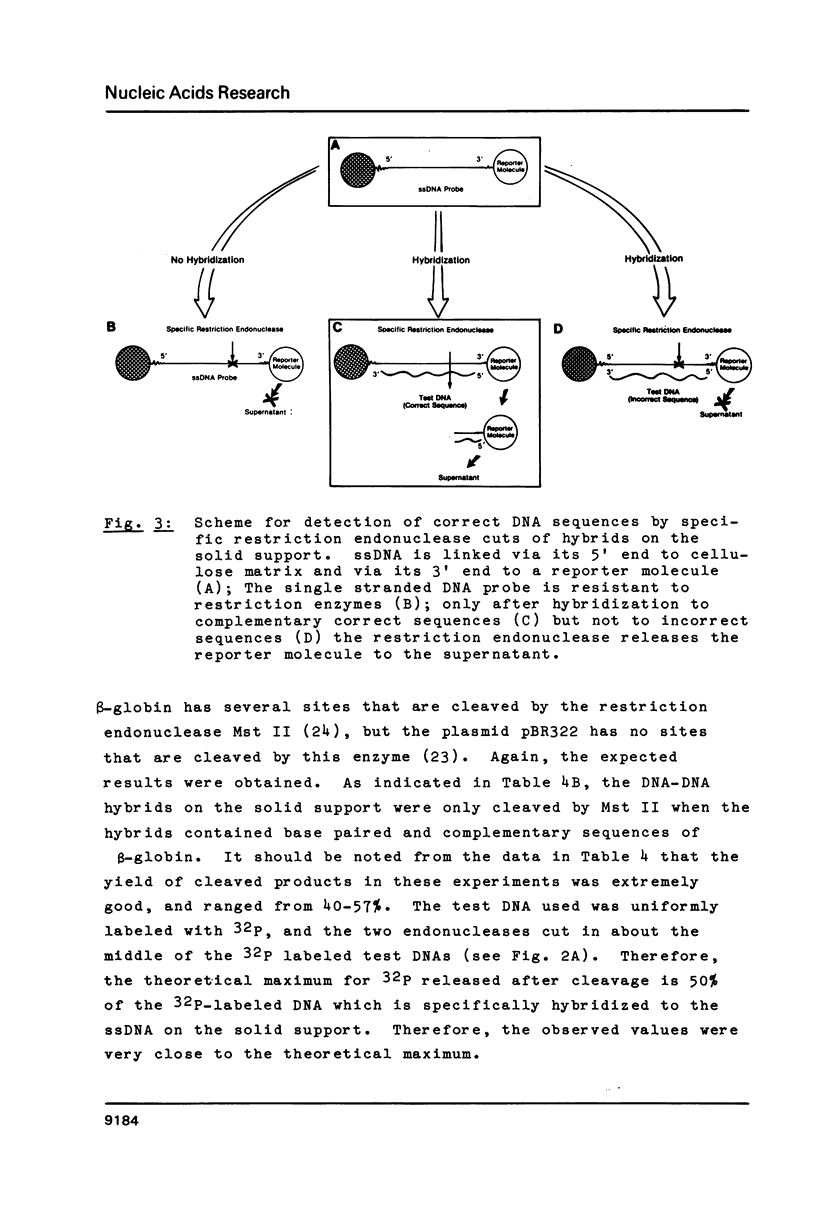
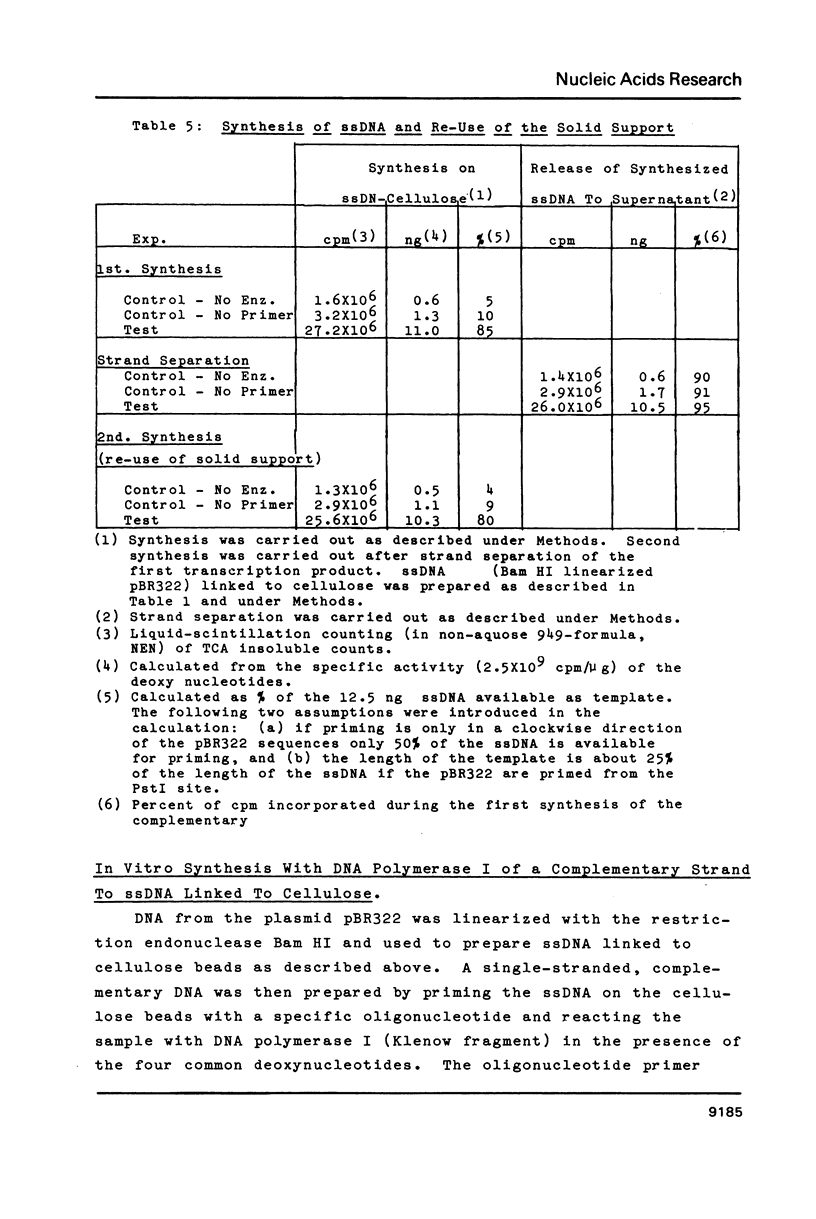
Abstract
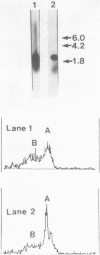
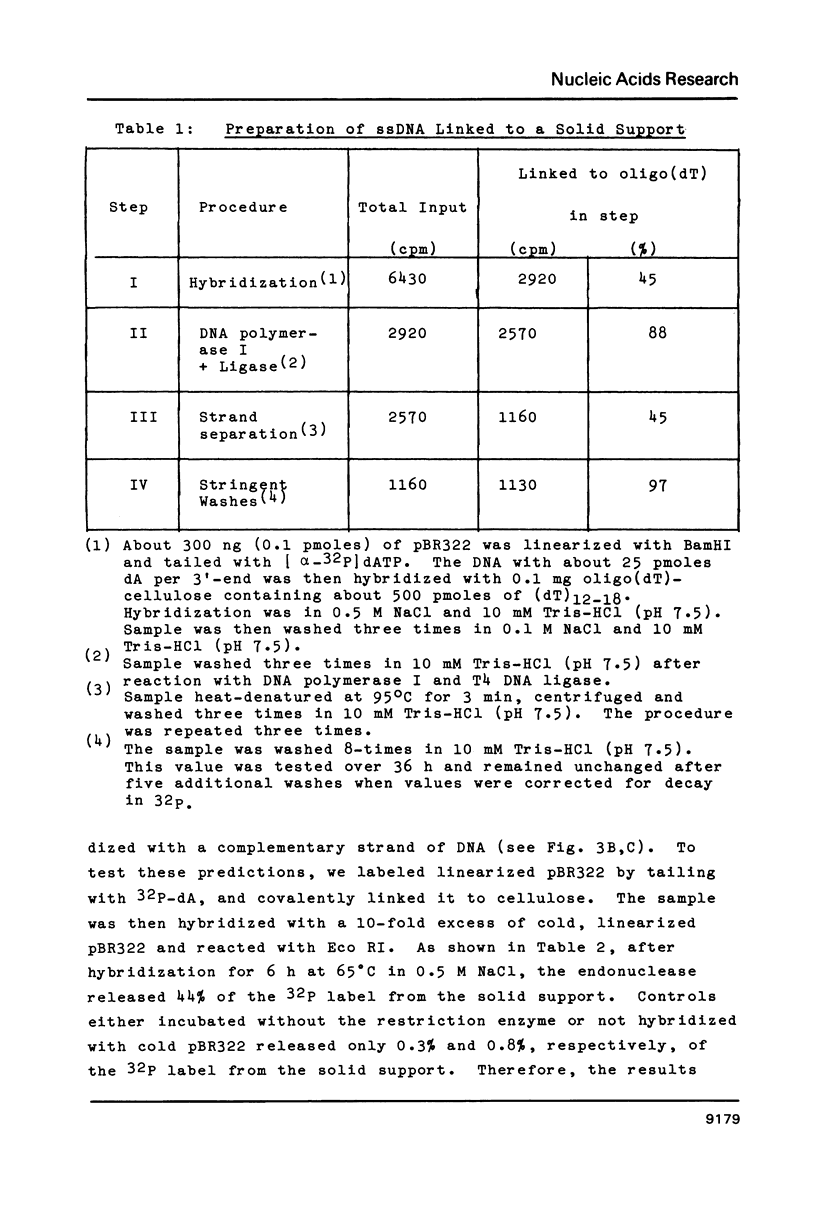
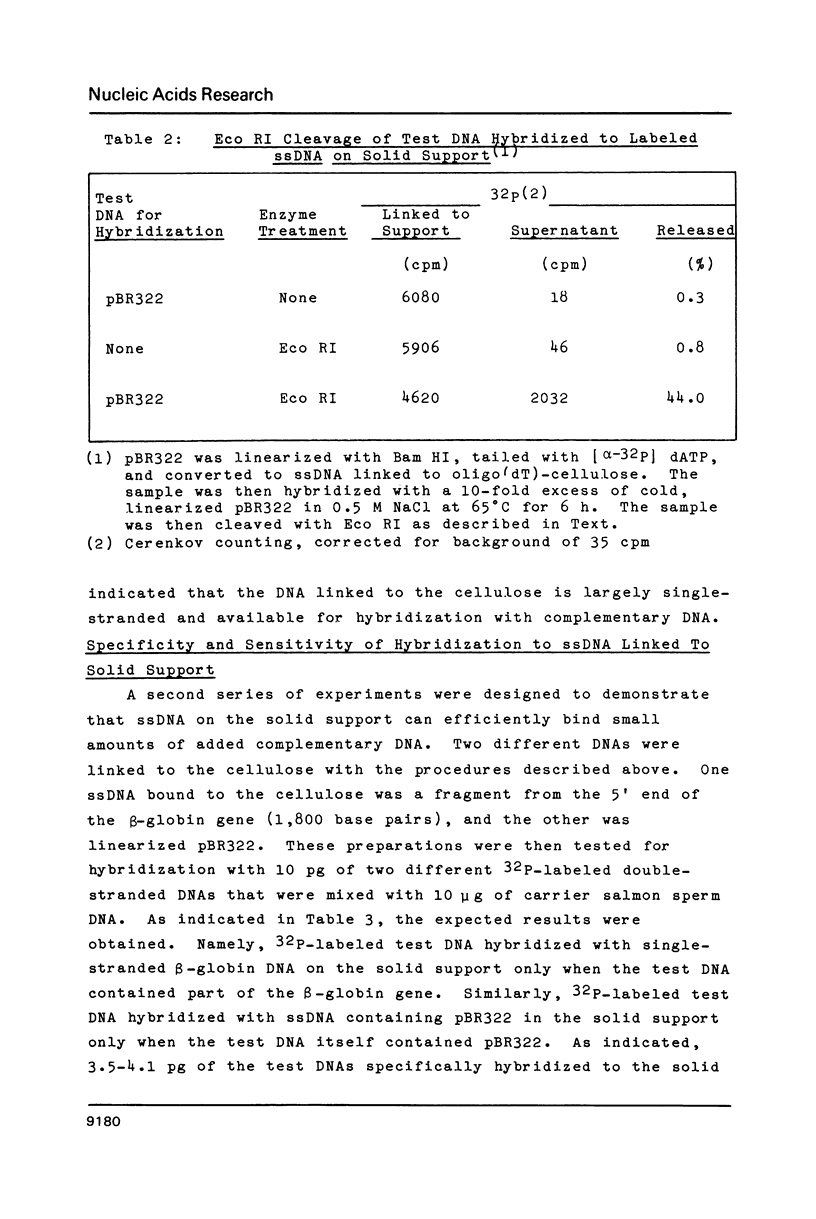
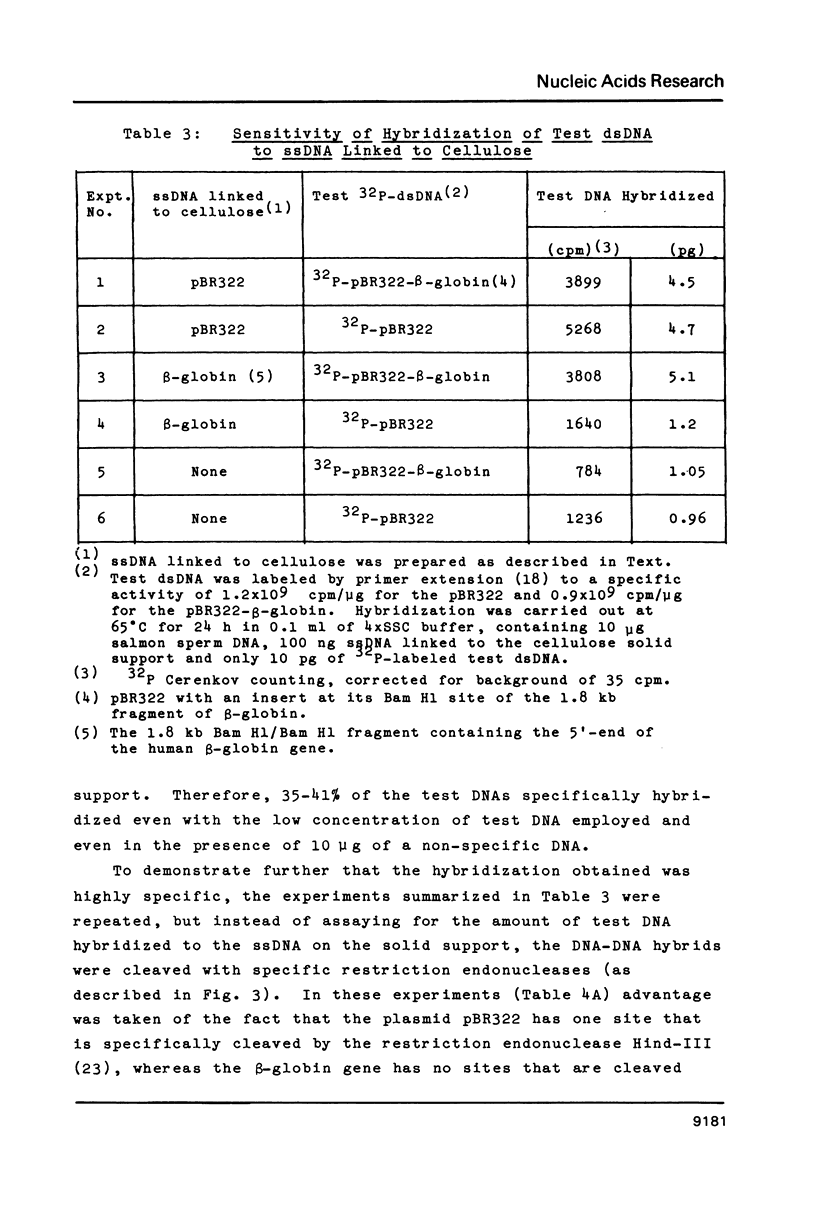
Single-stranded DNAs (ssDNAs) were covalently bound by a simple and efficient enzymatic method to a solid support matrix and used to develop several new procedures for gene analysis. The novel procedure to prepare a ssDNA stably coupled to a solid support employed T4 DNA ligase to link covalently oligo (dT)-cellulose and (dA)-tailed DNA. Beginning with essentially any double stranded DNA the procedure generates a ssDNA linked by its 5' end to a cellulose matrix in a concentration of over 500 ng per mg. DNA from the plasmid pBR322 (4300 bp) and a fragment of the beta-globin gene (1800 bp) were coupled to the solid support and used for several experiments. The ssDNAs on the cellulose efficiently hybridized with as little as 5 pg of complementary double-stranded DNAs. The DNA hybrids formed on the solid support were specifically and efficiently cleaved by restriction endonucleases. These specific restriction cuts were utilized for the diagnosis of correct sequences. In addition, the ssDNA on the solid support served as an efficient template for the synthesis of complementary ssDNAs. The complementary synthesized ssDNAs were uniformly labeled, more than two kilobases in size, and largely full length. About 85% of the ssDNA linked to cellulose was available for the synthesis of complementary DNA, and after strand-separation, the preparation was reusable for the synthesis of additional complementary DNA.