Abstract
The asymmetric unit of the title compound, C15H15NO, contains two independent molecules, which differ in the dihedral angle between the aromatic rings [48.98 (9) and 57.48 (8)°]. The methyl groups in para positions are disordered over two equally occupied positions. An intramolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bond occurs. The crystal structure is stabilized by intermolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds which link the molecules into chains running along the b axis.
Related literature
For the preparation of the title compound, see: Gowda et al. (2003 ▶). For our study of the effect of substituents on the structures and other aspects of N-(aryl)-amides, see: Bhat & Gowda (2000 ▶); Bowes et al. (2003 ▶); Gowda et al. (2008 ▶, 2009 ▶); Saeed et al. (2010 ▶).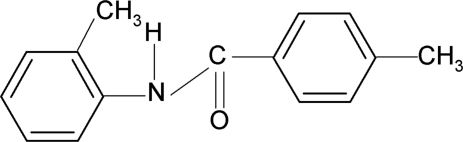
Experimental
Crystal data
C15H15NO
M r = 225.28
Triclinic,

a = 7.2964 (6) Å
b = 9.9075 (5) Å
c = 18.1347 (13) Å
α = 88.331 (5)°
β = 82.892 (6)°
γ = 79.558 (5)°
V = 1279.29 (15) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.07 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.88 × 0.09 × 0.06 mm
Data collection
Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur diffractometer with a Ruby (Gemini Cu) detector
Absorption correction: analytical [CrysAlis RED (Oxford Diffraction, 2009 ▶), based on expressions derived by Clark & Reid (1995 ▶)] T min = 0.968, T max = 0.996
18269 measured reflections
4354 independent reflections
1602 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.088
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.042
wR(F 2) = 0.097
S = 0.74
4354 reflections
311 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.12 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.11 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis CCD (Oxford Diffraction, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis CCD; data reduction: CrysAlis RED (Oxford Diffraction, 2009 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and Mercury (Macrae et al., 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: enCIFer (Allen et al., 2004 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811018770/bt5550sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811018770/bt5550Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811018770/bt5550Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1A⋯O2 | 0.86 | 2.05 | 2.878 (2) | 163 |
| N2—H2A⋯O1i | 0.86 | 2.05 | 2.883 (2) | 162 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
MF and JK thank the Grant Agency of the Slovak Republic (grant No. VEGA 1/0817/08) and the Structural Funds, Interreg IIIA, for financial support in purchasing the diffractometer. VZR thanks the University Grants Commission, Government of India, New Delhi, for the award of a research fellowship.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The structural aspects of N-aryl amides are of interest due to their chemical and biological importance (Bhat & Gowda, 2000; Bowes et al., 2003; Gowda et al., 2008, 2009; Saeed et al., 2010). In the present work, as part of a study of the substituent effects on the structures of benzanilides (Gowda, et al., 2008, 2009), the structure of 4-methyl-N-(2-methylphenyl)benzamide (I) has been determined (Fig.1). The asymmetric unit of (I) contains two independent molecules. In the crystal, the ortho-methyl substituent in the anilino ring is positioned syn to the N–H bond in one of the molecules and anti in the other molecule. Further, the N—H and C=O bonds in the C—NH—C(O)—C segment are anti to each other in both the molecules, similar to that observed in 2-methyl-N-(4-methylphenyl)benzamide (II)(Gowda et al., 2008) and 4-methyl-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)benzamide (III) (Gowda et al., 2009) and, with similar bond parameters.
The central amide group –NHCO– is tilted to the anilino ring with the C2—C1—N1—C8 and C6—C1—N1—C8 torsion angles of -118.2 (3)° and 63.9 (3)° in molecule 1, and the C17—C16—N2—C23 and C21—C16—N2—C23 torsion angles of -86.8 (3)° and 97.6 (3)° in molecule 2, while the C10—C9—C8—N1 and C14—C9—C8—N1 torsion angles in molecule 1, and and the C25—C24—C23—N2 and C29—C24—C23—N2 torsion angles in molecule 2 are -13.4 (4)° and 171.7 (2)°, and -150.4 (2)° and 27.9 (4)°, respectively.
