Abstract
We present an unusual case of renal cell cancer (RCC) which relapsed with duodenal metastasis and unveiled itself by gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. An 80-year old Caucasian gentleman with history of renal cell cancer status post nephrectomy 11 mo previously, presented with syncope and melena. Computed tomography scan of the abdomen revealed heterogeneous soft tissue mass in the right nephrectomy bed invading the duodenum. Upper GI endoscopic biopsy confirmed the presence of recurrent renal cell cancer. However, due to extensive metastatic disease, the patient was placed on palliative chemotherapy as surgical options were ruled out. Our case report reiterates the fact that renal cell carcinoma can recur with gastrointestinal manifestations and, although a rarity, it should be considered in a patient with a history of malignancy who presents with these symptoms.
Keywords: Duodenal metastasis, Renal cell cancer, Upper gastrointestinal bleed
INTRODUCTION
Occult upper gastrointestinal bleed can be a vexing problem to the physician. Malignant causes of upper gastrointestinal (GI) bleed account for 1%-4% of cases and the duodenum is the least frequent site involved. Renal cell cancer (RCC) behaves unpredictably and has a diverse range of clinical manifestations. Metastasis to the small intestine is rare and can present as gastrointestinal bleeding. The purpose of this case report is to present the clinical entity of metastatic malignancy of the duodenum as an unusual cause of GI bleeding[1,2].
CASE REPORT
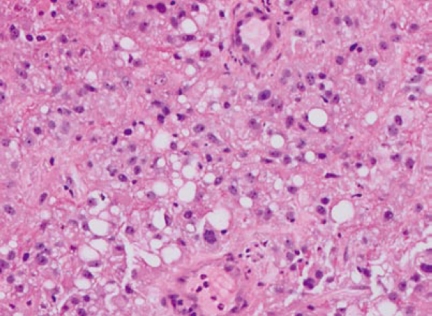
An 80-year old Caucasian male with history of renal cell cancer (clear cell type with focal areas of sarcomatoid differentiation with documented renal vein invasion but no extension beyond Gerota’s fascia and negative ureteral margins, Figure 1) status post right sided nephrectomy 11 mo previously, was admitted for evaluation of syncope. History was suggestive of black tarry stools for the past three months. Examination revealed pallor and orthostatic hypotension. Labs revealed anemia with hemoglobin/hematocrit (Hb/Hct) of 5.6/16 for which he received blood transfusion.
Figure 1.
Histopathology of the nephrectomy specimen showing clear cell type renal cancer.
Computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen revealed a large heterogeneous soft tissue mass in the right nephrectomy bed invading the distal second/proximal third portion of the duodenum (Figure 2), suspicious for recurrent renal cell cancer. Endoscopic biopsy of the fungating duodenal mass (Figure 3) showed large cell malignant epithelial neoplasm with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, in sheets and clusters and occasional mitotic figures (Figure 4), compatible with the histopathology of the nephrectomy specimen from the previous year; thus clinching the diagnosis. Metastatic workup showed lung metastasis and lytic lesions involving the L2 vertebra.
Figure 2.
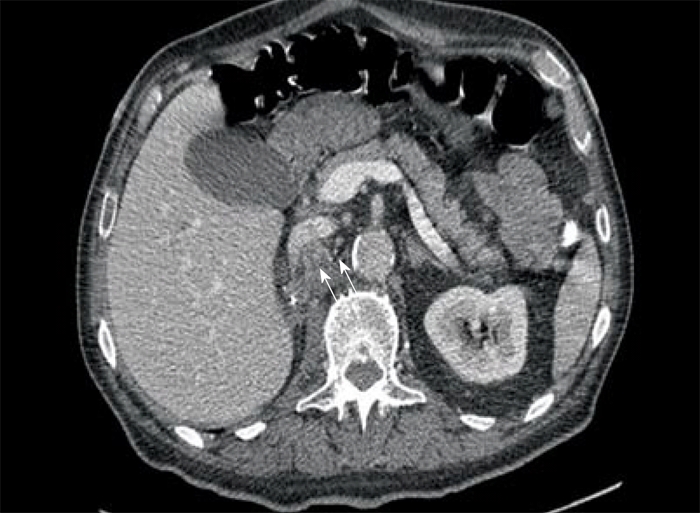
Computed tomography scan of abdomen showing heterogeneous soft tissue mass extending into the duodenum from right nephrectomy bed.
