Abstract
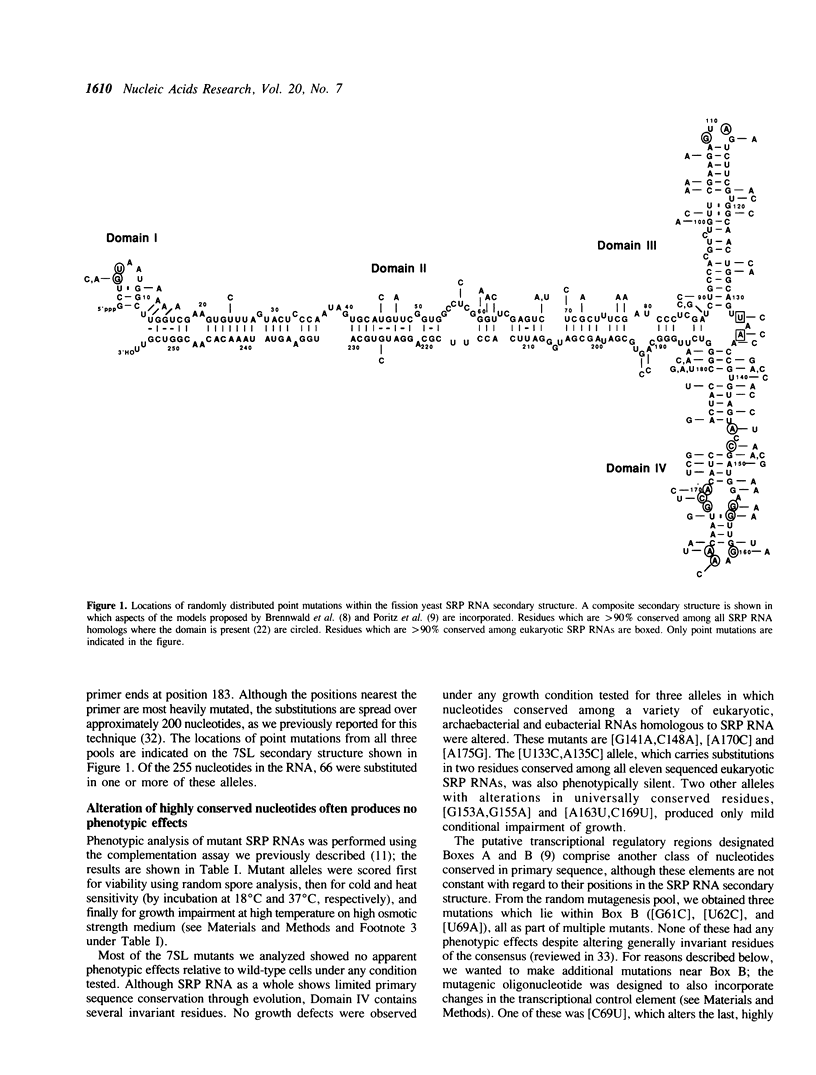
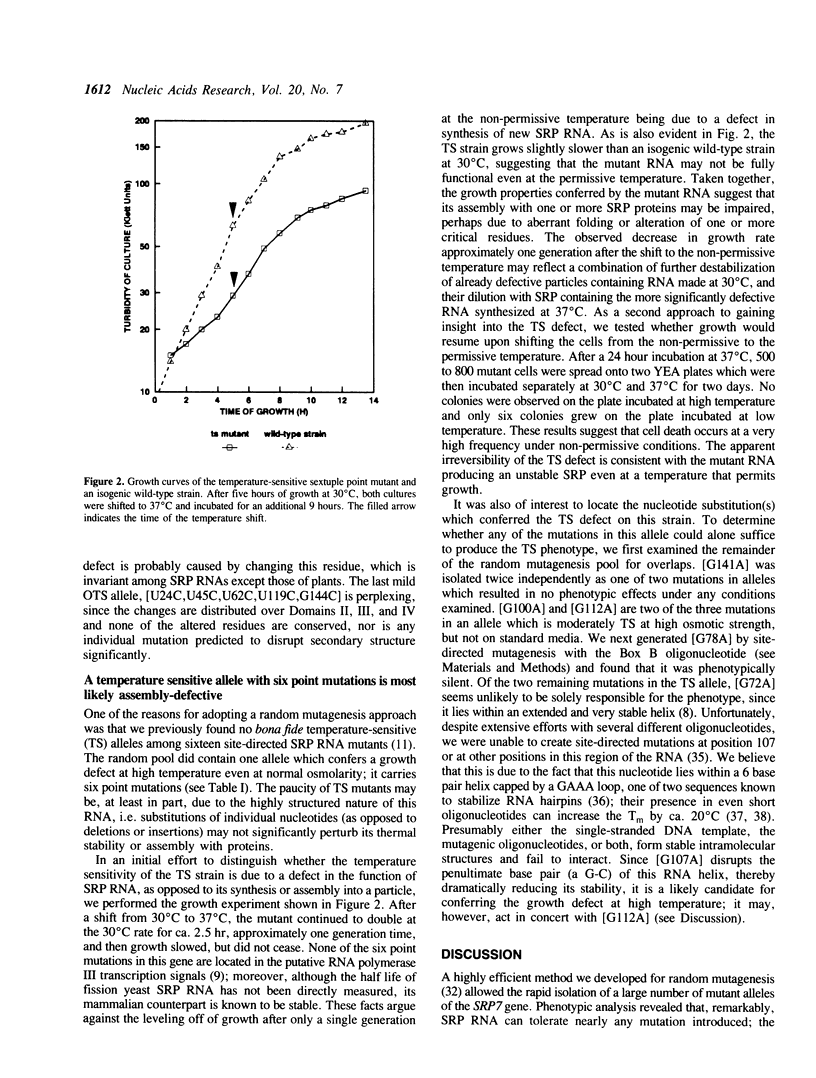
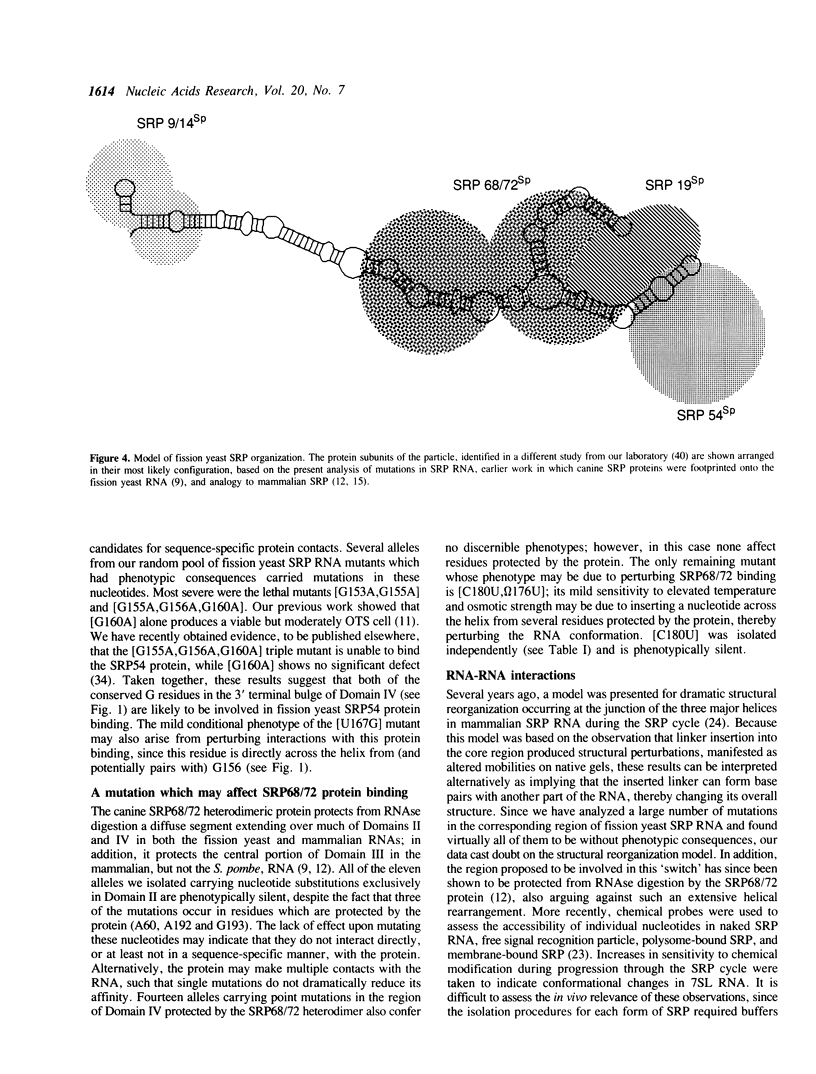
Signal recognition particle (SRP), a ribonucleoprotein composed of six polypeptides and one RNA subunit, serves as an adaptor between the cytoplasmic protein synthetic machinery and the translocation apparatus of the endoplasmic reticulum. To begin constructing a functional map of the 7SL RNA component of SRP, we extensively mutagenized the Schizosaccharomyces pombe SRP7 gene. Phenotypes are reported for fifty-two mutant alleles derived from random point mutagenesis, seven alleles created by site-directed mutagenesis to introduce restriction sites into the SRP7 gene, nine alleles designed to pinpoint conditional lesions, and three alleles with extra nucleotides inserted at position 84. Our data indicate that virtually all single nucleotide changes as well as many multiple substitutions in this highly structured RNA are phenotypically silent. Six lethal alleles and eleven which result in sensitivity to the combination of high temperature and elevated osmotic strength were identified. These mutations cluster in conserved regions which, in the mammalian RNA, are protected from nucleolytic agents by SRP proteins. The effects of mutations in the presumptive binding site for a fission yeast SRP 9/14 homolog indicate that both the identity of a conserved residue and the secondary structure within which it is embedded are functionally important. The phenotypes of mutations in Domain IV suggest particular residues as base-specific contacts for the fission yeast SRP54 protein. A single allele which confers temperature-sensitivity in the absence of osmotic perturbants was identified in this study; the growth properties of the mutant strain suggest that the encoded RNA is somewhat defective even at the permissive temperature, and is most likely unable to correctly assemble with SRP proteins at the nonpermissive temperature.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreazzoli M., Gerbi S. A. Changes in 7SL RNA conformation during the signal recognition particle cycle. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):767–777. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08008.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgaize D. B., Fournier M. J. Initiation of translation is impaired in E. coli cells deficient in 4.5S RNA. Nature. 1987 Jan 15;325(6101):281–284. doi: 10.1038/325281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennwald P., Liao X., Holm K., Porter G., Wise J. A. Identification of an essential Schizosaccharomyces pombe RNA homologous to the 7SL component of signal recognition particle. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1580–1590. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. Mutations in the gene for EF-G reduce the requirement for 4.5S RNA in the growth of E. coli. