Abstract
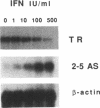
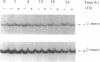
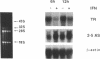
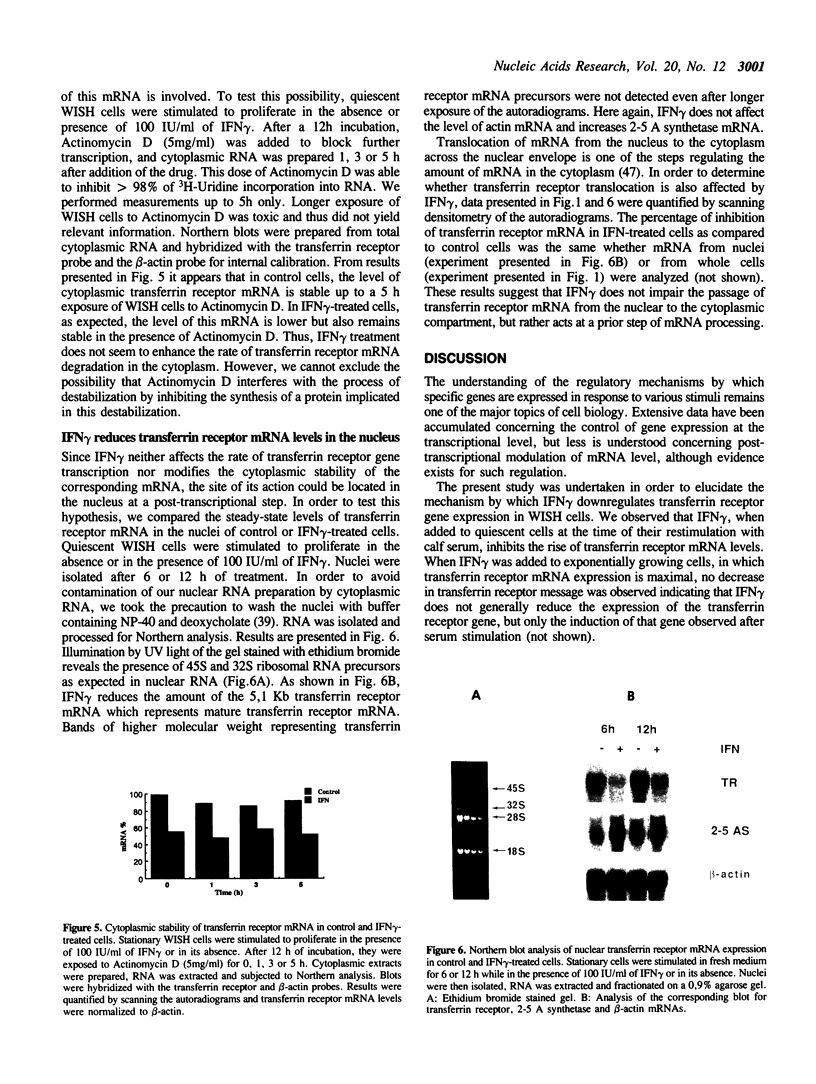
IFN gamma inhibits the rise in transferrin receptor mRNA level which is normally observed when stationary WISH cells are stimulated to proliferate. This effect is not attributable to a change in the transcription rate of the transferrin receptor gene or in the cytoplasmic stability of the mRNA. The IFN gamma-induced reduction of the transferrin receptor mRNA content is already present at the nuclear level to an extent comparable to that observed in whole cells. Thus, IFN gamma does not impair the passage of this mRNA from the nuclear to the cytoplasmic compartment but probably interferes with a nuclear post-transcriptional event during the processing of the immature transferrin receptor mRNA. Two different levels of regulation of transferrin receptor mRNA have been previously reported. Iron modulates the cytoplasmic stability of this mRNA through the binding of a specific cytoplasmic factor, whereas cell growth variation influences the transcription of this gene. Our results suggest the existence of another mechanism of regulation for transferrin receptor gene expression not so far considered. Furthermore, the distinction between the mechanism of regulation exerted by IFN gamma and that exerted by cell proliferation on transferrin receptor gene expression suggests that, in WISH cells, the IFN-induced transferrin receptor decay is not a consequence of cell growth arrest but rather one of the causes of the antiproliferative effect of IFN through iron deprivation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackrill A. M., Reid L. E., Gilbert C. S., Gewert D. R., Porter A. C., Lewin A. R., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Differential response of the human 6-16 and 9-27 genes to alpha and gamma interferons. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 11;19(3):591–598. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.3.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alonso S., Minty A., Bourlet Y., Buckingham M. Comparison of three actin-coding sequences in the mouse; evolutionary relationships between the actin genes of warm-blooded vertebrates. J Mol Evol. 1986;23(1):11–22. doi: 10.1007/BF02100994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benech P., Mory Y., Revel M., Chebath J. Structure of two forms of the interferon-induced (2'-5') oligo A synthetase of human cells based on cDNAs and gene sequences. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2249–2256. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein P., Ross J. Poly(A), poly(A) binding protein and the regulation of mRNA stability. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Sep;14(9):373–377. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besancon F., Bourgeade M. F., Testa U. Inhibition of transferrin receptor expression by interferon-alpha in human lymphoblastoid cells and mitogen-induced lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13074–13080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besançon F., Silbermann F., Dron M., Tovey M. G., Thang M. N., Bourgeade M. F. Relationship between inhibition of cell growth and of transferrin receptor expression by interferon (IFN) alpha: studies in IFN-sensitive and IFN-resistant Daudi cells. J Gen Virol. 1987 Oct;68(Pt 10):2647–2654. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-10-2647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham P. M., Chou T. B., Mims I., Zachar Z. On/off regulation of gene expression at the level of splicing. Trends Genet. 1988 May;4(5):134–138. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90136-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeade M. F., Silbermann F., Thang M. N., Besancon F. Reduction of transferrin receptor expression by interferon gamma in a human cell line sensitive to its antiproliferative effect. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 30;153(3):897–903. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81312-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J. L., Hentze M. W., Koeller D. M., Caughman S. W., Rouault T. A., Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. Iron-responsive elements: regulatory RNA sequences that control mRNA levels and translation. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):924–928. doi: 10.1126/science.2452485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Justesen J., Madsen P. S., Lovmand J., Pedersen Ratz G., Celis A. Major proteins induced and down-regulated by interferons in human cultured cells: identification of a unique set of proteins induced by interferon-alpha in epithelial, fibroblast, and lymphoid cells. Leukemia. 1987 Dec;1(12):800–813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chebath J., Benech P., Hovanessian A., Galabru J., Revel M. Four different forms of interferon-induced 2',5'-oligo(A) synthetase identified by immunoblotting in human cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3852–3857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo F., Colombo M., Staempfli S., Santoro C., Marone M., Frank R., Delius H., Cortese R. Structure of gene and pseudogenes of human apoferritin H. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):721–736. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani C., Mechti N., Piechaczyk M., Lebleu B., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Increased rate of degradation of c-myc mRNA in interferon-treated Daudi cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4896–4899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einat M., Resnitzky D., Kimchi A. Close link between reduction of c-myc expression by interferon and, G0/G1 arrest. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):597–600. doi: 10.1038/313597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faltynek C. R., McCandless S., Baglioni C. Treatment of lymphoblastoid cells with interferon decreases insulin binding. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Nov;121(2):437–441. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041210224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudas J. M., Knight G. B., Pardee A. B. Nuclear posttranscriptional processing of thymidine kinase mRNA at the onset of DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4705–4709. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haile D. J., Hentze M. W., Rouault T. A., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. Regulation of interaction of the iron-responsive element binding protein with iron-responsive RNA elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5055–5061. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. A., Gray P. W., Adams D. O. Expression of the transferrin receptor on murine peritoneal macrophages is modulated by in vitro treatment with interferon gamma. Cell Immunol. 1984 Dec;89(2):478–488. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90348-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentze M. W. Determinants and regulation of cytoplasmic mRNA stability in eukaryotic cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Nov 11;1090(3):281–292. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90191-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentze M. W., Rouault T. A., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. Oxidation-reduction and the molecular mechanism of a regulatory RNA-protein interaction. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):357–359. doi: 10.1126/science.2711187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonak G. J., Knight E., Jr Selective reduction of c-myc mRNA in Daudi cells by human beta interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1747–1750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeller D. M., Casey J. L., Hentze M. W., Gerhardt E. M., Chan L. N., Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. A cytosolic protein binds to structural elements within the iron regulatory region of the transferrin receptor mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3574–3578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Sharp P. A. Electrophoretic separation of complexes involved in the splicing of precursors to mRNAs. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):845–855. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90066-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krönke M., Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Greene W. C. Sequential expression of genes involved in human T lymphocyte growth and differentiation. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1593–1598. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn L. C., McClelland A., Ruddle F. H. Gene transfer, expression, and molecular cloning of the human transferrin receptor gene. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90304-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lappin D. F., Birnie G. D., Whaley K. Interferon-mediated transcriptional and post-transcriptional modulation of complement gene expression in human monocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 26;194(1):177–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19443.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibold E. A., Munro H. N. Cytoplasmic protein binds in vitro to a highly conserved sequence in the 5' untranslated region of ferritin heavy- and light-subunit mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2171–2175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel P. Biochemistry of interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:251–282. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Reich N., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-induced nuclear factors that bind a shared promoter element correlate with positive and negative transcriptional control. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):383–393. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. L., Garber E. A., Wang E., Caliguiri L. A., Schellekens H., Goldberg A. R., Tamm I. Reduced synthesis of pp60src and expression of the transformation-related phenotype in interferon-treated Rous sarcoma virus-transformed rat cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;3(9):1656–1664. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.9.1656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall A. H., Alper D., Hiscott J. Modulation of nuclear proto-oncogene expression and cellular growth in myeloid leukemic cells by human interferon alpha. J Cell Physiol. 1988 May;135(2):324–331. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041350221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland A., Kühn L. C., Ruddle F. H. The human transferrin receptor gene: genomic organization, and the complete primary structure of the receptor deduced from a cDNA sequence. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):267–274. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurs E., Hovanessian A. G. Alpha-interferon inhibits the expression of heavy chain mu messenger RNA in Daudi cells. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1689–1696. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02997.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllner E. W., Kühn L. C. A stem-loop in the 3' untranslated region mediates iron-dependent regulation of transferrin receptor mRNA stability in the cytoplasm. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllner E. W., Neupert B., Kühn L. C. A specific mRNA binding factor regulates the iron-dependent stability of cytoplasmic transferrin receptor mRNA. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):373–382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90851-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neckers L. M., Tsuda H., Weiss E., Pluznik D. H. Differential expression of c-myc and the transferrin receptor in G1 synchronized M1 myeloid leukemia cells. J Cell Physiol. 1988 May;135(2):339–344. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041350223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen D., Kühn L. C. Noncoding 3' sequences of the transferrin receptor gene are required for mRNA regulation by iron. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1287–1293. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02366.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelosi E., Testa U., Louache F., Thomopoulos P., Salvo G., Samoggia P., Peschle C. Expression of transferrin receptors in phytohemagglutinin-stimulated human T-lymphocytes. Evidence for a three-step model. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3036–3042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer L. M., Donner D. B., Tamm I. Interferon-alpha down-regulates insulin receptors in lymphoblastoid (Daudi) cells. Relationship to inhibition of cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3665–3670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. C., Chernajovsky Y., Dale T. C., Gilbert C. S., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Interferon response element of the human gene 6-16. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):85–92. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02786.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao K., Harford J. B., Rouault T., McClelland A., Ruddle F. H., Klausner R. D. Transcriptional regulation by iron of the gene for the transferrin receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):236–240. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimoldi D., Samid D., Flessate D. M., Friedman R. M. Transcriptional inhibition of Ha-ras in interferon-induced revertants of ras-transformed mouse cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Sep 15;48(18):5157–5162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samid D., Chang E. H., Friedman R. M. Biochemical correlates of phenotypic reversion in interferon-treated mouse cells transformed by a human oncogene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Feb 29;119(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91612-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder H. C., Wenger R., Ugarković D., Friese K., Bachmann M., Müller W. E. Differential effect of insulin and epidermal growth factor on the mRNA translocation system and transport of specific poly(A+) mRNA and poly(A-) mRNA in isolated nuclei. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 6;29(9):2368–2378. doi: 10.1021/bi00461a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Testa U., Kühn L., Petrini M., Quaranta M. T., Pelosi E., Peschle C. Differential regulation of iron regulatory element-binding protein(s) in cell extracts of activated lymphocytes versus monocytes-macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):13925–13930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaessen R. T., Houweling A., van der Eb A. J. Post-transcriptional control of class I MHC mRNA expression in adenovirus 12-transformed cells. Science. 1987 Mar 20;235(4795):1486–1488. doi: 10.1126/science.3823900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vakalopoulou E., Schaack J., Shenk T. A 32-kilodalton protein binds to AU-rich domains in the 3' untranslated regions of rapidly degraded mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3355–3364. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil J., Epstein C. J., Epstein L. B., Sedmak J. J., Sabran J. L., Grossberg S. E. A unique set of polypeptides is induced by gamma interferon in addition to those induced in common with alpha and beta interferons. Nature. 1983 Feb 3;301(5899):437–439. doi: 10.1038/301437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. R. Transcriptional regulation of interferon-stimulated genes. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Aug 15;200(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb21041.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrana J. L., Overall C. M., Sodek J. Regulation of the expression of a secreted acidic protein rich in cysteine (SPARC) in human fibroblasts by transforming growth factor beta. Comparison of transcriptional and post-transcriptional control with fibronectin and type I collagen. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Apr 23;197(2):519–528. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15940.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoon K. C., Karasaki Y., zur Nedden D. L., Hu R. Q., Arnheiter H. Modulation of epidermal growth factor receptors by human alpha interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8226–8230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]