Figure 3.
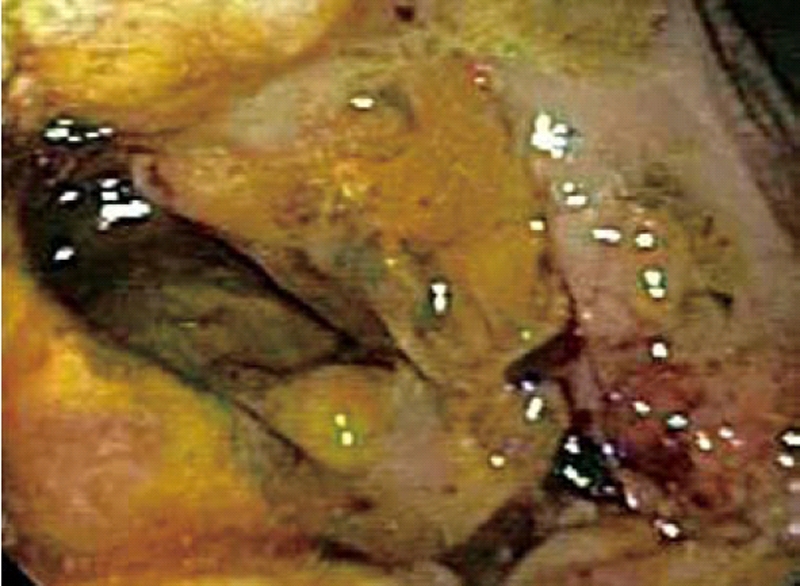
Endoscopic picture of fungating mass in the duodenum.
Figure 4.
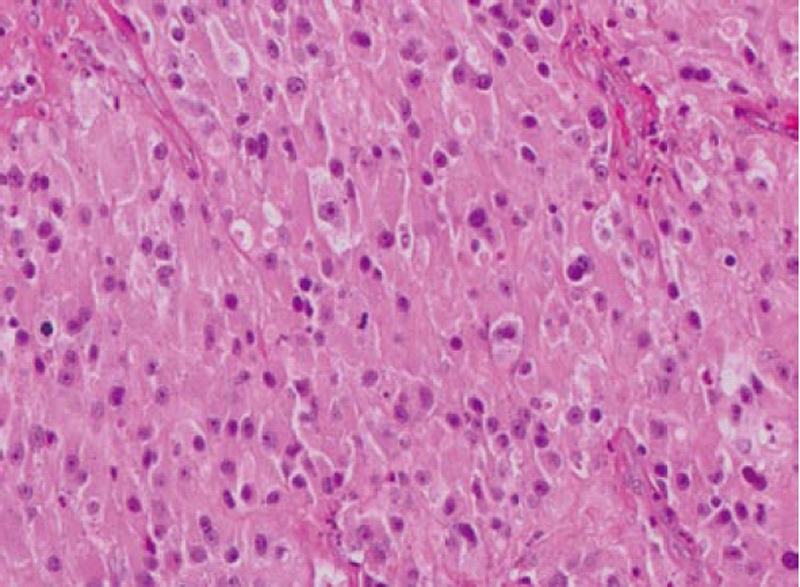
Duodenal biopsy showing large cell malignant epithelial neoplasm with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and occasional mitotic figures.
Surgical options were ruled out and he was started on sorafenib (tyrosine kinase inhibitor). His disease progressed subsequently and he was eventually started on everolimus with little change in his condition. He received multiple blood transfusions due to persistent GI bleeding and died 10 mo later.
DISCUSSION
GI bleeding is quite challenging and, of all the causes of upper gastrointestinal bleed, neoplasms account for only 1%-4% of cases. Tumors of the small intestine account for 0.35% of all malignancies. They could be either primaries or metastatic lesions, of which metastatic lesions are more common. Of all the neoplasms, melanoma and lung cancer have the highest rates of metastasizing to the intestines[1,2].
