Abstract
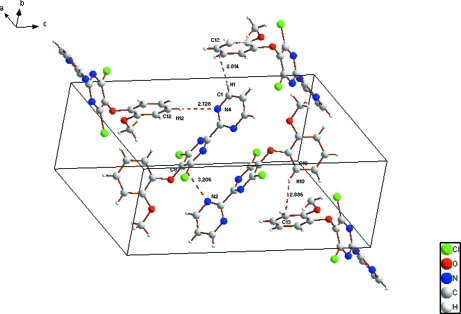
In the title compound, C15H10Cl2N4O2, the dichloropyrimidine and methoxyphenoxy parts are approximately perpendicular [dihedral angle = 89.9 (9)°]. The dihedral angle between the two pyrimidine rings is 36.3 (4)° In the crystal, there are no hydrogen bonds but the molecules are held together by short intermolecular C⋯N [3.206 (3) Å] contacts and C—H⋯π interactions.
Related literature
For the use of 2,2′-bipyrimidine as a ligand in inorganic and organometallic chemistry, see: Fabrice et al. (2008 ▶); Hunziker & Ludi (1977 ▶). It was first synthesized by Bly and Mellon (1962 ▶) utilizing the Ullmann coupling of 2-bromopyrimidine in the presence of metallic copper.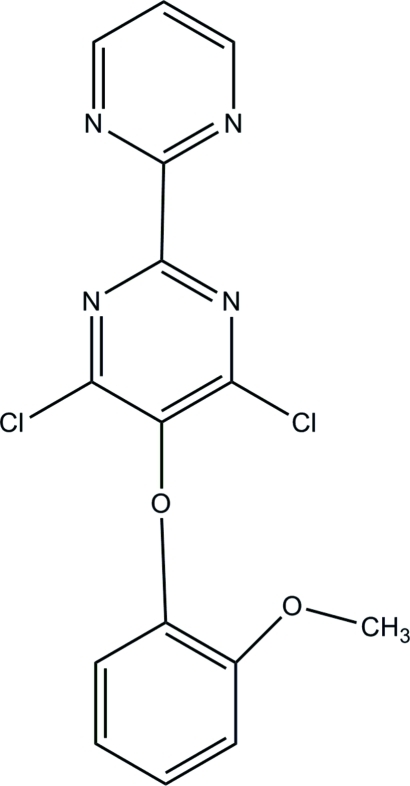
Experimental
Crystal data
C15H10Cl2N4O2
M r = 349.17
Monoclinic,

a = 10.716 (2) Å
b = 8.1112 (18) Å
c = 18.601 (5) Å
β = 106.486 (3)°
V = 1550.3 (6) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.43 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.22 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm
Data collection
Siemens SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.911, T max = 0.926
8106 measured reflections
2733 independent reflections
2319 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.027
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.042
wR(F 2) = 0.114
S = 1.08
2733 reflections
209 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.26 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.54 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Siemens, 1996 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Siemens, 1996 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681101419X/fl2331sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681101419X/fl2331Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. C—H⋯π interactions (Å, °).
Cg is the centroid of the C9–C14 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1—H1⋯Cgi | 0.93 | 2.87 | 3.760 (3) | 161 |
Symmetry code: (i) 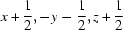 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (20761002), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi (No. 0832080) and the Innovation Project of Guangxi University for Nationlities (No. gxun-chx2010080).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
2,2'-Bipyrimidine has been used as a ligand in inorganic and organometallic chemistry (Hunziker & Ludi, 1977; Fabrice et al., 2008) and exhibits remarkable stability in acidic medium. It was first synthesized by Bly and Mellon (1962) utilizing the Ullmann coupling of 2-bromopyrimidine in the presence of metallic copper. As part of our studies on the synthesis and characterization of these compounds, we report here the crystal structure of (I).
In (I) the dichloropyrimidine and the methoxyphenoxy are approximately perpendicular (dihedral angle of 89.90 (91) °). The dihedral angle between the two pyrimidine rings is 36.25 (38)° (Fig. 1).
The molecules are linked by intermolecular C—H···N , C—H···C and C···N short contacts. C12—H12···N4, C12···N4=3.639 (3), H12···N4=2.728 (3), and C12—H12···N4=166.49; C8···N2=3.206 (3); C1—H1···C12, C1···C12=3.725 (3), H1···C12=2.814 (3), and C1—H1···C12=166.14; C10—H10···C13, C10···C13=3.694 (3)), H10···C13=2.886 (3), and C13—H10···C10=146.05.
