Abstract
Monocytic differentiation is orchestrated by complex networks that are not fully understood. This study further elucidates the involvement of transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β (C/EBPβ). Initially, we demonstrated a marked increase in nuclear C/EBPβ-liver-enriched activating protein* (LAP*)/liver-enriched activating protein (LAP) levels and LAP/liver-enriched inhibiting protein (LIP) ratios in phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)-treated differentiating THP-1 premonocytic cells accompanied by reduced proliferation. To directly study C/EBPβ effects on monocytic cells, we generated novel THP-1-derived (low endogenous C/EBPβ) cell lines stably overexpressing C/EBPβ isoforms. Most importantly, cells predominantly overexpressing LAP* (C/EBPβ-long), but not those overexpressing LIP (C/EBPβ-short), exhibited a reduced proliferation, with no effect on morphology. PMA-induced inhibition of proliferation was attenuated in C/EBPβ-short cells. In C/EBPβWT macrophage-like cells (high endogenous C/EBPβ), we measured a reduced proliferation/cycling index compared with C/EBPβKO. The typical macrophage morphology was only observed in C/EBPβWT, whereas C/EBPβKO stayed round. C/EBPα did not compensate for C/EBPβ effects on proliferation/morphology. Serum reduction, an independent approach known to inhibit proliferation, induced macrophage morphology in C/EBPβKO macrophage-like cells but not THP-1. In PMA-treated THP-1 and C/EBPβ-long cells, a reduced phosphorylation of cell cycle repressor retinoblastoma was found. In addition, C/EBPβ-long cells showed reduced c-Myc expression accompanied by increased CDK inhibitor p27 and reduced cyclin D1 levels. Finally, C/EBPβ-long and C/EBPβWT cells exhibited low E2F1 and cyclin E levels, and C/EBPβ overexpression was found to inhibit cyclin E1 promoter-dependent transcription. Our results suggest that C/EBPβ reduces monocytic proliferation by affecting the retinoblastoma/E2F/cyclin E pathway and that it may contribute to, but is not directly required for, macrophage morphology. Inhibition of proliferation by C/EBPβ may be important for coordinated monocytic differentiation.
Keywords: C/EBP Transcription Factor, Cell Differentiation, E2F Transcription Factor, Macrophage, Retinoblastoma (Rb), C/EBP beta, Cyclin E, Monocyte, Morphology, Proliferation
Introduction
Monocytic differentiation from several progenitor stages to the monocyte/macrophage is orchestrated by a complex network involving a coordinated set of regulatory proteins, including PU.1, CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins (C/EBPs),4 MafB, and Egr-1 (1, 2). The transcription factor C/EBPβ has been suggested to play a crucial role in the positive or negative regulation of genes involved in differentiation/proliferation as well as inflammatory and malignant processes (3). Transcription of the C/EBPβ gene results in the expression of a single mRNA product yielding the formation of three different C/EBPβ isoforms by alternative translation (4). The two larger isoforms (liver-enriched activating protein* (LAP*; i.e. full-length C/EBPβ) and its slightly shorter version LAP) contain a dimerization and a DNA binding domain, a negative regulatory region, and several transactivation domains, whereas the considerably shorter variant, liver-enriched inhibiting protein (LIP), does not contain these transactivation domains (3). The expression/activation of C/EBPβ is regulated in a complex way (e.g. by transcriptional mechanisms, mTOR-mediated alternative translation, post-translational modifications, and protein-protein interactions) (5–8).
C/EBP transcription factors, and C/EBPβ in particular, have long been implicated in the regulation of monocyte/macrophage differentiation, whereas C/EBPα appears to be more important for the maturation of granulocytes (2). In this context, it has been proposed that commitment decisions leading to the generation of either macrophages or granulocytes are mainly controlled by PU.1 and C/EBP transcription factors (1, 2). It has also been shown that enforced expression of C/EBPβ in B cells and of C/EBPα in B cells and myelomonocytic HF-6 cells is sufficient for at least partly reprogramming cells toward a monocyte/macrophage-like phenotype (9, 10), whereas in 32D hematopoietic cells, C/EBPβ is also able to induce granulocytic differentiation (11). Interestingly, deltanoid-induced monocytic differentiation of HL-60 cells depends on both C/EBPβ and retinoblastoma protein (Rb) (12), and in U937 cells it has been shown that during phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)-induced differentiation the hypophosphorylated Rb interacts directly with C/EBPβ, thus promoting its activation (13). In addition, the proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 (Pyk2), associated with PMA-induced macrophage spreading and motility, is induced in monocyte/macrophages by C/EBPβ (14). Recently, it has been suggested that PMA- or deltanoid-induced differentiation of leukemic U937 cells is mediated via C/EBPβ and PU.1 in an NDRG1-dependent manner (15), and it has been shown that C/EBPβ is necessary for full transcriptional activation of PU.1 at the interleukin 1β, chitotriosidase, and myeloid differentiation factor 2 promoters (7, 16, 17). Here it should also be mentioned that C/EBPβ coordinates the expression of a variety of genes in monocytic cells (e.g. coding for cytokines as well as signaling and scavenging molecules that are involved in the coordination of innate and adaptive immunity) (3, 8, 18–20).
In summary, the exact role of C/EBPβ in the differentiation of premonocytic cells toward mature monocyte/macrophages is not yet fully understood. To further elucidate the involvement of C/EBPβ in monocytic differentiation, a new experimental tool was generated (i.e. THP-1-derived premonocytic cell lines (low amounts of endogenous C/EBPβ) that stably overexpress either predominantly the largest C/EBPβ isoform LAP* or exclusively the smaller isoform LIP). As a second model, we used C/EBPβWT (high endogenous C/EBPβ) and C/EBPβKO macrophage-like cell lines (18). Our results suggest that C/EBPβ reduces monocytic proliferation by affecting the Rb/E2F/cyclin E pathway, presumably required for coordinated differentiation. Furthermore, C/EBPβ may contribute to, but is not directly required for, the development of macrophage morphology.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Reagents
PMA as well as the actin and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) antibodies were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. The TATA box-binding protein (TBP) antibody was obtained from Abcam (Cambridge, UK); the antibodies detecting C/EBPβ (H-7), cyclin D1 (A-12), cyclin E (E-4), E2F1, and β-tubulin were from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Heidelberg, Germany); and antibodies directed against C/EBPα, total Rb, phospho-Rb Ser608, phospho-Rb Ser780, phospho-Rb Ser795, p27, p15, and c-Myc (D84C12) were from Cell Signaling (Danvers, MA). All secondary horseradish-coupled antibodies were purchased from Vector Laboratories (Peterborough, UK), and the allophycocyanin-coupled secondary antibody (used for flow cytometry) was obtained from BD Biosciences (Heidelberg, Germany). For chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), the C-19 anti-C/EBPβ (batch sc-150X, Santa Cruz Biotechnology) was used (positive control, anti-H3, pab1791, Abcam; negative control, rabbit IgG, Millipore (Billerica, MA)).
Differentiation of Monocytic Cells and Culture of Macrophage-like Cells
For the experiments, the human premonocytic cell line THP-1 (DSMZ, Brunswick, Germany) and murine macrophage-like cells (C/EBPβ wild type (C/EBPβWT), C/EBPβ knock-out (C/EBPβKO), and C/EBPβRE (C/EBPβKO retransfected with the plasmid pZeo SV2+ containing the full-length C/EBPβ sequence) (8, 18)) were used. The cells were cultivated at 37 °C with 5% CO2 and 95% humidity in RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 7.5% FCS, 100 units/ml penicillin, and 100 μg/ml streptomycin (Biochrom, Berlin, Germany). To induce monocytic differentiation of THP-1 cells or to stimulate C/EBPβWT and C/EBPβKO cells, 1, 10, or 100 nm PMA was added up to 72 h prior to subsequent analysis.
Retroviral Vector, Vector Production, and Stable Transduction of THP-1 Cells
The gammaretroviral vector SF91.IRES.eGFP.PRE was described previously (21). DNA fragments containing the human full-length wild-type C/EBPβ coding sequence or the truncated sequence coding exclusively for C/EBPβ-LIP (GenBankTM accession number NM_005194.2) were cloned into the NotI site before the IRES.eGFP cassette. Cell-free retroviral supernatants were produced after transient transfection of the 293T-based packaging cell line Phoenix-gp using a VSV-g envelope according to the previously described procedure (21, 22). Viral titers determined on human HT1080 fibroblasts by flow cytometry were in the range of 1–8 × 106 IU/ml. Spin transductions of 2 × 105 THP-1 cells using a multiplicity of infection of 20 in the presence of 4 μg/ml protamine sulfate were done as described previously (22). The efficiency of viral transduction was calculated by determination of the fluorescence emitted by co-expressed eGFP using flow cytometry (FACSCalibur or LSR II, both BD Biosciences) and achieved ∼10%. Following cell sorting, a cell population containing >90% eGFP-positive cells was isolated (23). Subsequently, single cell cultures were established by serial dilutions in 96-well plates and selected for C/EBPβ protein expression by flow cytometry using the primary C/EBPβ antibody, the allophycocyanin-coupled secondary antibody, and the Cytofix/Cytoperm Kit (BD Biosciences) as well as Western blot analysis. Two cell lines were identified, either overexpressing predominantly the largest C/EBPβ isoform LAP* (termed C/EBPβ-long) or exclusively C/EBPβ-LIP (termed C/EBPβ-short). A third cell line transduced with the empty vector (termed SF91) was established as a control. Stock aliquots were created containing 3 × 106 cells each and stored at −150 °C. For subsequent analyses, 3 × 106 cells were cultivated in 75-cm2 flasks in a volume of 30 ml of medium.
