Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are posttranscriptional regulatory molecules that have been implicated in the regulation of immune responses, but their role in the immune response to Plasmodium infection is unknown. We studied the expression of selected miRNAs following infection of CBA mice with Plasmodium berghei ANKA (PbA), which causes cerebral malaria (CM), or Plasmodium berghei K173 (PbK), which causes severe malaria but without cerebral complications, termed non-CM. The differential expression profiles of selected miRNAs (let-7i, miR-27a, miR-150, miR-126, miR-210, and miR-155) were analyzed in mouse brain and heart tissue by quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR). We identified three miRNAs that were differentially expressed in the brain of PbA-infected CBA mice: let7i, miR-27a, and miR-150. In contrast, no miRNA changes were detected in the heart, an organ with no known pathology during acute malaria. To investigate the involvement of let-7i, miR-27a, and miR-150 in CM-resistant mice, we assessed the expression levels in gamma interferon knockout (IFN-γ−/−) mice on a C57BL/6 genetic background. The expression of let-7i, miR-27a, and miR-150 was unchanged in both wild-type (WT) and IFN-γ−/− mice following infection. Overexpression of these three miRNAs during PbA, but not PbK, infection in WT mice may be critical for the triggering of the neurological syndrome via regulation of their potential downstream targets. Our data suggest that in the CBA mouse at least, miRNA may have a regulatory role in the pathogenesis of severe malaria.
INTRODUCTION
Cerebral malaria (CM) is a major complication of Plasmodium falciparum infection, which remains a major public health issue worldwide. CM is characterized by unarousable coma and neurological sequelae. This debilitating syndrome accounts for the majority of the one million malaria-induced deaths annually (33, 51). Numerous studies have extensively documented the dynamic interactions between host cell sequestration, a deregulated inflammatory response, and the homeostatic dysfunction observed in cases of CM (30, 31, 66). However, the underlying pathogenesis is poorly understood and remains a hotly debated topic (32, 46, 68).
Despite promising therapeutic agents, no treatment provides complete amelioration in humans or mice (24, 67). Mouse models have been an invaluable tool for the study of the underlying pathogenesis of CM (20, 31, 32). Murine models selectively mimic either the CM syndrome or a nonencephalitic syndrome, depending on the parasite strain used as well as the strain of inbred mouse (15, 39, 58). A model for CM is infection with Plasmodium berghei ANKA (PbA) in CBA or C57BL/6 mice, leading to fatal disease with cerebral pathology within 10 days (25). Conversely, infecting CBA or C57BL/6 mice with P. berghei K173 (PbK) leads to a fatal disease due to hyperparasitemia and anemia approximately 14 days postinfection (48, 56).
Even with well-documented, inbred, murine CM models, little is known about the mechanisms responsible for the deregulation of immune responses that is seen in cases of CM (20, 31, 47). Recently, microRNAs (miRNAs) have emerged as important regulators of pathophysiological conditions modeled in vitro (36, 73) and in vivo (65). miRNAs are short (20 to 24 nucleotides) endogenous noncoding RNAs that control gene expression at the posttranscriptional level by inhibiting translation or inducing degradation of target messenger mRNAs by binding to their 3′ untranslated regions (6, 11, 22).
This ability to bind to mRNA targets increases the functional power of miRNAs to regulate the expression of multiple genes (3, 4, 14, 40). They represent an important class of regulatory molecules in a wide range of biological processes, including metabolism, development, cell proliferation and differentiation, hematopoiesis, oncogenesis, and apoptosis (reviewed in references 1, 6, 10, and 23). Abnormal miRNA expression has been associated with diabetes, cancer, heart diseases, neurological diseases, and immune function in disease (16, 36, 42, 57, 62). miRNAs have gained recognition for their importance in regulating gene expression following parasitic and bacterial infections. One group has demonstrated a let-7-dependent induction of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), which could be modulated upon stimulation with Cryptosporidium parvum (12). Furthermore, upon challenge with either C. parvum or lipopolysaccharide (LPS), the levels of let-7i were repressed in vitro by a mechanism involving NF-κB (50). Also, Helicobacter pylori was able to induce increased miR-155 expression in epithelial cells in vitro (70).