The packing of molecules linked by N—H···O hydrogen bonds into infinite chains is shown in Fig. 2.
Experimental
The title compound was prepared according to the method described by Gowda et al. (2003). The purity of the compound was checked by determining its melting point. It was characterized by recording its infrared and NMR spectra. needle-like colourless single crystals of the title compound were obtained by slow evaporation from an ethanol solution of the compound (0.5 g in about 30 ml of ethanol) at room temperature.
Refinement
All H atoms were visible in difference maps and then treated as riding atoms with C–H distances of 0.93Å (C-aromatic), 0.96Å (C-methyl) and N—H = 0.86 Å. The Uiso(H) values were set at 1.2 Ueq(C-aromatic, N) and 1.5 Ueq(C-methyl). The methyl groups in p-position of the aromatic ring are disordered over two equally occupied positions rotated with respect to each other by 60°.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of the title compound showing the atom labelling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms are represented as small spheres of arbitrary radii.
Fig. 2.
Part of the crystal structure of the title compound. Molecular chains are generated by N—H···O hydrogen bonds which are shown by dashed lines. H atoms not involved in intermolecular bonding have been omitted.
Crystal data
| C15H15NO | Z = 4 |
| Mr = 225.28 | F(000) = 480 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.170 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 7.2964 (6) Å | Cell parameters from 2440 reflections |
| b = 9.9075 (5) Å | θ = 3.5–29.3° |
| c = 18.1347 (13) Å | µ = 0.07 mm−1 |
| α = 88.331 (5)° | T = 293 K |
| β = 82.892 (6)° | Needle, colorless |
| γ = 79.558 (5)° | 0.88 × 0.09 × 0.06 mm |
| V = 1279.29 (15) Å3 |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur diffractometer with a Ruby (Gemini Cu) detector | 4354 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1602 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.088 |
| ω scans | θmax = 24.7°, θmin = 4.1° |
| Absorption correction: analytical [CrysAlis RED (Oxford Diffraction, 2009), based on expressions derived by Clark & Reid (1995)] | h = −8→8 |
| Tmin = 0.968, Tmax = 0.996 | k = −11→11 |
| 18269 measured reflections | l = −21→21 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.042 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.097 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 0.74 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0367P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4354 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 311 parameters | Δρmax = 0.12 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.11 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. CrysAlis RED (Oxford Diffraction, 2009) Analytical numeric absorption correction using a multifaceted crystal model based on expressions derived (Clark & Reid, 1995). |
