Abstract
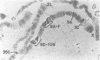
The 1.688 g/cm3 class of Drosophila satellite DNA is predominantly localized to the centromeric heterochromatin of the X chromosome. We report here the existence of 1.688 satellite related (SR) DNA arrays present at numerous locations throughout the euchromatic portion of the X. Unlike their heterochromatic counterparts, euchromatic SRs consist of a small number of repeating units (usually 2-4), each of which is 63-81% identical to the 359-bp monomer of the 1.688 satellite. Although it appears that SR DNA arrays are not transcribed, in at least two cases, they are located adjacent to transcriptionally active genes. SR sequences also have significant similarity to a previously described Drosophila middle repeat found almost exclusively in the X euchromatin. It seems likely that these X linked sequences are required for sex chromosome specific functions.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Brutlag D. Different regions of a complex statellite DNA vary in size and sequence of the repeating unit. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 5;135(2):483–500. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90448-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh T., Brutlag D. Sequence and sequence variation within the 1.688 g/cm3 satellite DNA of Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 5;135(2):465–481. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90447-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda M. I., Kernan M. J., Kreber R., Ganetzky B., Baker B. S. The maleless protein associates with the X chromosome to regulate dosage compensation in Drosophila. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):935–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90439-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinger L., Varshavsky A. Protein D1 preferentially binds A + T-rich DNA in vitro and is a component of Drosophila melanogaster nucleosomes containing A + T-rich satellite DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7152–7156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifschytz E., Lindsley D. L. The role of X-chromosome inactivation during spermatogenesis (Drosophila-allocycly-chromosome evolution-male sterility-dosage compensation). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):182–186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucchesi J. C., Manning J. E. Gene dosage compensation in Drosophila melanogaster. Adv Genet. 1987;24:371–429. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sass H., Meselson M. Dosage compensation of the Drosophila pseudoobscura Hsp82 gene and the Drosophila melanogaster Adh gene at ectopic sites in D. melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6795–6799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss F., Varshavsky A. A protein binds to a satellite DNA repeat at three specific sites that would be brought into mutual proximity by DNA folding in the nucleosome. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):889–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90424-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartof K. D., Hobbs C., Jones M. A structural basis for variegating position effects. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):869–878. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90422-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring G. L., Pollack J. C. Cloning and characterization of a dispersed, multicopy, X chromosome sequence in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2843–2847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard H. F. The genomics of long tandem arrays of satellite DNA in the human genome. Genome. 1989;31(2):737–744. doi: 10.1139/g89-132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]