Experimental
A solution of 4,6-Dichloro-5-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-2,2'-bipyrimidine (10 mmol) in 50ml toluene was refluxed for 1h with stirring then filtered, washed several times with ethanol and dried in vacuo, to produce a powder of the title compound. The powder was added to 50ml toluene with stirring until completely dissolved. Finally, colourless crystals suitable for data collection were obtained by slow evaporation of the toluene at room temperature. Elemental analysis calculate: Elemental analysis: found: C, 51.60; H, 2.89; N, 16.05; calc. for C15H10Cl2N4O2: C,51.53; H, 2.93; N, 16.11.
Refinement
Data collection-2102 independent reflections but 2101 in Refinement. H atoms on C atoms were positoned geometrically and refined using a riding model with C—H = 0.96Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The structure of the title compound (I) showing 50% probability displacement ellipsoids and the atom-numbering scheme.
Fig. 2.
Crystal packing of (I) showing the short contacts interactions as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C15H10Cl2N4O2 | F(000) = 712 |
| Mr = 349.17 | Dx = 1.496 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 10.716 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 3720 reflections |
| b = 8.1112 (18) Å | θ = 2.6–27.4° |
| c = 18.601 (5) Å | µ = 0.43 mm−1 |
| β = 106.486 (3)° | T = 296 K |
| V = 1550.3 (6) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.22 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer | 2733 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2319 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.027 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 2.0° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −12→12 |
| Tmin = 0.911, Tmax = 0.926 | k = −9→9 |
| 8106 measured reflections | l = −22→16 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.042 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.114 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.08 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0522P)2 + 0.7172P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2733 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 209 parameters | Δρmax = 0.26 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.54 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl2 | 0.35488 (7) | 0.23438 (8) | 0.95225 (4) | 0.0698 (2) | |
| Cl1 | −0.12322 (6) | 0.00465 (9) | 0.81525 (4) | 0.0697 (2) | |
| O1 | 0.09431 (17) | 0.24803 (18) | 0.84012 (8) | 0.0514 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.04052 (18) | −0.1321 (2) | 0.93028 (10) | 0.0461 (4) | |
| O2 | −0.01418 (17) | 0.4733 (2) | 0.74474 (9) | 0.0564 (4) | |
| N3 | 0.25212 (18) | −0.0303 (2) | 0.99122 (9) | 0.0434 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.07696 (19) | −0.3406 (2) | 1.05310 (10) | 0.0509 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.1789 (2) | −0.2855 (3) | 1.03313 (11) | 0.0394 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.1558 (2) | −0.1388 (3) | 0.98205 (11) | 0.0399 (5) | |
| N4 | 0.29885 (19) | −0.3461 (2) | 1.05286 (11) | 0.0504 (5) | |
| C9 | 0.1043 (2) | 0.2281 (3) | 0.76750 (11) | 0.0401 (5) | |
| C8 | 0.1164 (2) | 0.1136 (3) | 0.88636 (11) | 0.0437 (5) | |
| C13 | 0.0568 (2) | 0.3436 (3) | 0.64467 (12) | 0.0480 (5) | |
| H13 | 0.0179 | 0.4242 | 0.6099 | 0.058* | |
| C14 | 0.0468 (2) | 0.3523 (3) | 0.71727 (11) | 0.0403 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.1243 (2) | 0.2156 (3) | 0.62364 (12) | 0.0512 (6) | |
