Abstract
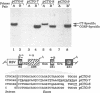
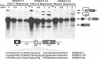
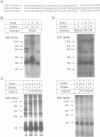
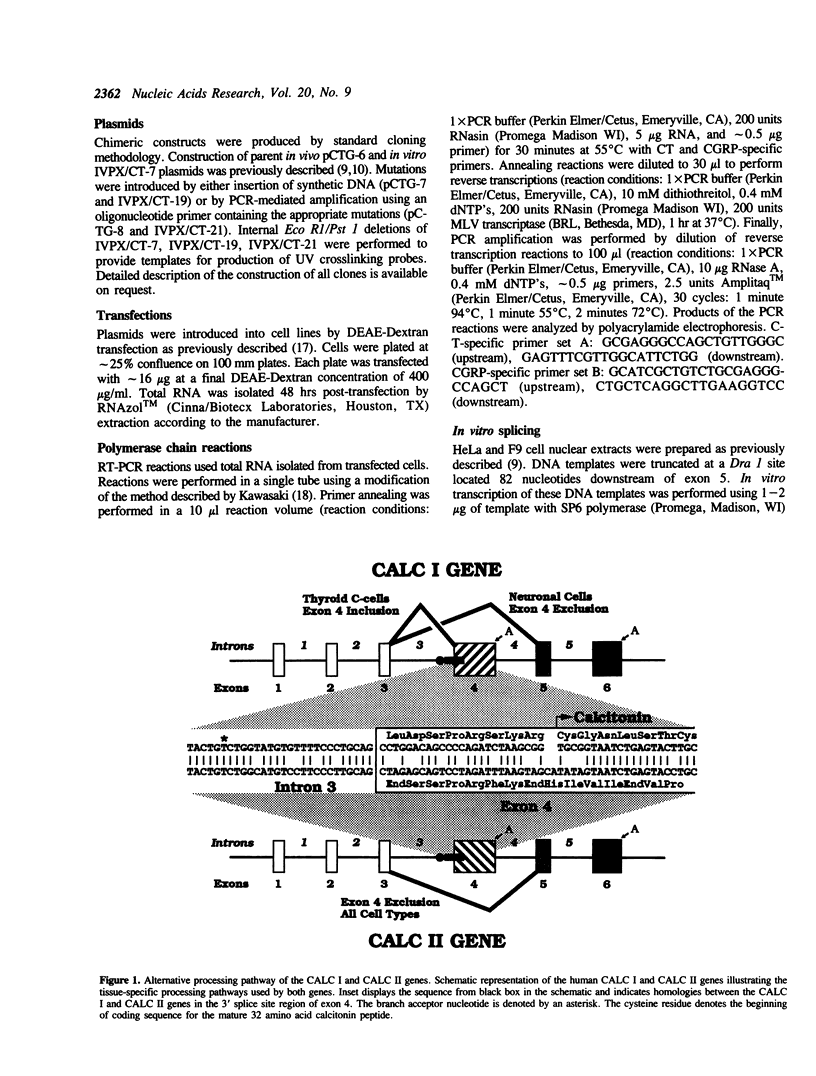
Transcripts derived from the 6 exon CALC I gene are differentially processed in a tissue-specific fashion to include or exclude a calcitonin-specific exon 4. All cell types which transcribe a second calcitonin/CGRP gene, CALC II, exclude exon 4. Substitution of the first 30 nucleotides of CALC I exon 4 with analogous CALC II sequence was sufficient to prevent recognition of exon 4 in in vitro or in vivo RNA splicing systems. UV crosslinking detected a approximately 66 kDa RNA-binding protein in HeLa nuclear extract which interacted with CALC I proximal exon sequence, but not CALC II or mutant sequences. UV crosslinking of this protein was inhibited by addition of nuclear extract from a cell type which normally causes exclusion of exon 4. These results identify an important regulatory element within exon 4 and support a model in which calcitonin production requires protein interaction with this sequence to facilitate exon recognition.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adema G. J., van Hulst K. L., Baas P. D. Uridine branch acceptor is a cis-acting element involved in regulation of the alternative processing of calcitonin/CGRP-l pre-mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 25;18(18):5365–5373. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.18.5365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alevizaki M., Shiraishi A., Rassool F. V., Ferrier G. J., MacIntyre I., Legon S. The calcitonin-like sequence of the beta CGRP gene. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 29;206(1):47–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81338-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amara S. G., Jonas V., Rosenfeld M. G., Ong E. S., Evans R. M. Alternative RNA processing in calcitonin gene expression generates mRNAs encoding different polypeptide products. Nature. 1982 Jul 15;298(5871):240–244. doi: 10.1038/298240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker B. S. Sex in flies: the splice of life. Nature. 1989 Aug 17;340(6234):521–524. doi: 10.1038/340521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berget S. M., Robberson B. L. U1, U2, and U4/U6 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins are required for in vitro splicing but not polyadenylation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):691–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90344-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitbart R. E., Andreadis A., Nadal-Ginard B. Alternative splicing: a ubiquitous mechanism for the generation of multiple protein isoforms from single genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:467–495. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T. A., Ordahl C. P. Nucleotide substitutions within the cardiac troponin T alternative exon disrupt pre-mRNA alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7905–7921. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cote G. J., Abruzzese R. V., Lips C. J., Gagel R. F. Transfection of calcitonin gene regulatory elements into a cell culture model of the C cell. J Bone Miner Res. 1990 Feb;5(2):165–171. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650050210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cote G. J., Nguyen I. N., Berget S. M., Gagel R. F. Calcitonin exon sequences influence alternative RNA processing. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Nov;4(11):1744–1749. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-11-1744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cote G. J., Nguyen I. N., Lips C. J., Berget S. M., Gagel R. F. Validation of an in vitro RNA processing system for CT/CGRP precursor mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3601–3606. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeson R. B., Hedjran F., Yeakley J. M., Guise J. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Alternative production of calcitonin and CGRP mRNA is regulated at the calcitonin-specific splice acceptor. Nature. 1989 Sep 7;341(6237):76–80. doi: 10.1038/341076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedley M. L., Maniatis T. Sex-specific splicing and polyadenylation of dsx pre-mRNA requires a sequence that binds specifically to tra-2 protein in vitro. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):579–586. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90090-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman D. M., Ricci W. M., Finn L. A. Alternative splicing of tropomyosin pre-mRNAs in vitro and in vivo. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1627–1638. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshijima K., Inoue K., Higuchi I., Sakamoto H., Shimura Y. Control of doublesex alternative splicing by transformer and transformer-2 in Drosophila. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):833–836. doi: 10.1126/science.1902987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höppener J. W., Steenbergh P. H., Slebos R. J., Visser A., Lips C. J., Jansz H. S., Bechet J. M., Lenoir G. M., Born W., Haller-Brem S. Expression of the second calcitonin/calcitonin gene-related peptide gene in Ewing sarcoma cell lines. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Apr;64(4):809–817. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-4-809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff S. E., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Splice commitment dictates neuron-specific alternative RNA processing in calcitonin/CGRP gene expression. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):517–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff S. E., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Complex transcriptional units: diversity in gene expression by alternative RNA processing. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1091–1117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lips C. J., Geerdink R. A., Nieuwenhuis M. G., van der Sluys Veer J. Evolutionary pathways of the calcitonin (CALC) genes. Henry Ford Hosp Med J. 1989;37(3-4):201–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattox W., Baker B. S. Autoregulation of the splicing of transcripts from the transformer-2 gene of Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):786–796. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. A role for exon sequences and splice-site proximity in splice-site selection. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):681–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. G., Amara S. G., Evans R. M. Alternative RNA processing: determining neuronal phenotype. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1315–1320. doi: 10.1126/science.6089345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenbergh P. H., Höppener J. W., Zandberg J., Visser A., Lips C. J., Jansz H. S. Structure and expression of the human calcitonin/CGRP genes. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 1;209(1):97–103. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81091-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolow D. T., Berget S. M. Identification of nuclear proteins that specifically bind to RNAs containing 5' splice sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):320–324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli M., Saito H. Regulation of tissue-specific alternative splicing: exon-specific cis-elements govern the splicing of leukocyte common antigen pre-mRNA. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):787–796. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03439.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zillmann M., Zapp M. L., Berget S. M. Gel electrophoretic isolation of splicing complexes containing U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):814–821. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]