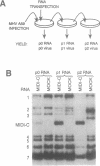
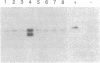
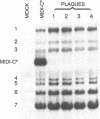
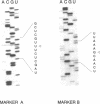
Abstract
We describe a novel strategy to site-specifically mutagenize the genome of an RNA virus by exploiting homologous RNA recombination between synthetic defective interfering (DI) RNA and the viral RNA. The construction of a full-length cDNA clone, pMIDI, of a DI RNA of coronavirus MHV strain A59 was reported previously (R.G. Van der Most, P.J. Bredenbeek, and W.J.M. Spaan (1991). J. Virol. 65, 3219-3226). RNA transcribed from this construct, is replicated efficiently in MHV-infected cells. Marker mutations introduced in MIDI RNA were replaced by the wild-type residues during replication. More importantly, however, these genetic markers were introduced into viral genome: even in the absence of positive selection MHV recombinants could be isolated. This finding provides new prospects for the study of coronavirus replication using recombinant DNA techniques. As a first application, we describe the rescue of the temperature sensitive mutant MHV Albany-4 using DI-directed mutagenesis. Possibilities and limitations of this strategy are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlquist P., French R., Janda M., Loesch-Fries L. S. Multicomponent RNA plant virus infection derived from cloned viral cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7066–7070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison R., Thompson C., Ahlquist P. Regeneration of a functional RNA virus genome by recombination between deletion mutants and requirement for cowpea chlorotic mottle virus 3a and coat genes for systemic infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1820–1824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banner L. R., Keck J. G., Lai M. M. A clustering of RNA recombination sites adjacent to a hypervariable region of the peplomer gene of murine coronavirus. Virology. 1990 Apr;175(2):548–555. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90439-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baric R. S., Fu K., Schaad M. C., Stohlman S. A. Establishing a genetic recombination map for murine coronavirus strain A59 complementation groups. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):646–656. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90530-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bujarski J. J., Kaesberg P. Genetic recombination between RNA components of a multipartite plant virus. 1986 May 29-Jun 4Nature. 321(6069):528–531. doi: 10.1038/321528a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Groot R. J., Andeweg A. C., Horzinek M. C., Spaan W. J. Sequence analysis of the 3'-end of the feline coronavirus FIPV 79-1146 genome: comparison with the genome of porcine coronavirus TGEV reveals large insertions. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):370–376. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90097-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enami M., Luytjes W., Krystal M., Palese P. Introduction of site-specific mutations into the genome of influenza virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3802–3805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fichot O., Girard M. An improved method for sequencing of RNA templates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6162–6162. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn Y. S., Grakoui A., Rice C. M., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Mapping of RNA- temperature-sensitive mutants of Sindbis virus: complementation group F mutants have lesions in nsP4. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1194–1202. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1194-1202.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn Y. S., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Mapping of RNA- temperature-sensitive mutants of Sindbis virus: assignment of complementation groups A, B, and G to nonstructural proteins. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3142–3150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3142-3150.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann M. A., Brian D. A. The 5' end of coronavirus minus-strand RNAs contains a short poly(U) tract. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6331–6333. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6331-6333.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Baltimore D. Defective viral particles and viral disease processes. Nature. 1970 Apr 25;226(5243):325–327. doi: 10.1038/226325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis T. C., Kirkegaard K. The polymerase in its labyrinth: mechanisms and implications of RNA recombination. Trends Genet. 1991 Jun;7(6):186–191. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90434-R. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keck J. G., Matsushima G. K., Makino S., Fleming J. O., Vannier D. M., Stohlman S. A., Lai M. M. In vivo RNA-RNA recombination of coronavirus in mouse brain. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1810–1813. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1810-1813.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keck J. G., Soe L. H., Makino S., Stohlman S. A., Lai M. M. RNA recombination of murine coronaviruses: recombination between fusion-positive mouse hepatitis virus A59 and fusion-negative mouse hepatitis virus 2. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1989–1998. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1989-1998.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keck J. G., Stohlman S. A., Soe L. H., Makino S., Lai M. M. Multiple recombination sites at the 5'-end of murine coronavirus RNA. Virology. 1987 Feb;156(2):331–341. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90413-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkegaard K., Baltimore D. The mechanism of RNA recombination in poliovirus. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):433–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90600-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koetzner C. A., Parker M. M., Ricard C. S., Sturman L. S., Masters P. S. Repair and mutagenesis of the genome of a deletion mutant of the coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus by targeted RNA recombination. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):1841–1848. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.1841-1848.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara M., Omata T., Kameda A., Semler B. L., Itoh H., Wimmer E., Nomoto A. In vitro phenotypic markers of a poliovirus recombinant constructed from infectious cDNA clones of the neurovirulent Mahoney strain and the attenuated Sabin 1 strain. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):786–792. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.786-792.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koolen M. J., Osterhaus A. D., Van Steenis G., Horzinek M. C., Van der Zeijst B. A. Temperature-sensitive mutants of mouse hepatitis virus strain A59: isolation, characterization and neuropathogenic properties. Virology. 1983 Mar;125(2):393–402. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90211-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusters J. G., Jager E. J., Niesters H. G., van der Zeijst B. A. Sequence evidence for RNA recombination in field isolates of avian coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus. Vaccine. 1990 Dec;8(6):605–608. doi: 10.1016/0264-410X(90)90018-H. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Monica N., Meriam C., Racaniello V. R. Mapping of sequences required for mouse neurovirulence of poliovirus type 2 Lansing. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):515–525. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.515-525.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Zhao B. T., Hori H., Bray M. Infectious RNA transcribed from stably cloned full-length cDNA of dengue type 4 virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5139–5143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Baric R. S., Makino S., Keck J. G., Egbert J., Leibowitz J. L., Stohlman S. A. Recombination between nonsegmented RNA genomes of murine coronaviruses. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):449–456. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.449-456.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M. Coronavirus: organization, replication and expression of genome. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:303–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.001511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. J., Shieh C. K., Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., La Monica N., Tuler J., Bagdzhadzhyan A., Lai M. M. The complete sequence (22 kilobases) of murine coronavirus gene 1 encoding the putative proteases and RNA polymerase. Virology. 1991 Feb;180(2):567–582. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90071-I. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig S., Jackson A. C., Hahn C. S., Griffin D. E., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Molecular basis of Sindbis virus neurovirulence in mice. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2329–2336. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2329-2336.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luytjes W., Krystal M., Enami M., Parvin J. D., Palese P. Amplification, expression, and packaging of foreign gene by influenza virus. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1107–1113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90766-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackett M., Smith G. L. Vaccinia virus expression vectors. J Gen Virol. 1986 Oct;67(Pt 10):2067–2082. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-10-2067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Fleming J. O., Keck J. G., Stohlman S. A., Lai M. M. RNA recombination of coronaviruses: localization of neutralizing epitopes and neuropathogenic determinants on the carboxyl terminus of peplomers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6567–6571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Keck J. G., Stohlman S. A., Lai M. M. High-frequency RNA recombination of murine coronaviruses. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):729–737. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.729-737.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Taguchi F., Fujiwara K. Defective interfering particles of mouse hepatitis virus. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90420-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Taguchi F., Hirano N., Fujiwara K. Analysis of genomic and intracellular viral RNAs of small plaque mutants of mouse hepatitis virus, JHM strain. Virology. 1984 Nov;139(1):138–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90335-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Yokomori K., Lai M. M. Analysis of efficiently packaged defective interfering RNAs of murine coronavirus: localization of a possible RNA-packaging signal. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6045–6053. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6045-6053.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters P. S., Sturman L. S. Background paper. Functions of the coronavirus nucleocapsid protein. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1990;276:235–238. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5823-7_32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mi S., Durbin R., Huang H. V., Rice C. M., Stollar V. Association of the Sindbis virus RNA methyltransferase activity with the nonstructural protein nsP1. Virology. 