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| O1 | 0.3561 (3) | 0.83584 (15) | 0.23183 (11) | 0.0969 (7) | |
| N1 | 0.3243 (3) | 0.62248 (17) | 0.26640 (11) | 0.0687 (7) | |
| H1A | 0.3695 | 0.5366 | 0.2607 | 0.082* | |
| C1 | 0.1559 (5) | 0.6596 (2) | 0.31651 (18) | 0.0614 (8) | |
| C2 | 0.1579 (5) | 0.6225 (2) | 0.39053 (18) | 0.0622 (8) | |
| C3 | −0.0084 (6) | 0.6555 (3) | 0.43740 (17) | 0.0776 (9) | |
| H3A | −0.0099 | 0.6321 | 0.4875 | 0.093* | |
| C4 | −0.1703 (5) | 0.7216 (3) | 0.4122 (2) | 0.0857 (10) | |
| H4A | −0.2804 | 0.7421 | 0.4447 | 0.103* | |
| C5 | −0.1687 (5) | 0.7572 (3) | 0.3388 (2) | 0.0881 (10) | |
| H5A | −0.2783 | 0.8021 | 0.3212 | 0.106* | |
| C6 | −0.0056 (6) | 0.7270 (3) | 0.29071 (17) | 0.0768 (9) | |
| H6A | −0.0048 | 0.7522 | 0.2409 | 0.092* | |
| C7 | 0.3332 (5) | 0.5461 (3) | 0.41909 (16) | 0.0928 (10) | |
| H7A | 0.3634 | 0.4553 | 0.3987 | 0.139* | |
| H7B | 0.3129 | 0.5403 | 0.4723 | 0.139* | |
| H7C | 0.4352 | 0.5940 | 0.4044 | 0.139* | |
| C8 | 0.4170 (4) | 0.7118 (2) | 0.22826 (14) | 0.0648 (8) | |
| C9 | 0.5994 (4) | 0.6581 (2) | 0.18350 (14) | 0.0590 (7) | |
| C10 | 0.6996 (5) | 0.5260 (2) | 0.18947 (15) | 0.0772 (9) | |
| H10A | 0.6467 | 0.4619 | 0.2194 | 0.093* | |
| C11 | 0.8757 (5) | 0.4888 (3) | 0.15171 (16) | 0.0832 (9) | |
| H11A | 0.9396 | 0.3994 | 0.1565 | 0.100* | |
| C12 | 0.9607 (5) | 0.5800 (3) | 0.10686 (15) | 0.0772 (9) | |
| C13 | 0.8592 (5) | 0.7099 (3) | 0.09924 (15) | 0.0803 (10) | |
| H13A | 0.9114 | 0.7729 | 0.0682 | 0.096* | |
| C14 | 0.6840 (5) | 0.7481 (2) | 0.13623 (15) | 0.0736 (9) | |
| H14A | 0.6192 | 0.8367 | 0.1297 | 0.088* | |
| C15 | 1.1607 (5) | 0.5405 (3) | 0.06924 (18) | 0.1129 (12) | |
| H15A | 1.2388 | 0.4932 | 0.1042 | 0.135* | 0.50 |
| H15B | 1.2072 | 0.6218 | 0.0518 | 0.135* | 0.50 |
| H15C | 1.1624 | 0.4816 | 0.0280 | 0.135* | 0.50 |
| H15D | 1.2459 | 0.5820 | 0.0963 | 0.135* | 0.50 |
| H15E | 1.1741 | 0.5717 | 0.0194 | 0.135* | 0.50 |
| H15F | 1.2029 | 0.4415 | 0.0714 | 0.135* | 0.50 |
| O2 | 0.3997 (3) | 0.32712 (14) | 0.26391 (11) | 0.0970 (7) | |
| N2 | 0.4584 (3) | 0.10245 (17) | 0.23914 (11) | 0.0622 (6) | |
| H2A | 0.4231 | 0.0247 | 0.2478 | 0.075* | |
| C16 | 0.6234 (4) | 0.1063 (2) | 0.18894 (17) | 0.0541 (7) | |
| C17 | 0.6124 (4) | 0.1340 (2) | 0.11454 (19) | 0.0665 (8) | |
| C18 | 0.7779 (6) | 0.1290 (3) | 0.06697 (17) | 0.0799 (9) | |
| H18A | 0.7723 | 0.1486 | 0.0168 | 0.096* | |
| C19 | 0.9474 (5) | 0.0960 (3) | 0.0923 (2) | 0.0806 (9) | |
| H19A | 1.0564 | 0.0931 | 0.0595 | 0.097* | |
