Abstract
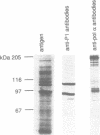
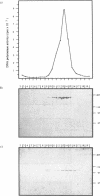
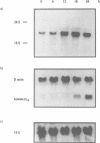
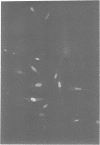
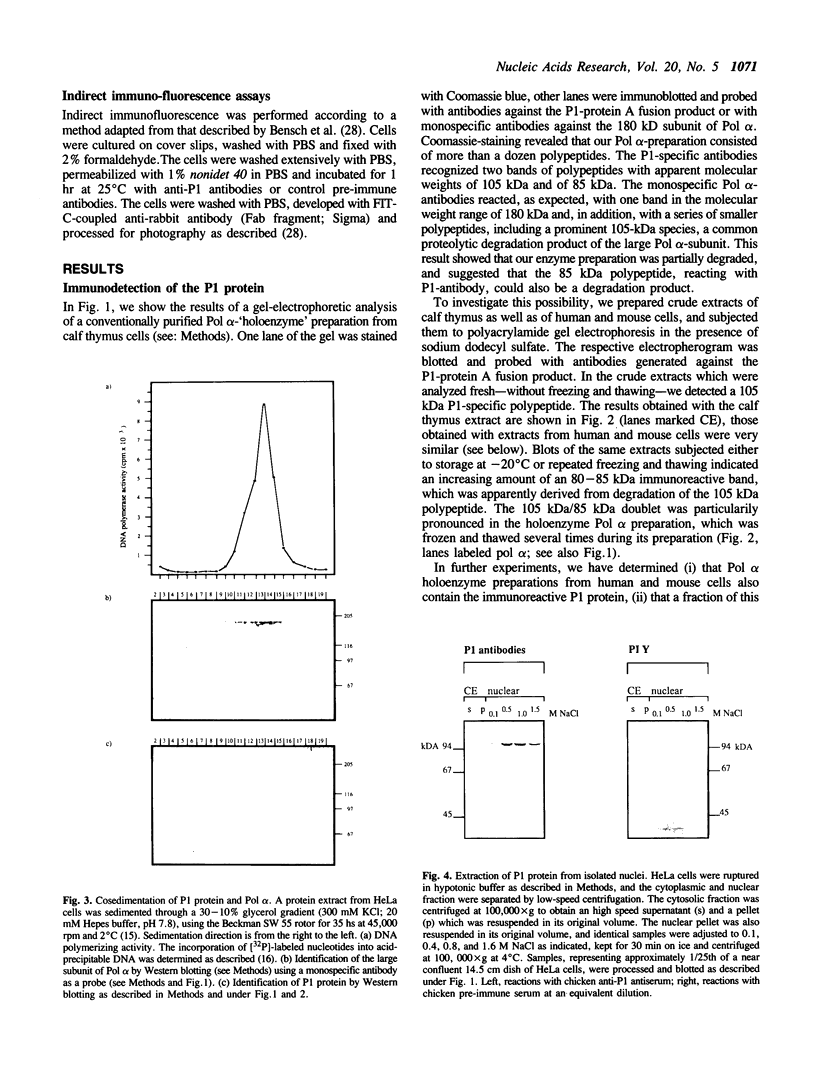
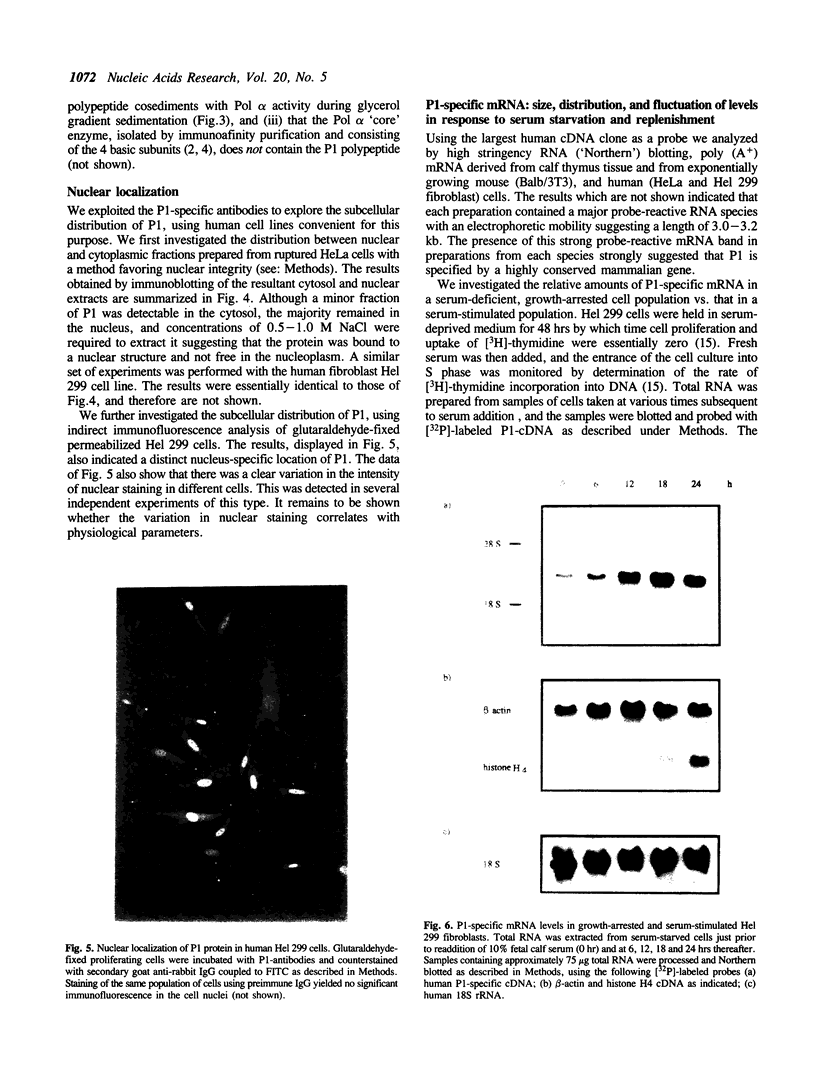
Polyclonal antibodies were raised against a multiprotein 'holoenzyme' form of calf thymus DNA polymerase alpha-primase and used to probe a human cDNA-protein expression library constructed in the lambda gt11 vector. The probe identified a series of cDNA clones derived from a 3.2 kb mRNA which encodes a novel 105 kDa polypeptide, the P1 protein. In intact cells, the P1 protein was specifically associated with the nucleus, and in cell extracts, it was associated with complex forms of DNA polymerase alpha-primase. The synthesis of human P1-specific mRNA was stimulated upon addition of fresh serum to growth-arrested cells, and RNA blot analyses with the human P1-cDNA probe indicated that P1 is encoded by a strictly conserved mammalian gene. The amino acid sequence deduced from a 240-codon open reading frame resident in the largest human P1-cDNA (0.84 kb) displayed greater than 96% identity with that deduced from the equivalent segment of a 795-codon open reading frame of a larger mouse P1-cDNA (2.8 kb). Throughout its length, the primary structure of mammalian P1 displayed strong homology with that of Mcm3, a 125 kDa yeast protein thought to be involved in the initiation of DNA replication (Gibson et al. 1990. Mol. Cell. Biol. 10: 5707-5720). The P1-Mcm3 homology, the strong conservation of P1 among mammals, its nuclear localization, and its association with the replication-specific DNA polymerase alpha strongly suggest an important role of the P1 protein in the replication of mammalian DNA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borowiec J. A., Dean F. B., Bullock P. A., Hurwitz J. Binding and unwinding--how T antigen engages the SV40 origin of DNA replication. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90730-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J. Animal virus DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:671–717. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins K. L., Kelly T. J. Effects of T antigen and replication protein A on the initiation of DNA synthesis by DNA polymerase alpha-primase. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2108–2115. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornreiter I., Höss A., Arthur A. K., Fanning E. SV40 T antigen binds directly to the large subunit of purified DNA polymerase alpha. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3329–3336. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07533.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster K., Lüthi-Steinmann K., Barnes M., McMaster G., Ferrari E., Eliassen K., Khan N., Brown N., Hübscher U. Cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding a catalytically active fragment of calf thymus DNA polymerase alpha. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Oct 15;140(1):21–27. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. p53 and DNA polymerase alpha compete for binding to SV40 T antigen. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):456–458. doi: 10.1038/329456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gassmann M., Thömmes P., Weiser T., Hübscher U. Efficient production of chicken egg yolk antibodies against a conserved mammalian protein. FASEB J. 1990 May;4(8):2528–2532. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.8.1970792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson S. I., Surosky R. T., Tye B. K. The phenotype of the minichromosome maintenance mutant mcm3 is characteristic of mutants defective in DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5707–5720. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond R. A., Foster K. A., Berchthold M. W., Gassmann M., Holmes A. M., Hübscher U., Brown N. C. Calcium-dependent calmodulin-binding proteins associated with mammalian DNA polymerase alpha. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Dec 20;951(2-3):315–321. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90101-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K. M., Lee A., Chen E., Botstein D. A group of interacting yeast DNA replication genes. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):958–969. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hübscher U., Gerschwiler P., McMaster G. K. A mammalian DNA polymerase alpha holoenzyme functioning on defined in vivo-like templates. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1513–1519. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01348.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König H., Riedel H. D., Knippers R. Reactions in vitro of the DNA polymerase-primase from Xenopus laevis eggs. A role for ATP in chain elongation. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Oct 3;135(3):435–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07670.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Villasante A., Sherline P., Cowan N. J. Brain-specific expression of MAP2 detected using a cloned cDNA probe. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2098–2105. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkas L. H., Hickey R. J., Li C., Pedersen N., Baril E. F. A 21S enzyme complex from HeLa cells that functions in simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 10;29(27):6362–6374. doi: 10.1021/bi00479a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasheuer H. P., Grosse F. Immunoaffinity-purified DNA polymerase alpha displays novel properties. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8458–8466. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi H., Prem veer Reddy G., Pardee A. B. Rapid incorporation of label from ribonucleoside disphosphates into DNA by a cell-free high molecular weight fraction from animal cell nuclei. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):443–451. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90464-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):161–170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottiger H. P., Hübscher U. Mammalian DNA polymerase alpha holoenzymes with possible functions at the leading and lagging strand of the replication fork. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3993–3997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottiger H., Frei P., Hässig M., Hübscher U. Mammalian DNA polymerase alpha: a replication competent holoenzyme form from calf thymus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 25;15(12):4789–4807. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.12.4789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Tjian R. T-antigen-DNA polymerase alpha complex implicated in simian virus 40 DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4077–4087. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. Initiation of eukaryotic DNA replication in vitro. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:197–245. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelander L., Berg P. Isolation and characterization of expressible cDNA clones encoding the M1 and M2 subunits of mouse ribonucleotide reductase. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3433–3442. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thömmes P., Fett R., Schray B., Kunze N., Knippers R. The core region of human glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase homologies with the Escherichia coli and yeast enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 24;16(12):5391–5406. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.12.5391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thömmes P., Reiter T., Knippers R. Synthesis of DNA polymerase alpha analyzed by immunoprecipitation from synchronously proliferating cells. Biochemistry. 1986 Mar 25;25(6):1308–1314. doi: 10.1021/bi00354a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vishwanatha J. K., Coughlin S. A., Wesolowski-Owen M., Baril E. F. A multiprotein form of DNA polymerase alpha from HeLa cells. Resolution of its associated catalytic activities. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6619–6628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T. S. Eukaryotic DNA polymerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:513–552. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T. S., Hu S. Z., Korn D. DNA primase from KB cells. Characterization of a primase activity tightly associated with immunoaffinity-purified DNA polymerase-alpha. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1854–1865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. W., Paborsky L. R., Fisher P. A., Wang T. S., Korn D. Structural and enzymological characterization of immunoaffinity-purified DNA polymerase alpha.DNA primase complex from KB cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7958–7968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan H., Gibson S., Tye B. K. Mcm2 and Mcm3, two proteins important for ARS activity, are related in structure and function. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):944–957. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]