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) has unpredictable clinical manifestations, usually 25%-30% of patients are found to have metastases at diagnosis and a further 30%-50% with local disease develops metastases in due course of time[1,2].
Patients after radical nephrectomy usually present within a year with recurrence but can present after many years, warranting lifelong surveillance[3]. RCC has the potential to metastasize to almost any site but the most common sites are lung (75%), lymph nodes (36%), bone (20%), liver (18%), adrenal glands, kidney, brain, heart, spleen, intestine and skin[4]. 4% of RCC metastasize to the GI tract and account for 7.1% of all metastatic tumors to the small intestine[4,5]. The duodenum is the least frequent site of metastasis, with the periampullary region the most common site followed by the duodenal bulb[3]. A literature review lists all reported cases of renal cell cancer with duodenal metastasis (Table 1).
Table 1.
Case series of all reported cases of duodenal metastasis secondary to renal cell cancer
| Year | Authors | Years after nephrectomy | Presentation | Diagnosis | Part of duodenum involved | Course and outcome |
| 2007 | Haffner | 2 | Severe anemia, chronic GI bleed | CT scan of abdomen, endoscopy | Second and first | Surgical resection |
| 2006 | Segawa | 13 | Fatigue, weight loss, GI bleed | Endoscopy and biopsy | Second | Palliative care. Died in 5 mo |
| 2006 | Bhatia | 1 | Abdominal lump, Jaundice | Endoscopy and biopsy | Second | Palliative treatment. Lost to follow up |
| 2006 | Harish | 3 | Acute upper GI bleed | Endoscopy and biopsy | Second | En-bloc pancreatico-duodenectomy, no other metastatic lesion, disease free for 2 years |
| 2004 | Loualidi | 2 | Weakness, exertional dyspnea, occult GI blood loss | Endoscopy and biopsy | Second | Palliative radiotherapy. Alive for three years |
| 2004 | Chang | 9 | Acute massive upper GI bleed | Endoscopy and biopsy | Second | Surgery |
| 2002 | Lisli | NA | Acute upper GI bleed | Endoscopy and biopsy | Second | Nephrectomy and en-bloc metastasectomy |
| 2001 | Mendoza | 2 | Epigastric pain, Nausea, vomiting | ERCP and biopsy | Second | Necrotizing pancreatitis. Palliative care |
| 2001 | Hashimoto | 11 | Upper GI bleed | Endoscopy and biopsy | Second | Total pancreatectomy and duodenectomy |
| 1999 | Yavascaogulu | NA | Flank pain | Endoscopy and biopsy and CT scan | Second | Pylorus preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy. Recurrence free for 1 year |
| 1998 | Janzen | 17.5 | Melena | Endoscopy and biopsy | Second | Total pancreatectomy, duodenectomy, cholystectomy, splenectomy. Discharged home alive |
| 1996 | Gastaca | 8 | Weakness, palpitations, GI bleed | Endoscopy and biopsy | Second | Duodenal resection. Did well for two years |
| 1996 | Toh | 10 | Duodenal obstruction | CT scan and surgical excision biopsy | First and Second | Duodenectomy and discharged |
| 1994 | Vesga | 9 | Acute upper GI bleed | Endoscopy and biopsy | Second | Duodenal and pancreatic resection |
| 1987 | Lynch-Nyhan | 1 | Massive upper GI bleed | Endoscopy and biopsy | Second | Gastroduodenal artery embolization. 6 mo documented survival |
| 6 | Obstructive Jaundice and hematobilia | Endoscopy and biopsy | Second | Gastroduodenal artery embolization. Died 6 mo later | ||
| 2 | Melena | CT scan | Second | Duodenal and caval extension. Refused treatment |
GI: Gastrointestinal; CT: Computed tomography.
Duodenal metastases usually present as acute or chronic gastrointestinal hemorrhage, duodenal obstruction, perforation, duodenal intussusception or as obstructive jaundice[5]. The involvement is usually the result of direct infiltration, lymphatic, hematogenous or transcoelomic spread[3]. Of note, our case of duodenal metastasis was through direct infiltration from the recurrent mass in the right nephrectomy bed. In the case of right sided renal cell carcinoma, the probability of duodenal metastasis is always higher because of the greater risk of loco-regional invasion.