| C20 | 0.9594 (5) | 0.0668 (3) | 0.1660 (2) | 0.0866 (9) | |
| H20A | 1.0757 | 0.0432 | 0.1834 | 0.104* | |
| C21 | 0.7952 (5) | 0.0732 (2) | 0.21414 (16) | 0.0737 (9) | |
| H21A | 0.8018 | 0.0546 | 0.2644 | 0.088* | |
| C22 | 0.4253 (5) | 0.1644 (4) | 0.08421 (19) | 0.1311 (13) | |
| H22A | 0.3592 | 0.0897 | 0.0962 | 0.197* | |
| H22B | 0.4455 | 0.1755 | 0.0312 | 0.197* | |
| H22C | 0.3524 | 0.2473 | 0.1060 | 0.197* | |
| C23 | 0.3531 (4) | 0.2138 (2) | 0.27375 (14) | 0.0615 (8) | |
| C24 | 0.1817 (4) | 0.1941 (2) | 0.32233 (13) | 0.0551 (7) | |
| C25 | 0.0317 (4) | 0.3016 (2) | 0.33069 (14) | 0.0659 (8) | |
| H25A | 0.0424 | 0.3857 | 0.3080 | 0.079* | |
| C26 | −0.1335 (4) | 0.2853 (2) | 0.37224 (15) | 0.0718 (8) | |
| H26A | −0.2340 | 0.3584 | 0.3766 | 0.086* | |
| C27 | −0.1537 (4) | 0.1625 (3) | 0.40784 (14) | 0.0667 (8) | |
| C28 | −0.0014 (4) | 0.0571 (2) | 0.40096 (14) | 0.0663 (8) | |
| H28A | −0.0101 | −0.0255 | 0.4256 | 0.080* | |
| C29 | 0.1638 (4) | 0.0716 (2) | 0.35820 (13) | 0.0618 (8) | |
| H29A | 0.2639 | −0.0017 | 0.3535 | 0.074* | |
| C30 | −0.3368 (4) | 0.1441 (3) | 0.45296 (17) | 0.1005 (10) | |
| H30A | −0.3499 | 0.1904 | 0.4996 | 0.121* | 0.50 |
| H30B | −0.3368 | 0.0481 | 0.4618 | 0.121* | 0.50 |
| H30C | −0.4397 | 0.1821 | 0.4260 | 0.121* | 0.50 |
| H30D | −0.3245 | 0.0952 | 0.4985 | 0.121* | 0.50 |
| H30E | −0.4078 | 0.0901 | 0.4238 | 0.121* | 0.50 |
| H30F | −0.4215 | 0.2321 | 0.4626 | 0.121* | 0.50 |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0967 (17) | 0.0388 (9) | 0.1473 (19) | −0.0146 (10) | 0.0214 (13) | −0.0057 (10) |
| N1 | 0.092 (2) | 0.0376 (11) | 0.0721 (16) | −0.0128 (12) | 0.0087 (15) | −0.0023 (11) |
| C1 | 0.072 (3) | 0.0414 (14) | 0.071 (2) | −0.0138 (16) | −0.001 (2) | −0.0075 (14) |
| C2 | 0.075 (3) | 0.0501 (14) | 0.062 (2) | −0.0146 (15) | −0.006 (2) | −0.0012 (14) |
| C3 | 0.085 (3) | 0.0691 (18) | 0.077 (2) | −0.0195 (18) | 0.007 (2) | −0.0019 (16) |
| C4 | 0.079 (3) | 0.078 (2) | 0.099 (3) | −0.024 (2) | 0.013 (2) | −0.0113 (19) |
| C5 | 0.067 (3) | 0.082 (2) | 0.117 (3) | −0.0108 (17) | −0.018 (3) | −0.012 (2) |
| C6 | 0.088 (3) | 0.0662 (17) | 0.078 (2) | −0.0120 (18) | −0.018 (2) | −0.0020 (16) |
| C7 | 0.097 (3) | 0.0908 (19) | 0.088 (2) | −0.0066 (19) | −0.018 (2) | 0.0073 (16) |
| C8 | 0.084 (2) | 0.0408 (14) | 0.071 (2) | −0.0161 (16) | −0.0057 (17) | −0.0070 (14) |
| C9 | 0.080 (2) | 0.0410 (14) | 0.0574 (18) | −0.0154 (15) | −0.0075 (16) | −0.0022 (13) |
| C10 | 0.091 (3) | 0.0512 (16) | 0.086 (2) | −0.0196 (17) | 0.008 (2) | 0.0036 (14) |
| C11 | 0.092 (3) | 0.0567 (16) | 0.094 (2) | −0.0100 (17) | 0.012 (2) | −0.0026 (16) |
| C12 | 0.090 (3) | 0.0732 (19) | 0.067 (2) | −0.0194 (19) | 0.0062 (19) | −0.0126 (16) |
