Abstract
In the title molecule, C16H12F2N2O, the pyrazole ring adopts a slight envelope conformation with the methylene C atom deviating by 0.114 (3) Å from the mean plane of the other four atoms [maximum deviation = 0.021 (3) Å]. The dihedral angles between the four essentially planar atoms of the pyrazole ring and the fluoro-substituted benzene rings are 2.6 (2) and 82.2 (2)°. The dihedral angle between the two benzene rings is 83.7 (2)°. The crystal packing is stabilized by weak intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Related literature
For the biological activity of pyrazolines, see: Hes et al. (1978 ▶); Manna et al. (2005 ▶); Amir et al. (2008 ▶); Regaila et al. (1979 ▶); Sarojini et al. (2010 ▶). For their importance in organic synthesis, see: Bhaskarreddy et al. (1997 ▶); Klimova et al. (1999 ▶). For related structures, see: Butcher et al. (2007 ▶); Cui & Li (2010 ▶); Fun et al. (2010a
▶,b
▶); Jasinski et al. (2010a
▶,b
▶); Baktır et al. (2011 ▶).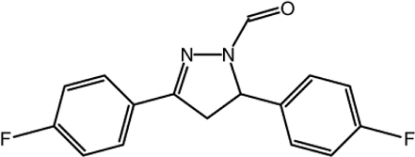
Experimental
Crystal data
C16H12F2N2O
M r = 286.28
Triclinic,
a = 6.2141 (9) Å
b = 6.7802 (8) Å
c = 17.9857 (9) Å
α = 96.727 (4)°
β = 90.254 (4)°
γ = 116.791 (5)°
V = 670.39 (13) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.11 mm−1
T = 294 K
0.30 × 0.20 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID-S diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (Blessing, 1995 ▶) T min = 0.968, T max = 0.989
14070 measured reflections
2736 independent reflections
1011 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.095
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.062
wR(F 2) = 0.206
S = 0.94
2736 reflections
191 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.33 e Å−3
Data collection: CrystalClear (Rigaku/MSC, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: CrystalClear; data reduction: CrystalClear; program(s) used to solve structure: SIR97 (Altomare et al., 1999 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681101587X/lh5239sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681101587X/lh5239Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681101587X/lh5239Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C4—H4⋯O1i | 0.93 | 2.50 | 3.421 (5) | 171 |
| C11—H11⋯O1ii | 0.93 | 2.39 | 3.296 (5) | 165 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 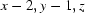 ; (ii)
; (ii) 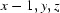 .
.
Acknowledgments
ZB and MA thank the Unit of the Scientific Research Projects of Erciyes University, Turkey, for the research grant FBD-10–2949, and for support of the data collection at Atatürk University, Turkey. SS and BN thank Mangalore University and the UGC SAP for financial assistance for the purchase of chemicals. HSY thanks the UOM for sabbatical leave.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Pyrazolines have been reported to exhibit a broad spectrum of biological activies such as antitumor, antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, antiparasitic, anti-tubercular and insecticidal activities (Hes et al., 1978; Manna et al., 2005; Amir et al., 2008). Some of these compounds have also antioxidant, anti-diabetic, anaesthetic and analgesic properties (Sarojini et al., 2010; Regaila et al., 1979). In addition, pyrazolines have played a crucial part in the development of theory in heterocyclic chemistry and also used extensively in organic synthesis (Klimova et al., 1999 and Bhaskarreddy et al., 1997).
The crystal structure of some pyrazoline derivatives viz., 3-(4-methylphenyl)-5-[4-(methylthio)phenyl]-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazole-1-carbaldehyde (Butcher et al., 2007) and 5-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-methyl-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazole-1-carbaldehyde (Cui & Li, 2010) have been reported. In view of the importance of pyrazoline derivatives and in continuation of our work on synthesis of various derivatives of 4,4'-diflouro chalcone (Fun et al., 2010a,b; Jasinski et al., 2010a,b; Baktır et al., 2011), the title compound (I) is synthesized and its crystal structure is reported herein.
