Abstract
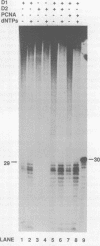
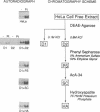
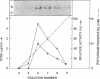
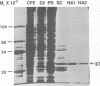
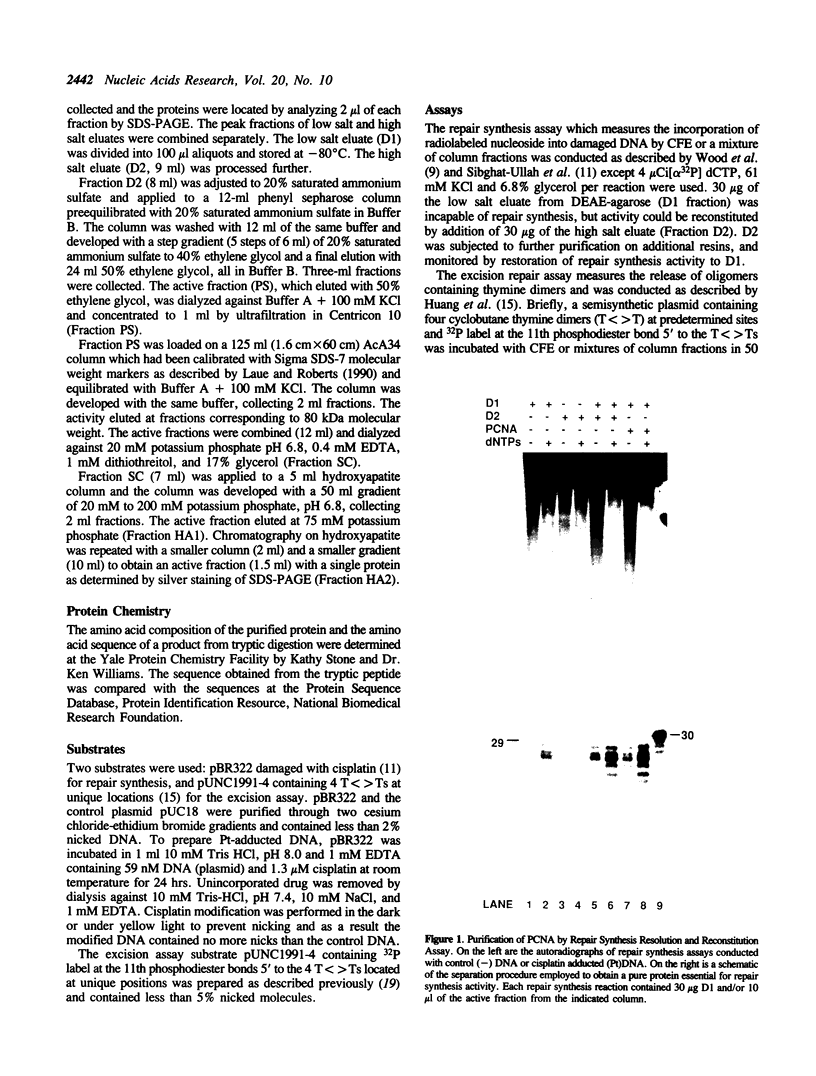
Human cell free extracts carry out nucleotide excision repair in vitro. The extract is readily separated into two fractions by chromatography on a DEAE column. Neither the low salt (0.1 M KCl) nor the high salt (0.8 M KCl) fractions are capable of repair synthesis but the combination of the two restore the repair synthesis activity. Using the repair synthesis assay we purified a protein of 37 kDa from the high salt fraction which upon addition to the low salt fraction restores repair synthesis activity. Amino acid sequence analysis, amino acid composition and immunobloting with PCNA antibodies revealed that the 37 kDa protein is the proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) known to stimulate DNA Polymerases δ and ε. By using an assay which specifically measures the excision of thymine dimers we found that PCNA is not required for the actual excision reaction per se but increases the extent of excision by enabling the excision repair enzyme to turn over catalytically.