| C13 | 0.105 (3) | 0.0621 (18) | 0.071 (2) | −0.0251 (18) | 0.014 (2) | −0.0009 (15) |
| C14 | 0.104 (3) | 0.0491 (15) | 0.066 (2) | −0.0159 (17) | 0.0013 (19) | 0.0037 (14) |
| C15 | 0.113 (3) | 0.106 (2) | 0.112 (3) | −0.019 (2) | 0.019 (3) | −0.0098 (19) |
| O2 | 0.1053 (17) | 0.0411 (9) | 0.1356 (17) | −0.0257 (10) | 0.0425 (13) | −0.0120 (10) |
| N2 | 0.0637 (17) | 0.0417 (11) | 0.0764 (16) | −0.0172 (11) | 0.0228 (14) | −0.0052 (10) |
| C16 | 0.057 (2) | 0.0420 (13) | 0.063 (2) | −0.0137 (14) | 0.0015 (19) | −0.0012 (13) |
| C17 | 0.052 (2) | 0.0700 (16) | 0.074 (2) | −0.0101 (14) | −0.001 (2) | 0.0147 (15) |
| C18 | 0.075 (3) | 0.093 (2) | 0.071 (2) | −0.0203 (18) | 0.000 (2) | 0.0133 (15) |
| C19 | 0.070 (3) | 0.094 (2) | 0.078 (3) | −0.0254 (19) | 0.009 (2) | −0.0146 (17) |
| C20 | 0.060 (3) | 0.117 (2) | 0.086 (3) | −0.0205 (18) | −0.012 (2) | −0.0166 (19) |
| C21 | 0.074 (3) | 0.0844 (19) | 0.064 (2) | −0.0216 (18) | −0.002 (2) | −0.0082 (15) |
| C22 | 0.074 (3) | 0.192 (4) | 0.116 (3) | 0.002 (2) | −0.012 (3) | 0.040 (2) |
| C23 | 0.069 (2) | 0.0423 (14) | 0.0704 (19) | −0.0121 (14) | 0.0078 (16) | −0.0048 (13) |
| C24 | 0.063 (2) | 0.0440 (14) | 0.0565 (18) | −0.0142 (14) | 0.0097 (15) | −0.0070 (12) |
| C25 | 0.068 (2) | 0.0494 (15) | 0.076 (2) | −0.0110 (16) | 0.0076 (18) | −0.0050 (13) |
| C26 | 0.066 (2) | 0.0655 (17) | 0.078 (2) | −0.0011 (15) | 0.0018 (18) | −0.0082 (15) |
| C27 | 0.068 (2) | 0.0765 (18) | 0.0561 (19) | −0.0220 (18) | 0.0075 (17) | −0.0103 (15) |
| C28 | 0.074 (2) | 0.0588 (16) | 0.064 (2) | −0.0177 (16) | 0.0077 (17) | −0.0007 (13) |
| C29 | 0.070 (2) | 0.0498 (15) | 0.0624 (19) | −0.0120 (13) | 0.0097 (16) | −0.0049 (13) |
| C30 | 0.084 (3) | 0.111 (2) | 0.102 (3) | −0.0272 (19) | 0.022 (2) | −0.0060 (17) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C8 | 1.229 (2) | O2—C23 | 1.233 (2) |
| N1—C8 | 1.336 (3) | N2—C23 | 1.347 (3) |
| N1—C1 | 1.432 (3) | N2—C16 | 1.423 (3) |
| N1—H1A | 0.8596 | N2—H2A | 0.8594 |
| C1—C6 | 1.374 (4) | C16—C21 | 1.368 (4) |
| C1—C2 | 1.383 (3) | C16—C17 | 1.378 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.385 (4) | C17—C18 | 1.389 (4) |
| C2—C7 | 1.506 (4) | C17—C22 | 1.511 (4) |
| C3—C4 | 1.367 (4) | C18—C19 | 1.354 (4) |
| C3—H3A | 0.9300 | C18—H18A | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.367 (4) | C19—C20 | 1.369 (4) |
| C4—H4A | 0.9300 | C19—H19A | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.376 (4) | C20—C21 | 1.385 (4) |
| C5—H5A | 0.9300 | C20—H20A | 0.9300 |
| C6—H6A | 0.9300 | C21—H21A | 0.9300 |
| C7—H7A | 0.9600 | C22—H22A | 0.9600 |
| C7—H7B | 0.9600 | C22—H22B | 0.9600 |
| C7—H7C | 0.9600 | C22—H22C | 0.9600 |
| C8—C9 | 1.488 (3) | C23—C24 | 1.477 (3) |
| C9—C10 | 1.387 (3) | C24—C25 | 1.379 (3) |