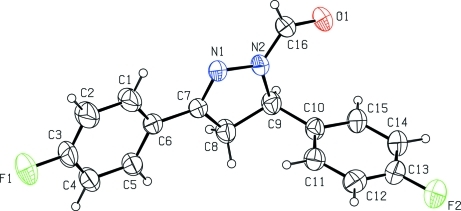
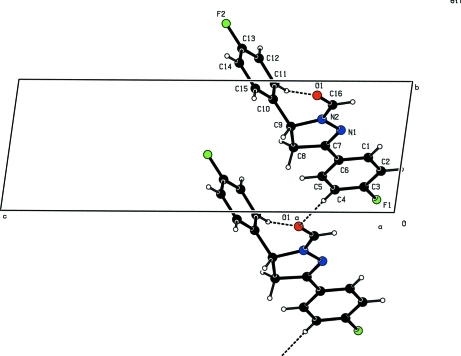
The molecular structure of the title compound is shown in Fig. 1. The pyrazole ring adopts a slight envelope comformation with the methylene C atom (C8) deviating by 0.114 (3)Å from the mean-plane of the other four atoms (C7/C9/N1/N2 with maximum deviation 0.021 (3)Å for N1). The dihedral angles between the four essentially planar atoms of the pyrazole ring and fluoro-substituted benzene rings are 2.6 (2) and 82.2 (2)°, respectively. The dihedral angle between the two benzene rings is 83.7 (2)°. The crystal packing is stabilized by weak intermolecular C—H···O hydrogen bonds (Fig .2).
Experimental
A mixture of (2E)-1,3-bis(4-fluorophenyl)prop-2-en-1-one (2.44 g, 0.01 mol) and hydrazine hydrate (0.5 ml, 0.01 mol) in 20 ml formic acid was refluxed for 8 h. The reaction mixture was cooled and poured into 50 ml ice-cold water. The precipitate was collected by filtration and purified by recrystallization from ethanol. The single-crystal was grown from DMF by slow evaporation method and yield of the compound was 86%. (m. p.: 408 K).
Refinement
All H atoms were positioned geometrically [C—H = 0.93 and 0.97 Å] and allowed to ride on their parent C atoms, with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C). Owing to the large number of weak high-angle reflections, the ratio of observed to unique reflections is low (37%).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The title molecule with displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms are drawn at the 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.
Hydrogen bonding of the title compound viewed along the a axis. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dotted lines (symmetry code: (a) x-2, y-1, z).
Crystal data
| C16H12F2N2O | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 286.28 | F(000) = 296 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.418 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 6.2141 (9) Å | Cell parameters from 1748 reflections |
| b = 6.7802 (8) Å | θ = 2.3–26.3° |
| c = 17.9857 (9) Å | µ = 0.11 mm−1 |
| α = 96.727 (4)° | T = 294 K |
| β = 90.254 (4)° | Prism, pale yellow |
| γ = 116.791 (5)° | 0.30 × 0.20 × 0.10 mm |
| V = 670.39 (13) Å3 |
Data collection
| Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID-S diffractometer | 2736 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Sealed Tube | 1011 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite Monochromator | Rint = 0.095 |
| Detector resolution: 10.0000 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 26.5°, θmin = 3.4° |
| dtprofit.ref scans | h = −7→7 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (Blessing, 1995) | k = −8→8 |
| Tmin = 0.968, Tmax = 0.989 | l = −22→22 |
| 14070 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.062 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.206 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 0.94 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0812P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2736 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 191 parameters | Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.33 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement on F2 for ALL reflections except those flagged by the user for potential systematic errors. Weighted R-factors wR and all goodnesses of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The observed criterion of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating -R-factor-obs etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| F1 | −0.7910 (4) | 0.0976 (4) | 0.04914 (14) | 0.1334 (11) | |
| F2 | 0.7113 (5) | 1.4342 (4) | 0.49400 (14) | 0.1284 (11) | |
