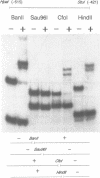
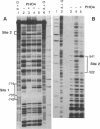
Abstract
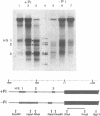
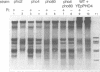
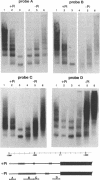
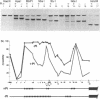
PHO8 encodes an alkaline phosphatase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae whose transcription is regulated by the phosphate concentration in the medium. This occurs through the action of several positive and negative regulatory proteins, also involved in the regulation of other members of the phosphatase gene family. A central role is played by PHO4, the gene encoding a DNA binding regulatory protein. Digestion experiments with DNasel, micrococcal nuclease and 20 different restriction nucleases show that under conditions of PHO8 repression, there is a highly ordered chromatin structure at the promoter consisting of three hypersensitive regions, approximately 820 to 690, 540 to 510, and 230 to 160 bp upstream of the initiation codon. These hypersensitive sites are surrounded by DNA organized in nucleosomes. Gel shift analysis and in vitro footprinting revealed the presence of two PHO4 binding sites at the PHO8 promoter: a low affinity site at -728 and a high affinity site at -532. Each one is located within a hypersensitive site. Upon derepression of PHO8, the chromatin structure changes significantly: The two upstream hypersensitive sites containing the PHO4 binding sites merge, resulting in a long region of hypersensitivity. This transition is PHO4 dependent. However, not all of the promoter becomes nucleosome free. Instead, as a novel feature, regions of intermediate accessibility are generated upstream and downstream of the third hypersensitive site, the latter region encompassing the TATA-box. The available data fit best into a concept that these regions are organized in unstable or partly unfolded nucleosomes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almer A., Hörz W. Nuclease hypersensitive regions with adjacent positioned nucleosomes mark the gene boundaries of the PHO5/PHO3 locus in yeast. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2681–2687. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04551.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almer A., Rudolph H., Hinnen A., Hörz W. Removal of positioned nucleosomes from the yeast PHO5 promoter upon PHO5 induction releases additional upstream activating DNA elements. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2689–2696. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04552.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arndt K. T., Styles C., Fink G. R. Multiple global regulators control HIS4 transcription in yeast. Science. 1987 Aug 21;237(4817):874–880. doi: 10.1126/science.3303332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braus G., Mösch H. U., Vogel K., Hinnen A., Hütter R. Interpathway regulation of the TRP4 gene of yeast. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):939–945. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03455.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fascher K. D., Schmitz J., Hörz W. Role of trans-activating proteins in the generation of active chromatin at the PHO5 promoter in S. cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2523–2528. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07432.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi N., Oshima Y. Specific cis-acting sequence for PHO8 expression interacts with PHO4 protein, a positive regulatory factor, in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):785–794. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko Y., Hayashi N., Toh-e A., Banno I., Oshima Y. Structural characteristics of the PHO8 gene encoding repressible alkaline phosphatase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1987;58(1):137–148. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko Y., Tamai Y., Toh-e A., Oshima Y. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of PHO8 expression by PHO regulatory genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):248–252. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Garrard W. T. Transcription-induced nucleosome 'splitting': an underlying structure for DNase I sensitive chromatin. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):607–615. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Commitment and activation at pol II promoters: a tail of protein-protein interactions. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1161–1164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90675-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacheva G. A., Guschin D. Y., Preobrazhenskaya O. V., Karpov V. L., Ebralidse K. K., Mirzabekov A. D. Change in the pattern of histone binding to DNA upon transcriptional activation. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90399-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa N., Oshima Y. Functional domains of a positive regulatory protein, PHO4, for transcriptional control of the phosphatase regulon in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2224–2236. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlović B., Hörz W. The chromatin structure at the promoter of a glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae reflects its functional state. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5513–5520. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Gann A. A. Activators and targets. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):329–331. doi: 10.1038/346329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph H., Hinnen A. The yeast PHO5 promoter: phosphate-control elements and sequences mediating mRNA start-site selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1340–1344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Larsen P. L., Varshavsky A. Mapping protein-DNA interactions in vivo with formaldehyde: evidence that histone H4 is retained on a highly transcribed gene. Cell. 1988 Jun 17;53(6):937–947. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90469-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straka C., Hörz W. A functional role for nucleosomes in the repression of a yeast promoter. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):361–368. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07957.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F. Structural changes in nucleosomes during transcription: strip, split or flip? Trends Genet. 1991 Jun;7(6):175–177. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90429-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh-E A., Nakamura H., Oshima Y. A gene controlling the synthesis of non specific alkaline phosphatase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 25;428(1):182–192. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel K., Hinnen A. The yeast phosphatase system. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Dec;4(12):2013–2017. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00560.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel K., Hörz W., Hinnen A. The two positively acting regulatory proteins PHO2 and PHO4 physically interact with PHO5 upstream activation regions. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2050–2057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]