| C9—C14 | 1.391 (3) | C24—C29 | 1.380 (3) |
| C10—C11 | 1.372 (3) | C25—C26 | 1.373 (3) |
| C10—H10A | 0.9300 | C25—H25A | 0.9300 |
| C11—C12 | 1.378 (3) | C26—C27 | 1.384 (3) |
| C11—H11A | 0.9300 | C26—H26A | 0.9300 |
| C12—C13 | 1.375 (3) | C27—C28 | 1.376 (3) |
| C12—C15 | 1.520 (4) | C27—C30 | 1.515 (3) |
| C13—C14 | 1.362 (3) | C28—C29 | 1.378 (3) |
| C13—H13A | 0.9300 | C28—H28A | 0.9300 |
| C14—H14A | 0.9300 | C29—H29A | 0.9300 |
| C15—H15A | 0.9600 | C30—H30A | 0.9600 |
| C15—H15B | 0.9600 | C30—H30B | 0.9600 |
| C15—H15C | 0.9600 | C30—H30C | 0.9600 |
| C15—H15D | 0.9887 | C30—H30D | 0.9501 |
| C15—H15E | 0.9457 | C30—H30E | 1.0098 |
| C15—H15F | 0.9744 | C30—H30F | 0.9793 |
| C8—N1—C1 | 124.69 (19) | C23—N2—C16 | 123.84 (18) |
| C8—N1—H1A | 117.6 | C23—N2—H2A | 117.9 |
| C1—N1—H1A | 117.7 | C16—N2—H2A | 118.3 |
| C6—C1—C2 | 120.9 (3) | C21—C16—C17 | 119.8 (3) |
| C6—C1—N1 | 120.3 (3) | C21—C16—N2 | 119.3 (3) |
| C2—C1—N1 | 118.7 (3) | C17—C16—N2 | 120.7 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 117.7 (3) | C16—C17—C18 | 118.6 (3) |
| C1—C2—C7 | 121.3 (3) | C16—C17—C22 | 121.2 (3) |
| C3—C2—C7 | 121.0 (3) | C18—C17—C22 | 120.2 (3) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 121.9 (3) | C19—C18—C17 | 121.2 (3) |
| C4—C3—H3A | 119.0 | C19—C18—H18A | 119.4 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 119.0 | C17—C18—H18A | 119.4 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.3 (3) | C18—C19—C20 | 120.5 (3) |
| C3—C4—H4A | 120.3 | C18—C19—H19A | 119.7 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 120.3 | C20—C19—H19A | 119.7 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.3 (3) | C19—C20—C21 | 118.8 (3) |
| C4—C5—H5A | 119.8 | C19—C20—H20A | 120.6 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 119.8 | C21—C20—H20A | 120.6 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 119.9 (3) | C16—C21—C20 | 121.1 (3) |
| C1—C6—H6A | 120.1 | C16—C21—H21A | 119.5 |
| C5—C6—H6A | 120.1 | C20—C21—H21A | 119.5 |
| C2—C7—H7A | 109.5 | C17—C22—H22A | 109.5 |
| C2—C7—H7B | 109.5 | C17—C22—H22B | 109.5 |
| H7A—C7—H7B | 109.5 | H22A—C22—H22B | 109.5 |
| C2—C7—H7C | 109.5 | C17—C22—H22C | 109.5 |
| H7A—C7—H7C | 109.5 | H22A—C22—H22C | 109.5 |
| H7B—C7—H7C | 109.5 | H22B—C22—H22C | 109.5 |
| O1—C8—N1 | 120.8 (2) | O2—C23—N2 | 120.2 (2) |
| O1—C8—C9 | 120.7 (2) | O2—C23—C24 | 122.3 (2) |
| N1—C8—C9 | 118.4 (2) | N2—C23—C24 | 117.5 (2) |
| C10—C9—C14 | 116.8 (3) | C25—C24—C29 | 118.6 (2) |
| C10—C9—C8 | 124.5 (2) | C25—C24—C23 | 118.6 (2) |
| C14—C9—C8 | 118.5 (2) | C29—C24—C23 | 122.8 (2) |
| C11—C10—C9 | 120.8 (2) | C26—C25—C24 | 120.4 (2) |
| C11—C10—H10A | 119.6 | C26—C25—H25A | 119.8 |
| C9—C10—H10A | 119.6 | C24—C25—H25A | 119.8 |