IL-5 and IL-1-RA Protein Expression
The protein expression of interleukin (IL)-5 and IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1-RA) was determined in cell culture supernates of 2 × 106 C/EBPβ-long, C/EBPβ-short, and SF91 control cells (6-well plates, volume 2 ml/well) using the human cytokine array proteome profiler kit (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN) according to the manufacturer's instructions. In short, membranes carrying capture antibodies detecting the respective proteins were blocked for 1 h using array buffer 4. In this time period, 1 ml of each cell culture supernatant was incubated with 0.5 ml of array buffer 4 and 15 μl of biotin-labeled detection antibodies. Membranes were then incubated with the prepared supernates (4 °C, 18 h). Afterward, 2 ml of streptavidin-coupled horseradish peroxidase (diluted 1:2000 in array buffer 5) were added for 30 min, and the proteins were detected via chemiluminescence using SuperSignal West Femto Substrate (Perbio Science, Bonn, Germany) and the MF-ChemiBis 3.2 imaging system (Biostep, Jahnsdorf, Germany). Densitometry was performed using Scion Image (Scion Corp., Frederick, MD).
RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, and Real-time RT-PCR
2 × 106 C/EBPβ-long, C/EBPβ-short, and SF91 control cells were cultured in 6-well plates (volume 2 ml/well) in the absence (0 h) or presence of TNF (200 units, up to 6 h of stimulation). Cell lysis, total RNA isolation, validation of RNA concentration/purity, and generation of external standard curves are described elsewhere (24). Two μg of total RNA were reverse-transcribed as described previously (25). Expression of human IL-8 mRNA was assessed by real-time RT-PCR using a LightCycler 480, universal probe library probe 72 (Roche Applied Science), and specific primers (5′-AGACAGCAGAGCACACAAGC-3′ and 5′-ATGGTTCCTTCCGGTGGT-3′). For the amplification, a standard protocol for experiments using universal probe library probes was used (24). Normalization of cDNA amounts was performed as described (19).
Morphological Analysis
Cell morphology was analyzed at the indicated time points with the motorized inverted fluorescence microscope IX81 (Olympus, Hamburg, Germany) using the digital CCD camera C10600-10B (Hamamatsu Photonics, Hamamatsu City, Japan) and the CellR imaging software (Olympus) by counting total cells and cells with macrophage morphology in representative visual fields per well. The following features were defined as characteristic for macrophage morphology: flattened, spindle-shaped, amoeboid, and/or polygonal.
Protein Extraction, Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis, and Immunoblotting
For protein extraction from THP-1 cells, 1 × 106 or 3 × 106 cells/well were cultivated in 1.6 or 3 ml of medium in 12- or 6-well plates. Alternatively, 1.5 × 107 THP-1 cells were incubated in 30 ml of medium in 75-cm2 flasks. For protein extraction from adherent cells, 2 × 106 macrophage-like cells were cultivated in 6-well plates in a volume of 3 ml. Total, cytoplasmic, and nuclear cell extracts were isolated, and electrophoresis was performed with 12% (Rb, phospho-Rb, cyclin D1, p27, p15, and c-Myc) or 16% (C/EBPβ, C/EBPα, E2F1, and cyclin E) Tris/glycine-SDS gels as described previously (19). The proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose membranes using the Western blot technique. After transfer, the membranes were incubated with the respective primary antibodies, followed by incubation with the appropriate horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody. Proteins were visualized by chemiluminescence detection using the SuperSignal West Femto Substrate and the Bio-imaging system MF-ChemiBis 3.2.
Calculation of C/EBP Isoform Ratios and Determination of Rb Phosphorylation Status
First, intensities of (i) C/EBPβ-LAP*, LAP, and LIP protein bands; (ii) C/EBPα p42 and p30; or (iii) phospho-Rb and total Rb protein were quantified using the Bio-imaging system MF-ChemiBis 3.2 and the TotalLab TL100 analysis software (Nonlinear Dynamics, Newcastle, UK), including normalization on the basis of the respective loading control. Subsequently, the LAP/LIP ratio was calculated by dividing the combined LAP* and LAP value (denoted as LAP in the LAP/LIP ratio) by the respective LIP value (24). Equivalently, the p42/p30 ratio was calculated by dividing the p42 value by the respective p30 value. The Rb phosphorylation status was calculated by dividing the signal intensity measured for phospho-Rb by the signal intensity measured for total Rb protein.
Cell Proliferation Analysis
Cell proliferation of 2 × 106 THP-1 or macrophage-like cells, grown for 72 h in 75-cm2 flasks in a volume of 30 ml, was initially assessed by counting the respective cell number in a 10-μl cell suspension stained with 0.4% trypan blue solution (Sigma-Aldrich) in a Neubauer chamber (W. Schreck, Hofheim, Germany). For cell proliferation analyses under serum depletion, 1 × 105 macrophage-like cells were grown up to 96 h in 6-well plates (volume 3 ml) before cell counting was performed. In addition, proliferation was validated using a proliferation assay based on the measurement of metabolic activity (i.e. ATP levels) (ViaLight Plus Kit, Lonza (Basel, Switzerland)) (24). 1 × 104 THP-1 cells; 7 × 103 C/EBPβ-long, C/EBPβ-short, or SF91 control cells; or 5 × 103 macrophage-like cells were seeded in 96-well cell culture plates in a volume of 100 μl. Following incubation up to 96 h, 50 μl of cell lysis reagent was added, subsequently incubated for 10 min at room temperature, and stored at −80 °C until measurement. Following equilibration of all reagents and cell lysates to room temperature, 50 μl of ATP-monitoring reagent were added, and after 2 min, the light activity was measured as relative light units (RLU) in an Orion L microplate luminometer (Berthold Detection Systems, Pforzheim, Germany).
Cell Cycle Analysis
Cell cycle analysis was performed using the propidium iodide DNA staining-based Cycletest PLUS DNA Reagent Kit (BD Biosciences). 5 × 105 macrophage-like cells were incubated up to 48 h in 25-cm2 flasks in a volume of 7.5 ml of medium at 37 °C and harvested at the indicated time points by trypsinization. Following a washing step, cells were stored at −80 °C. For analyses, thawed samples were stained according to the manufacturer's instructions. Analysis of propidium iodide intercalation into DNA was performed using flow cytometry. The cycling index was calculated by adding the percentages of cells in S and G2M phases and dividing them by the percentage in G0G1 phase, (S + G2M)/G0G1.
Reporter Gene Assays
For the analysis of cyclin E and A promoter-dependent transcription, DNA fragments containing 1142 bp of the human cyclin E1 promoter region (located on chromosome 19; GenBankTM accession number: NC_000019.9) or 1012 bp of the human cyclin A2 promoter region (chromosome 4; NC_000004.11) were cloned into Promega's firefly luciferase reporter gene vector pGL3-basic. For the analysis of Rb promoter-dependent transcription, a DNA fragment containing 1567 bp of the human Rb promoter region (chromosome 13; NC_000013.1) was cloned into pGL4.10 (Promega). The reporter gene plasmids were co-transfected with the pTracer-CMV2-derived (Invitrogen) C/EBPβ expression plasmid pC/EBPβ-WT (0.5 or 0.9 μg each) and Renilla luciferase expression vector pRL-CMV (internal transfection/normalization control; 0.1 or 0.2 μg) into 1 × 106 THP-1 cells using a Nucleofector II (Lonza; program V001, Nucleofector Kit V) according to the manufacturer's instructions (controls: pGL4.10, pGL3-basic, and pTracer-CMV2). One day after transfection, cells were lysed with passive lysis buffer, and firefly as well as Renilla luciferase expression was assessed using the dual luciferase assay system (Promega) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Results were expressed as relative luciferase activity (i.e. firefly relative light units were divided by Renilla relative light units) (19).
ChIP Assay
1 × 107 SF91, C/EBPβ-long, and C/EBPβ-short cells were cultured in 75-cm2 flasks (volume 30 ml) and synchronized by serum depletion for 90 h. Synchronized cells were additionally grown for 2 h in 7.5% FCS-supplemented medium. Subsequently, the ChIP assay was performed as described previously (7). Detection of DNA fragments, that included potential C/EBPβ binding sites, was carried out by PCR analyses using specific primers for the human Rb promoter sequence −1892 to −1688 (5′-TTCAATTTATCAGGCTCCCA-3′ and 5′-CCAGTCCTACCTAACTTCAG-3′) or the human E2F1 promoter sequence −2122 to −1870 (5′-GCTTATGTGGTCTCTGTGGTCCC-3′ and 5′-GCAGCCTCAAATCACAGCTCC-3′). Negative and positive controls were performed according to Ref. 26. As a positive control, 1 × 106 THP-1 cells/ml were cultured for 48 h with or without 10 ng/ml TNF, and human matrix metalloproteinase 13 promoter sequence, including C/EBPβ binding motifs between −1081 and −650, was amplified.
Determination of Rb Protein Stability
1 × 107 C/EBPβ-long, SF91, and C/EBPβ-short cells were synchronized for 90 h (75-cm2 flasks, 20 ml). Subsequently, 1 × 106 cells/well were seeded in 12-well plates (1.5 ml) and incubated with 10 μg/ml cycloheximide (Calbiochem, Darmstadt, Germany) to arrest translation. Alternatively, non-synchronized cells were used. Whole cell extracts were harvested, and Rb levels were analyzed by Western blot up to 4 h. Rb protein half-life was calculated with Microsoft Office Excel 2003 using the polynomic curve equation.
Statistical Analysis
Using the GraphPad Prism 5 software (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA), the unpaired t test with Welch's correction or the one-sample t test was applied, and statistical significance was defined as p ≤ 0.05 (*) or p ≤ 0.01 (**).
