Abstract
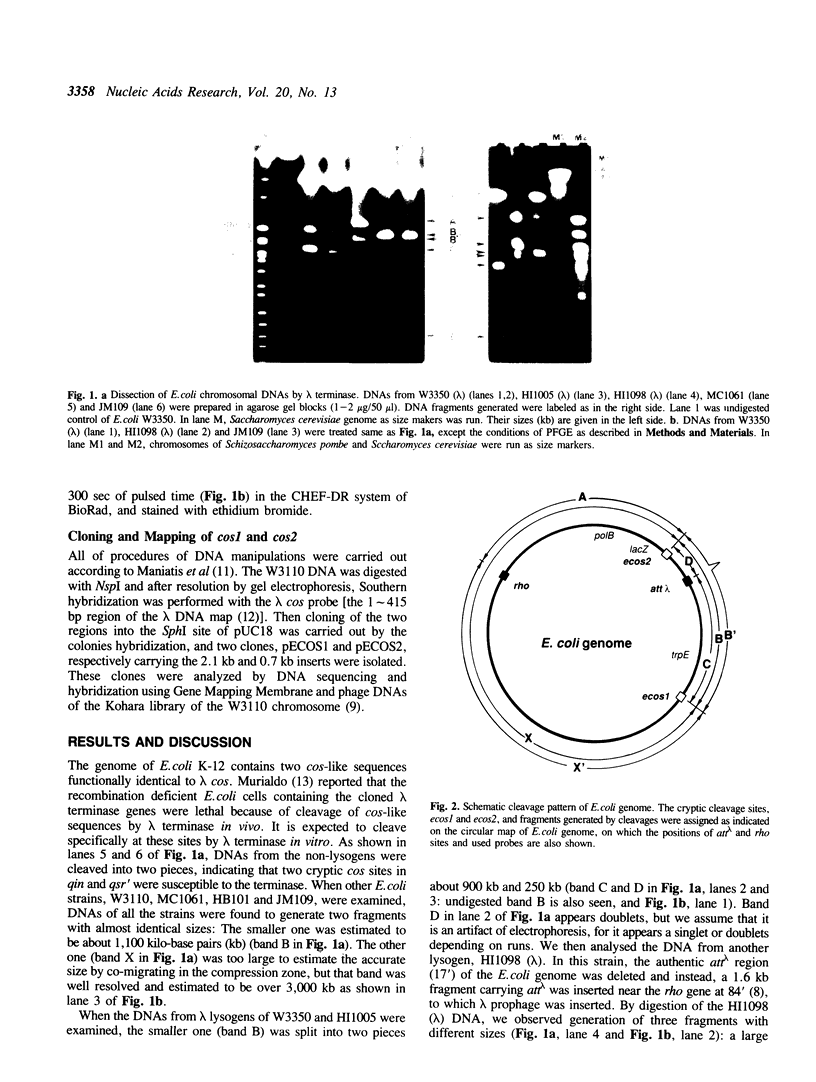
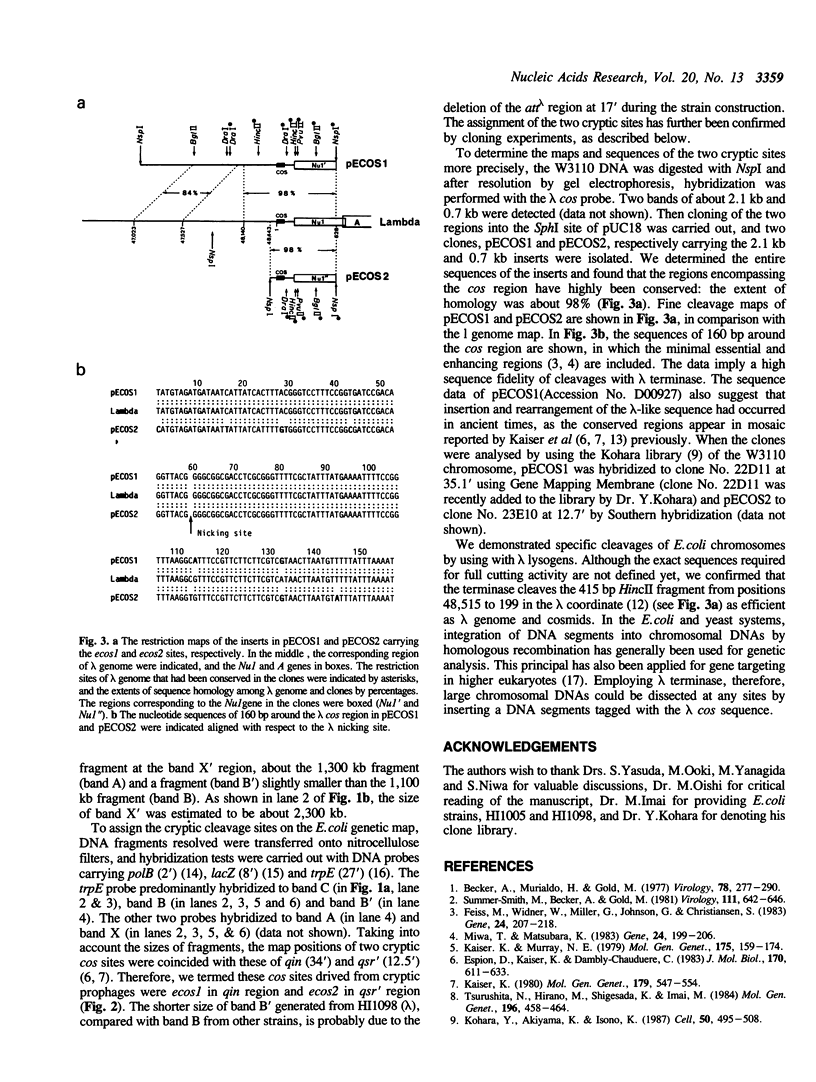
We have succeeded the targeted cleavage of chromosomes by lambda terminase that introduces double-strand cleavages in DNA recognizing the lambda cos sequence. When chromosomal DNAs of various Escherichia coli K-12 strains were subjected to terminase digestion, all were found to contain two common cleavage sites. Therefore, DNAs from lambda lysogens in which lambda DNA was inserted at different chromosomal sites were specifically cleaved at one more additional site. The two sites, termed ecos1 and ecos2, were mapped at approximately 35.1' and 12.7' of E. coli genetic map. The ecos1 and ecos2 sites were included in qin and qsr' regions, respectively. Therefore, the cleavage sites were associated with cryptic prophages. Sequences at the ecos1 and ecos2 sites showed 98% homology to the lambda cos sequence, indicating high fidelity of sequence recognition by the terminase. Since the strategy for integration of a DNA segment into chromosomal DNA through homologous recombination has been established, the dissection method that uses lambda terminase should be applicable for gene mapping as well as construction of macrophysical maps of larger genomes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker A., Murialdo H., Gold M. Studies on an in vitro system for the packaging and maturation of phage lambda DNA. Virology. 1977 May 1;78(1):277–290. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90099-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espion D., Kaiser K., Dambly-Chaudiere C. A third defective lambdoid prophage of Escherichia coli K12 defined by the lambda derivative, lambdaqin111. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 5;170(3):611–633. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80124-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feiss M., Widner W., Miller G., Johnson G., Christiansen S. Structure of the bacteriophage lambda cohesive end site: location of the sites of terminase binding (cosB) and nicking (cosN). Gene. 1983 Oct;24(2-3):207–218. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90081-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki H., Nakata A., Walker G. C., Shinagawa H. The Escherichia coli polB gene, which encodes DNA polymerase II, is regulated by the SOS system. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6268–6273. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6268-6273.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser K., Murray N. E. Physical characterisation of the "Rac prophage" in E. coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Sep;175(2):159–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00425532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser K. The origin of Q-independent derivatives of phage lambda. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;179(3):547–554. doi: 10.1007/BF00271744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalnins A., Otto K., Rüther U., Müller-Hill B. Sequence of the lacZ gene of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):593–597. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01468.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. L., Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Disruption of the proto-oncogene int-2 in mouse embryo-derived stem cells: a general strategy for targeting mutations to non-selectable genes. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):348–352. doi: 10.1038/336348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa T., Matsubara K. Lambda phage DNA sequences affecting the packaging process. Gene. 1983 Oct;24(2-3):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90080-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murialdo H. Lethal effect of lambda DNA terminase in recombination deficient Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jul;213(1):42–49. doi: 10.1007/BF00333396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner-Smith M., Becker A., Gold M. DNA packaging in the lambdoid phages: the role of lambda genes Nu1 and A. Virology. 1981 Jun;111(2):642–646. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90363-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurushita N., Hirano M., Shigesada K., Imai M. Isolation and characterization of rho mutants of Escherichia coli with increased transcription termination activities. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(3):458–464. doi: 10.1007/BF00436193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanofsky C., Platt T., Crawford I. P., Nichols B. P., Christie G. E., Horowitz H., VanCleemput M., Wu A. M. The complete nucleotide sequence of the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6647–6668. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