| C10—C11—C12 | 121.9 (3) | C25—C26—C27 | 121.5 (3) |
| C10—C11—H11A | 119.1 | C25—C26—H26A | 119.3 |
| C12—C11—H11A | 119.1 | C27—C26—H26A | 119.3 |
| C13—C12—C11 | 117.3 (3) | C28—C27—C26 | 117.7 (3) |
| C13—C12—C15 | 121.2 (3) | C28—C27—C30 | 120.9 (2) |
| C11—C12—C15 | 121.5 (3) | C26—C27—C30 | 121.4 (3) |
| C14—C13—C12 | 121.4 (3) | C27—C28—C29 | 121.3 (2) |
| C14—C13—H13A | 119.3 | C27—C28—H28A | 119.4 |
| C12—C13—H13A | 119.3 | C29—C28—H28A | 119.4 |
| C13—C14—C9 | 121.7 (2) | C28—C29—C24 | 120.5 (2) |
| C13—C14—H14A | 119.1 | C28—C29—H29A | 119.7 |
| C9—C14—H14A | 119.1 | C24—C29—H29A | 119.7 |
| C12—C15—H15A | 109.5 | C27—C30—H30A | 109.5 |
| C12—C15—H15B | 109.5 | C27—C30—H30B | 109.5 |
| H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 | H30A—C30—H30B | 109.5 |
| C12—C15—H15C | 109.5 | C27—C30—H30C | 109.5 |
| H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 | H30A—C30—H30C | 109.5 |
| H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 | H30B—C30—H30C | 109.5 |
| C12—C15—H15D | 109.4 | C27—C30—H30D | 115.3 |
| H15A—C15—H15D | 54.8 | H30A—C30—H30D | 58.1 |
| H15B—C15—H15D | 57.7 | H30B—C30—H30D | 52.6 |
| H15C—C15—H15D | 141.1 | H30C—C30—H30D | 135.2 |
| C12—C15—H15E | 112.3 | C27—C30—H30E | 110.2 |
| H15A—C15—H15E | 138.2 | H30A—C30—H30E | 140.3 |
| H15B—C15—H15E | 53.8 | H30B—C30—H30E | 57.9 |
| H15C—C15—H15E | 57.7 | H30C—C30—H30E | 54.3 |
| H15D—C15—H15E | 107.7 | H30D—C30—H30E | 105.2 |
| C12—C15—H15F | 110.8 | C27—C30—H30F | 111.6 |
| H15A—C15—H15F | 54.7 | H30A—C30—H30F | 58.1 |
| H15B—C15—H15F | 139.7 | H30B—C30—H30F | 138.8 |
| H15C—C15—H15F | 57.4 | H30C—C30—H30F | 53.7 |
| H15D—C15—H15F | 106.4 | H30D—C30—H30F | 109.3 |
| H15E—C15—H15F | 110.1 | H30E—C30—H30F | 104.5 |
| C8—N1—C1—C6 | 63.9 (3) | C23—N2—C16—C21 | 97.6 (3) |
| C8—N1—C1—C2 | −118.2 (3) | C23—N2—C16—C17 | −86.8 (3) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.1 (3) | C21—C16—C17—C18 | −0.7 (3) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −177.9 (2) | N2—C16—C17—C18 | −176.4 (2) |
| C6—C1—C2—C7 | 178.8 (2) | C21—C16—C17—C22 | 177.1 (2) |
| N1—C1—C2—C7 | 0.8 (3) | N2—C16—C17—C22 | 1.4 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.4 (4) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | 0.8 (4) |
| C7—C2—C3—C4 | −178.2 (2) | C22—C17—C18—C19 | −177.0 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.5 (4) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | −0.1 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.1 (4) | C18—C19—C20—C21 | −0.7 (4) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.6 (3) | C17—C16—C21—C20 | 0.0 (3) |
| N1—C1—C6—C5 | 177.3 (2) | N2—C16—C21—C20 | 175.7 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.6 (4) | C19—C20—C21—C16 | 0.8 (4) |
