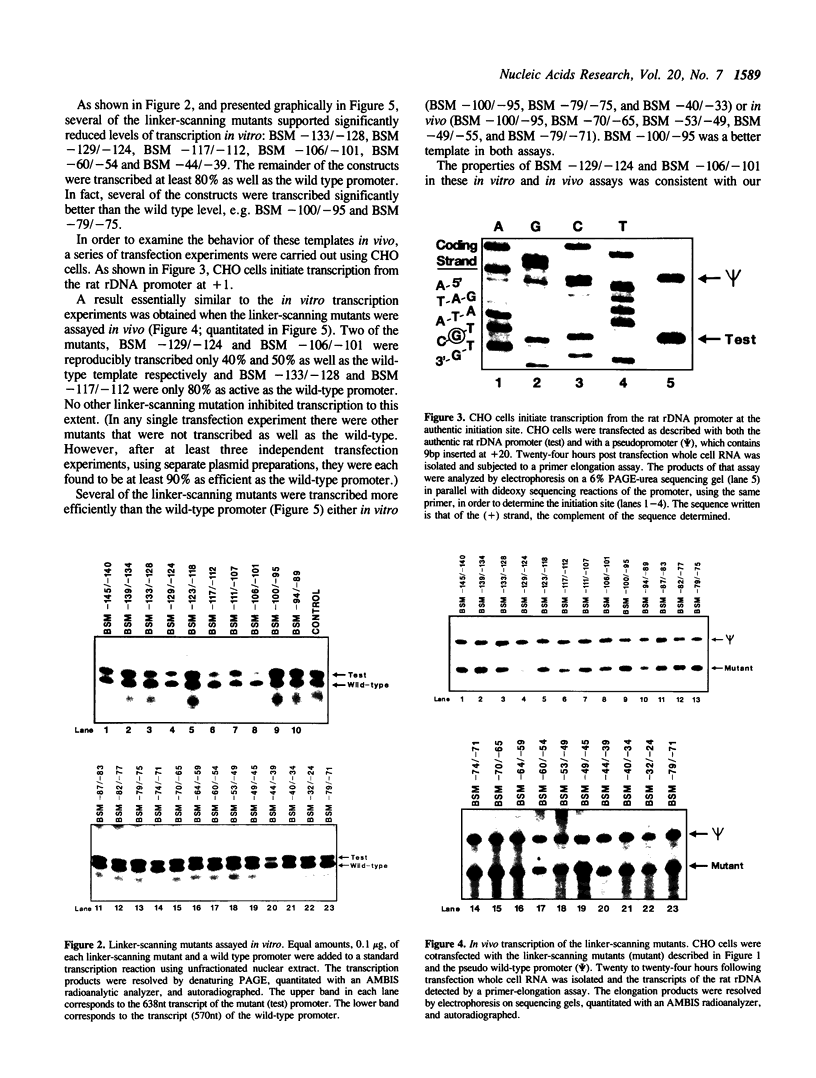
Abstract
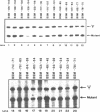
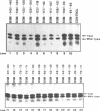
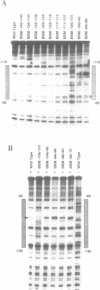
To investigate the mechanism of transcription of the rat ribosomal DNA (rDNA) promoter, a series of 23 linker-scanning mutants were constructed and assayed in transfected CHO cells and with cell-free extracts. With minor variation, the results of the in vitro and in vivo assays paralleled one another. For example, these assays demonstrated that the mutagenesis of bases from -133 to -124, and those from -106 to -101 of the rDNA promoter significantly inhibited transcription both in vivo and in vitro. Both of these sites lie within the upstream promoter element (UPE) of the rDNA promoter. Several constructs, in particular one that mutated the bases between -49 and -45, were better promoters in vivo than the wild-type promoter. DNAse footprinting experiments with purified UBF, an RNA polymerase I transcription factor, demonstrated the importance of the bases between -106 and -101 for the binding of that factor, providing a positive correlation between the transcription experiments and the binding of UBF to the rDNA promoter.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bateman E., Paule M. R. Promoter occlusion during ribosomal RNA transcription. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):985–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90113-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. P., Jantzen H. M., Tjian R. Assembly of alternative multiprotein complexes directs rRNA promoter selectivity. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):943–954. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. P., Learned R. M., Jantzen H. M., Tjian R. Functional cooperativity between transcription factors UBF1 and SL1 mediates human ribosomal RNA synthesis. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1192–1197. doi: 10.1126/science.3413483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy B. G., Yang-Yen H. F., Rothblum L. I. Additional RNA polymerase I initiation site within the nontranscribed spacer region of the rat rRNA gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2388–2396. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy B., Haglund R., Rothblum L. I. Regions upstream from the core promoter of the rat ribosomal gene are required for the formation of a stable transcription initiation complex by RNA polymerase I in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 14;909(2):133–144. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Kuhn A., Bartsch I., Rosenbauer H. A transcription terminator located upstream of the mouse rDNA initiation site affects rRNA synthesis. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):901–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90805-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haglund R. E., Rothblum L. I. Isolation, fractionation and reconstitution of a nuclear extract capable of transcribing ribosomal DNA. Mol Cell Biochem. 1987 Jan;73(1):11–20. doi: 10.1007/BF00229371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltiner M. M., Smale S. T., Tjian R. Two distinct promoter elements in the human rRNA gene identified by linker scanning mutagenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):227–235. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S. L., Ryan K., Sollner-Webb B. The promoter-proximal rDNA terminator augments initiation by preventing disruption of the stable transcription complex caused by polymerase read-in. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):212–223. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S. L., Sollner-Webb B. The mouse ribosomal DNA promoter has more stringent requirements in vivo than in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4970–4973. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S., Sollner-Webb B. A transcriptional terminator is a novel element of the promoter of the mouse ribosomal RNA gene. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):891–900. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90804-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Admon A., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Nucleolar transcription factor hUBF contains a DNA-binding motif with homology to HMG proteins. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):830–836. doi: 10.1038/344830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. H., Learned R. M., Tjian R. Analysis of clustered point mutations in the human ribosomal RNA gene promoter by transient expression in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):669–673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Cordes S., Tjian R. Purification and characterization of a transcription factor that confers promoter specificity to human RNA polymerase I. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1358–1369. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Learned T. K., Haltiner M. M., Tjian R. T. Human rRNA transcription is modulated by the coordinate binding of two factors to an upstream control element. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):847–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90559-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandal R. K. The organization and transcription of eukaryotic ribosomal RNA genes. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1984;31:115–160. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60376-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McStay B., Frazier M. W., Reeder R. H. xUBF contains a novel dimerization domain essential for RNA polymerase I transcription. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):1957–1968. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.1957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McStay B., Reeder R. H. A termination site for Xenopus RNA polymerase I also acts as an element of an adjacent promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):913–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90806-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McStay B., Reeder R. H. An RNA polymerase I termination site can stimulate the adjacent ribosomal gene promoter by two distinct mechanisms in Xenopus laevis. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1240–1251. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Arnheim N. Species-specific rDNA transcription is due to promoter-specific binding factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):221–227. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Financsek I., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Fractionation and reconstitution of factors required for accurate transcription of mammalian ribosomal RNA genes: identification of a species-dependent initiation factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6659–6670. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Mahony D. J., Rothblum L. I. Identification of two forms of the RNA polymerase I transcription factor UBF. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3180–3184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Mahony D. J., Xie W. Q., Smith S. D., Singer H. A., Rothblum L. I. Differential phosphorylation and localization of the transcription factor UBF in vivo in response to serum deprivation. In vitro dephosphorylation of UBF reduces its transactivation properties. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):35–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikaard C. S., Smith S. D., Reeder R. H., Rothblum L. rUBF, an RNA polymerase I transcription factor from rats, produces DNase I footprints identical to those produced by xUBF, its homolog from frogs. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3810–3812. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Pennock D., McStay B., Roan J., Tolentino E., Walker P. Linker scanner mutagenesis of the Xenopus laevis ribosomal gene promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 25;15(18):7429–7441. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.18.7429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothblum L. I., Reddy R., Cassidy B. Transcription initiation site of rat ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7345–7362. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. D., Oriahi E., Lowe D., Yang-Yen H. F., O'Mahony D., Rose K., Chen K., Rothblum L. I. Characterization of factors that direct transcription of rat ribosomal DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3105–3116. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. D., Oriahi E., Yang-Yen H. F., Xie W. Q., Chen C., Rothblum L. I. Interaction of RNA polymerase I transcription factors with a promoter in the nontranscribed spacer of rat ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1677–1685. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Tower J. Transcription of cloned eukaryotic ribosomal RNA genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:801–830. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tower J., Culotta V. C., Sollner-Webb B. Factors and nucleotide sequences that direct ribosomal DNA transcription and their relationship to the stable transcription complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3451–3462. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windle J. J., Sollner-Webb B. Two distant and precisely positioned domains promote transcription of Xenopus laevis rRNA genes: analysis with linker-scanning mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4585–4593. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie W. Q., O'Mahony D. J., Smith S. D., Rothblum L. Complementary in vivo and in vitro analyses of the interactions between the cis-acting elements of the rat rDNA promoter. 1991 May 29-Jun 12Mol Cell Biochem. 104(1-2):127–135. doi: 10.1007/BF00229812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie W. Q., Rothblum L. I. Rapid, small-scale RNA isolation from tissue culture cells. Biotechniques. 1991 Sep;11(3):324, 326-7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehring W. A., Greenleaf A. L. The carboxyl-terminal repeat domain of RNA polymerase II is not required for transcription factor Sp1 to function in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8351–8353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]