Currently, it is unknown whether miRNAs play a role in the pathogenesis of CM. Murine CM pathogenesis is multifaceted and involves apoptosis (38, 69), immune modulation (31), cytoadhesion (5), and possibly hypoxia (53). We chose six miRNAs involved in these signaling events.
Using quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR), we analyzed the relative expression levels of these miRNAs in the brain and heart tissues of the experimental groups. The miRNA expression profile in the heart was deemed a control, since there is no described pathology associated with CM in that organ.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Mice and parasite inoculation.
CBA mice, 7 weeks old, and wild-type (WT) C57BL/6 mice, 9 weeks old, were purchased from the Animal Resources Centre (Canning Vale, Western Australia). Gamma interferon knockout (IFN-γ−/−) mice were obtained from G. Karupiah, Australian National University, Canberra, Australia, and bred in-house. IFN-γ−/− mice have been backcrossed to C57BL/6 mice 10 times (17). All mice were handled according to approved protocols of the University of Sydney Animal Ethics Committee (approval number K20/7-2006/3/4434). Mice were fed a commercial rodent pellet diet and had access to water ad libitum. Experimental mice were studied under pathogen-free conditions and monitored daily. For experiments using CBA mice, three groups of seven mice were maintained: not infected (NI), PbA infected, and PbK infected. Experiments using C57BL/6 WT and IFN-γ−/− mice were designed with two groups of seven mice each: NI and PbA infected.
Plasmodium infection was induced by intraperitoneal injection of parasitized red blood cells (PbA, 1 + 106 cells/mouse; and PbK, 2 + 106 cells/mouse). The PbA and PbK stabilates were prepared as previously described (25). Mice were euthanized 7 days postinoculation. Parasitemia was monitored by counting 500 erythrocytes in Diff-Quick-stained thin blood smears.
miRNA extraction.
Seven days postinfection, brain and heart tissue were removed from infected and noninfected mice. Organs were homogenized in 1 ml TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen). Chloroform (0.2 ml) was added, and the sample was shaken vigorously and centrifuged to achieve phase separation. Precipitation of RNA from the aqueous phase was achieved with the addition of 500 μl of isopropanol and pelleted at 12,000 + g for 10 min. RNA was washed with 75% (vol/vol) ethanol and redissolved in water. The concentration of RNA was determined using NanoDrop ND-1000 spectrophotometry (NanoDrop Tech). The purity of the preparation of RNA was assessed by calculating the ratio at 260 and 280 nm. All RNA preparations had a ratio of absorbance (260/280 nm) greater than 1.8.
cDNA synthesis and PCR.
cDNA synthesis and PCR were performed using a commercial kit (NCode miRNA first-strand cDNA synthesis and qRT-PCR kit; Invitrogen) per the manufacturer's instructions. The starting miRNA concentration was set at 500 ng. An aliquot (2.5 μl) of the cDNA was used for PCR using specific forward primers for the selected miRNA and the reverse primer a universal qPCR primer. Reactions were performed in triplicate by qRT-PCR with a LightCycler type II (Roche) using a SYBR green master mix. Expression levels of the selected miRNA in PbA- and PbK-infected mice were compared with those in noninfected controls after normalization against the housekeeping gene (miR-U6) using the cycle threshold (ΔΔCT) method (43).
Plasmodium DNA PCR assay.