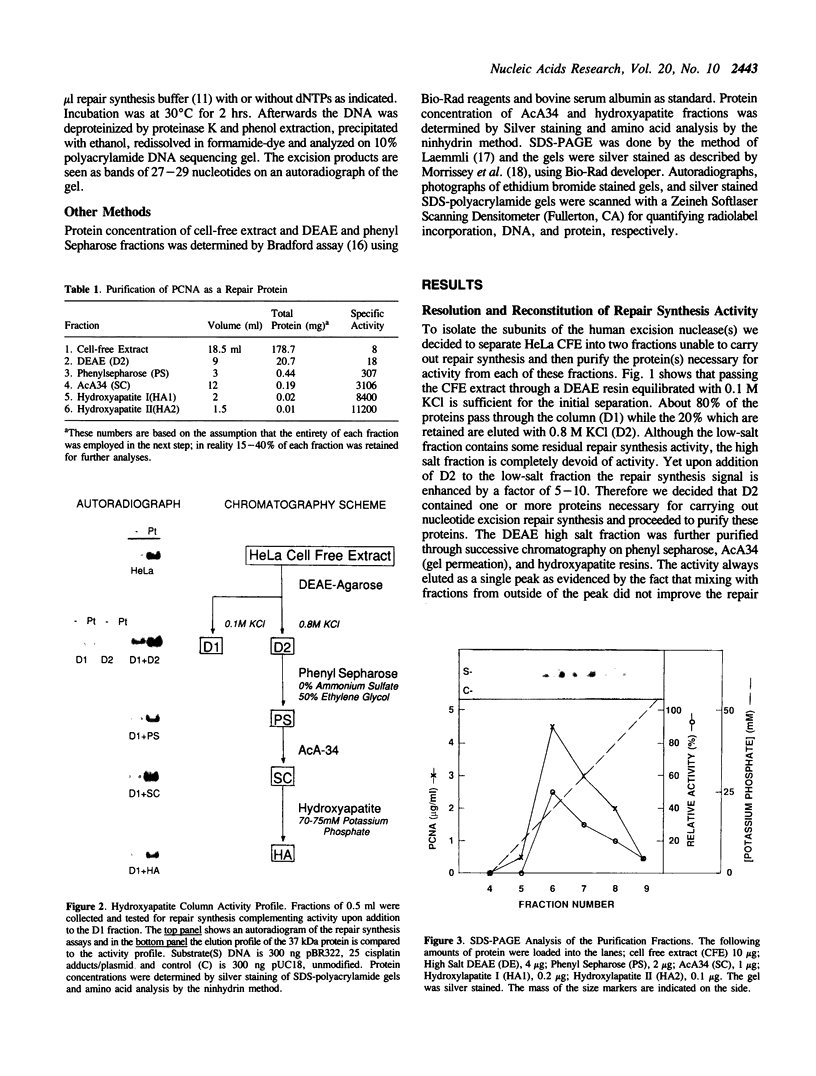
Full text
PDF
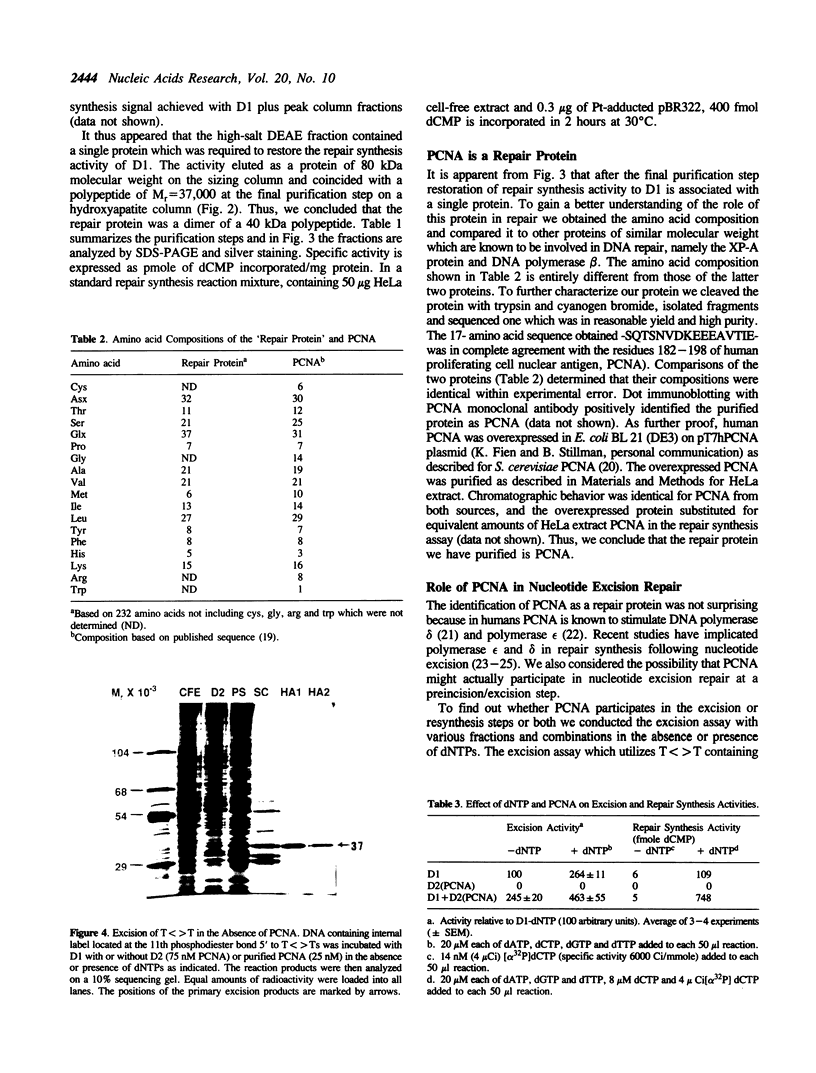

Images in this article
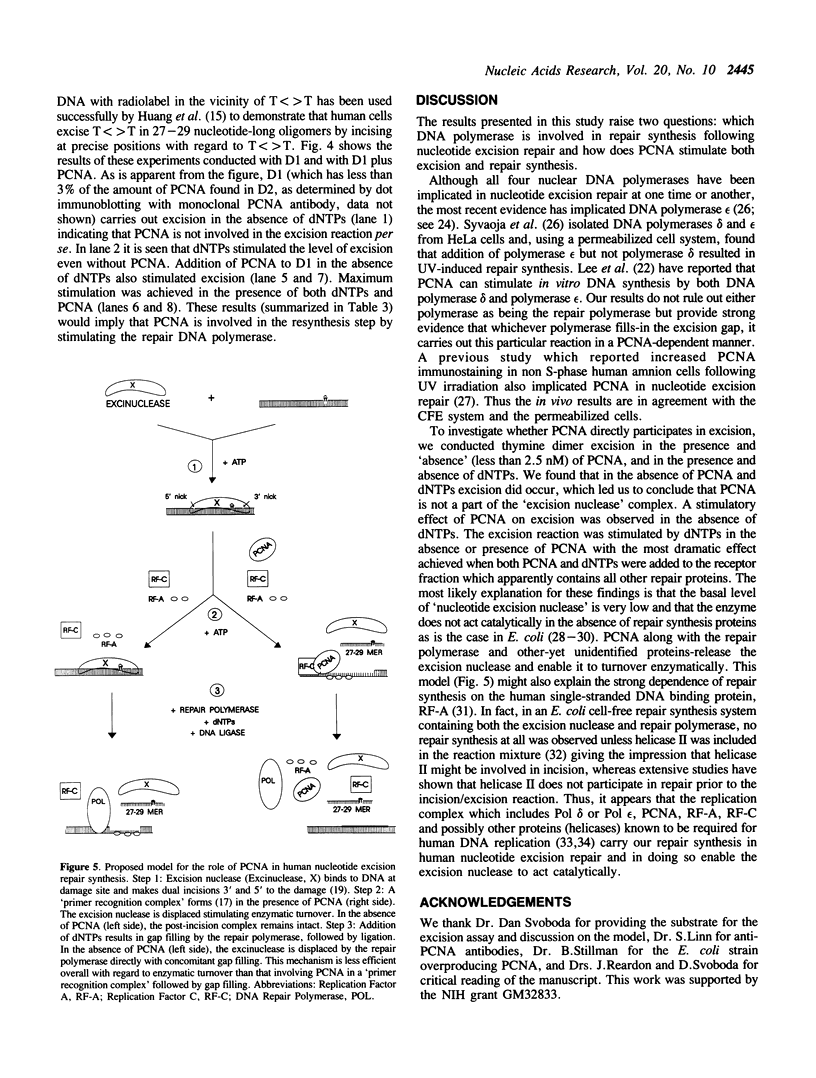
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almendral J. M., Huebsch D., Blundell P. A., Macdonald-Bravo H., Bravo R. Cloning and sequence of the human nuclear protein cyclin: homology with DNA-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1575–1579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron P. R., Kushner S. R., Grossman L. Involvement of helicase II (uvrD gene product) and DNA polymerase I in excision mediated by the uvrABC protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4925–4929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Madsen P. Increased nuclear cyclin/PCNA antigen staining of non S-phase transformed human amnion cells engaged in nucleotide excision DNA repair. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 15;209(2):277–283. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81127-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coverley D., Kenny M. K., Munn M., Rupp W. D., Lane D. P., Wood R. D. Requirement for the replication protein SSB in human DNA excision repair. Nature. 1991 Feb 7;349(6309):538–541. doi: 10.1038/349538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fien K., Stillman B. Identification of replication factor C from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a component of the leading-strand DNA replication complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):155–163. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. C., Svoboda D. L., Reardon J. T., Sancar A. Human nucleotide excision nuclease removes thymine dimers from DNA by incising the 22nd phosphodiester bond 5' and the 6th phosphodiester bond 3' to the photodimer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3664–3668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain I., Chaney S. G., Sancar A. Repair of cis-platinum-DNA adducts by ABC excinuclease in vivo and in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):817–823. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.817-823.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain I., Van Houten B., Thomas D. C., Abdel-Monem M., Sancar A. Effect of DNA polymerase I and DNA helicase II on the turnover rate of UvrABC excision nuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6774–6778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano Y., Fujiwara Y. Defective thymine dimer excision from xeroderma pigmentosum chromatin and its characteristic catalysis by cell-free extracts. Carcinogenesis. 1983 Nov;4(11):1419–1424. doi: 10.1093/carcin/4.11.1419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeney S., Linn S. A critical review of permeabilized cell systems for studying mammalian DNA repair. Mutat Res. 1990 Sep-Nov;236(2-3):239–252. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(90)90008-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. H., Pan Z. Q., Kwong A. D., Burgers P. M., Hurwitz J. Synthesis of DNA by DNA polymerase epsilon in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22707–22717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Samuels M., Sharp P. A. In vitro transcription: whole-cell extract. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:568–582. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01038-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortelmans K., Friedberg E. C., Slor H., Thomas G., Cleaver J. E. Defective thymine dimer excision by cell-free extracts of xeroderma pigmentosum cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2757–2761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orren D. K., Selby C. P., Hearst J. E., Sancar A. Post-incision steps of nucleotide excision repair in Escherichia coli. Disassembly of the UvrBC-DNA complex by helicase II and DNA polymerase I. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):780–788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon J. T., Spielmann P., Huang J. C., Sastry S., Sancar A., Hearst J. E. Removal of psoralen monoadducts and crosslinks by human cell free extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 11;19(17):4623–4629. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.17.4623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins P., Jones C. J., Biggerstaff M., Lindahl T., Wood R. D. Complementation of DNA repair in xeroderma pigmentosum group A cell extracts by a protein with affinity for damaged DNA. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3913–3921. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04961.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibghat-Ullah, Sancar A. Substrate overlap and functional competition between human nucleotide excision repair and Escherichia coli photolyase and (a)BC excision nuclease. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 19;29(24):5711–5718. doi: 10.1021/bi00476a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibghatullah, Husain I., Carlton W., Sancar A. Human nucleotide excision repair in vitro: repair of pyrimidine dimers, psoralen and cisplatin adducts by HeLa cell-free extract. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4471–4484. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syvaoja J., Linn S. Characterization of a large form of DNA polymerase delta from HeLa cells that is insensitive to proliferating cell nuclear antigen. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2489–2497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syväoja J., Suomensaari S., Nishida C., Goldsmith J. S., Chui G. S., Jain S., Linn S. DNA polymerases alpha, delta, and epsilon: three distinct enzymes from HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6664–6668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Miura N., Satokata I., Miyamoto I., Yoshida M. C., Satoh Y., Kondo S., Yasui A., Okayama H., Okada Y. Analysis of a human DNA excision repair gene involved in group A xeroderma pigmentosum and containing a zinc-finger domain. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):73–76. doi: 10.1038/348073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Melendy T., Stillman B. Sequential initiation of lagging and leading strand synthesis by two different polymerase complexes at the SV40 DNA replication origin. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):534–539. doi: 10.1038/346534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Stillman B. Replication factors required for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. II. Switching of DNA polymerase alpha and delta during initiation of leading and lagging strand synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1961–1968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T. S. Eukaryotic DNA polymerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:513–552. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber C. A., Salazar E. P., Stewart S. A., Thompson L. H. ERCC2: cDNA cloning and molecular characterization of a human nucleotide excision repair gene with high homology to yeast RAD3. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1437–1447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08260.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeda G., van Ham R. C., Vermeulen W., Bootsma D., van der Eb A. J., Hoeijmakers J. H. A presumed DNA helicase encoded by ERCC-3 is involved in the human repair disorders xeroderma pigmentosum and Cockayne's syndrome. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):777–791. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90122-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser T., Gassmann M., Thömmes P., Ferrari E., Hafkemeyer P., Hübscher U. Biochemical and functional comparison of DNA polymerases alpha, delta, and epsilon from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10420–10428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. D. Repair of pyrimidine dimer ultraviolet light photoproducts by human cell extracts. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 17;28(21):8287–8292. doi: 10.1021/bi00447a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. D., Robins P., Lindahl T. Complementation of the xeroderma pigmentosum DNA repair defect in cell-free extracts. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):97–106. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90491-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]