RESULTS
Increase in C/EBPβ Isoforms and LAP/LIP Ratio in Differentiating THP-1 Premonocytic Cells, Accompanied by Reduced Proliferation
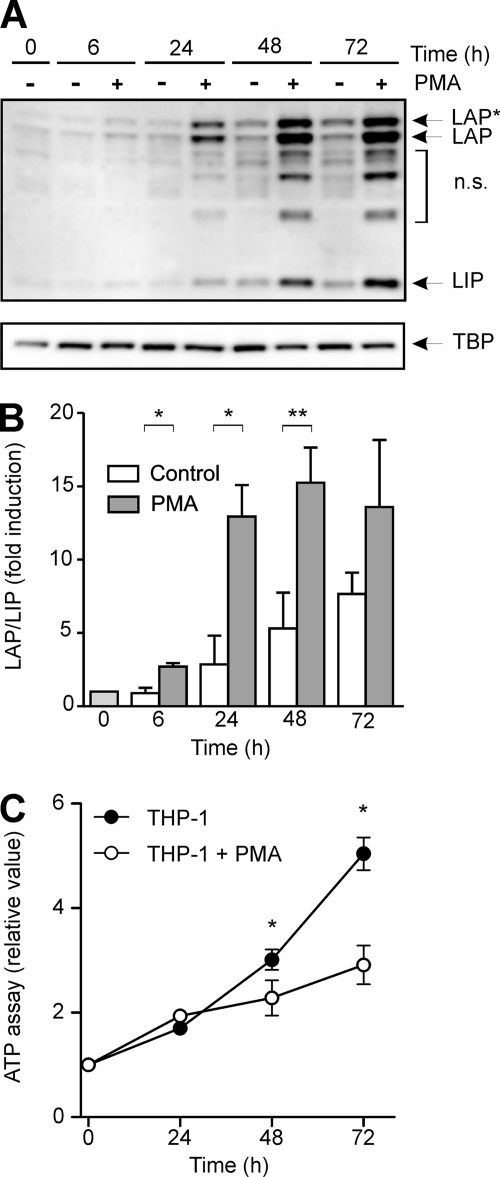
In initial experiments, premonocytic THP-1 cells were differentiated with increasing doses of PMA up to 72 h. This treatment induces a dramatic change of morphology, which means, as has been established earlier, that the premonocytic round THP-1 cells become adherent, displaying macrophage morphology and functionality (27) (data not shown). Under this condition, the levels of C/EBPβ isoforms were assessed by Western blot analysis. In these experiments, we observed a significant increase in the larger C/EBPβ isoforms LAP* and LAP and, to a lesser extent, the smaller LIP protein in nuclear extracts (Fig. 1A), which was mirrored by a significant increase in the LAP/LIP ratio as measured by densitometry (Fig. 1B). It should be mentioned that the level of C/EBPβ isoforms in unstimulated control cells also increased slightly over time (Fig. 1A). Furthermore, PMA-incubated THP-1 cells exhibited a significant reduction of proliferation as measured by ATP proliferation assays and cell count analysis compared with the untreated control (Fig. 1C) (data not shown).
FIGURE 1.
Increase in C/EBPβ isoforms as well as LAP/LIP ratio in differentiating THP-1 premonocytic cells, accompanied by impaired proliferation. A, premonocytic THP-1 cells were incubated with 100 nm PMA up to 72 h. Nuclear C/EBPβ levels were measured by Western blot analysis. The C/EBPβ isoforms LAP*, LAP, and LIP are indicated by arrows. TBP was used as a loading control. n.s., nonspecific bands. B, the LAP/LIP ratio was determined by densitometry in which the respective ratio in unstimulated cells at 0 h was defined as 1 (mean ± S.D. (error bars), n = 3). Statistical significance with p ≤ 0.05 (*) or p ≤ 0.01 (**) is indicated. C, ATP proliferation assays were performed using the experimental conditions described above. The respective proliferation value at 0 h was defined as 1, and the relative proliferation values were calculated (mean ± S.D., n = 3). The asterisks indicate statistical significance with p ≤ 0.05.
Generation of Premonocytic Cell Lines Stably Overexpressing C/EBPβ Isoforms
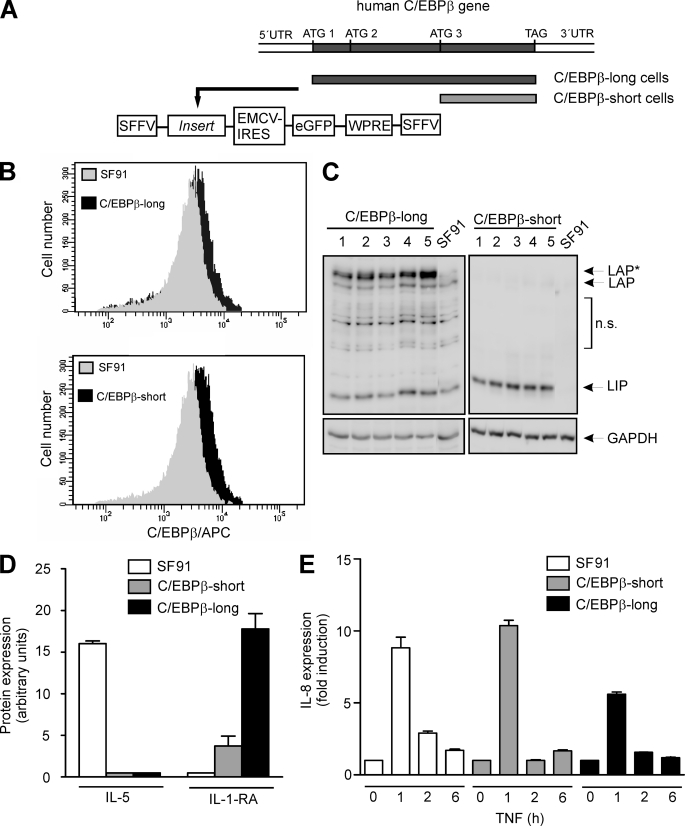
To investigate potential direct effects of C/EBPβ on proliferation and/or morphology in monocytic cells, we generated THP-1-derived cell lines stably overexpressing C/EBPβ isoforms. THP-1 cells were selected because they represent an established monocytic cell model (27) in which a relatively low endogenous C/EBPβ level can be detected according to their premonocytic developmental stage (see also Fig. 1A). Based on the complete human C/EBPβ mRNA sequence consisting of one single exon, including three alternative start codons, DNA fragments covering the complete C/EBPβ coding sequence (first start codon, ATG1) or the sequence starting at the third start codon (ATG3), thus only coding for C/EBPβ-LIP, were cloned into the vector SF91.IRES.eGFP.PRE (Fig. 2A) (also see “Experimental Procedures”). VSV-g pseudotyped virus particles produced from the packaging cell line Phoenix-gp were used to transduce THP-1 cells with a multiplicity of infection of 20. Following cell sorting and isolation of cell populations, single cell cultures were established by serial dilutions and selected for C/EBPβ protein expression by FACS analysis and Western blot (Fig. 2, B and C). These experiments showed that cells stably transduced with the complete C/EBPβ sequence (termed C/EBPβ-long) predominantly overexpressed the largest isoform LAP*, whereas, as expected, C/EBPβ-LIP-transduced cells (termed C/EBPβ-short) overexpressed only LIP, always compared with the levels of endogenous C/EBPβ proteins.
FIGURE 2.
Generation of stably transduced cells and monitoring gene expression. A, using PCR, DNA fragments were generated covering either the complete C/EBPβ coding sequence (from ATG1 to TAG; used for generation of C/EBPβ-long cells), including all three start codons for the alternative translation, or the sequence starting at the third start codon (from ATG3 to TAG), thus only coding for LIP (used for generation of C/EBPβ-short cells). The amplified fragments were cloned into the gammaretroviral vector SF91.IRES.eGFP. A schematic illustration of stably transduced functionally relevant regions containing the insert is shown. For generation of the control cell line SF91 the empty vector was used. SFFV-LTR, SFF virus long terminal repeat; EMCV-IRES, EMC virus internal ribosomal entry site; WPRE, WH virus post-transcriptional regulatory element. B, successful stable transduction of THP-1 cells was monitored using FACS analysis. Following incubation of 1 × 106 cells for 24 h, C/EBPβ proteins were tagged using the primary C/EBPβ antibody and an allophycocyanin-coupled secondary antibody. FACS analysis reveals endogenous C/EBPβ expression in SF91 control cells (gray) as well as C/EBPβ overexpression (black) in C/EBPβ-long and C/EBPβ-short cells. C, validation of C/EBPβ expression in C/EBPβ-long and C/EBPβ-short cells. Following an incubation phase for 24 h after seeding, C/EBPβ levels were measured by Western blot analysis in total cell extracts of 1 × 106 stably transduced THP-1 cells derived from five representative single cell cultures. LAP*, LAP, and LIP are indicated (loading control, GAPDH). Please note that for the blot of the extracts derived from C/EBPβ-short cells, a short exposure time was selected in order to reduce the signal of the endogenous C/EBPβ isoforms. For further experiments, the clones exhibiting the strongest C/EBPβ expression were selected (C/EBPβ-long, clone 5; C/EBPβ-short, clone 3). n.s., nonspecific bands. D, protein expression of IL-5 and IL-1-RA was determined in supernates of unstimulated SF91, C/EBPβ-short, and C/EBPβ-long cells using the proteome profiler technique (n = 4, mean ± S.D. (error bars)). E, SF91, C/EBPβ-short, and C/EBPβ-long cells were incubated with TNF up to 6 h, and the production of IL-8 mRNA was determined using real-time RT-PCR (mean ± S.D., n = 2).