Brain tissue was collected from mice as aforementioned, snap-frozen, and stored at −80°C. Brains were homogenized in 0.5 ml of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) using 0.7-mm zirconia beads (Biospec) and a FastPrep FP120 homogenizer (Savant). Genomic DNA was isolated from 50 μl of homogenate using a High Pure PCR template preparation kit (Roche, Switzerland). The gene for carbamoyl phosphate synthetase has been sequenced for both PbA (GenBank accession number XM674283) and PbK (AF286897) strains. Primers were designed to have a 100% match to the PbA and PbK gene sequence. Levels of parasite DNA were expressed relative to levels of the mouse gene product tyrosine 3-monooxygenase activation protein, zeta polypeptide (YWHAZ; NM_011740). PCR amplification was performed with a 20-μl reaction using Immomix (Bioline, United Kingdom) with added SYBR green (Invitrogen) and a 200 nM concentration of the primer. A “touchdown” amplification protocol was used with a Rotor-Gene 3000 (Corbett Research, Australia). The protocol consisted of 95°C for 15 s, 60°C for 15 s and then decreasing by 1°C/cycle for 5 cycles (then 55°C for the remaining 30 cycles), and 72°C for 20 s (35 cycles total). Serial dilutions of DNA from PbA- and PbK-infected mice were used to demonstrate that the P. berghei sequence is amplified with the same efficiency from the PbA and PbK templates and that this efficiency was also similar to that of amplification of the mouse gene. Purity of the PCR products was assessed by melting curve analysis. Cycle threshold (CT) values were determined for the parasite and mouse genes, and the parasite burden was expressed as 1/(parasite gene CT − mouse gene CT). The following primers were used: P. berghei carbamoyl phosphate synthetase forward (Fwd), TAAAACTGCTATTCAAACCGCC; reverse (Rev), GCTACCCCATTCTAGTGCGTACT; YWHAZ Fwd, TGTCACCAACCATTCCAACTTG; Rev, ACACTGAGTGGAGCCAGAAAGA.
Statistical analysis.
Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism, version 5 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA). The relative expression values were analyzed using the nonparametric Kruskal-Wallis test. When appropriate, post hoc tests (Dunn's multiple comparison tests) were applied. Intergroup comparisons were considered significant for P values less than 0.05.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Increased expression of let-7i, miR-150, and miR-27a following PbA infection in the brain.
P. falciparum and P. berghei infections trigger multifaceted cascades of events that lead to microvascular obstruction and to the dysregulation of immune and inflammatory processes, ultimately causing CM (20, 31, 60). Previous studies have strongly implicated some miRNAs (let-7i, miR-27a, miR-150, miR-210, miR-155, and miR-126) in the regulation of normal immune and inflammatory responses (7, 12, 55, 71).
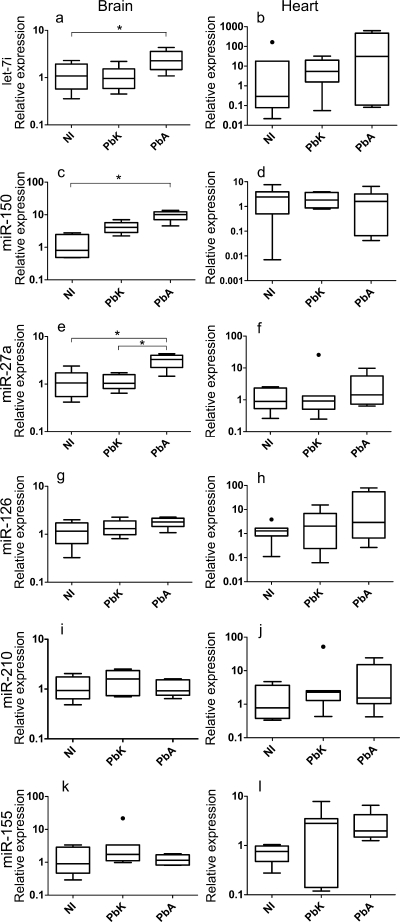
We first compared brain and heart miRNA expression levels between infected (PbA and PbK) and noninfected (NI) CBA mice. Using qRT-PCR with forward primers specific for the selected miRNA, we observed a distinct expression profile in the brains of PbA- and PbK-infected and NI mice. Our selected miRNAs were expressed at detectable levels in the brain under normal physiological conditions, but their expression levels after the inoculation of PbA and/or PbK were altered in most cases. We found significant changes among the three groups in the expression of let-7i (Fig. 1a) (P = 0.017), miR-150 (Fig. 1c) (P < 0.001), and miR-27a (Fig. 1e) (P = 0.006) in the brain tissue, with expression remaining unchanged in the heart tissue (P was >0.05 for all three miRNAs) (Fig. 1). These results suggested a role for these miRNAs in cerebral pathology, since their altered expression levels coincide with increased levels of circulating inflammatory cytokines and apoptosis within the brain (38).
