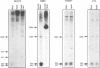Abstract
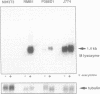
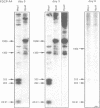
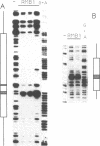
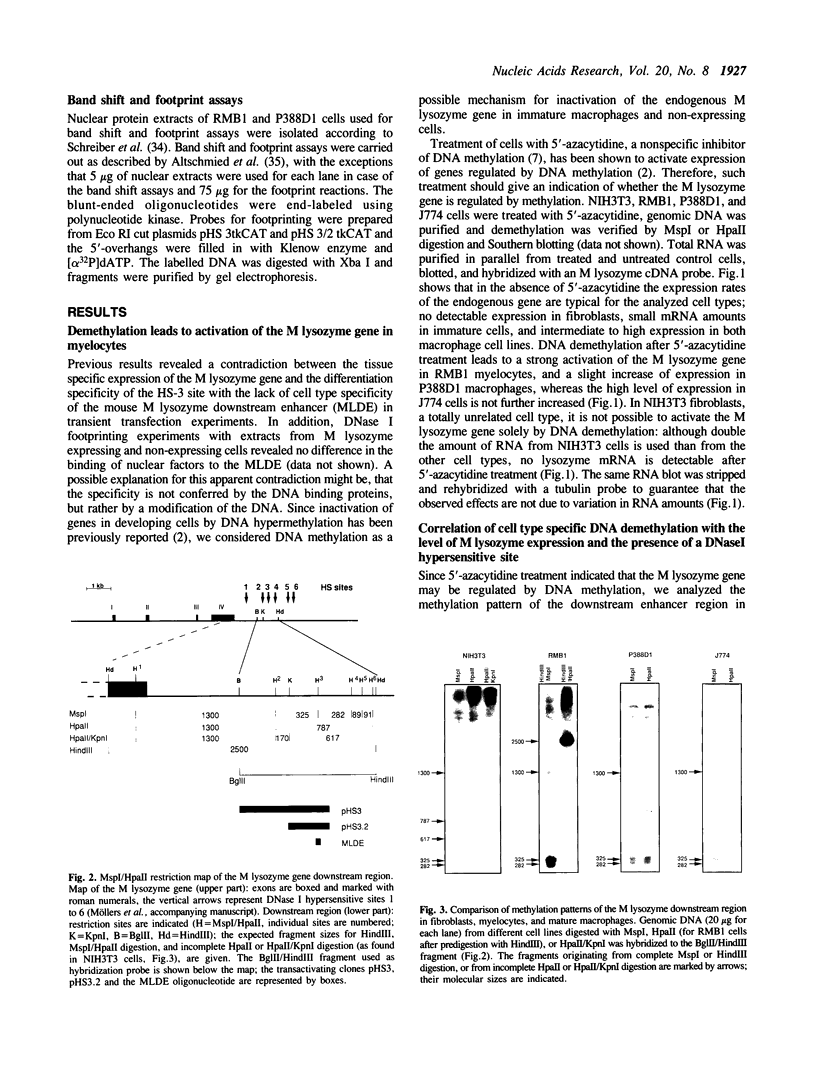
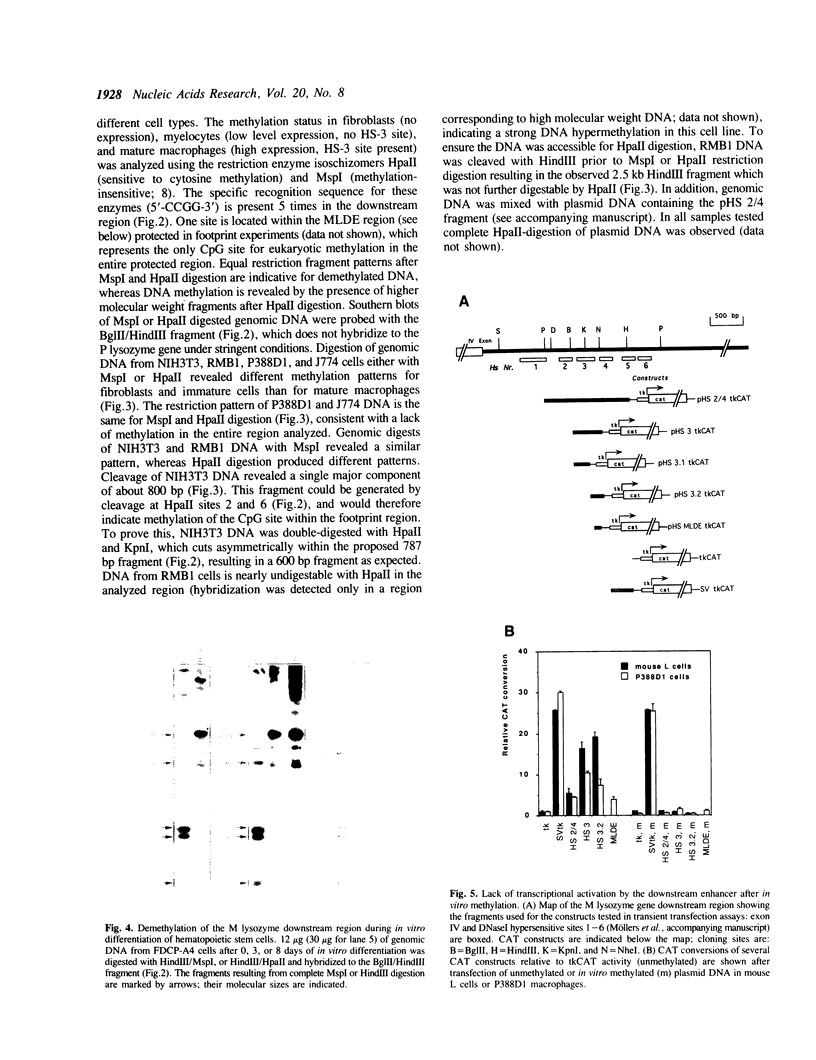
Lysozyme gene expression is a specific marker for the macrophage/granulocyte lineage of hematopoietic differentiation in mammals, its expression being gradually increased during maturation. Analysis of the mechanisms regulating mouse M lysozyme gene expression during myeloid differentiation revealed a complicated pattern of DNase I hypersensitive sites (HS sites) within the flanking regions of the gene. The HS-3 site, located in the 3'-flanking region of the gene, overlapped with an enhancer element, which is the only strong enhancer identified in the vicinity of the gene. We demonstrate a positive correlation between undermethylation of the entire 3'-flanking region, the appearance of the HS-3 site, and M lysozyme gene expression during in vitro differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells. We furthermore show that methylation of a single CpG site within the enhancer core element, only observed in immature macrophage cells in vivo, is sufficient to inhibit nuclear factor binding to this element in vitro and to inhibit its transactivation potential in DNA transfection experiments.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschmied J., Muller M., Baniahmad A., Steiner C., Renkawitz R. Cooperative interaction of chicken lysozyme enhancer sub-domains partially overlapping with a steroid receptor binding site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):4975–4991. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.4975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baniahmad A., Steiner C., Köhne A. C., Renkawitz R. Modular structure of a chicken lysozyme silencer: involvement of an unusual thyroid hormone receptor binding site. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):505–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90532-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschhausen G., Wittig B., Graessmann M., Graessmann A. Chromatin structure is required to block transcription of the methylated herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1177–1181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H. DNA methylation and gene activity. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):3–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90479-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi O. R., Engel J. D. Developmental regulation of beta-globin gene switching. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross M., Mangelsdorf I., Wedel A., Renkawitz R. Mouse lysozyme M gene: isolation, characterization, and expression studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6232–6236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross M., Renkawitz R. Repetitive sequence involvement in the duplication and divergence of mouse lysozyme genes. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1283–1288. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08237.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W. DNA methylation and gene activity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:93–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S. Understanding the molecular mechanism by which methylation influences gene expression. Trends Genet. 1989 Feb;5(2):35–36. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90016-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. S., Garrard W. T. Nuclease hypersensitive sites in chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:159–197. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Götz F., Schulze-Forster K., Wagner H., Kröger H., Simon D. Transcription inhibition of SV40 by in vitro DNA methylation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Nov 30;1087(3):323–329. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90006-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Schaffner W. CpG methylation of the cAMP-responsive enhancer/promoter sequence TGACGTCA abolishes specific factor binding as well as transcriptional activation. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):612–619. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. A. Altering gene expression with 5-azacytidine. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):485–486. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90192-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshet I., Lieman-Hurwitz J., Cedar H. DNA methylation affects the formation of active chromatin. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):535–543. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90263-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leenen P. J., Jansen A. M., van Ewijk W. Murine macrophage cell lines can be ordered in a linear differentiation sequence. Differentiation. 1986;32(2):157–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1986.tb00568.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Baltimore D. NF-kappa B: a pleiotropic mediator of inducible and tissue-specific gene control. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90833-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland M. The effect of sequence specific DNA methylation on restriction endonuclease cleavage. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):5859–5866. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.5859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Wang C., Tjian R. Positive and negative regulation of transcription in vitro: enhancer-binding protein AP-2 is inhibited by SV40 T antigen. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):847–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Baltimore D. An inducible transcription factor activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus in T cells. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):711–713. doi: 10.1038/326711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosales R., Vigneron M., Macchi M., Davidson I., Xiao J. H., Chambon P. In vitro binding of cell-specific and ubiquitous nuclear proteins to the octamer motif of the SV40 enhancer and related motifs present in other promoters and enhancers. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3015–3025. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02607.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saluz H. P., Feavers I. M., Jiricny J., Jost J. P. Genomic sequencing and in vivo footprinting of an expression-specific DNase I-hypersensitive site of avian vitellogenin II promoter reveal a demethylation of a mCpG and a change in specific interactions of proteins with DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6697–6700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with 'mini-extracts', prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6419–6419. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Muller M., Kaltschmidt C., Renkawitz R. Many transcription factors interact synergistically with steroid receptors. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1418–1420. doi: 10.1126/science.3201230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyfert V. L., McMahon S. B., Glenn W. D., Yellen A. J., Sukhatme V. P., Cao X. M., Monroe J. G. Methylation of an immediate-early inducible gene as a mechanism for B cell tolerance induction. Science. 1990 Nov 9;250(4982):797–800. doi: 10.1126/science.2237429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner C., Kaltschmidt C. An automated method for calcium phosphate-mediated gene transfer. Trends Genet. 1989 May;5(5):138–138. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner C., Muller M., Baniahmad A., Renkawitz R. Lysozyme gene activity in chicken macrophages is controlled by positive and negative regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):4163–4178. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.4163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. P., Simkevich C. P., Holness M. A., Kang A. H., Raghow R. In vitro methylation of the promoter and enhancer of Pro alpha 1(I) collagen gene leads to its transcriptional inactivation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2549–2556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt F., Molloy P. L. Cytosine methylation prevents binding to DNA of a HeLa cell transcription factor required for optimal expression of the adenovirus major late promoter. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1136–1143. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wölfl S., Schräder M., Wittig B. Lack of correlation between DNA methylation and transcriptional inactivation: the chicken lysozyme gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):271–275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]