Abstract
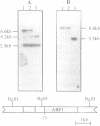
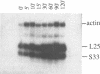
ABF1 is a multifunctional protein present in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, involved in transcription-activation and -repression as well as in DNA-replication. Several lines of evidence indicate the occurrence in the related species Kluyveromyces lactis of a protein having similar properties to those of ABF1 in S. cerevisiae. In order to identify conserved functional domains in ABF1, we have cloned and sequenced the gene encoding the ABF1-homologue from K. lactis. KIABF1 is much smaller than ScABF1 (54.6 vs. 81.7 kD). It exhibits extensive homology with its S. cerevisiae counterpart in the N-terminal region. The C-terminal domain however, is divergent, with the striking exception of a stretch of 20 amino acids, which is virtually identical in the two proteins. KIABF1 can substitute ABF1 in S. cerevisiae, emphasizing the conservation of the multiple functions of this protein.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brand A. H., Micklem G., Nasmyth K. A yeast silencer contains sequences that can promote autonomous plasmid replication and transcriptional activation. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):709–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della Seta F., Ciafré S. A., Marck C., Santoro B., Presutti C., Sentenac A., Bozzoni I. The ABF1 factor is the transcriptional activator of the L2 ribosomal protein genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2437–2441. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F., Stillman B. Similarity between the transcriptional silencer binding proteins ABF1 and RAP1. Science. 1989 Nov 24;246(4933):1034–1038. doi: 10.1126/science.2511628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsman J. C., van Heeswijk W. C., Grivell L. A. Yeast general transcription factor GFI: sequence requirements for binding to DNA and evolutionary conservation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 11;18(9):2769–2776. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.9.2769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Yocum R. R., Gifford P. A GAL10-CYC1 hybrid yeast promoter identifies the GAL4 regulatory region as an upstream site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7410–7414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halfter H., Kavety B., Vandekerckhove J., Kiefer F., Gallwitz D. Sequence, expression and mutational analysis of BAF1, a transcriptional activator and ARS1-binding protein of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4265–4272. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08612.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamil K. G., Nam H. G., Fried H. M. Constitutive transcription of yeast ribosomal protein gene TCM1 is promoted by uncommon cis- and trans-acting elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4328–4341. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herruer M. H., Mager W. H., Woudt L. P., Nieuwint R. T., Wassenaar G. M., Groeneveld P., Planta R. J. Transcriptional control of yeast ribosomal protein synthesis during carbon-source upshift. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10133–10144. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herruer M. H., Mager W. H., Woudt L. P., Nieuwint R. T., Wassenaar G. M., Groeneveld P., Planta R. J. Transcriptional control of yeast ribosomal protein synthesis during carbon-source upshift. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10133–10144. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Cottrelle P., Cool M., Vignais M. L., Thiele D., Marck C., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. A general upstream binding factor for genes of the yeast translational apparatus. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3539–3547. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04114.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsen B. K., Pelham H. R. A conserved heptapeptide restrains the activity of the yeast heat shock transcription factor. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):369–375. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07958.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M. A model fungal gene regulatory mechanism: the GAL genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Dec;51(4):458–476. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.4.458-476.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraakman L. S., Mager W. H., Grootjans J. J., Planta R. J. Functional analysis of the promoter of the gene encoding the acidic ribosomal protein L45 in yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Oct 8;1090(2):204–210. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90102-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leer R. J., Van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. Conserved sequences upstream of yeast ribosomal protein genes. Curr Genet. 1985;9(4):273–277. doi: 10.1007/BF00419955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager W. H., Planta R. J. Multifunctional DNA-binding proteins mediate concerted transcription activation of yeast ribosomal protein genes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):351–355. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90193-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner J. N., Yamamoto K. R. Regulatory crosstalk at composite response elements. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):423–426. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90168-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mylin L. M., Gerardot C. J., Hopper J. E., Dickson R. C. Sequence conservation in the Saccharomyces and Kluveromyces GAL11 transcription activators suggests functional domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5345–5350. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode P. R., Sweder K. S., Oegema K. F., Campbell J. L. The gene encoding ARS-binding factor I is essential for the viability of yeast. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12A):1926–1939. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12a.1926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathern J. N., Higgins D. R. Recovery of plasmids from yeast into Escherichia coli: shuttle vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:319–329. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignais M. L., Woudt L. P., Wassenaar G. M., Mager W. H., Sentenac A., Planta R. J. Specific binding of TUF factor to upstream activation sites of yeast ribosomal protein genes. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1451–1457. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02386.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woudt L. P., Mager W. H., Nieuwint R. T., Wassenaar G. M., van der Kuyl A. C., Murre J. J., Hoekman M. F., Brockhoff P. G., Planta R. J. Analysis of upstream activation sites of yeast ribosomal protein genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):6037–6048. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.6037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray L. V., Jr, Witte M. M., Dickson R. C., Riley M. I. Characterization of a positive regulatory gene, LAC9, that controls induction of the lactose-galactose regulon of Kluyveromyces lactis: structural and functional relationships to GAL4 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1111–1121. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]