| H12 | 0.1311 | 0.2112 | 0.5749 | 0.061* | |
| C6 | 0.2308 (2) | 0.0942 (3) | 0.94339 (11) | 0.0446 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.2172 (3) | −0.5496 (3) | 1.11929 (13) | 0.0580 (6) | |
| H2 | 0.2305 | −0.6438 | 1.1490 | 0.070* | |
| C15 | −0.0513 (3) | 0.6175 (3) | 0.69994 (17) | 0.0712 (8) | |
| H15A | −0.1114 | 0.5880 | 0.6528 | 0.107* | |
| H15B | 0.0245 | 0.6674 | 0.6914 | 0.107* | |
| H15C | −0.0920 | 0.6943 | 0.7255 | 0.107* | |
| C10 | 0.1703 (2) | 0.1008 (3) | 0.74643 (12) | 0.0501 (6) | |
| H10 | 0.2076 | 0.0185 | 0.7806 | 0.060* | |
| C11 | 0.1813 (2) | 0.0952 (3) | 0.67400 (13) | 0.0537 (6) | |
| H11 | 0.2272 | 0.0100 | 0.6596 | 0.064* | |
| C3 | 0.0986 (3) | −0.4745 (3) | 1.09680 (13) | 0.0564 (6) | |
| H3 | 0.0303 | −0.5180 | 1.1124 | 0.068* | |
| C7 | 0.0238 (2) | −0.0064 (3) | 0.88345 (12) | 0.0457 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.3157 (3) | −0.4805 (3) | 1.09624 (14) | 0.0589 (7) | |
| H1 | 0.3978 | −0.5289 | 1.1113 | 0.071* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl2 | 0.0869 (5) | 0.0571 (4) | 0.0554 (4) | −0.0231 (3) | 0.0039 (3) | 0.0114 (3) |
| Cl1 | 0.0610 (4) | 0.0732 (5) | 0.0600 (4) | 0.0094 (3) | −0.0073 (3) | 0.0149 (3) |
| O1 | 0.0831 (11) | 0.0397 (9) | 0.0335 (8) | 0.0168 (8) | 0.0197 (8) | 0.0094 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0521 (11) | 0.0438 (10) | 0.0403 (10) | 0.0047 (8) | 0.0095 (8) | 0.0056 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0784 (11) | 0.0468 (9) | 0.0461 (9) | 0.0198 (8) | 0.0209 (8) | 0.0144 (7) |
| N3 | 0.0577 (11) | 0.0390 (10) | 0.0316 (9) | 0.0020 (8) | 0.0094 (8) | 0.0035 (7) |
| N2 | 0.0617 (12) | 0.0495 (11) | 0.0446 (10) | 0.0045 (9) | 0.0203 (9) | 0.0101 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0534 (12) | 0.0357 (11) | 0.0291 (10) | 0.0028 (9) | 0.0115 (9) | −0.0003 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0518 (12) | 0.0379 (11) | 0.0307 (10) | 0.0062 (9) | 0.0127 (9) | 0.0015 (8) |
| N4 | 0.0558 (11) | 0.0447 (11) | 0.0490 (11) | 0.0080 (9) | 0.0121 (9) | 0.0089 (9) |
| C9 | 0.0471 (11) | 0.0431 (12) | 0.0286 (10) | −0.0003 (9) | 0.0084 (8) | 0.0024 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0639 (14) | 0.0369 (11) | 0.0313 (10) | 0.0119 (10) | 0.0151 (10) | 0.0058 (9) |
| C13 | 0.0564 (13) | 0.0493 (13) | 0.0362 (11) | −0.0062 (10) | 0.0095 (10) | 0.0082 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0436 (11) | 0.0402 (12) | 0.0357 (11) | −0.0011 (9) | 0.0087 (9) | 0.0036 (9) |
| C12 | 0.0572 (14) | 0.0628 (15) | 0.0355 (12) | −0.0119 (11) | 0.0164 (10) | −0.0054 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0624 (13) | 0.0374 (11) | 0.0334 (10) | −0.0003 (10) | 0.0124 (10) | 0.0003 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0844 (18) | 0.0406 (13) | 0.0435 (13) | 0.0036 (12) | 0.0093 (12) | 0.0116 (10) |
| C15 | 0.0818 (19) | 0.0533 (16) | 0.0810 (19) | 0.0250 (14) | 0.0273 (15) | 0.0276 (14) |
| C10 | 0.0566 (13) | 0.0499 (14) | 0.0410 (12) | 0.0122 (11) | 0.0090 (10) | 0.0039 (10) |
| C11 | 0.0554 (13) | 0.0608 (15) | 0.0465 (13) | 0.0065 (12) | 0.0171 (11) | −0.0070 (11) |
| C3 | 0.0767 (17) | 0.0511 (14) | 0.0449 (13) | −0.0041 (12) | 0.0228 (12) | 0.0099 (11) |
| C7 | 0.0530 (13) | 0.0463 (13) | 0.0350 (11) | 0.0105 (10) | 0.0079 (9) | 0.0040 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0678 (16) | 0.0462 (14) | 0.0581 (15) | 0.0152 (12) | 0.0103 (13) | 0.0121 (11) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cl2—C6 | 1.722 (2) | C8—C6 | 1.384 (3) |