Gene Expression Monitoring in Newly Generated Cell Lines
In initial experiments, gene expression was monitored on protein and mRNA levels in C/EBPβ-long, C/EBPβ-short, and SF91 control cells, showing differing expression profiles in all three cell lines. For example, in unstimulated SF91 cells, we found a significant expression of IL-5, whereas in C/EBPβ-transduced cells, no expression of this protein was found (Fig. 2D). On the other hand, a higher expression of IL-1-RA was found in C/EBPβ-long cells compared with C/EBPβ-short cells, and no expression of this protein was found in SF91 (Fig. 2D). When we stimulated these cell lines with TNF, we found a significant increase in IL-8 mRNA in SF91 and C/EBPβ-short cells, which was partly inhibited in C/EBPβ-long cells (Fig. 2E). When we further monitored functional aspects of these cells, we detected a significantly reduced proliferation of C/EBPβ-long cells (see below). Therefore, following our initial working hypothesis, we decided to focus on the effect of C/EBPβ isoforms on proliferation and underlying mechanisms in the present paper.
Cell Proliferation but Not Morphology Is Affected in Premonocytic C/EBPβ-long Cells
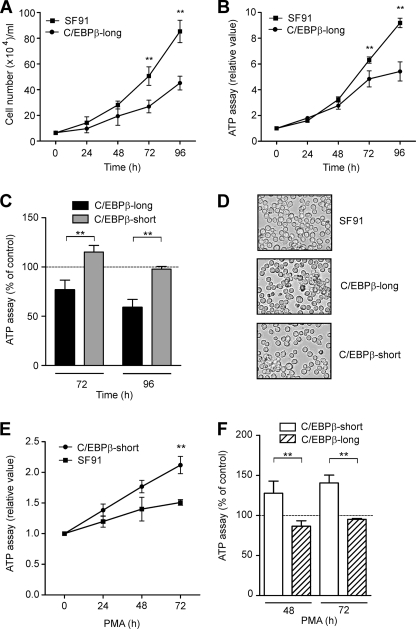
C/EBPβ-long and C/EBPβ-short cells were cultured over a period of 96 h. Remarkably, C/EBPβ-long cells exhibited a reduced proliferation as measured by cell count analysis (Fig. 3A) and confirmed by ATP proliferation assays (Fig. 3B), compared with cells stably transduced with the empty vector (SF91). In contrast, no effect on proliferation was observed in cells exclusively overexpressing the smaller isoform LIP (Fig. 3C). Under the mentioned conditions, the morphology of the stably transduced THP-1 cell lines was monitored. Up to 72 h, we detected a comparable morphology of the transductants as well as the control cell line (Fig. 3D). These experiments suggest that C/EBPβ-LAP*, but not LIP, can specifically inhibit cellular proliferation of premonocytic cells, but neither one affects cell morphology.
FIGURE 3.
Cell proliferation of monocytic C/EBPβ-long but not C/EBPβ-short cells is inhibited, with no change in morphology. A, C/EBPβ-long and SF91 control cells were cultivated up to 96 h, and cell count analysis was performed (mean ± S.D. (error bars), n = 7). B, C/EBPβ-long and SF91 control cells were incubated up to 96 h, and ATP proliferation assays were performed (mean ± S.D., n = 3). RLU, relative light units. C, C/EBPβ-long and C/EBPβ-short cells were cultivated up to 96 h, and ATP proliferation assays were performed (mean ± S.D., n = 3). The proliferation values for SF91 cells were set as the 100% control (dashed line). D, the morphology of stably transduced THP-1 cells was analyzed 24 h after seeding using light microscopy (magnification, ×100). E, C/EBPβ-short and SF91 control cells were incubated in the presence of 50 nm PMA up to 72 h, and ATP proliferation assays were performed. The respective proliferation value at 0 h was defined as 1, and relative proliferation values were calculated (mean ± S.D., n = 3). F, C/EBPβ-short and C/EBPβ-long cells were cultivated in the presence of 50 nm PMA up to 72 h, and ATP proliferation assays were performed (mean ± S.D., n = 3). The proliferation values for PMA-stimulated SF91 cells were set as the 100% control (dashed line). The asterisks indicate statistical significance with p ≤ 0.01.
PMA-induced Inhibition of Proliferation Is Attenuated in C/EBPβ-short Cells
As shown in Fig. 1, PMA increased the levels of the larger C/EBPβ isoforms, a process which is associated with reduced proliferation. Therefore, we tested the effect of stable overexpression of C/EBPβ-isoforms on PMA-induced inhibition of proliferation. Cells were treated with PMA up to 72 h, and ATP proliferation assays were performed. Interestingly, PMA-treated C/EBPβ-short cells exhibited an increased cell proliferation compared with PMA-treated SF91 control cells (Fig. 3E). In contrast, in PMA-treated C/EBPβ-long cells, similar ATP levels were measured compared with PMA-treated control cells (Fig. 3F). These experiments indicate that overexpression of LIP is able to overcome the PMA-mediated inhibition of proliferation and could be interpreted as indicating that LIP is able to antagonize the inhibitory effects of longer C/EBPβ isoforms on proliferation.
Proliferation and Cycling Index Are Reduced in C/EBPβWT Macrophage-like Cells Compared with the Knock-out
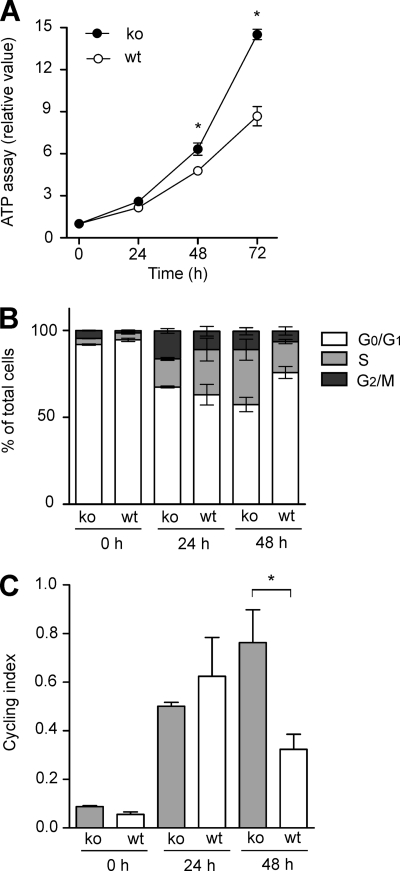
To further analyze the functionality of C/EBPβ, macrophage-like C/EBPβWT (high endogenous C/EBPβ) and C/EBPβKO cells were used. Both cell lines, regardless of the presence/absence of C/EBPβ, express specific macrophage markers (18). As expected, in C/EBPβKO cells, no C/EBPβ protein could be detected in control experiments (data not shown) and in earlier studies of our group (19). Consistent with the data mentioned above, C/EBPβWT cells displayed a reduced proliferation as assessed using ATP proliferation assays and cell count analysis, compared with the knock-out cells (Fig. 4A) (data not shown). As a next step, cell cycle analysis was performed by propidium iodide staining (FACS analysis), and the cycling index was calculated. Following arrest of the cell cycle by contact inhibition, the cells were incubated up to 48 h, and cell cycle analysis was performed (Fig. 4B). These experiments showed that in C/EBPβWT macrophage-like cells, a higher amount of cells was arrested in the G0G1 phase, which was also reflected by a lower cycling index (S + G2M)/G0G1 at 48 h in the presence of C/EBPβ (Fig. 4C). Our data demonstrate that C/EBPβ inhibits proliferation also in more differentiated macrophage-like cells.
FIGURE 4.
Inhibition of proliferation and reduced cycling index in C/EBPβWT macrophage-like cells. A, C/EBPβWT and C/EBPβKO macrophage-like cells were cultivated as described (see “Experimental Procedures”) up to 72 h, and ATP proliferation assays were performed. The respective proliferation value at 0 h was defined as 1, and relative proliferation values were calculated (mean ± S.D. (error bars), n = 3). B, the cell cycle was arrested by contact inhibition, and propidium iodide staining was analyzed by FACS analysis following further incubation for 24 and 48 h (mean ± S.D., n = 3). The percentage of total cells in the G0G1, S, or G2M phase, respectively, was calculated. C, for the experiments shown in B, the cycling index (S + G2M)/G0G1 was calculated (mean ± S.D., n = 3). The asterisks indicate statistical significance with p ≤ 0.05.
Induction of Macrophage Morphology Is Impaired in C/EBPβKO Macrophage-like Cells
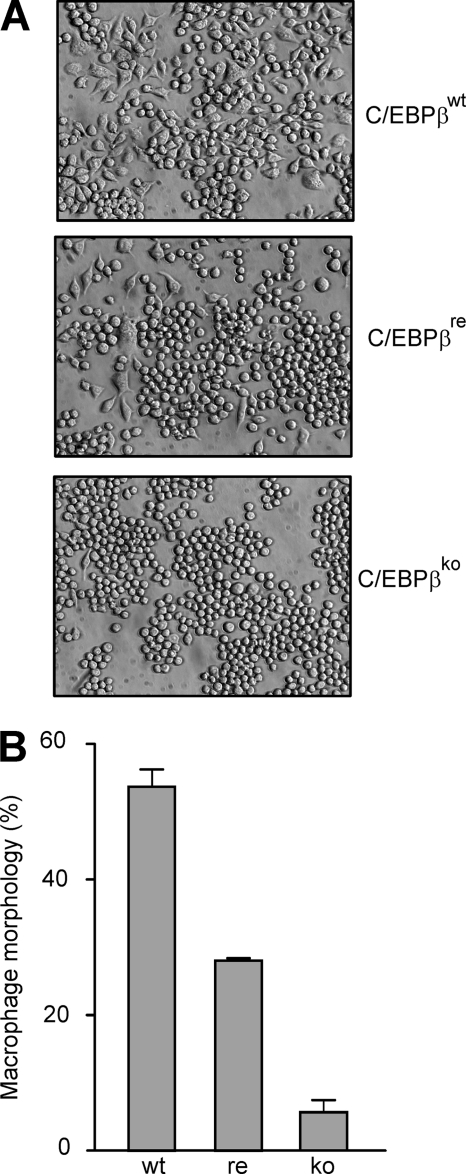
As a next step, the morphology of C/EBPβWT and C/EBPβKO macrophage-like cells was analyzed. Remarkably, when we cultivated these two cell lines for 24 h, a dramatic difference in the morphology was observed; in the presence of C/EBPβ, more than 50% of the cells displayed the characteristic macrophage-like morphology (flattened, spindle-shaped, amoeboid, polygonal) (Fig. 5, A and B). In contrast, in the absence of C/EBPβ, only a very low amount (∼5%) of this macrophage-like morphology was seen, and most of the cells stayed round. When C/EBPβ was retransfected into the macrophage-like cells, we observed an intermediate situation, which means that ∼25% of the cells displayed macrophage morphology. These data suggest that C/EBPβ is able to contribute to the maintenance of macrophage morphology in fully differentiated cells.
