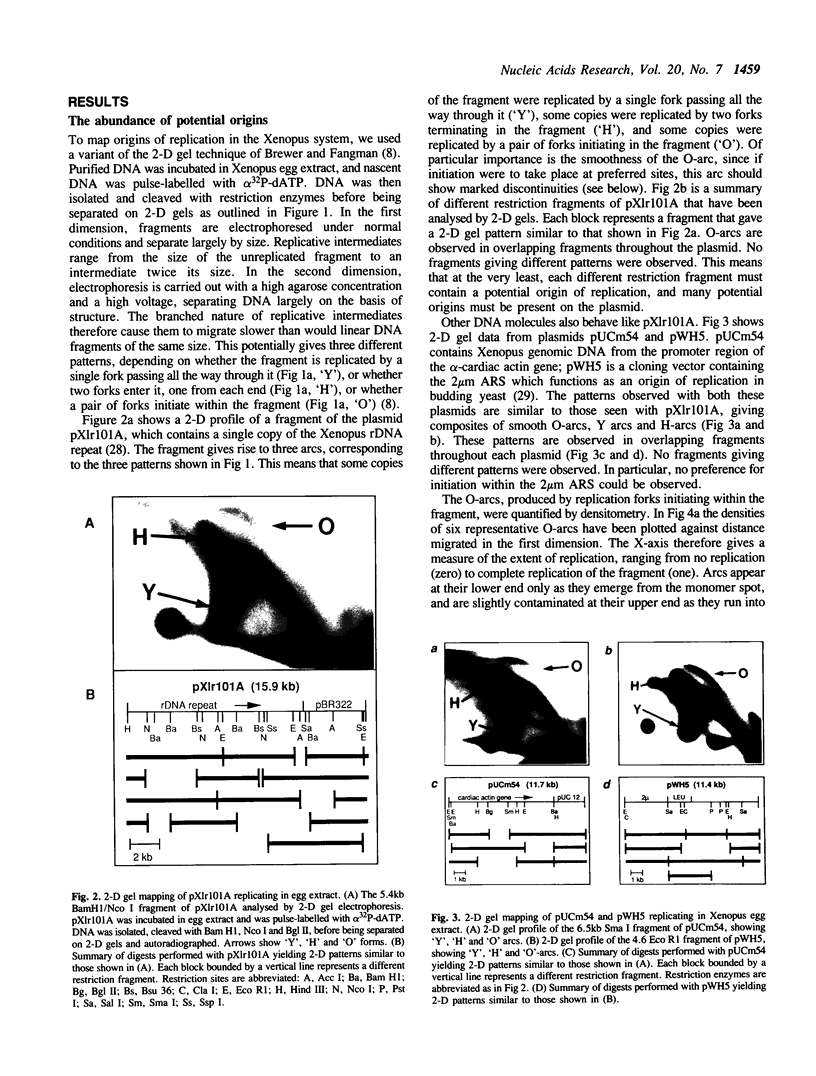
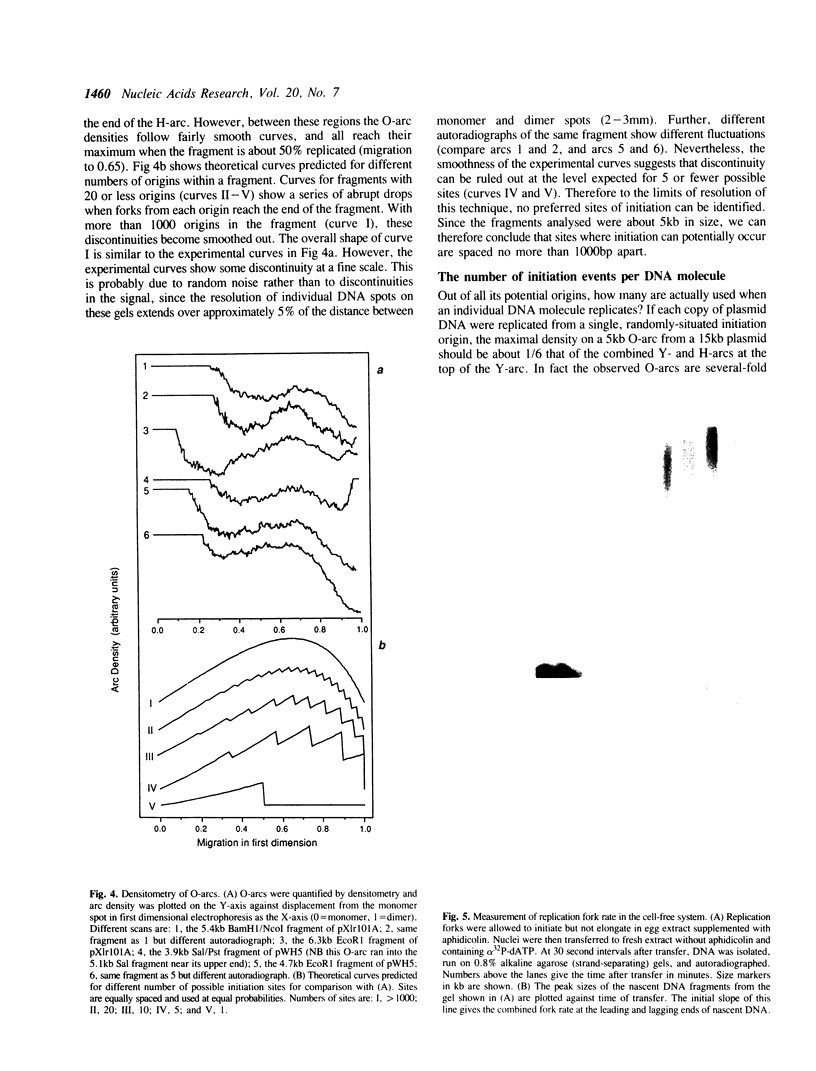
Abstract
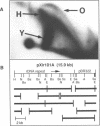
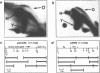
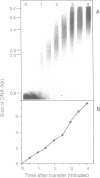
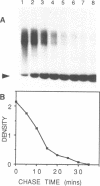
Cell-free extracts of Xenopus eggs will replicate plasmid DNA molecules under normal cell cycle control. We have used the neutral/neutral 2-D gel technique to map the sites at which DNA replication initiates in this system. Three different plasmids were studied: one containing the Xenopus rDNA repeat, one containing single copy Xenopus genomic DNA, and another containing the yeast 2 microns replication origin. 2-D gel profiles show that many potential sites of initiation are present on each plasmid, and are randomly situated at the level of resolution of this technique (500-1000 bp). Despite the abundance of sites capable of supporting the initiation of replication, pulse-chase experiments suggest that only a single randomly situated initiation event occurs on each DNA molecule. Once initiation has taken place, conventional replication forks appear to move away from this site at a rate of about 10nt/second, similar to the rate observed in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakken A., Morgan G., Sollner-Webb B., Roan J., Busby S., Reeder R. H. Mapping of transcription initiation and termination signals on Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):56–60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blow J. J., Dilworth S. M., Dingwall C., Mills A. D., Laskey R. A. Chromosome replication in cell-free systems from Xenopus eggs. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1987 Dec 15;317(1187):483–494. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1987.0075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blow J. J., Laskey R. A. Initiation of DNA replication in nuclei and purified DNA by a cell-free extract of Xenopus eggs. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):577–587. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90622-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blow J. J., Nurse P. A cdc2-like protein is involved in the initiation of DNA replication in Xenopus egg extracts. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):855–862. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90261-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blow J. J., Sheehan M. A., Watson J. V., Laskey R. A. Nuclear structure and the control of DNA replication in the Xenopus embryo. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1989;12:183–195. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1989.supplement_12.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blow J. J., Sleeman A. M. Replication of purified DNA in Xenopus egg extract is dependent on nuclear assembly. J Cell Sci. 1990 Mar;95(Pt 3):383–391. doi: 10.1242/jcs.95.3.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blow J. J., Watson J. V. Nuclei act as independent and integrated units of replication in a Xenopus cell-free DNA replication system. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1997–2002. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02463.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. J., Fangman W. L. A replication fork barrier at the 3' end of yeast ribosomal RNA genes. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):637–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. J., Fangman W. L. The localization of replication origins on ARS plasmids in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):463–471. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90642-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D., Dawid I. B. Specific gene amplification in oocytes. Oocyte nuclei contain extrachromosomal replicas of the genes for ribosomal RNA. Science. 1968 Apr 19;160(3825):272–280. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3825.272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burhans W. C., Vassilev L. T., Caddle M. S., Heintz N. H., DePamphilis M. L. Identification of an origin of bidirectional DNA replication in mammalian chromosomes. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):955–965. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90270-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callan H. G. Replication of DNA in the chromosomes of eukaryotes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1972 Apr 18;181(1062):19–41. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1972.0039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celniker S. E., Campbell J. L. Yeast DNA replication in vitro: initiation and elongation events mimic in vivo processes. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):201–213. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90420-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudette M. F., Benbow R. M. Replication forks are underrepresented in chromosomal DNA of Xenopus laevis embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5953–5957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand R. Eucaryotic DNA: organization of the genome for replication. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):317–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R. M., Laskey R. A. Regulated replication of DNA microinjected into eggs of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):761–771. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90439-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel S. S., Krysan P. J., Tran C. T., Calos M. P. Autonomous DNA replication in human cells is affected by the size and the source of the DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2263–2272. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A., Riggs A. D. On the mechanism of DNA replication in mammalian chromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):327–341. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A., Spotila L. D., Nawotka K. A., el-Assouli S. M., Davis L. R. The in vivo replication origin of the yeast 2 microns plasmid. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):473–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90643-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A., Zhu J. G., Davis L. R., Newlon C. S. Close association of a DNA replication origin and an ARS element on chromosome III of the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14A):6373–6384. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearsey S. Structural requirements for the function of a yeast chromosomal replicator. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90326-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krysan P. J., Haase S. B., Calos M. P. Isolation of human sequences that replicate autonomously in human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1026–1033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linskens M. H., Huberman J. A. Ambiguities in results obtained with 2D gel replicon mapping techniques. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):647–652. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linskens M. H., Huberman J. A. Organization of replication of ribosomal DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4927–4935. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McTiernan C. F., Stambrook P. J. Initiation of SV40 DNA replication after microinjection into Xenopus eggs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jul 18;782(3):295–303. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(84)90065-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshull J., Blow J. J., Hunt T. Translation of cyclin mRNA is necessary for extracts of activated xenopus eggs to enter mitosis. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):947–956. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90628-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méchali M., Kearsey S. Lack of specific sequence requirement for DNA replication in Xenopus eggs compared with high sequence specificity in yeast. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):55–64. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90526-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J. Nuclear reconstitution in vitro: stages of assembly around protein-free DNA. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):205–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90424-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palzkill T. G., Newlon C. S. A yeast replication origin consists of multiple copies of a small conserved sequence. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):441–450. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90164-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan M. A., Mills A. D., Sleeman A. M., Laskey R. A., Blow J. J. Steps in the assembly of replication-competent nuclei in a cell-free system from Xenopus eggs. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;106(1):1–12. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinchcomb D. T., Struhl K., Davis R. W. Isolation and characterisation of a yeast chromosomal replicator. Nature. 1979 Nov 1;282(5734):39–43. doi: 10.1038/282039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umek R. M., Kowalski D. The ease of DNA unwinding as a determinant of initiation at yeast replication origins. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):559–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90469-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umek R. M., Linskens M. H., Kowalski D., Huberman J. A. New beginnings in studies of eukaryotic DNA replication origins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 23;1007(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn J. P., Dijkwel P. A., Hamlin J. L. Replication initiates in a broad zone in the amplified CHO dihydrofolate reductase domain. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1075–1087. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90071-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A., Maundrell K., Heyer W. D., Beach D., Nurse P. Vectors for the construction of gene banks and the integration of cloned genes in Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Plasmid. 1986 Mar;15(2):156–158. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(86)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]