| C1—N1—C8—O1 | −3.2 (4) | C16—N2—C23—O2 | −1.5 (4) |
| C1—N1—C8—C9 | 174.6 (3) | C16—N2—C23—C24 | 177.9 (3) |
| O1—C8—C9—C10 | 164.4 (3) | O2—C23—C24—C25 | 28.9 (4) |
| N1—C8—C9—C10 | −13.4 (4) | N2—C23—C24—C25 | −150.4 (2) |
| O1—C8—C9—C14 | −10.5 (4) | O2—C23—C24—C29 | −152.7 (2) |
| N1—C8—C9—C14 | 171.7 (2) | N2—C23—C24—C29 | 27.9 (4) |
| C14—C9—C10—C11 | 1.7 (4) | C29—C24—C25—C26 | −1.7 (4) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | −173.2 (3) | C23—C24—C25—C26 | 176.6 (2) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | 0.3 (4) | C24—C25—C26—C27 | 1.1 (4) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | −2.1 (4) | C25—C26—C27—C28 | 0.8 (4) |
| C10—C11—C12—C15 | 176.0 (3) | C25—C26—C27—C30 | −179.3 (3) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | 1.9 (4) | C26—C27—C28—C29 | −2.0 (4) |
| C15—C12—C13—C14 | −176.2 (3) | C30—C27—C28—C29 | 178.0 (2) |
| C12—C13—C14—C9 | 0.1 (4) | C27—C28—C29—C24 | 1.4 (4) |
| C10—C9—C14—C13 | −2.0 (4) | C25—C24—C29—C28 | 0.5 (4) |
| C8—C9—C14—C13 | 173.3 (3) | C23—C24—C29—C28 | −177.8 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1A···O2 | 0.86 | 2.05 | 2.878 (2) | 163 |
| N2—H2A···O1i | 0.86 | 2.05 | 2.883 (2) | 162 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y−1, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BT5550).
References
- Allen, F. H., Johnson, O., Shields, G. P., Smith, B. R. & Towler, M. (2004). J. Appl. Cryst. 37, 335–338.
- Bhat, D. K. & Gowda, B. T. (2000). J. Indian Chem. Soc. 77, 279–284.
- Bowes, K. F., Glidewell, C., Low, J. N., Skakle, J. M. S. & Wardell, J. L. (2003). Acta Cryst. C59, o1–o3. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Clark, R. C. & Reid, J. S. (1995). Acta Cryst. A51, 887–897.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Gowda, B. T., Jyothi, K., Paulus, H. & Fuess, H. (2003). Z. Naturforsch. Teil A, 58, 225–230.
- Gowda, B. T., Tokarčík, M., Kožíšek, J., Sowmya, B. P. & Fuess, H. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o1494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Gowda, B. T., Tokarčík, M., Kožíšek, J., Sowmya, B. P. & Fuess, H. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o1612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Oxford Diffraction (2009). CrysAlis CCD and CrysAlis RED Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Yarnton, England.
- Saeed, A., Arshad, M. & Simpson, J. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o2808–o2809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811018770/bt5550sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811018770/bt5550Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811018770/bt5550Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