| O1 | 0.9124 (4) | 0.8903 (4) | 0.23729 (12) | 0.0822 (9) | |
| N1 | 0.3094 (4) | 0.6264 (4) | 0.16479 (13) | 0.0621 (9) | |
| N2 | 0.5069 (4) | 0.7082 (4) | 0.21640 (12) | 0.0621 (9) | |
| C1 | −0.1494 (6) | 0.4185 (7) | 0.08534 (18) | 0.1019 (16) | |
| C2 | −0.3750 (7) | 0.3162 (8) | 0.0481 (2) | 0.120 (2) | |
| C3 | −0.5702 (6) | 0.1944 (7) | 0.0858 (2) | 0.0937 (16) | |
| C4 | −0.5512 (6) | 0.1715 (5) | 0.1584 (2) | 0.0798 (14) | |
| C5 | −0.3241 (6) | 0.2737 (5) | 0.19570 (18) | 0.0718 (12) | |
| C6 | −0.1199 (5) | 0.3980 (5) | 0.15912 (16) | 0.0643 (11) | |
| C7 | 0.1190 (5) | 0.5070 (5) | 0.19872 (15) | 0.0583 (11) | |
| C8 | 0.1722 (5) | 0.4922 (5) | 0.27855 (16) | 0.0728 (12) | |
| C9 | 0.4427 (5) | 0.6519 (5) | 0.29283 (15) | 0.0650 (11) | |
| C10 | 0.5095 (5) | 0.8590 (5) | 0.34783 (15) | 0.0637 (11) | |
| C11 | 0.3760 (6) | 0.9769 (6) | 0.34948 (17) | 0.0713 (11) | |
| C12 | 0.4417 (7) | 1.1706 (6) | 0.39825 (19) | 0.0820 (16) | |
| C13 | 0.6424 (7) | 1.2450 (6) | 0.4449 (2) | 0.0873 (16) | |
| C14 | 0.7786 (7) | 1.1343 (6) | 0.44657 (19) | 0.0870 (14) | |
| C15 | 0.7124 (6) | 0.9408 (6) | 0.39679 (17) | 0.0774 (14) | |
| C16 | 0.7313 (6) | 0.8185 (5) | 0.19475 (18) | 0.0696 (12) | |
| H1 | −0.01520 | 0.50270 | 0.06000 | 0.1230* | |
| H2 | −0.39330 | 0.33040 | −0.00210 | 0.1440* | |
| H4 | −0.68760 | 0.08870 | 0.18310 | 0.0960* | |
| H5 | −0.30840 | 0.25880 | 0.24590 | 0.0860* | |
| H8A | 0.13880 | 0.34140 | 0.28510 | 0.0870* | |
| H8B | 0.07740 | 0.53940 | 0.31210 | 0.0870* | |
| H9 | 0.52740 | 0.57050 | 0.30870 | 0.0780* | |
| H11 | 0.23920 | 0.92430 | 0.31700 | 0.0850* | |
| H12 | 0.35050 | 1.24820 | 0.39910 | 0.0990* | |
| H14 | 0.91270 | 1.18720 | 0.48020 | 0.1040* | |
| H15 | 0.80540 | 0.86500 | 0.39630 | 0.0930* | |
| H16 | 0.75090 | 0.84190 | 0.14480 | 0.0830* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| F1 | 0.0603 (14) | 0.164 (2) | 0.142 (2) | 0.0304 (15) | −0.0376 (13) | −0.0172 (17) |
| F2 | 0.1089 (18) | 0.1004 (17) | 0.133 (2) | 0.0232 (15) | 0.0018 (15) | −0.0407 (15) |
| O1 | 0.0474 (13) | 0.0936 (18) | 0.0902 (17) | 0.0222 (13) | −0.0112 (12) | −0.0025 (13) |
| N1 | 0.0507 (15) | 0.0728 (18) | 0.0553 (14) | 0.0242 (14) | −0.0057 (12) | −0.0030 (12) |
| N2 | 0.0451 (15) | 0.0734 (18) | 0.0576 (14) | 0.0203 (14) | −0.0060 (11) | −0.0010 (12) |
| C1 | 0.059 (2) | 0.159 (4) | 0.061 (2) | 0.027 (2) | −0.0034 (17) | 0.011 (2) |
| C2 | 0.070 (3) | 0.187 (5) | 0.074 (2) | 0.037 (3) | −0.015 (2) | 0.001 (3) |
| C3 | 0.052 (2) | 0.105 (3) | 0.107 (3) | 0.028 (2) | −0.022 (2) | −0.016 (2) |
| C4 | 0.051 (2) | 0.072 (2) | 0.104 (3) | 0.0191 (18) | −0.0005 (18) | 0.004 (2) |
| C5 | 0.059 (2) | 0.069 (2) | 0.080 (2) | 0.0242 (18) | −0.0004 (17) | 0.0038 (17) |
| C6 | 0.053 (2) | 0.075 (2) | 0.0613 (18) | 0.0286 (18) | −0.0030 (14) | −0.0025 (15) |
| C7 | 0.0502 (19) | 0.066 (2) | 0.0554 (17) | 0.0254 (16) | 0.0004 (14) | 0.0000 (14) |
| C8 | 0.063 (2) | 0.074 (2) | 0.068 (2) | 0.0199 (18) | −0.0071 (15) | 0.0074 (16) |
| C9 | 0.061 (2) | 0.070 (2) | 0.0583 (17) | 0.0253 (17) | −0.0090 (14) | 0.0073 (15) |
| C10 | 0.0568 (19) | 0.072 (2) | 0.0541 (17) | 0.0232 (17) | −0.0080 (14) | 0.0042 (15) |
| C11 | 0.065 (2) | 0.084 (2) | 0.0618 (18) | 0.032 (2) | −0.0040 (15) | 0.0066 (17) |
| C12 | 0.085 (3) | 0.086 (3) | 0.075 (2) | 0.040 (2) | 0.0065 (19) | 0.0061 (19) |
| C13 | 0.082 (3) | 0.077 (3) | 0.080 (2) | 0.022 (2) | 0.002 (2) | −0.0147 (19) |
| C14 | 0.069 (2) | 0.095 (3) | 0.078 (2) | 0.026 (2) | −0.0154 (18) | −0.011 (2) |
| C15 | 0.064 (2) | 0.091 (3) | 0.066 (2) | 0.029 (2) | −0.0137 (16) | −0.0044 (18) |
| C16 | 0.050 (2) | 0.081 (2) | 0.072 (2) | 0.0268 (18) | −0.0002 (16) | 0.0009 (17) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| F1—C3 | 1.352 (5) | C10—C15 | 1.385 (5) |