Diagnosis of duodenal metastases as a cause of GI bleeding is a challenge due to its rarity and hence low index of suspicion. For diagnostic purposes, duodenal lesions may be apparent on barium studies or abdominal computer tomography demonstrating thickening of the wall or folds in the involved segment. Endoscopy reveals non-ulcerative mass; submucosal tumor masses with elevation and ulceration at the apex (volcano lesions) or multiple nodules of various sizes with ulceration at the apex[5,6]. If lesions are in the submucosal position, regular biopsy specimens may not be sufficient to clinch the diagnosis and may need aggressive biopsy techniques using jumbo forceps or surgical biopsy to obtain sufficient tissue for diagnosis[5]. Although biopsy of a duodenal mass entails the possibility or rather the certainty of further hemorrhage, it is absolutely necessary to document the recurrence of disease unless palliation is the treatment goal.
Management is entirely dependent on the general condition and concurrent metastases at other sites. Usually duodenal metastasis occurs when there is widespread nodal and visceral involvement with evidence of disease elsewhere in the body[7] as in our patient but case reports of RCC with solitary duodenal metastasis have been published. In the latter case, choice of treatment is metastasectomy[3], while in the former the goal is more of palliative nature including palliative surgical procedures (proximal diversion in case of obstruction, gastroduodenal artery embolization in case of bleed)[8], radiotherapy, chemotherapy (Sorafenib, Sunitinib, Sirolimus, Everolimus) or immunotherapy (Interleukin 2). People with metastatic disease generally do poorly with average survival being 4 mo and only 10% of these patients survive for one year[3].
In conclusion, our case report reiterates the fact that renal cell carcinoma can recur with gastrointestinal manifestations and, although a rarity, it should be considered in a patient with a history of malignancy who presents with these symptoms. A complete evaluation, especially endoscopic examination and biopsy, should be carried out in such patients for aggressive surgical management or palliative treatment, taking into consideration the procedural risks. Awareness of this entity and a high index of suspicion are mandatory for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Footnotes
Peer reviewers: Atsushi Imagawa, MD, Department of Gastroenterology, Tsuyama Central Hospital, 1756 Kawasaki Tsuyama-city, Okayama 708-0841, Japan; Seong Woo Jeon, MD, PhD, Assistant Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University Hospital, 50, Samduk-2Ga, Chung-gu, Daegu 700-721, South Korea
S- Editor Wang JL L- Editor Roemmele A E- Editor Ma WH
References
- 1.Sadler GJ, Anderson MR, Moss MS, Wilson PG. Metastases from renal cell carcinoma presenting as gastrointestinal bleeding: two case reports and a review of the literature. BMC Gastroenterol. 2007;7:4. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-7-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Loualidi A, Spooren PF, Grubben MJ, Blomjous CE, Goey SH. Duodenal metastasis: an uncommon cause of occult small intestinal bleeding. Neth J Med. 2004;62:201–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bhatia A, Das A, Kumar Y, Kochhar R. Renal cell carcinoma metastasizing to duodenum: a rare occurrence. Diagn Pathol. 2006;1:29. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-1-29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lynch-Nyhan A, Fishman EK, Kadir S. Diagnosis and management of massive gastrointestinal bleeding owing to duodenal metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 1987;138:611–613. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)43275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nabi G, Gandhi G, Dogra PN. Diagnosis and management of duodenal obstruction due to renal cell carcinoma. Trop Gastroenterol. 2001;22:47–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hsu CC, Chen JJ, Changchien CS. Endoscopic features of metastatic tumors in the upper gastrointestinal tract. Endoscopy. 1996;28:249–253. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1005437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hashimoto M, Miura Y, Matsuda M, Watanabe G. Concomitant duodenal and pancreatic metastases from renal cell carcinoma: report of a case. Surg Today. 2001;31:180–183. doi: 10.1007/s005950170208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chang WT, Chai CY, Lee KT. Unusual upper gastrointestinal bleeding due to late metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: a case report. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2004;20:137–141. doi: 10.1016/S1607-551X(09)70098-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]