FIGURE 5.
The amount of cells with macrophage morphology is reduced in C/EBPβKO macrophage-like cell cultures. C/EBPβWT, C/EBPβRE, and C/EBPβKO macrophage-like cells were incubated as described for 24 h. A, cell morphology was analyzed by light microscopy (magnification, ×200). B, the amount of cells displaying macrophage morphology (defined as described under “Experimental Procedures”) was calculated relative to the total cell number (mean ± S.D. (error bars); two representative experiments of six are shown).
Nuclear and Cytoplasmic C/EBPα Levels in Differentiating THP-1 Cells as Well as C/EBPβWT and C/EBPβKO Macrophage-like Cells
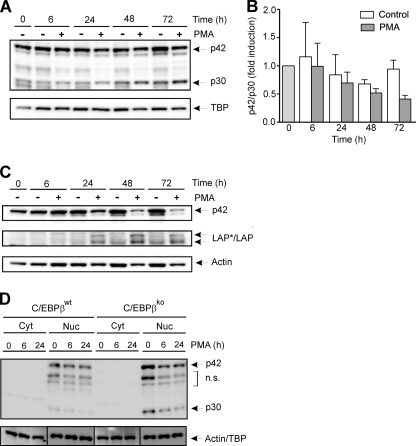
It has been suggested that C/EBPα and C/EBPβ may replace each other due to structural, regulatory, and functional similarities (3). Therefore, the protein levels of C/EBPα isoforms p42 and p30 were analyzed in premonocytic cells as well as further differentiated macrophage-like cells. In PMA-treated THP-1 cells, a slight decrease of nuclear C/EBPα p42 was found, accompanied by a slight increase in p30 (Fig. 6A), thus resulting in a reduced p42/p30 ratio (Fig. 6B). In the cytoplasm, a significant reduction of p42 over this time period was measured (Fig. 6C), whereas the levels of C/EBPβ increased, albeit to a much lower extent compared with the nucleus (see Fig. 1A). Only weak signals for p30 or LIP were detected in the cytoplasm (data not shown). These results, together with the data presented in Fig. 1, A and B, demonstrate a differential regulation of C/EBPα and C/EBPβ proteins in differentiating premonocytic cells. We also monitored the levels of C/EBPα proteins in both C/EBPβWT and C/EBPβKO macrophage-like cells. In C/EBPβWT cells, a low level of C/EBPα (p42 and p30) was detected in the nucleus (Fig. 6D). In C/EBPβKO cells, p42 and p30 were modestly higher than in C/EBPβWT cells as reported earlier (18) and were reduced by treatment with PMA. These data indicate that C/EBPα proteins did not compensate for C/EBPβ functions on proliferation and morphology as investigated above.
FIGURE 6.
Levels of C/EBPα p42 and p30 in PMA-treated THP-1 cells as well as C/EBPβWT and C/EBPβKO macrophage-like cells. A, premonocytic THP-1 cells were incubated with 100 nm PMA up to 72 h. Nuclear levels of C/EBPα p42 and p30 isoforms were determined by Western blot analysis (loading control, TBP). B, the nuclear p42/p30 ratio in three experiments performed as described in A was determined by densitometry in which the respective ratio in unstimulated cells at 0 h was defined as 1 (mean ± S.D. (error bars), n = 3). C, cells were incubated as described in A, and cytoplasmic levels of C/EBPα-p42 and LAP*/LAP were measured by Western blot analysis (loading control, actin). D, C/EBPβWT and C/EBPβKO macrophage-like cells were incubated with 100 nm PMA up to 24 h. The cytoplasmic/nuclear levels of C/EBPα proteins (p42 and p30) were determined and are indicated by arrows. TBP (nucleus) and actin (cytoplasm) were used as loading controls. n.s., nonspecific bands.
Inhibition of Proliferation by Serum Depletion Induces Macrophage Morphology in C/EBPβKO Macrophage-like Cells but Not in THP-1 Cells
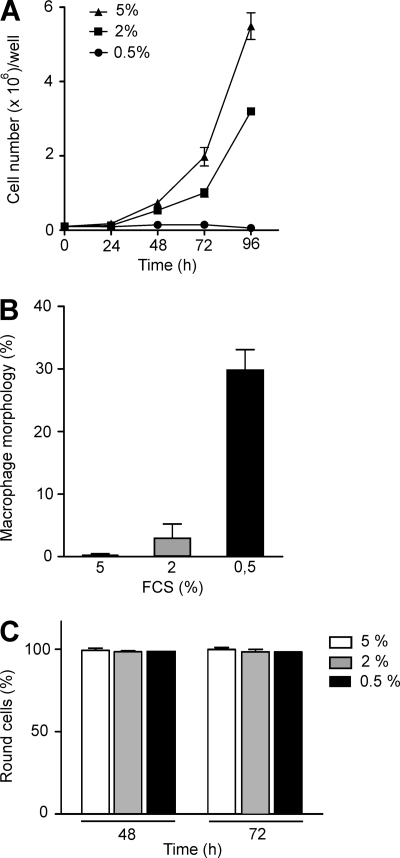
To evaluate whether inhibition of proliferation per se affects monocytic cell morphology, we applied serum depletion as an independent cellular condition to inhibit proliferation in the further differentiated C/EBPβKO model as well as premonocytic THP-1. When the serum concentration was reduced from 5 to 0.5%, in both THP-1 cells and CEBPβKO cells, a complete inhibition of proliferation was observed (Fig. 7A) (data not shown). Following serum depletion from 5 to 2%, we observed basically no change in morphology (round cells) in the macrophage-like CEBPβKO cells within 72 h (Fig. 7B). Remarkably, when the FCS concentration was further reduced to 0.5%, a significant induction of macrophage morphology was observed, which was assessed as described above (Fig. 7B). In contrast, no change in morphology was observed following serum depletion down to 0.5% in THP-1 cells that sustained their round morphology up to 72 h (Fig. 7C). These experiments show that the reduction of proliferation as a mechanism itself leads to an induction of macrophage morphology in further differentiated but not premonocytic cells, and even more important, these data demonstrate that C/EBPβ is not directly required for the development of macrophage morphology.
FIGURE 7.
Inhibition of proliferation by serum depletion induces macrophage morphology in C/EBPβKO macrophage-like cells but not in premonocytic THP-1 cells. A, C/EBPβKO cells were incubated in 6-well plates up to 96 h in the presence of decreasing serum concentrations (5% down to 0.5%), and cell count analysis was performed (mean ± S.D. (error bars), n = 3). B, C/EBPβKO cells were incubated with decreasing serum concentrations as described in A. The morphology of the cells was analyzed by light microscopy, and the amount of cells with macrophage morphology was determined at 72 h (mean ± S.D., n = 3). C, THP-1 cells were incubated up to 72 h in the presence of decreasing serum concentrations (5% down to 0.5%), and the morphology of cells was evaluated (mean ± S.D., n = 3).
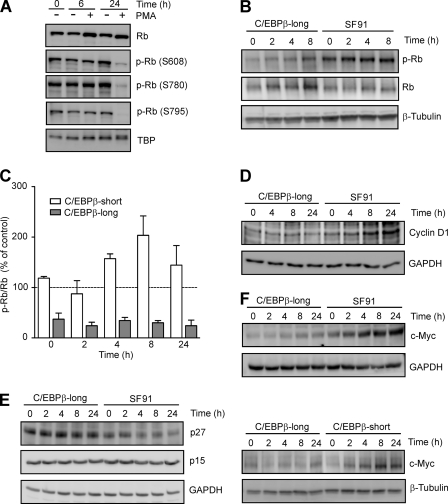
Hypophosphorylation of Rb in PMA-treated THP-1 and C/EBPβ-long Cells but Not C/EBPβ-short Cells
C/EBPβ cooperates with the Rb protein, which in its hypophosphorylated form is a major repressor of the cell cycle (28, 29). Therefore, the level and phosphorylation status of Rb were examined by Western blot analysis during monocytic differentiation. When THP-1 cells were exposed to PMA for 24 h, slightly increased nuclear Rb levels were measured (Fig. 8A). Under the same condition, a considerable reduction of Rb phosphorylation was detected (Fig. 8A) using three phospho-Rb antibodies (Ser608, Ser780, and Ser795) (30). To further investigate whether an increase in C/EBPβ is directly accompanied by reduced Rb phosphorylation, the phospho-modification of this protein was assessed in stably transduced cell lines. The degree of Rb phosphorylation was calculated by dividing the densitometry signal for phospho-Rb (residue Ser780) by that for total Rb protein. These experiments showed a significant hypophosphorylation of Rb in C/EBPβ-long cells compared with SF91 control (Fig. 8B) or C/EBPβ-short cells (Fig. 8C). These data suggest that an increase in the larger C/EBPβ isoforms is accompanied by an increase in hypophosphorylated Rb. It should be mentioned that in C/EBPβ-long cells, somewhat in contrast to PMA-treated THP-1 cells, we observed higher levels of total Rb compared with C/EBPβ-short and SF91 cells (Fig. 8B) (data not shown). Further experiments revealed neither direct binding of C/EBPβ to the Rb promoter (ChIP analysis) nor an effect on Rb promoter-dependent reporter gene expression and a comparable Rb stability in all three stably transduced cell lines (data not shown), indicating that the longer C/EBPβ isoforms affect Rb levels preferentially in non-differentiated THP-1 cells by indirect mechanisms.
