Abstract
The replication dependent histone transcripts terminate with a highly conserved stem-loop structure. This feature distinguishes them from most other eukaryotic mRNAs which end with a poly(A) tail. The 3' terminus of histone mRNA is a main determinant for rapid turnover of these transcripts. In this study, we report the identification of two cytoplasmic protein complexes that interact in a sequence specific fashion with 3' terminal sequences of a mouse histone H4 and a human histone H2A mRNA. The binding activities are conserved from frog to man. At least a fraction of one of the protein complexes appears to be specifically associated with polysomes. The evidence for an involvement of the observed protein complexes in turnover of histone transcripts is discussed.
Full text
PDF

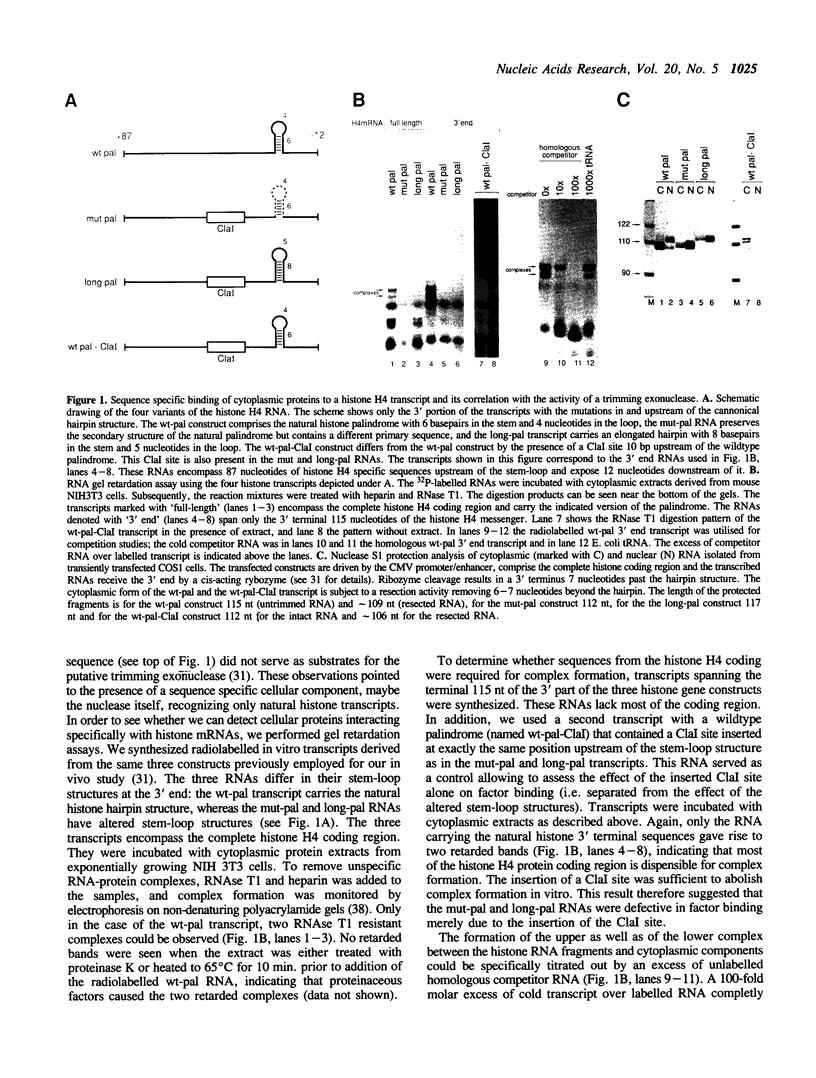





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Binder R., Hwang S. P., Ratnasabapathy R., Williams D. L. Degradation of apolipoprotein II mRNA occurs via endonucleolytic cleavage at 5'-AAU-3'/5'-UAA-3' elements in single-stranded loop domains of the 3'-noncoding region. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16910–16918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohjanen P. R., Petryniak B., June C. H., Thompson C. B., Lindsten T. An inducible cytoplasmic factor (AU-B) binds selectively to AUUUA multimers in the 3' untranslated region of lymphokine mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3288–3295. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. mRNA decay: finding the right targets. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):9–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer G. An A + U-rich element RNA-binding factor regulates c-myc mRNA stability in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2460–2466. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capasso O., Bleecker G. C., Heintz N. Sequences controlling histone H4 mRNA abundance. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1825–1831. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02437.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J. L., Hentze M. W., Koeller D. M., Caughman S. W., Rouault T. A., Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. Iron-responsive elements: regulatory RNA sequences that control mRNA levels and translation. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):924–928. doi: 10.1126/science.2452485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckner R., Ellmeier W., Birnstiel M. L. Mature mRNA 3' end formation stimulates RNA export from the nucleus. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3513–3522. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04915.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay D. A., Sisodia S. S., Cleveland D. W. Autoregulatory control of beta-tubulin mRNA stability is linked to translation elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5763–5767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgiev O., Birnstiel M. L. The conserved CAAGAAAGA spacer sequence is an essential element for the formation of 3' termini of the sea urchin H3 histone mRNA by RNA processing. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):481–489. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03654.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gick O., Krämer A., Keller W., Birnstiel M. L. Generation of histone mRNA 3' ends by endonucleolytic cleavage of the pre-mRNA in a snRNP-dependent in vitro reaction. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1319–1326. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04362.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D. A., Shelness G. S., Nicosia M., Williams D. L. Estrogen-induced destabilization of yolk precursor protein mRNAs in avian liver. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2625–2631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves R. A., Pandey N. B., Chodchoy N., Marzluff W. F. Translation is required for regulation of histone mRNA degradation. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):615–626. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90240-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm J., Dathan N. A., Mattaj I. W. Functional analysis of mutant Xenopus U2 snRNAs. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):159–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90878-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris M. E., Böhni R., Schneiderman M. H., Ramamurthy L., Schümperli D., Marzluff W. F. Regulation of histone mRNA in the unperturbed cell cycle: evidence suggesting control at two posttranscriptional steps. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2416–2424. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Sive H. L., Roeder R. G. Regulation of human histone gene expression: kinetics of accumulation and changes in the rate of synthesis and in the half-lives of individual histone mRNAs during the HeLa cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):539–550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N. The regulation of histone gene expression during the cell cycle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 26;1088(3):327–339. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90122-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabnick K. S., Housman D. E. Determinants that contribute to cytoplasmic stability of human c-fos and beta-globin mRNAs are located at several sites in each mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3244–3250. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeller D. M., Casey J. L., Hentze M. W., Gerhardt E. M., Chan L. N., Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. A cytosolic protein binds to structural elements within the iron regulatory region of the transferrin receptor mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3574–3578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Sharp P. A. Electrophoretic separation of complexes involved in the splicing of precursors to mRNAs. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):845–855. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90066-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krowczynska A., Yenofsky R., Brawerman G. Regulation of messenger RNA stability in mouse erythroleukemia cells. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 20;181(2):231–239. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90087-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruys V., Marinx O., Shaw G., Deschamps J., Huez G. Translational blockade imposed by cytokine-derived UA-rich sequences. Science. 1989 Aug 25;245(4920):852–855. doi: 10.1126/science.2672333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird-Offringa I. A., de Wit C. L., Elfferich P., van der Eb A. J. Poly(A) tail shortening is the translation-dependent step in c-myc mRNA degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6132–6140. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. Y., Brawerman G. Pulse-labeled ribonucleic acid complexes released by dissociation of rat liver polysomes. Biochemistry. 1971 Feb 2;10(3):510–516. doi: 10.1021/bi00779a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B. J., Chodchoy N., Marzluff W. F., Skoultchi A. I. Coupling of replication type histone mRNA levels to DNA synthesis requires the stem-loop sequence at the 3' end of the mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6189–6193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malter J. S. Identification of an AUUUA-specific messenger RNA binding protein. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):664–666. doi: 10.1126/science.2814487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluff W. F., Pandey N. B. Multiple regulatory steps control histone mRNA concentrations. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):49–52. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munroe D., Jacobson A. mRNA poly(A) tail, a 3' enhancer of translational initiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3441–3455. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllner E. W., Kühn L. C. A stem-loop in the 3' untranslated region mediates iron-dependent regulation of transferrin receptor mRNA stability in the cytoplasm. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllner E. W., Neupert B., Kühn L. C. A specific mRNA binding factor regulates the iron-dependent stability of cytoplasmic transferrin receptor mRNA. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):373–382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90851-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osley M. A. The regulation of histone synthesis in the cell cycle. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:827–861. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.004143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen D., Kühn L. C. Noncoding 3' sequences of the transferrin receptor gene are required for mRNA regulation by iron. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1287–1293. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02366.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey N. B., Marzluff W. F. The stem-loop structure at the 3' end of histone mRNA is necessary and sufficient for regulation of histone mRNA stability. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4557–4559. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey N. B., Sun J. H., Marzluff W. F. Different complexes are formed on the 3' end of histone mRNA with nuclear and polyribosomal proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5653–5659. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltz S. W., Brewer G., Kobs G., Ross J. Substrate specificity of the exonuclease activity that degrades H4 histone mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9382–9388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Kobs G. H4 histone messenger RNA decay in cell-free extracts initiates at or near the 3' terminus and proceeds 3' to 5'. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 20;188(4):579–593. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(86)80008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Peltz S. W., Kobs G., Brewer G. Histone mRNA degradation in vivo: the first detectable step occurs at or near the 3' terminus. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4362–4371. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Davis R. W. The poly(A) binding protein is required for poly(A) shortening and 60S ribosomal subunit-dependent translation initiation. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):857–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90938-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Blume J. E., Nielsen D. A. Regulation of messenger RNA stability in eukaryotic cells. Bioessays. 1987 May;6(5):221–226. doi: 10.1002/bies.950060507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyu A. B., Greenberg M. E., Belasco J. G. The c-fos transcript is targeted for rapid decay by two distinct mRNA degradation pathways. Genes Dev. 1989 Jan;3(1):60–72. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sittman D. B., Graves R. A., Marzluff W. F. Histone mRNA concentrations are regulated at the level of transcription and mRNA degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1849–1853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sive H. L., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Regulation of human histone gene expression during the HeLa cell cycle requires protein synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2723–2734. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauber C., Lüscher B., Eckner R., Lötscher E., Schümperli D. A signal regulating mouse histone H4 mRNA levels in a mammalian cell cycle mutant and sequences controlling RNA 3' processing are both contained within the same 80-bp fragment. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3297–3303. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04643.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vakalopoulou E., Schaack J., Shenk T. A 32-kilodalton protein binds to AU-rich domains in the 3' untranslated regions of rapidly degraded mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3355–3364. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T., Treisman R. Removal of poly(A) and consequent degradation of c-fos mRNA facilitated by 3' AU-rich sequences. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):396–399. doi: 10.1038/336396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong R., Roeder R. G., Heintz N. The primary structure and expression of four cloned human histone genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 11;11(21):7409–7425. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.21.7409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]