Abstract
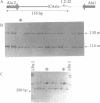
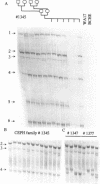
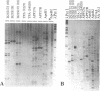
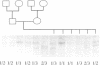
Microsatellites, such as (TG)n found at random throughout the genome, or as 3' extensions of Alu sequences are being increasingly used as genetic markers because of their pluriallelic character. The search for polymorphic microsatellites is time consuming, however, as it is necessary to sequence clones containing the microsatellites sequences in order to design specific PCR primers before testing for polymorphism, which does not always occur. We propose here a new approach to generate polymorphic markers, based on the amplification of microsatellites at the 3' end of Alu sequences, without the need for cloning or sequencing steps.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batzer M. A., Gudi V. A., Mena J. C., Foltz D. W., Herrera R. J., Deininger P. L. Amplification dynamics of human-specific (HS) Alu family members. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3619–3623. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellis M., Gérard A., Charlieu J. P., Marçais B., Brun M. E., Viegas-Péquignot E., Carter D. A., Roizès G. Construction and characterization of a partial library of yeast artificial chromosomes from human chromosome 21. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 May;10(4):301–310. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Economou E. P., Bergen A. W., Warren A. C., Antonarakis S. E. The polydeoxyadenylate tract of Alu repetitive elements is polymorphic in the human genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2951–2954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein N., Nahor O., Silver J. The 3' ends of alu repeats are highly polymorphic. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 11;18(15):4634–4634. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.15.4634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffais R., André P. M., Thibon M. K-tuple frequency in the human genome and polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3887–3891. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo Z., Sharma V., Litt M. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the D21S13E locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7470–7470. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7470-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litt M., Luty J. A. A hypervariable microsatellite revealed by in vitro amplification of a dinucleotide repeat within the cardiac muscle actin gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):397–401. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. L., Ledbetter S. A., Corbo L., Victoria M. F., Ramírez-Solis R., Webster T. D., Ledbetter D. H., Caskey C. T. Alu polymerase chain reaction: a method for rapid isolation of human-specific sequences from complex DNA sources. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6686–6690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orita M., Sekiya T., Hayashi K. DNA sequence polymorphisms in Alu repeats. Genomics. 1990 Oct;8(2):271–278. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90282-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J. D., Rabinovitch P. S., Burmer G. C. Targeted gene walking polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 11;19(11):3055–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.11.3055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., May P. E. Abundant class of human DNA polymorphisms which can be typed using the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):388–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuliani G., Hobbs H. H. A high frequency of length polymorphisms in repeated sequences adjacent to Alu sequences. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 May;46(5):963–969. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]