1989 Jun;170(2):385–391. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90429-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omata T., Kohara M., Kuge S., Komatsu T., Abe S., Semler B. L., Kameda A., Itoh H., Arita M., Wimmer E. Genetic analysis of the attenuation phenotype of poliovirus type 1. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):348–358. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.348-358.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachuk C. J., Bredenbeek P. J., Zoltick P. W., Spaan W. J., Weiss S. R. Molecular cloning of the gene encoding the putative polymerase of mouse hepatitis coronavirus, strain A59. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90520-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. E., Wimmer E. Production of guanidine-resistant and -dependent poliovirus mutants from cloned cDNA: mutations in polypeptide 2C are directly responsible for altered guanidine sensitivity. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):793–796. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.793-796.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Cloned poliovirus complementary DNA is infectious in mammalian cells. Science. 1981 Nov 20;214(4523):916–919. doi: 10.1126/science.6272391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasschaert D., Duarte M., Laude H. Porcine respiratory coronavirus differs from transmissible gastroenteritis virus by a few genomic deletions. J Gen Virol. 1990 Nov;71(Pt 11):2599–2607. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-11-2599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. M., Grakoui A., Galler R., Chambers T. J. Transcription of infectious yellow fever RNA from full-length cDNA templates produced by in vitro ligation. New Biol. 1989 Dec;1(3):285–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. M., Levis R., Strauss J. H., Huang H. V. Production of infectious RNA transcripts from Sindbis virus cDNA clones: mapping of lethal mutations, rescue of a temperature-sensitive marker, and in vitro mutagenesis to generate defined mutants. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3809–3819. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3809-3819.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki D., Barkhimer D. B., Sawicki S. G., Rice C. M., Schlesinger S. Temperature sensitive shut-off of alphavirus minus strand RNA synthesis maps to a nonstructural protein, nsP4. Virology. 1990 Jan;174(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90052-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki S. G., Sawicki D. L. Coronavirus transcription: subgenomic mouse hepatitis virus replicative intermediates function in RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1050–1056. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1050-1056.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaad M. C., Stohlman S. A., Egbert J., Lum K., Fu K., Wei T., Jr, Baric R. S. Genetics of mouse hepatitis virus transcription: identification of cistrons which may function in positive and negative strand RNA synthesis. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):634–645. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90529-Z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz B., Routledge E., Siddell S. G. Murine coronavirus nonstructural protein ns2 is not essential for virus replication in transformed cells. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4784–4791. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4784-4791.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethna P. B., Hung S. L., Brian D. A. Coronavirus subgenomic minus-strand RNAs and the potential for mRNA replicons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5626–5630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaan W. J., Rottier P. J., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A. Isolation and identification of virus-specific mRNAs in cells infected with mouse hepatitis virus (MHV-A59). Virology. 1981 Jan 30;108(2):424–434. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90449-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaan W., Cavanagh D., Horzinek M. C. Coronaviruses: structure and genome expression. J Gen Virol. 1988 Dec;69(Pt 12):2939–2952. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-12-2939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaan W., Delius H., Skinner M., Armstrong J., Rottier P., Smeekens S., van der Zeijst B. A., Siddell S. G. Coronavirus mRNA synthesis involves fusion of non-contiguous sequences. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1839–1844. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01667.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesley R. D., Woods R. D., Cheung A. K. Genetic basis for the pathogenesis of transmissible gastroenteritis virus. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4761–4766. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4761-4766.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokomori K., Lai M. M. Mouse hepatitis virus S RNA sequence reveals that nonstructural proteins ns4 and ns5a are not essential for murine coronavirus replication. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5605–5608. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5605-5608.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Most R. G., Bredenbeek P. J., Spaan W. J. A domain at the 3' end of the polymerase gene is essential for encapsidation of coronavirus defective interfering RNAs. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3219–3226. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3219-3226.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]