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):825–833. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90620-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. Time of action of 4.5 S RNA in Escherichia coli translation. J Mol Biol. 1989 Sep 5;209(1):79–90. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90171-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:873–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundelfinger E. D., Krause E., Melli M., Dobberstein B. The organization of the 7SL RNA in the signal recognition particle. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 11;11(21):7363–7374. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.21.7363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heus H. A., Pardi A. Structural features that give rise to the unusual stability of RNA hairpins containing GNRA loops. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):191–194. doi: 10.1126/science.1712983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg U. C., Walter P., Johnson A. E. Photocrosslinking of the signal sequence of nascent preprolactin to the 54-kilodalton polypeptide of the signal recognition particle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8604–8608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurzchalia T. V., Wiedmann M., Girshovich A. S., Bochkareva E. S., Bielka H., Rapoport T. A. The signal sequence of nascent preprolactin interacts with the 54K polypeptide of the signal recognition particle. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):634–636. doi: 10.1038/320634a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen N., Zwieb C. SRP-RNA sequence alignment and secondary structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 25;19(2):209–215. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauffer L., Garcia P. D., Harkins R. N., Coussens L., Ullrich A., Walter P. Topology of signal recognition particle receptor in endoplasmic reticulum membrane. 1985 Nov 28-Dec 4Nature. 318(6044):334–338. doi: 10.1038/318334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao X. B., Brennwald P., Wise J. A. Genetic analysis of Schizosaccharomyces pombe 7SL RNA: a structural motif that includes a conserved tetranucleotide loop is important for function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4137–4141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao X. B., Wise J. A. A simple high-efficiency method for random mutagenesis of cloned genes using forced nucleotide misincorporation. Gene. 1990 Mar 30;88(1):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90066-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poritz M. A., Bernstein H. D., Strub K., Zopf D., Wilhelm H., Walter P. An E. coli ribonucleoprotein containing 4.5S RNA resembles mammalian signal recognition particle. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1111–1117. doi: 10.1126/science.1701272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poritz M. A., Siegel V., Hansen W., Walter P. Small ribonucleoproteins in Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Yarrowia lipolytica homologous to signal recognition particle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4315–4319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poritz M. A., Strub K., Walter P. Human SRP RNA and E. coli 4.5S RNA contain a highly homologous structural domain. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):4–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribes V., Dehoux P., Tollervey D. 7SL RNA from Schizosaccharomyces pombe is encoded by a single copy essential gene. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):231–237. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02804.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribes V., Römisch K., Giner A., Dobberstein B., Tollervey D. E. coli 4.5S RNA is part of a ribonucleoprotein particle that has properties related to signal recognition particle. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):591–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90454-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römisch K., Webb J., Lingelbach K., Gausepohl H., Dobberstein B. The 54-kD protein of signal recognition particle contains a methionine-rich RNA binding domain. J Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;111(5 Pt 1):1793–1802. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.5.1793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel V., Walter P. Binding sites of the 19-kDa and 68/72-kDa signal recognition particle (SRP) proteins on SRP RNA as determined in protein-RNA "footprinting". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1801–1805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel V., Walter P. Each of the activities of signal recognition particle (SRP) is contained within a distinct domain: analysis of biochemical mutants of SRP. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):39–49. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90529-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel V., Walter P. Elongation arrest is not a prerequisite for secretory protein translocation across the microsomal membrane. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;100(6):1913–1921. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.6.1913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel V., Walter P. Removal of the Alu structural domain from signal recognition particle leaves its protein translocation activity intact. Nature. 