Fig. 1.
Inflammation-associated miRNAs in brain and heart tissues in cases of cerebral (PbA) versus noncerebral (PbK) malaria and NI tissues. Box plots show miRNA expression levels measured for NI and PbK- and PbA-infected brain and heart tissues, expressed as normalized values using miR-U6 as the endogenous control. The horizontal line denotes the median value, the box encompasses the upper and lower quartiles, whiskers show 1.5+ the interquartile range (Tukey), and outliers are denoted with a closed circle. We detected a significant increase in the expression of let-7i (P value of 0.017), miR-27a (0.006), and miR-150 (<0.001) in brain tissue following PbA infection. If the Kruskal-Wallis test was significant, post hoc tests were carried out. The results of these are denoted in the plot with horizontal bars and asterisks (*, P < 0.05). No changes were discernible in miR-126 (P = 0.16), miR-155 (P = 0.31), and miR-210 (P = 0.34) following infection. No changes in expression were detected in heart tissue. These data represent results of three independent experiments, with 7 animals in each group.
The difference between the two strains of parasite could not be attributed to differences in parasitemia, because the parasite loads in the brain vessels were comparable (Fig. 2) and it is known that plasmodia do not express miRNA (72). Mice inoculated with PbA-infected erythrocytes became moribund on day 7, displaying neurological signs, including partial paralysis, seizures, and coma. No such signs were present in the PbK-infected group, which progress to severe malarial anemia, with hyperparasitemia 14 days postinfection (47, 48).
Fig. 2.
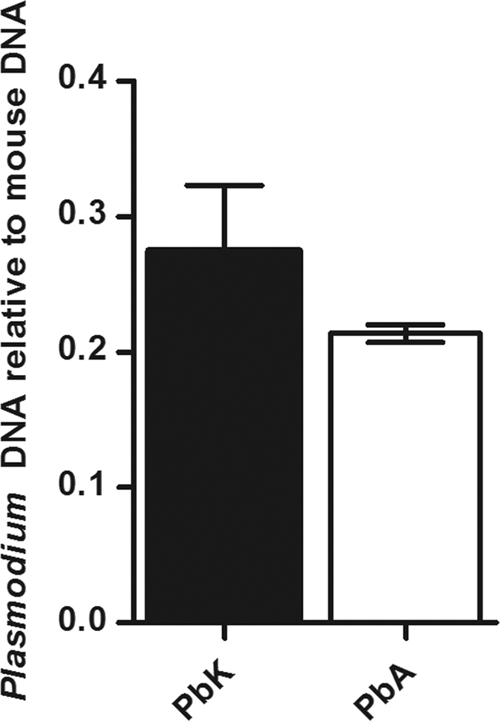
Parasite burden in the brain of PbA- and PbK-infected CBA mice. Plasmodium DNA PCR assay was performed with brain tissue sampled from mice at 7 days postinfection. Parasite DNA could not be detected in the control mice (noninfected). Parasite burden is expressed as 1/(parasite gene CT − mouse gene CT). No difference in parasite load was observed (n = 5 animals per group).
Having demonstrated that PbA and PbK infections induced changes in certain miRNAs, we searched for their potential targets, particularly those pertaining to the cerebral syndrome. Analysis of predicted targets from an open-access database, miRBase (http://www.miRbase.org) (26), that encapsulates algorithms from TargetScan (41) and PicTar (37) allowed correlations between microRNAs and their gene targets, particularly those regulating inflammation-associated protein expression, innate pathogen recognition, apoptosis, and immune function.
