Abstract
A guanine-rich single-stranded DNA from the human immunoglobulin switch region was shown by Sen and Gilbert [Nature, (1988) 334, 364-366] to be able to self-associate to form a stable four-stranded parallel DNA structure. Topoisomerase II did not cleave the single-stranded DNA molecule. Surprisingly, the enzyme did cleave the same DNA sequence when it was annealed into the four-stranded structure. The two cleavage sites observed were the same as those found when this DNA molecule was paired with a complementary molecule to create a normal B-DNA duplex. These cleavages were shown to be protein-linked and reversible by the addition of salt, suggesting a normal topoisomerase II reaction mechanism. In addition, an eight-stranded DNA molecule created by the association of a complementary oligonucleotide with the four-stranded structure was also cleaved by topoisomerase II despite being resistant to restriction endonuclease digestion. These results suggest that a single strand of DNA may possess the sequence information to direct topoisomerase II to a binding site, but the site must be base paired in a proper manner to do so. This demonstration of the ability of a four-stranded DNA molecule to be a substrate for an enzyme further suggests that these DNA structures may be present in cells.
Full text
PDF

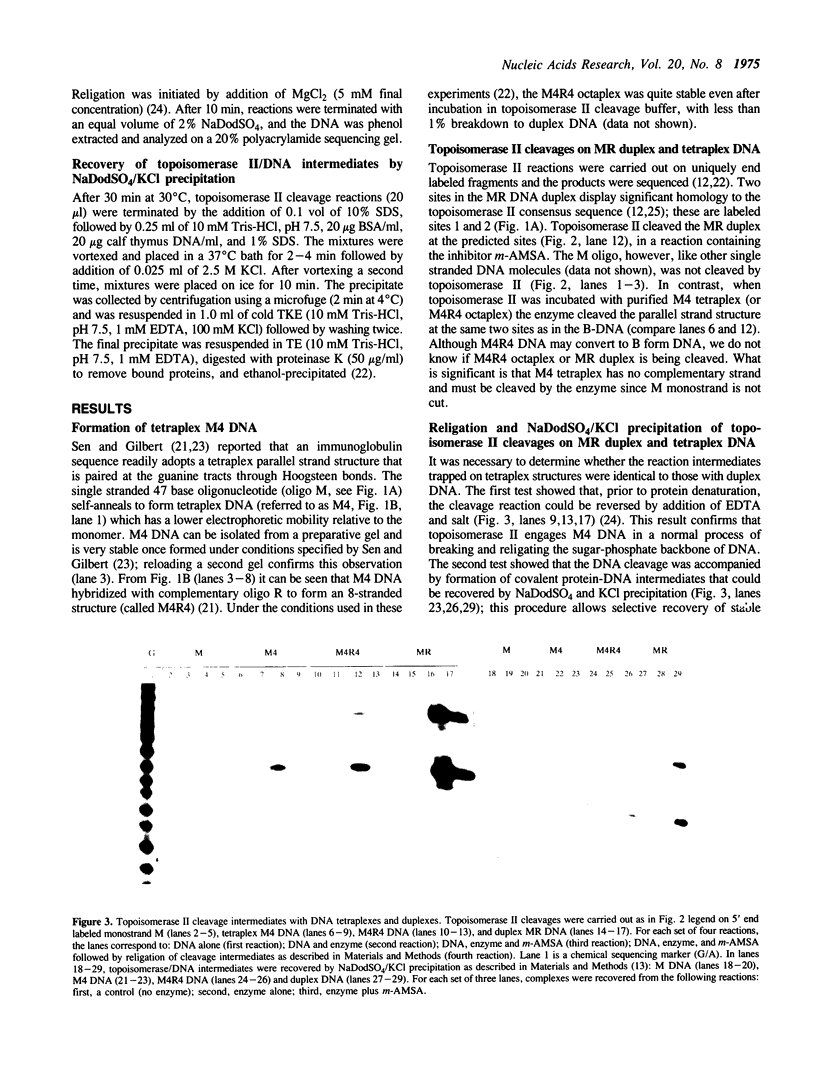


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berrios M., Osheroff N., Fisher P. A. In situ localization of DNA topoisomerase II, a major polypeptide component of the Drosophila nuclear matrix fraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4142–4146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carcamo J., Maldonado E., Cortes P., Ahn M. H., Ha I., Kasai Y., Flint J., Reinberg D. A TATA-like sequence located downstream of the transcription initiation site is required for expression of an RNA polymerase II transcribed gene. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1611–1622. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung I. K., Muller M. T. Aggregates of oligo(dG) bind and inhibit topoisomerase II activity and induce formation of large networks. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9508–9514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiNardo S., Voelkel K., Sternglanz R. DNA topoisomerase II mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: topoisomerase II is required for segregation of daughter molecules at the termination of DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2616–2620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Halligan B., Cooke C. A., Heck M. M., Liu L. F. Topoisomerase II is a structural component of mitotic chromosome scaffolds. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1706–1715. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale K. C., Osheroff N. Uncoupling the DNA cleavage and religation activities of topoisomerase II with a single-stranded nucleic acid substrate: evidence for an active enzyme-cleaved DNA intermediate. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 16;29(41):9538–9545. doi: 10.1021/bi00493a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Laemmli U. K. Cohabitation of scaffold binding regions with upstream/enhancer elements of three developmentally regulated genes of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):521–530. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90877-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm C., Goto T., Wang J. C., Botstein D. DNA topoisomerase II is required at the time of mitosis in yeast. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):553–563. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda H. Bacteriophage T4 DNA topoisomerase mediates illegitimate recombination in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):922–926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreuzer K. N. Recognition of single-stranded DNA by the bacteriophage T4-induced type II topoisomerase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5347–5354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Supercoiling of the DNA template during transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7024–7027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura-Masuda A., Ikeda H. The DNA gyrase of Escherichia coli participates in the formation of a spontaneous deletion by recA-independent recombination in vivo. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Feb;220(3):345–352. doi: 10.1007/BF00391737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller M. T., Mehta V. B. DNase I hypersensitivity is independent of endogenous topoisomerase II activity during chicken erythrocyte differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3661–3669. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller M. T., Pfund W. P., Mehta V. B., Trask D. K. Eukaryotic type I topoisomerase is enriched in the nucleolus and catalytically active on ribosomal DNA. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1237–1243. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03766.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller M. T., Spitzner J. R., DiDonato J. A., Mehta V. B., Tsutsui K., Tsutsui K. Single-strand DNA cleavages by eukaryotic topoisomerase II. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 1;27(22):8369–8379. doi: 10.1021/bi00422a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osheroff N., Zechiedrich E. L. Calcium-promoted DNA cleavage by eukaryotic topoisomerase II: trapping the covalent enzyme-DNA complex in an active form. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 14;26(14):4303–4309. doi: 10.1021/bi00388a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose D., Thomas W., Holm C. Segregation of recombined chromosomes in meiosis I requires DNA topoisomerase II. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):1009–1017. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90349-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen D., Gilbert W. A sodium-potassium switch in the formation of four-stranded G4-DNA. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):410–414. doi: 10.1038/344410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen D., Gilbert W. Formation of parallel four-stranded complexes by guanine-rich motifs in DNA and its implications for meiosis. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):364–366. doi: 10.1038/334364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapka R. M., Powelson M. A., Strayer J. M. Swiveling and decatenation of replicating simian virus 40 genomes in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):515–521. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzner J. R., Chung I. K., Muller M. T. Eukaryotic topoisomerase II preferentially cleaves alternating purine-pyrimidine repeats. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 11;18(1):1–11. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzner J. R., Muller M. T. A consensus sequence for cleavage by vertebrate DNA topoisomerase II. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 24;16(12):5533–5556. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.12.5533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzner J. R., Muller M. T. Application of a degenerate consensus sequence to quantify recognition sites by vertebrate DNA topoisomerase II. J Mol Recognit. 1989 Sep;2(2):63–74. doi: 10.1002/jmr.300020204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundquist W. I., Klug A. Telomeric DNA dimerizes by formation of guanine tetrads between hairpin loops. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):825–829. doi: 10.1038/342825a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trask D. K., Muller M. T. Biochemical characterization of topoisomerase I purified from avian erythrocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 11;11(9):2779–2800. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.9.2779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura T., Yanagida M. Isolation of type I and II DNA topoisomerase mutants from fission yeast: single and double mutants show different phenotypes in cell growth and chromatin organization. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1737–1744. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02040.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C., Caron P. R., Kim R. A. The role of DNA topoisomerases in recombination and genome stability: a double-edged sword? Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):403–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90002-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreb A., Collier D. A., Birshtein B. K., Wells R. D. Left-handed Z-DNA and intramolecular triplex formation at the site of an unequal sister chromatid exchange. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1352–1359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Raghuraman M. K., Cech T. R. Monovalent cation-induced structure of telomeric DNA: the G-quartet model. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):871–880. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90610-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang G. C., Kunze N., Baumgärtner B., Jiang Z. Y., Sapp M., Knippers R., Richter A. Molecular structures of two human DNA topoisomerase I retrosequences. Gene. 1990 Jul 16;91(2):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90095-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]