| F2—C13 | 1.358 (4) | C11—C12 | 1.380 (5) |
| O1—C16 | 1.225 (4) | C12—C13 | 1.356 (6) |
| N1—N2 | 1.390 (4) | C13—C14 | 1.363 (6) |
| N1—C7 | 1.299 (4) | C14—C15 | 1.388 (5) |
| N2—C9 | 1.478 (4) | C1—H1 | 0.9300 |
| N2—C16 | 1.337 (5) | C2—H2 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.379 (6) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C6 | 1.370 (4) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.360 (6) | C8—H8A | 0.9700 |
| C3—C4 | 1.344 (5) | C8—H8B | 0.9700 |
| C4—C5 | 1.387 (5) | C9—H9 | 0.9800 |
| C5—C6 | 1.388 (5) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C6—C7 | 1.461 (5) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C7—C8 | 1.497 (4) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C8—C9 | 1.534 (5) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C9—C10 | 1.506 (4) | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C10—C11 | 1.386 (5) | ||
| N2—N1—C7 | 107.5 (2) | C13—C14—C15 | 118.4 (4) |
| N1—N2—C9 | 113.9 (2) | C10—C15—C14 | 120.9 (4) |
| N1—N2—C16 | 120.5 (2) | O1—C16—N2 | 123.4 (3) |
| C9—N2—C16 | 125.6 (3) | C2—C1—H1 | 119.00 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 121.0 (4) | C6—C1—H1 | 119.00 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.0 (3) | C1—C2—H2 | 120.00 |
| F1—C3—C2 | 118.6 (3) | C3—C2—H2 | 121.00 |
| F1—C3—C4 | 119.2 (4) | C3—C4—H4 | 121.00 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 122.2 (4) | C5—C4—H4 | 121.00 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 118.7 (3) | C4—C5—H5 | 120.00 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.9 (3) | C6—C5—H5 | 120.00 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 118.1 (3) | C7—C8—H8A | 111.00 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 121.1 (3) | C7—C8—H8B | 111.00 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 120.8 (3) | C9—C8—H8A | 111.00 |
| N1—C7—C6 | 120.7 (3) | C9—C8—H8B | 111.00 |
| N1—C7—C8 | 113.8 (3) | H8A—C8—H8B | 109.00 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 125.5 (3) | N2—C9—H9 | 109.00 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 103.6 (2) | C8—C9—H9 | 109.00 |
| N2—C9—C8 | 100.7 (2) | C10—C9—H9 | 109.00 |
| N2—C9—C10 | 111.1 (2) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.00 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 116.5 (3) | C12—C11—H11 | 119.00 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 121.5 (3) | C11—C12—H12 | 121.00 |
| C9—C10—C15 | 120.4 (3) | C13—C12—H12 | 121.00 |
| C11—C10—C15 | 118.1 (3) | C13—C14—H14 | 121.00 |
| C10—C11—C12 | 121.4 (4) | C15—C14—H14 | 121.00 |
| C11—C12—C13 | 118.4 (4) | C10—C15—H15 | 120.00 |
| F2—C13—C12 | 119.9 (4) | C14—C15—H15 | 120.00 |
| F2—C13—C14 | 117.3 (4) | O1—C16—H16 | 118.00 |
| C12—C13—C14 | 122.8 (4) | N2—C16—H16 | 118.00 |
| C7—N1—N2—C9 | −4.2 (3) | C5—C6—C7—N1 | −178.8 (3) |
| C7—N1—N2—C16 | 173.1 (3) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | 2.3 (5) |
| N2—N1—C7—C8 | −1.3 (4) | C1—C6—C7—N1 | 0.1 (5) |
| N2—N1—C7—C6 | 179.7 (3) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −175.2 (3) |
| C16—N2—C9—C10 | 66.3 (4) | N1—C7—C8—C9 | 5.9 (4) |
| C16—N2—C9—C8 | −169.7 (3) | C7—C8—C9—N2 | −7.3 (3) |
| C9—N2—C16—O1 | −1.5 (5) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 112.8 (3) |
| N1—N2—C9—C8 | 7.4 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −40.0 (4) |
| N1—N2—C9—C10 | −116.5 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C15 | 142.1 (3) |
| N1—N2—C16—O1 | −178.4 (3) | N2—C9—C10—C15 | −103.5 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | −179.8 (4) | N2—C9—C10—C11 | 74.4 (4) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.3 (7) | C9—C10—C15—C14 | 178.6 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.9 (6) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −177.9 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.5 (7) | C15—C10—C11—C12 | 0.0 (5) |