The let-7 family is known to orchestrate a role in cellular proliferation and the innate immune response (8, 12, 50). In our study, let-7i expression across the groups is significantly altered, and the expression is significantly increased in PbA-infected CBA mice versus that in NI mice (P < 0.05) (Fig. 1a). In vitro studies show that let-7i mediates toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) expression via translational regulation and contributes to epithelial immune responses in cholangiocytes (12). The role of TLRs in the recognition of P. falciparum and their contribution to the cerebral syndrome have been controversial. Studies have shown that the microvascular damage induced by PbA infection is independent of TLR4 (63). Interestingly, these studies used C57BL/6 mice to draw these conclusions, and our data on the expression of let-7i in C57BL/6 mice reflects no change postinfection. However, the increase in expression of let-7i in CBA mice suggests a difference in host genetic factors affecting the role of TLR4 in response to Plasmodium. To date, TLR4 in PbA-infected CBA mice has not been studied.
Both strains of parasite induced an increase in the expression of miR-150 compared with that in NI mice, with PbA inducing a greater, and statistically significant, response (P < 0.05; P > 0.05 for PbK versus NI) (Fig. 1c and d). miR-150 is highly expressed in monocytes and is implicated in cell proliferation, development, and differentiation. miR-150 targets the c-Myb transcription factor, a gene related to cell proliferation and apoptosis. Accumulation of monocytes in the cerebral microvasculature has been associated with fatal murine CM (35). The sequestration of monocytes within the cerebral microvessels of PbK-infected mice is observed, although more are seen with PbA-infected mice (48). miR-150 may regulate the accumulation of monocytes and CD8+ T cells postinfection, and the increased relative expression can be indicative of their direct role in the fatal syndrome or in controlling the infection.
miR-27a expression was significantly increased in PbA-infected mice compared with that in both NI and PbK-infected mice (P < 0.05) (Fig. 1e and f), suggesting that miR-27a has the most specific CM fingerprint among our six selected miRNAs. Previously, miR-27a was reported to induce apoptosis, disrupt mitochondrial membrane potential, and increase TNF sensitivity in embryonic kidney cells in vitro (13). The Fas-associated death domain (FADD) was pinpointed as a potential target for miR-27a, and due to its involvement in regulating T cell proliferation and the NF-κB signaling pathway during inflammation (64), its upregulation in PbA-infected brain is not surprising (49, 74). The FADD is also known to heighten the sensitivity of cells to TNF, and this supports our data, as the expression of miR-27a coincides with an increase in TNF expression during PbA infection (18).
PbA and PbK infections have been studied closely to assess the delicate balance between a protective and deleterious role for T cells and IFN-γ in early- and late-stage Plasmodium infection. We know that mice infected with PbK display a transient peak of cytokines, particularly of IFN-γ, 24 h postinfection, which is absent in mice infected with PbA. It has been suggested that the early production of IFN-γ may be able to divert the disease course from the development of CM (47). Mice deficient in IFN-γ (i.e., IFN-γ −/− mice) do not develop CM (27, 59), and neutralizing anti-IFN-γ antibodies administered in the early course of infection also provide protection (24). The relevance of these observations to human CM has been suggested by studies of the induction of IFN-γ in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) by Plasmodium falciparum (2).
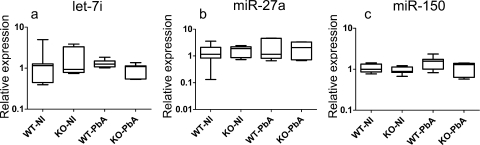
To evaluate the relationship between the expression levels of let-7i, miR-27a, and miR-150 and the development of the cerebral syndrome, their expression profiles were studied with the IFN-γ −/− model. Using C57BL/6 WT mice as controls, we found no changes in the expression levels of these miRNAs upon PbA infection in WT or knockout mice (Fig. 3a to c). Our data suggest that strain differences may be a factor in the study of miRNA expression. CBA and C57BL/6 mice have been highly studied as models of CM, although considerable differences in neuropathology have been reported (52). Our data show that the expression profiles of let-7i, miR-27a, and miR-150 are not the same in the two strains, and this could have implications for the study of CM pathogenesis in humans (21).