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arndt-Jovin D. J., Jovin T. M., Bähr W., Frischauf A. M., Marquardt M. Covalent attachment of DNA to agarose. Improved synthesis and use in affinity chromatography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):411–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashley P. L., MacDonald R. J. Synthesis of single-stranded hybridization probes from reusable DNA templates bound to solid support. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jul;140(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bünemann H. Immobilization of denatured DNA to macroporous supports: II. Steric and kinetic parameters of heterogeneous hybridization reactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7181–7196. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bünemann H., Westhoff P., Herrmann R. G. Immobilization of denatured DNA to macroporous supports: I. Efficiency of different coupling procedures. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7163–7180. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu B. C., Wahl G. M., Orgel L. E. Derivatization of unprotected polynucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6513–6529. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delius H., van Heerikhuizen H., Clarke J., Koller B. Separation of complementary strands of plasmid DNA using the biotin-avidin system and its application to heteroduplex formation and RNA/DNA hybridizations in electron microscopy. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5457–5469. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng G., Wu R. An improved procedure for utilizing terminal transferase to add homopolymers to the 3' termini of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):4173–4188. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.4173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilham P. T. Immobilized polynucleotides and nucleic acids. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1974;42(0):173–185. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-6982-0_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilham P. T. The synthesis of celluloses containing covalently bound nucleotides, polynucleotides, and nucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1968 Aug;7(8):2809–2813. doi: 10.1021/bi00848a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. L., Lifton R. P., Stark G. R., Williams J. G. Isolation of specific RNA's using DNA covalently linked to diazobenzyloxymethyl cellulose or paper. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:206–220. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Maniatis T., Melton D. A. Human beta-globin pre-mRNA synthesized in vitro is accurately spliced in Xenopus oocyte nuclei. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):681–694. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu N., Messing J. The making of strand-specific M13 probes. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley W. S., Stump K. H. A rapid procedure for isolation of large quantities of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I utilizing a lambdapolA transducing phage. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3206–3210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Efstratiadis A., O'Connell C., Maniatis T. The nucleotide sequence of the human beta-globin gene. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):647–651. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris C. E., Klement J. F., McAllister W. T. Cloning and expression of the bacteriophage T3 RNA polymerase gene. Gene. 1986;41(2-3):193–200. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90098-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss L. G., Moore J. P., Chan L. A simple, efficient method for coupling DNA to cellulose. Development of the method and application to mRNA purification. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12655–12658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noyes B. E., Stark G. R. Nucleic acid hybridization using DNA covalently coupled to cellulose. Cell. 1975 Jul;5(3):301–310. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90105-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poonian M. S., Schlabach A. J., Weissbach A. Covalent attachment of nucleic acids to agarose for affinity chromatography. Biochemistry. 1971 Feb 2;10(3):424–427. doi: 10.1021/bi00779a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potuzak H., Dean D. G. Affinity chromatography on columns containing nucleic acids. FEBS Lett. 1978 Apr 15;88(2):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80165-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricca G. A., Taylor J. M., Kalinyak J. E. Simple rapid method for the synthesis of radioactively labeled cDNA hybridization probes utilizing bacteriophage M13mp7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):724–728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venetianer P., Leder P. Enzymatic synthesis of solid phase-bound DNA sequences corresponding to specific mammalian genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):3892–3895. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson M. J., Suggs S. V., Miyoshi K., Bhatt R., Itakura K. A set of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide primers for DNA sequencing in the plasmid vector pBR322. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Jacquemin-Sablon A., Live T. R., Fareed G. C., Richardson C. C. Enzymatic breakage and joining of deoxyribonucleic acid. VI. Further purification and properties of polynucleotide ligase from Escherichia coli infected with bacteriophage T4. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 10;243(17):4543–4555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zielinski W. S., Orgel L. E. Oligomerization of activated derivatives of 3'-amino-3'-deoxyguanosine on poly(C) and poly(dC) templates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2469–2484. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]