1986 Mar 6;320(6057):81–84. doi: 10.1038/320081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strub K., Moss J., Walter P. Binding sites of the 9- and 14-kilodalton heterodimeric protein subunit of the signal recognition particle (SRP) are contained exclusively in the Alu domain of SRP RNA and contain a sequence motif that is conserved in evolution. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):3949–3959. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.3949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strub K., Walter P. Assembly of the Alu domain of the signal recognition particle (SRP): dimerization of the two protein components is required for efficient binding to SRP RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):777–784. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck J. C., Toschka H. Y., Specht T., Erdmann V. A. Common structural features between eukaryotic 7SL RNAs, eubacterial 4.5S RNA and scRNA and archaebacterial 7S RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7740–7740. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuerk C., Gauss P., Thermes C., Groebe D. R., Gayle M., Guild N., Stormo G., d'Aubenton-Carafa Y., Uhlenbeck O. C., Tinoco I., Jr CUUCGG hairpins: extraordinarily stable RNA secondary structures associated with various biochemical processes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1364–1368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlenbeck O. C. Tetraloops and RNA folding. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):613–614. doi: 10.1038/346613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Lingappa V. R. Mechanism of protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:499–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zopf D., Bernstein H. D., Johnson A. E., Walter P. The methionine-rich domain of the 54 kd protein subunit of the signal recognition particle contains an RNA binding site and can be crosslinked to a signal sequence. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4511–4517. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07902.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwieb C. Interaction of protein SRP19 with signal recognition particle RNA lacking individual RNA-helices. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 11;19(11):2955–2960. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.11.2955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwieb C. The secondary structure of the 7SL RNA in the signal recognition particle: functional implications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 11;13(17):6105–6124. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.17.6105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwieb C., Ullu E. Identification of dynamic sequences in the central domain of 7SL RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4639–4657. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