FIGURE 8.
Decreased Rb phosphorylation in PMA-treated THP-1 as well as C/EBPβ-long cells accompanied by decreased cyclin D1, increased p27, and decreased c-Myc levels. A, detection of hypophosphorylated Rb in THP-1 cells following exposure to PMA. THP-1 cells were incubated with 100 nm PMA up to 24 h. Nuclear total Rb protein and phosphorylated Rb protein (p-Rb; Ser608, Ser780, and Ser795) were detected by Western blot analysis. TBP was used as loading control. B, detection of hypophosphorylated Rb in C/EBPβ-long cells. C/EBPβ-long and SF91 cells were synchronized by serum starvation for 90 h and subsequently incubated in the presence of serum up to the indicated time points. Phospho-Rb (Ser780) and total Rb protein were monitored by Western blot analysis in whole cell extracts (loading control, β-tubulin). C, lower level of Rb phosphorylation in C/EBPβ-long compared with C/EBPβ-short cells. C/EBPβ-long, C/EBPβ-short, and SF91 cells were treated as described in B. The degree of Rb phosphorylation (Ser780) was calculated by dividing the signal for phospho-Rb (measured by densitometry) by that for total Rb protein. The phospho-Rb/Rb values in C/EBPβ-long and C/EBPβ-short cells were then compared with the respective values in SF91 control cells representing the 100% value at each time point (dashed line). Shown is the analysis of two experiments (mean ± S.D. (error bars)), which are representative of 10 independent experiments. D–F, decreased cyclin D1, increased p27, and reduced c-Myc levels in C/EBPβ-long cells. C/EBPβ-long, SF91, and C/EBPβ-short cells were cultured as described in B. Subsequently, protein levels of cyclin D1 (D), p27 and p15 (E), and c-Myc (F) were determined in whole cell extracts (loading control, GAPDH, or β-tubulin).
Reduced Cyclin D1, Increased p27, and Decreased c-Myc Levels in C/EBPβ-long Cells
Rb is phosphorylated by cyclin D·cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 (CDK4/6) complexes (29), which are regulated by the CDK inhibitor p27 (31). Therefore, the level of cyclin D1 as well as p27 was monitored by Western blot analysis in the stably transduced cell lines. These experiments demonstrated reduced cyclin D1 levels and at the same time increased p27 levels in C/EBPβ-long cells but not in SF91 or C/EBPβ-short cells (Fig. 8, D and E) (data not shown), whereas the concentration of CDK inhibitor p15 was not affected. C/EBPβ can act as a repressor of the transcription factor c-Myc (32), which is an activator of cyclin D1 (33) and a repressor of p27 expression (34). Therefore, the amount of c-Myc in the stably transduced cells was assessed using Western blot analysis. In C/EBPβ-long cells, markedly reduced levels of c-Myc were determined compared with SF91 controls or C/EBPβ-short cells (Fig. 8F). Our data suggest that the larger C/EBPβ isoforms suppress the expression of c-Myc, resulting in the up-regulation of p27 together with the repression of cyclin D1, finally leading to reduced Rb phosphorylation.
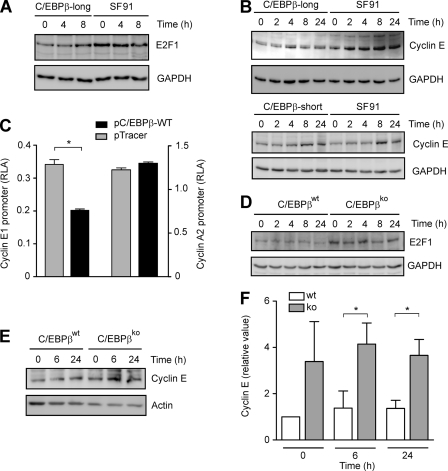
Reduced E2F1 and Cyclin E Levels in C/EBPβ-long and C/EBPβWT Macrophage-like Cells as Well as Inhibition of Cyclin E1 Promoter-dependent Transcription by C/EBPβ
Hypophosphorylated Rb and E2F isoforms are able to negatively regulate the expression of several cell cycle proteins, such as E2F1 itself and cyclin E (29, 35). Therefore, the levels of E2F1 and cyclin E were monitored by Western blot in stably transduced cells. In C/EBPβ-long cells, we observed significantly lower E2F1 as well as cyclin E levels compared with SF91 controls or C/EBPβ-short cells (Fig. 9, A and B) (data not shown). These experiments were supported by luciferase assays in which THP-1 cells were transiently co-transfected with pC/EBPβ-WT and the reporter gene plasmids hcE-pGL3 or hcA-pGL3, respectively. In pC/EBPβ-WT-transfected THP-1 cells, the cyclin E1 promoter-dependent transcription was significantly inhibited, whereas no effect was observed on cyclin A2 promoter-dependent expression (Fig. 9C). These data are consistent with additional experiments revealing lower levels of E2F1 (Fig. 9D) and cyclin E (Fig. 9, E and F) in C/EBPβWT macrophage-like cells compared with C/EBPβKO cells. These results imply that the larger C/EBPβ isoforms inhibit monocytic proliferation by reducing the levels of the cell cycle proteins E2F1 and cyclin E.
FIGURE 9.
Reduced E2F1 and cyclin E levels in C/EBPβ-long cells, inhibition of cyclin E1 promoter-dependent transcription by C/EBPβ, and reduced E2F1 and cyclin E expression in C/EBPβWT macrophage-like cells. A, C/EBPβ-long and SF91 cells were synchronized by serum starvation for 90 h and subsequently incubated in the presence of serum up to the indicated time points. Determination of E2F1 levels was performed in whole cell extracts using Western blot analysis (loading control, GAPDH). B, C/EBPβ-long, SF91, and C/EBPβ-short cells were treated as described in A. Determination of cyclin E levels was performed in whole cell extracts (loading control, GAPDH). C, THP-1 cells were transfected with cyclin E1 and A2 promoter-dependent luciferase reporter gene vectors hcE-pGL3 or hcA-pGL3, respectively, together with pC/EBPβ-WT (negative control, pTracer). Mean ± S.D. (error bars) of three independent experiments is shown, and the asterisk indicates statistical significance with p ≤ 0.05. RLA, relative luciferase activity. D, C/EBPβWT and C/EBPβKO macrophage-like cells were synchronized by serum starvation for 48 h and subsequently incubated in the presence of serum up to 24 h. Determination of E2F1 levels in whole cell extracts was performed using Western blot analysis (loading control, GAPDH). E, C/EBPβWT and C/EBPβKO macrophage-like cells were treated as described in D, and then cyclin E levels were determined (loading control, actin). F, cyclin E levels of experiments performed as described in E were assessed using densitometry and then corrected according to actin levels. Subsequently, cyclin E levels in C/EBPβKO cells were compared with levels in C/EBPβWT cells in which the value at 0 h was defined as 1 (mean ± S.D., n = 3). The asterisks indicate statistical significance with p ≤ 0.05.
DISCUSSION
The specific role of C/EBPβ in the orchestration of monocytic differentiation has only been partly delineated to date. Initial experiments showed a dramatic increase in the nuclear levels of the two larger C/EBPβ isoforms, LAP* and LAP, as well as the LAP/LIP ratio in PMA-treated differentiating premonocytic THP-1 cells, accompanied by a reduced proliferation. Under this condition, a change to macrophage morphology associated with specific macrophage functionality can be observed (27) (data not shown). To investigate the direct effects of C/EBPβ in premonocytic cells, we designed stably transduced THP-1-derived cell lines, which either predominantly overexpress the largest C/EBPβ isoform LAP* (C/EBPβ-long cells) or which exclusively overexpress the small isoform LIP (C/EBPβ-short cells). To our knowledge, this is the first time that a group succeeded in directly generating stably transduced monocytic cells overexpressing different C/EBPβ isoforms. Most importantly, C/EBPβ-long cells exhibited a significant reduction of proliferation compared with C/EBP-short or SF91 cells (transduced with the empty vector). These experiments strongly suggest that one of the major functions of C/EBPβ in differentiating monocytic cells is the inhibition of proliferation. Therefore, the presented study predominately focused on further characterizing mechanistic aspects of C/EBPβ-induced effects on monocytic proliferation. No change in morphology was observed when C/EBPβ-long transductants were cultured over several days, which would indicate that C/EBPβ is not able to activate the full genetic program (including changes in morphology) for monocytic differentiation.
Earlier results show that C/EBPβ inhibits proliferation in mouse keratinocytes and fibroblasts (36, 37), and knock-out of C/EBPβ in fibroblasts results in increased proliferation (38). Further studies in hepatoma cells demonstrate that LAP*/LAP is responsible for this effect by inducing cell cycle arrest and that the LZ dimerization and activation domains of LAP*/LAP are of critical importance (39). A very recent paper shows that mutation of the uORF initiation codon reduces LIP and increases the LAP/LIP ratio, resulting in repression of E2F-regulated genes and a delayed and blunted S-phase entry in hepatocytes (40). Interestingly, in this study and also in earlier experiments (39, 41), overexpression of LIP, in contrast to LAP*/LAP, does not inhibit the E2F1 promoter activity or the proliferation, respectively, which is mirrored by our experiments revealing that in the C/EBPβ-short cells, no effect on proliferation was observed. Here, it should also be mentioned that several reports show an inhibitory effect on LAP-induced proliferation arrest (39) or even a positive effect on proliferation by overexpressed LIP (42, 43). In contrast to our experiments, under these experimental conditions, a high overexpressed/endogenous level of LAP*/LAP was present, which may enable the inhibitory LIP to exert its negative effects on the active counterpart LAP. Interestingly, in our experiments, the PMA-induced inhibition of proliferation was attenuated in C/EBPβ-short cells. Therefore, in this situation, it could be speculated that the overexpressed LIP in C/EBPβ-short cells is able to exert inhibitory effects on the high PMA-induced endogenous C/EBPβ-LAP levels.