Fig. 3.
miR-27a, miR-150, and let-7i expression in the brains of PbA-infected C57BL/6 (WT) and IFN-γ−/− (KO) mice. miRNA expression levels were measured in noninfected (NI) and PbA-infected (PbA) brain tissues and expressed as normalized values using miR-U6 as the endogenous control. The line denotes median value, the box encompasses the upper and lower quartiles, and whiskers show 1.5+ the interquartile range (Tukey). No statistically significant difference was detected. These data represent results of two independent experiments, with 7 animals in each group.
No change observed in the expression profiling of miR-126, miR-155, and miR-210 or following Plasmodium challenge.
miR-126 is selectively expressed in endothelial cells and has been described as having a role in vascular inflammation, particularly in the regulation of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) (28). Numerous studies have shown that the expression of VCAM-1 on endothelial cells is upregulated in the brain vessels of CM mice (19, 44, 45, 54). Contrary to our prediction, we could not detect a change in miR-126 expression (Fig. 1g and h). Since miRNAs have several targets and several miRNAs orchestrate the regulation of downstream targets, the regulation of adhesion molecules on endothelial cells in CM is possibly more complex than what is indicated in a in vitro setting (28). Moreover, Harris et al. (28) found very limited expression of miR-126 in brain tissue compared to that in heart tissue, so the expression of other miRNAs could possibly be of relevance in this context (61).
miR-155 targets an important component of the inflammatory cascade, the negative regulator of IFN-γ signaling suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS1) (34). C57BL/6 mice lacking SOCS1 are resistant to CM upon PbA infection (9). miR-155 is known to be highly expressed in immune cell subsets, particularly in T cells, and regulates their differentiation and proliferation. We analyzed its expression in PbA- and PbK-infected CBA brain and heart tissues and found no changes compared to that in tissues from healthy mice (Fig. 1k and l).
miR-210 is involved in the regulation of genes pertaining to hypoxia, particularly hypoxia-inducible transcription factor 1α (HIF-1α) (29). Hypoxia is likely to be present in human and murine CM due to microvessel obstruction caused by cellular sequestration. We predicted an increase in the expression of miR-210 in the brain in PbA infection, reflecting the response of miR-210 expression to hypoxia. We detected no significant changes (Fig. 1i and j). We propose that the duration of time in which the tissue is hypoxic during PbA infection may be insufficient to induce a change in miR-210 expression.
Conclusions.
These findings show that alteration in the expression of miR-27a, miR-150, and let-7i is an event induced by infection of CBA mice with PbA and that the host genetic background may play a role in identifying a miRNA fingerprint of murine CM. Furthermore, our data suggest a potential link between alterations in miRNA expression and the pathogenesis of CM. To our knowledge, no other study has yet explored the possible roles of miRNAs in murine CM.
The upregulation of these miRNAs opens a new avenue for the investigation of gene regulation in the development of this neurological syndrome. This study provides a platform for the design of functional studies to elucidate the role of miRNA in CM pathogenesis, with a view to using miRNAs as targets for new therapeutic interventions.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work is supported by grants from the Australian Research Council and the National Health Medical Research Council, Australia. The support of the AL Kerr Bequest, Sydney Medical School, is also gratefully acknowledged.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print on 21 March 2011.