| C1—C2—C3—F1 | 179.0 (4) | C11—C10—C15—C14 | 0.6 (5) |
| F1—C3—C4—C5 | −179.3 (3) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.3 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.8 (6) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −1.3 (6) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.2 (5) | C11—C12—C13—F2 | −179.5 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.6 (5) | F2—C13—C14—C15 | −179.8 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 179.5 (3) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 1.9 (6) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | −178.8 (3) | C13—C14—C15—C10 | −1.6 (5) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C4—H4···O1i | 0.93 | 2.50 | 3.421 (5) | 171 |
| C11—H11···O1ii | 0.93 | 2.39 | 3.296 (5) | 165 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−2, y−1, z; (ii) x−1, y, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: LH5239).
References
- Altomare, A., Burla, M. C., Camalli, M., Cascarano, G. L., Giacovazzo, C., Guagliardi, A., Moliterni, A. G. G., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 115–119.
- Amir, M., Kumar, H. & Khan, S. A. (2008). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 18, 918–922. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Baktır, Z., Akkurt, M., Samshuddin, S., Narayana, B. & Yathirajan, H. S. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o328–o329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bhaskarreddy, D., Chandrasekhar, B. N., Padmavathi, V. & Sumathi, R. P. (1997). Synthesis, pp. 491–494.
- Blessing, R. H. (1995). Acta Cryst. A51, 33–38. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Butcher, R. J., Jasinski, J. P., Prasad, D. J., Narayana, B. & Yathirajan, H. S. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o4005–o4006.
- Cui, P. & Li, X.-L. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o2351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 837–838.
- Fun, H.-K., Hemamalini, M., Samshuddin, S., Narayana, B. & Yathirajan, H. S. (2010a). Acta Cryst. E66, o582–o583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Fun, H.-K., Hemamalini, M., Samshuddin, S., Narayana, B. & Yathirajan, H. S. (2010b). Acta Cryst. E66, o864–o865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hes, R. V., Wellinga, K. & Grosscurt, A. C. (1978). J. Agric. Food Chem. 26, 915–918.
- Jasinski, J. P., Guild, C. J., Samshuddin, S., Narayana, B. & Yathirajan, H. S. (2010a). Acta Cryst. E66, o1948–o1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Jasinski, J. P., Guild, C. J., Samshuddin, S., Narayana, B. & Yathirajan, H. S. (2010b). Acta Cryst. E66, o2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Klimova, E. I., Marcos, M., Klimova, T. B., Cecilio, A. T., Ruben, A. T. & Lena, R. R. (1999). J. Organomet. Chem. 585, 106–111.
- Manna, F., Chimenti, F., Fioravanti, R., Bolasco, A., Secci, D., Chimenti, P., Ferlini, C. & Scambia, G. (2005). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett . 15, 4632–4635. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Regaila, H. A., El-Bayonk, A. K. & Hammad, M. (1979). Egypt. J. Chem. 20, 197–202.
- Rigaku/MSC (2005). CrystalClear Rigaku/MSC, The Woodlands, Texas, USA.
- Sarojini, B. K., Vidyagayatri, M., Darshanraj, C. G., Bharath, B. R. & Manjunatha, H. (2010). Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 7, 214–224.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681101587X/lh5239sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681101587X/lh5239Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681101587X/lh5239Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report