When we monitored protein and mRNA expression of these newly generated cell lines, different expression patterns were found. For example, we detected no production of IL-5 in the supernatant of C/EBPβ isoform-transduced cell lines compared with SF91 control cells. In contrast, the production of IL-1-RA was dramatically induced in C/EBPβ-long compared with C/EBPβ-short cells, whereas no production of this protein was observed in SF91 cells at all. It should be mentioned that putative C/EBPβ binding sites have been identified in the IL-5 and IL-1-RA promoters, and it has also been demonstrated that C/EBPβ is involved in the regulation of both genes (44, 45). When we stimulated these cell lines, we found a significant increase in mRNA of IL-8, an NF-κB/C/EBPβ-dependent target gene (3), in SF91 and C/EBPβ-short cells, which was partly inhibited in C/EBPβ-long cells. Similar results were found for the stimulated expression of TNF and IL-1α (data not shown). It has been shown earlier that transient overexpression of the longer C/EBPβ isoforms and in some instances of C/EBPβ-LIP leads to the inhibition of NF-κB-dependent promoter constructs (including an IL-8 promoter fragment) (8, 46–48). Furthermore, in TNF tolerance, up-regulation of C/EBPβ has been made responsible for inhibitory effects on IL-8 expression (8, 48). Interestingly, higher levels of IL-6, which is also an NF-κB/C/EBPβ target gene, were found in C/EBPβKO mice (49). In resident primary C/EBPβWT macrophages, IL-6 mRNA was undetectable but constitutively present in C/EBPβKO macrophages (50). In this and another study (50, 51), the induction of TNF, IL-1β, and IL-6 was comparable in macrophages regardless of whether C/EBPβ was present. In contrast, in a macrophage cell line derived from C/EBPβKO mice, a partial inhibition of TNF- or LPS-induced mRNA expression of TNF, IL-1β, and IL-6 was observed, compared with C/EBPβWT cells (18). Overall, the different studies suggest that C/EBPβ isoforms are required for the inducible gene expression, for example, of several NF-κB target genes, but exhibit inhibitory effects when a certain concentration of these C/EBPβ proteins is reached. It has also been proposed that, depending on the specific nuclear composition in C/EBP factors, C/EBPβ gene products might act as repressors as the result of a prevalent function of the truncated inhibitory counterpart LIP and/or because the full-size C/EBPβ (LAP) is a weaker transcriptional activator than other C/EBP proteins (20).
Our experiments showed that the cellular proliferation and cycling index (S + G2M)/G0G1 were reduced in C/EBPβWT macrophage-like cells compared with the knock-out, which both confirms our results obtained with the stably transduced cells and suggests that C/EBPβ directly inhibits cellular proliferation also in differentiated cells. Interestingly, C/EBPβKO mice show a marked splenomegaly, peripheral lymph adenopathy, and enhanced hemopoiesis (20), which was interpreted as an extreme deregulation of myeloid cell proliferation (49). These data seem to fit our results and indicate that C/EBPβ, presumably together with other C/EBP proteins, such as C/EBPϵ (51), is responsible for the coordinated myeloid/monocytic cell differentiation by preventing excessive proliferation.
When we applied the knock-out model for morphological analyses, we found that the amount of differentiated cells (macrophage morphology) was significantly reduced in C/EBPβKO cells compared with the wild type. Differentiation usually coincides with an inhibition of proliferation (1), although it has been proposed that halting of the cell cycle is not absolutely necessary for monocytic maturation (52). Therefore, in our experiments, we wanted to investigate whether the inhibition of proliferation in monocytic cells is an inducing situation that gates the cell toward the differentiation process. Cellular proliferation was reduced by lowering the FCS concentration, which is an established procedure to arrest cell growth (53). When we applied this procedure, we observed a significant increase in macrophage morphology in the originally round C/EBPβKO macrophage-like cells, whereas the morphology of premonocytic THP-1 cells was not affected. These data indicate that inhibition of proliferation per se (i.e. by independent means, such as C/EBPβ-associated mechanisms or serum depletion) contributes to maintenance of macrophage morphology of further differentiated cells. Furthermore, our data demonstrate that C/EBPβ-regulated genes can contribute to but are not directly required for the morphological changes during monocytic differentiation.
Because C/EBPα and C/EBPβ exhibit structural, regulatory, and functional similarities (3), it is reasonable to speculate that C/EBPα and C/EBPβ may functionally replace each other. In PMA-treated THP-1 cells, a weak decrease of nuclear C/EBPα p42, as reported before in HL-60 cells (54), and a slight increase in p30, resulting in a reduced p42/p30 ratio, were found, which suggests a differential regulation of C/EBPβ and C/EBPα proteins. The analysis of C/EBPβKO cells revealed significant and (compared with the wild type) modestly higher levels of C/EBPα isoforms similar to those described earlier (18), which implies that C/EBPα proteins, albeit at elevated levels, do not compensate for C/EBPβ functions, at least under our conditions, similar to what was described for mammary gland epithelial cells (55). Here, it should also be mentioned that other reports have proposed that C/EBPα can also induce monocytic differentiation in B cells and myelomonocytic cells (10). However, the conditions of these experiments largely differ from our experimental conditions (use of B cells or myelomonocytic HF-6 cells, stimulation with retinoic acid, and ectopic C/EBPα expression).
C/EBPβ cooperates with the Rb protein, which in its hypophosphorylated form is a central repressor of the cell cycle and proliferation (28, 29). Our experiments demonstrated a marked hypophosphorylation of nuclear Rb during PMA-induced monocytic differentiation, similar to what was described earlier (56). The antibodies used in our study are directed against phosphorylated Rb serine residues Ser608, Ser780, and Ser795, which have been shown to mediate the disruption of Rb-E2F complexes following phosphorylation by cyclin D1-CDK4 (30). To investigate whether enhanced C/EBPβ concentrations are directly associated with Rb hypophosphorylation, we used the stably transduced cell lines overexpressing C/EBPβ isoforms. Remarkably, these studies showed a significant reduction of Rb phosphorylation in C/EBPβ-long cells and suggest that an increase in the larger C/EBPβ isoforms leads to elevated levels of hypophosphorylated Rb. Notably, the monocytic lineage commitment of human bone marrow progenitor cells can be correlated to high levels of hypophosphorylated Rb (57).
The Rb protein is phosphorylated by cyclin D-CDK4/6 complexes (29), which in turn are regulated by CDK inhibitors, such as p27 (31). Interestingly, our experiments found simultaneously decreased cyclin D1 and increased p27 levels in C/EBPβ-long cells. On the transcriptional level, C/EBPβ negatively regulates the transcription factor c-Myc (32), an activator of D-type cyclin (33) but a repressor of p27 expression (34). Indeed, our results revealed considerably lower levels of c-Myc in C/EBPβ-long cells compared with C/EBPβ-short and SF91 control cells, which implies that the larger C/EBPβ isoforms suppress the transcription of the c-myc gene. This inhibition of c-Myc expression may induce p27 and reduce cyclin D1 levels, resulting in lower amounts of active cyclin D-CDK4/6 complexes (31, 58) and finally leading to reduced Rb phosphorylation. This is in good agreement with the literature because increased C/EBPβ levels have been shown to be associated with increased p27 levels and delayed Rb phosphorylation events in epithelial cells (41).
Hypophosphorylated Rb family members bind to E2F transcription factor(s), in some instances presumably together with C/EBPβ (59), and act as strong transcriptional repressors, thus inhibiting the expression of E2F target genes including (autoregulated) E2F1 and cyclin E, which are necessary for cell cycle progression from G1 to S phase (29, 35, 60). Our experiments demonstrated reduced levels of E2F1 and cyclin E in C/EBPβ-long cells as well as C/EBPβWT macrophage-like cells compared with control cells or C/EBPβKO cells, respectively. Earlier studies have shown that an increase in the larger C/EBPβ isoforms and LAP/LIP ratio is accompanied by decreased E2F1 target gene expression, including cyclin E, and results in reduced cell proliferation (39–41). Consistent with this, we were able to reduce cyclin E1 promoter-dependent transcription by overexpression of C/EBPβ.
In summary, our experiments imply that the larger C/EBPβ isoforms inhibit proliferation in monocytic cells presumably by reducing Rb phosphorylation, thereby decreasing levels of cell cycle proteins such as E2F1 and cyclin E. In addition, CEBPβ proteins may contribute to, but are not directly required for, the morphological changes during monocytic differentiation. We propose that the C/EBPβ system belongs to regulatory modules controlling proliferation during the process of differentiation from the premonocytic cell to the monocyte/macrophage, thereby maintaining cellular homeostasis in inflammation and malignancy.
Acknowledgments
We thank Ines Kiralj, Elke Barczak, Iris Hacke, Martina Krautkrämer, and Hilke Siedersleben for excellent technical assistance. The C/EBPβWT, C/EBPβKO, and C/EBPβRE cell lines were kindly provided by Valeria Poli (University of Turin, Turin, Italy). We are also grateful to Nisar Peter Malek and Sharon Page for helpful discussions; Uta Kossatz-Böhlert, Immo Prinz, Stefanie Willenzon, and Katrin Serth for technical hints and experimental support; and Daphne Jost and Sandra C. Haas for participating in some of the experiments (Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany). Michael Rehli (University Hospital Regensburg, Germany) is gratefully acknowledged for support in establishing ChIP analysis.