| Cl1—C7 | 1.722 (2) | C13—C12 | 1.384 (3) |
| O1—C8 | 1.367 (2) | C13—C14 | 1.386 (3) |
| O1—C9 | 1.394 (2) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C7 | 1.320 (3) | C12—C11 | 1.371 (3) |
| N1—C5 | 1.335 (3) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| O2—C14 | 1.358 (3) | C2—C3 | 1.364 (4) |
| O2—C15 | 1.426 (3) | C2—C1 | 1.368 (4) |
| N3—C6 | 1.322 (3) | C2—H2 | 0.9300 |
| N3—C5 | 1.330 (3) | C15—H15A | 0.9600 |
| N2—C4 | 1.327 (3) | C15—H15B | 0.9600 |
| N2—C3 | 1.337 (3) | C15—H15C | 0.9600 |
| C4—N4 | 1.328 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.386 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.498 (3) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| N4—C1 | 1.338 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C9—C10 | 1.370 (3) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| C9—C14 | 1.393 (3) | C1—H1 | 0.9300 |
| C8—C7 | 1.380 (3) | ||
| C8—O1—C9 | 118.03 (16) | N3—C6—C8 | 123.3 (2) |
| C7—N1—C5 | 115.60 (19) | N3—C6—Cl2 | 117.29 (17) |
| C14—O2—C15 | 117.23 (18) | C8—C6—Cl2 | 119.36 (17) |
| C6—N3—C5 | 116.07 (19) | C3—C2—C1 | 117.1 (2) |
| C4—N2—C3 | 115.4 (2) | C3—C2—H2 | 121.4 |
| N2—C4—N4 | 127.39 (19) | C1—C2—H2 | 121.4 |
| N2—C4—C5 | 116.39 (19) | O2—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| N4—C4—C5 | 116.22 (19) | O2—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| N3—C5—N1 | 126.23 (19) | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| N3—C5—C4 | 117.52 (18) | O2—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| N1—C5—C4 | 116.23 (19) | H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C4—N4—C1 | 115.1 (2) | H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—C14 | 121.26 (19) | C9—C10—C11 | 119.7 (2) |
| C10—C9—O1 | 123.52 (18) | C9—C10—H10 | 120.1 |
| C14—C9—O1 | 115.15 (18) | C11—C10—H10 | 120.1 |
| O1—C8—C7 | 122.9 (2) | C12—C11—C10 | 119.8 (2) |
| O1—C8—C6 | 122.0 (2) | C12—C11—H11 | 120.1 |
| C7—C8—C6 | 114.86 (19) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.1 |
| C12—C13—C14 | 120.3 (2) | N2—C3—C2 | 122.3 (2) |
| C12—C13—H13 | 119.9 | N2—C3—H3 | 118.8 |
| C14—C13—H13 | 119.9 | C2—C3—H3 | 118.8 |
| O2—C14—C13 | 125.57 (19) | N1—C7—C8 | 123.9 (2) |
| O2—C14—C9 | 116.05 (18) | N1—C7—Cl1 | 116.80 (18) |
| C13—C14—C9 | 118.4 (2) | C8—C7—Cl1 | 119.30 (16) |
| C11—C12—C13 | 120.6 (2) | N4—C1—C2 | 122.6 (2) |
| C11—C12—H12 | 119.7 | N4—C1—H1 | 118.7 |
| C13—C12—H12 | 119.7 | C2—C1—H1 | 118.7 |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| Cg is the centroid of the C9–C14 ring. |
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C1—H1···Cgi | 0.93 | 2.87 | 3.760 (3) | 161 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1/2, −y−1/2, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: FL2331).
References
- Bly, D. D. & Mellon, M. G. (1962). J. Org. Chem. 27, 2945–2946.
- Fabrice, P., Patr, H., Kamal, B. & Cyri, T. (2008). Inorg Chim Acta, 361, 373–379.
- Hunziker, M. & Ludi, A. (1977). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 99, 7370–7371.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Siemens (1996). SMART and SAINT Siemens Analytical X-ray Instruments Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681101419X/fl2331sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681101419X/fl2331Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report