Abstract
The protooncogene Ets-1 is a member of the c-Ets family of genes originally identified through their sequence homology to the v-ets gene of the avian erythroblastosis virus E26. Ets-like factors are characterised by a conserved 85 amino acid domain which appears to be essential for binding to purine rich DNA sequences. Sequences binding to Ets-1 were selected from a random oligonucleotide pool by immunoprecipitation and amplified using the Polymerase Chain Reaction. Oligonucleotides enriched by this procedure were cloned in plasmids and sequenced. Alignment of DNA sequences revealed GGAA and GGAT cores at about a 1.4:1 ratio. Preferred sequences were identified both 5' and 3' of the GGAW core, extending the binding site to ACMGGAWRTT. Analysis of the flanking sequences associated with GGAA and GGAT cores revealed differences which may have compensated for the generally lower affinity of binding sites containing a GGAT core. Lastly mutational analysis of one particular Ets-1 binding site was used to establish the relative importance for binding of some nucleotides within the core and to show that Ets-1 and the closely related Ets-2 proteins bind to similar sequences.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bankier A. T., Weston K. M., Barrell B. G. Random cloning and sequencing by the M13/dideoxynucleotide chain termination method. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:51–93. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-David Y., Giddens E. B., Letwin K., Bernstein A. Erythroleukemia induction by Friend murine leukemia virus: insertional activation of a new member of the ets gene family, Fli-1, closely linked to c-ets-1. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):908–918. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat N. K., Fisher R. J., Fujiwara S., Ascione R., Papas T. S. Temporal and tissue-specific expression of mouse ets genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3161–3165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat N. K., Komschlies K. L., Fujiwara S., Fisher R. J., Mathieson B. J., Gregorio T. A., Young H. A., Kasik J. W., Ozato K., Papas T. S. Expression of ets genes in mouse thymocyte subsets and T cells. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):672–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat N. K., Thompson C. B., Lindsten T., June C. H., Fujiwara S., Koizumi S., Fisher R. J., Papas T. S. Reciprocal expression of human ETS1 and ETS2 genes during T-cell activation: regulatory role for the protooncogene ETS1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3723–3727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosselut R., Duvall J. F., Gégonne A., Bailly M., Hémar A., Brady J., Ghysdael J. The product of the c-ets-1 proto-oncogene and the related Ets2 protein act as transcriptional activators of the long terminal repeat of human T cell leukemia virus HTLV-1. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3137–3144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07511.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulukos K. E., Pognonec P., Begue A., Galibert F., Gesquière J. C., Stéhelin D., Ghysdael J. Identification in chickens of an evolutionarily conserved cellular ets-2 gene (c-ets-2) encoding nuclear proteins related to the products of the c-ets proto-oncogene. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):697–705. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02865.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burtis K. C., Thummel C. S., Jones C. W., Karim F. D., Hogness D. S. The Drosophila 74EF early puff contains E74, a complex ecdysone-inducible gene that encodes two ets-related proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):85–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. H. The proto-oncogene c-ets is preferentially expressed in lymphoid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2993–3000. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghysdael J., Gegonne A., Pognonec P., Dernis D., Leprince D., Stehelin D. Identification and preferential expression in thymic and bursal lymphocytes of a c-ets oncogene-encoded Mr 54,000 cytoplasmic protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1714–1718. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghysdael J., Yaniv M. Nuclear oncogenes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;3(3):484–491. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90077-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlin S. D., Bosselut R., Gégonne A., Ghysdael J., Brady J. N. Sequence-specific interaction of the Ets1 protein with the long terminal repeat of the human T-lymphotropic virus type I. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5513–5523. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5513-5523.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunther C. V., Nye J. A., Bryner R. S., Graves B. J. Sequence-specific DNA binding of the proto-oncoprotein ets-1 defines a transcriptional activator sequence within the long terminal repeat of the Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):667–679. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman A., Wasylyk B. Nuclear targets for transcription regulation by oncogenes. Trends Genet. 1991 Feb;7(2):49–54. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90231-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho I. C., Bhat N. K., Gottschalk L. R., Lindsten T., Thompson C. B., Papas T. S., Leiden J. M. Sequence-specific binding of human Ets-1 to the T cell receptor alpha gene enhancer. Science. 1990 Nov 9;250(4982):814–818. doi: 10.1126/science.2237431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim F. D., Urness L. D., Thummel C. S., Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Celada A., Van Beveren C., Maki R. A., Gunther C. V., Nye J. A. The ETS-domain: a new DNA-binding motif that recognizes a purine-rich core DNA sequence. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1451–1453. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Celada A., Van Beveren C., Maki R. A. The macrophage and B cell-specific transcription factor PU.1 is related to the ets oncogene. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi S., Fisher R. J., Fujiwara S., Jorcyk C., Bhat N. K., Seth A., Papas T. S. Isoforms of the human ets-1 protein: generation by alternative splicing and differential phosphorylation. Oncogene. 1990 May;5(5):675–681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMarco K., Thompson C. C., Byers B. P., Walton E. M., McKnight S. L. Identification of Ets- and notch-related subunits in GA binding protein. Science. 1991 Aug 16;253(5021):789–792. doi: 10.1126/science.1876836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leprince D., Gegonne A., Coll J., de Taisne C., Schneeberger A., Lagrou C., Stehelin D. A putative second cell-derived oncogene of the avian leukaemia retrovirus E26. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):395–397. doi: 10.1038/306395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz T., Graf T. Fusion of the nuclear oncoproteins v-Myb and v-Ets is required for the leukemogenicity of E26 virus. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90142-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz T., Graf T. v-myb and v-ets transform chicken erythroid cells and cooperate both in trans and in cis to induce distinct differentiation phenotypes. Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):369–380. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn M. F., Seeburg P. H., Moscovici C., Duesberg P. H. Tripartite structure of the avian erythroblastosis virus E26 transforming gene. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):391–395. doi: 10.1038/306391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn M., Weiher H., Bullock P., Duesberg P. Avian erythroblastosis virus E26: nucleotide sequence of the tripartite onc gene and of the LTR, and analysis of the cellular prototype of the viral ets sequence. Virology. 1984 Dec;139(2):330–339. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90378-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
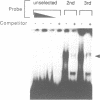
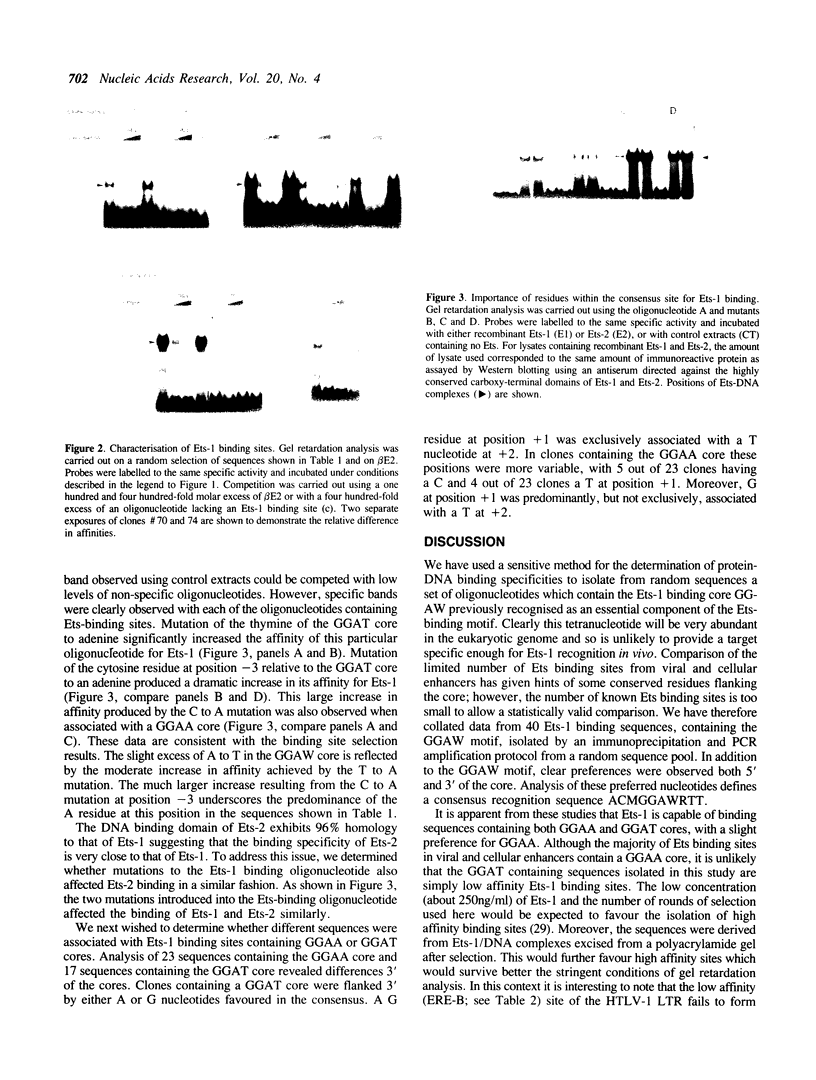
- Pollock R., Treisman R. A sensitive method for the determination of protein-DNA binding specificities. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6197–6204. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Beug H., Kornfeld S., Graf T. Transformation of both erythroid and myeloid cells by E26, an avian leukemia virus that contains the myb gene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):643–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao V. N., Huebner K., Isobe M., ar-Rushdi A., Croce C. M., Reddy E. S. elk, tissue-specific ets-related genes on chromosomes X and 14 near translocation breakpoints. Science. 1989 Apr 7;244(4900):66–70. doi: 10.1126/science.2539641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao V. N., Papas T. S., Reddy E. S. erg, a human ets-related gene on chromosome 21: alternative splicing, polyadenylation, and translation. Science. 1987 Aug 7;237(4815):635–639. doi: 10.1126/science.3299708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Flores P., Begue A., Leprince D., Stehelin D. The c-ets proto-oncogenes encode transcription factors that cooperate with c-Fos and c-Jun for transcriptional activation. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):191–193. doi: 10.1038/346191a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Gutman A., Nicholson R., Wasylyk B. The c-Ets oncoprotein activates the stromelysin promoter through the same elements as several non-nuclear oncoproteins. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1127–1134. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08053.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. K., McWilliams M. J., Lapis P., Lautenberger J. A., Schweinfest C. W., Papas T. S. Mammalian ets-1 and ets-2 genes encode highly conserved proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7862–7866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]