This work was supported by the Stiftung für Pathobiochemie und Molekulare Diagnostik der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Klinische Chemie und Laboratoriumsmedizin.
- C/EBP
- CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein
- PMA
- phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate
- LAP
- liver-enriched activating protein
- LIP
- liver-enriched inhibiting protein
- Rb
- retinoblastoma protein
- TBP
- TATA box-binding protein
- eGFP
- enhanced green fluorescence protein
- CDK
- cyclin-dependent kinase.
REFERENCES
- 1. Auffray C., Sieweke M. H., Geissmann F. (2009) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 27, 669–692 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Friedman A. D. (2007) Oncogene 26, 6816–6828 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Ramji D. P., Foka P. (2002) Biochem. J. 365, 561–575 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Xiong W., Hsieh C. C., Kurtz A. J., Rabek J. P., Papaconstantinou J. (2001) Nucleic Acids Res. 29, 3087–3098 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Calkhoven C. F., Müller C., Leutz A. (2000) Genes Dev. 14, 1920–1932 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Nerlov C. (2007) Trends Cell Biol. 17, 318–324 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Pham T. H., Langmann S., Schwarzfischer L., El Chartouni C., Lichtinger M., Klug M., Krause S. W., Rehli M. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282, 21924–21933 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Zwergal A., Quirling M., Saugel B., Huth K. C., Sydlik C., Poli V., Neumeier D., Ziegler-Heitbrock H. W., Brand K. (2006) J. Immunol. 177, 665–672 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Xie H., Ye M., Feng R., Graf T. (2004) Cell 117, 663–676 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Matsushita H., Nakajima H., Nakamura Y., Tsukamoto H., Tanaka Y., Jin G., Yabe M., Asai S., Ono R., Nosaka T., Sugita K., Morimoto A., Hayashi Y., Hotta T., Ando K., Miyachi H. (2008) Oncogene 27, 6749–6760 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Wang Q. F., Friedman A. D. (2002) Blood 99, 2776–2785 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Ji Y., Studzinski G. P. (2004) Cancer Res. 64, 370–377 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Chen P. L., Riley D. J., Chen-Kiang S., Lee W. H. (1996) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93, 465–469 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Park M. H., Park S. Y., Kim Y. (2008) FEBS Lett. 582, 415–422 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Chen S., Han Y. H., Zheng Y., Zhao M., Yan H., Zhao Q., Chen G. Q., Li D. (2009) Leuk. Res. 33, 1108–1113 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Yang Z., Wara-Aswapati N., Chen C., Tsukada J., Auron P. E. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 21272–21277 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Tissières P., Araud T., Ochoda A., Drifte G., Dunn-Siegrist I., Pugin J. (2009) J. Biol. Chem. 284, 26261–26272 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Gorgoni B., Maritano D., Marthyn P., Righi M., Poli V. (2002) J. Immunol. 168, 4055–4062 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Cappello C., Zwergal A., Kanclerski S., Haas S. C., Kandemir J. D., Huber R., Page S., Brand K. (2009) Cell. Signal. 21, 1918–1924 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Screpanti I., Romani L., Musiani P., Modesti A., Fattori E., Lazzaro D., Sellitto C., Scarpa S., Bellavia D., Lattanzio G. (1995) EMBO J. 14, 1932–1941 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Li Z., Schwieger M., Lange C., Kraunus J., Sun H., van den Akker E., Modlich U., Serinsöz E., Will E., von Laer D., Stocking C., Fehse B., Schiedlmeier B., Baum C. (2003) Exp. Hematol. 31, 1206–1214 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Schambach A., Bohne J., Chandra S., Will E., Margison G. P., Williams D. A., Baum C. (2006) Mol. Ther. 13, 391–400 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Kraunus J., Schaumann D. H., Meyer J., Modlich U., Fehse B., Brandenburg G., von Laer D., Klump H., Schambach A., Bohne J., Baum C. (2004) Gene Ther. 11, 1568–1578 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Haas S. C., Huber R., Gutsch R., Kandemir J. D., Cappello C., Krauter J., Duyster J., Ganser A., Brand K. (2010) Br. J. Haematol. 148, 777–790 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Huber R., Kunisch E., Glück B., Egerer R., Sickinger S., Kinne R. W. (2003) Z. Rheumatol. 62, 378–389 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Hayashida M., Okazaki K., Fukushi J., Sakamoto A., Iwamoto Y. (2009) Arthritis Rheum. 60, 708–716 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Basheeruddin K., Rechtoris C., Mazzone T. (1992) J. Biol. Chem. 267, 1219–1224 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Sebastian T., Johnson P. F. (2006) Cell Cycle 5, 953–957 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Macleod K. F. (2008) Nat. Rev. Cancer 8, 769–781 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Adams P. D. (2001) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1471, M123-M133 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Chu I. M., Hengst L., Slingerland J. M. (2008) Nat. Rev. Cancer 8, 253–267 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Berberich-Siebelt F., Berberich I., Andrulis M., Santner-Nanan B., Jha M. K., Klein-Hessling S., Schimpl A., Serfling E. (2006) J. Immunol. 176, 4843–4851 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Yu Q., Ciemerych M. A., Sicinski P. (2005) Oncogene 24, 7114–7119 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Yang W., Shen J., Wu M., Arsura M., FitzGerald M., Suldan Z., Kim D. W., Hofmann C. S., Pianetti S., Romieu-Mourez R., Freedman L. P., Sonenshein G. E. (2001) Oncogene 20, 1688–1702 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Araki K., Nakajima Y., Eto K., Ikeda M. A. (2003) Oncogene 22, 7632–7641 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Zhu S., Oh H. S., Shim M., Sterneck E., Johnson P. F., Smart R. C. (1999) Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 7181–7190 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Lee S., Shuman J. D., Guszczynski T., Sakchaisri K., Sebastian T., Copeland T. D., Miller M., Cohen M. S., Taunton J., Smart R. C., Xiao Z., Yu L. R., Veenstra T. D., Johnson P. F. (2010) Mol. Cell. Biol. 30, 2621–2635 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Gagliardi M., Maynard S., Miyake T., Rodrigues N., Tjew S. L., Cabannes E., Bedard P. A. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278, 43846–43854 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Buck M., Turler H., Chojkier M. (1994) EMBO J. 13, 851–860 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Wethmar K., Bégay V., Smink J. J., Zaragoza K., Wiesenthal V., Dörken B., Calkhoven C. F., Leutz A. (2010) Genes Dev. 24, 15–20 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Gheorghiu I., Deschênes C., Blais M., Boudreau F., Rivard N., Asselin C. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276, 44331–44337 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Zahnow C. A., Cardiff R. D., Laucirica R., Medina D., Rosen J. M. (2001) Cancer Res. 61, 261–269 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Orellana D., Liu X., Wang G. L., Jin J., Iakova P., Timchenko N. A. (2010) J. Biol. Chem. 285, 23444–23456 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Li-Weber M., Giaisi M., Krammer P. H. (2001) Eur. J. Immunol. 31, 3694–3703 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Gabay C., Smith M. F., Eidlen D., Arend W. P. (1997) J. Clin. Invest. 99, 2930–2940 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Stein B., Cogswell P. C., Baldwin A. S., Jr. (1993) Mol. Cell. Biol. 13, 3964–3974 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Prösch S., Heine A. K., Volk H. D., Krüger D. H. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276, 40712–40720 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Weber M., Sydlik C., Quirling M., Nothdurfter C., Zwergal A., Heiss P., Bell S., Neumeier D., Ziegler-Heitbrock H. W., Brand K. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278, 23586–23593 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Screpanti I., Musiani P., Bellavia D., Cappelletti M., Aiello F. B., Maroder M., Frati L., Modesti A., Gulino A., Poli V. (1996) J. Exp. Med. 184, 1561–1566 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Tanaka T., Akira S., Yoshida K., Umemoto M., Yoneda Y., Shirafuji N., Fujiwara H., Suematsu S., Yoshida N., Kishimoto T. (1995) Cell 80, 353–361 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Akagi T., Thoennissen N. H., George A., Crooks G., Song J. H., Okamoto R., Nowak D., Gombart A. F., Koeffler H. P. (2010) PLoS One 5, e15419 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Studzinski G. P., Rathod B., Wang Q. M., Rao J., Zhang F. (1997) Exp. Cell Res. 232, 376–387 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Ramp U., Gerharz C. D., Doehmer J., Oster O., Gabbert H. E. (1990) Virchows Arch. B Cell Pathol. Incl. Mol. Pathol. 59, 271–280 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Müller C., Bremer A., Schreiber S., Eichwald S., Calkhoven C. F. (2010) EMBO J. 29, 897–909 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Seagroves T. N., Krnacik S., Raught B., Gay J., Burgess-Beusse B., Darlington G. J., Rosen J. M. (1998) Genes Dev. 12, 1917–1928 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Traore K., Trush M. A., George M., Jr., Spannhake E. W., Anderson W., Asseffa A. (2005) Leuk. Res. 29, 863–879 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Bergh G., Ehinger M., Olsson I., Jacobsen S. E., Gullberg U. (1999) Blood 94, 1971–1978 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Hidalgo M., Rowinsky E. K. (2000) Oncogene 19, 6680–6686 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Sebastian T., Malik R., Thomas S., Sage J., Johnson P. F. (2005) EMBO J. 24, 3301–3312 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Chen H. Z., Tsai S. Y., Leone G. (2009) Nat. Rev. Cancer 9, 785–797 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]