REFERENCES
- 1. Ambros V. 2004. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431:350–355 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Artavanis-Tsakonas K., Riley E. M. 2002. Innate immune response to malaria: rapid induction of IFN-gamma from human NK cells by live Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. J. Immunol. 169:2956–2963 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Asirvatham A. J., et al. 2008. MicroRNA targets in immune genes and the Dicer/Argonaute and ARE machinery components. Mol. Immunol. 45:1995–2006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Baltimore D., et al. 2008. MicroRNAs: new regulators of immune cell development and function. Nat. Immunol. 9:839–845 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Baptista F. G., et al. 2010. Accumulation of Plasmodium berghei-infected red blood cells in the brain is crucial for the development of cerebral malaria in mice. Infect. Immun. 78:4033–4039 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Bartel D. P. 2004. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Belair C., Darfeuille F., Staedel C. 2009. Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer: possible role of microRNAs in this intimate relationship. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 15:806–812 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Bueno M. J., et al. 2010. Multiple E2F-induced microRNAs prevent replicative stress in response to mitogenic signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 30:2983–2995 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Bullen D. V., et al. 2003. The lack of suppressor of cytokine signalling-1 (SOCS1) protects mice from the development of cerebral malaria caused by Plasmodium berghei ANKA. Parasite Immunol. 25:113–118 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Calin G. A., Croce C. M. 2006. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat. Rev. Cancer 6:857–866 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Castanotto D., et al. 2009. CRM1 mediates nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling of mature microRNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 106:21655–21659 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Chen X.-M., et al. 2007. A cellular micro-RNA, let-7i, regulates Toll-like receptor 4 expression and contributes to cholangiocyte immune responses against Cryptosporidium parvum infection. J. Biol. Chem. 282:28929–28938 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Chhabra R., et al. 2009. Upregulation of miR-23a–27a-24-2 cluster induces caspase-dependent and -independent apoptosis in human embryonic kidney cells. PLoS One 4:e5848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Cobb B. S., et al. 2006. A role for Dicer in immune regulation. J. Exp. Med. 203:2519–2527 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Combes V., De Souza J. B., Rénia L., Hunt N. H., Grau G. E. 2005. Cerebral malaria: Which parasite? Which model? Drug Discov. Today Dis. Models 2:141–147 [Google Scholar]
- 16. Dahlberg J. E., et al. 2007. Micromanagement during the innate immune response. Sci. STKE 2007:pe25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Dalton D. K., et al. 1993. Multiple defects of immune cell function in mice with disrupted interferon-gamma genes. Science 259:1739–1742 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. de Kossodo S., Grau G. E. 1993. Role of cytokines and adhesion molecules in malaria immunopathology. Stem Cells 11:41–48 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Delahaye N. F., et al. 2006. Gene-expression profiling discriminates between cerebral malaria (CM)-susceptible mice and CM-resistant mice. J. Infect. Dis. 193:312–321 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. de Souza J. B., et al. 2010. Cerebral malaria: why experimental murine models are required to understand the pathogenesis of disease. Parasitology 137:755–772 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. de Souza J. B., Riley E. M. 2002. Cerebral malaria: the contribution of studies in animal models to our understanding of immunopathogenesis. Microbes Infect. 4:291–300 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Engels B. M., Hutvagner G. 2006. Principles and effects of microRNA-mediated post-transcriptional gene regulation. Oncogene 25:6163–6169 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Esquela-Kerscher A., Slack F. J. 2006. Oncomirs—microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 6:259–269 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Golenser J., et al. 2006. Conventional and experimental treatment of cerebral malaria. Int. J. Parasitol. 36:583–593 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Grau G. E., et al. 1986. L3T4+ T lymphocytes play a major role in the pathogenesis of murine cerebral malaria. J. Immunol. 137:2348–2354 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Griffiths-Jones S., et al. 2006. miRBase: microRNA sequences, targets and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res. 34(Suppl. 1):D140–D144 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Hansen A. M., Chaudhri G., Hunt N. H. 1999. Role of immune mediators in the pathology of experimental murine cerebral malaria. Redox Rep. 4:321–322 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Harris T. A., et al. 2008. MicroRNA-126 regulates endothelial expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105:1516–1521 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Huang X., Le Q. T., Giaccia A. J. 2010. MiR–210-micromanager of the hypoxia pathway. Trends Mol. Med. 16:230–237 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Hunt N. H., et al. 2006. Immunopathogenesis of cerebral malaria. Int. J. Parasitol. 36:569–582 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Hunt N. H., Grau G. E. 2003. Cytokines: accelerators and brakes in the pathogenesis of cerebral malaria. Trends Immunol. 24:491–499 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Hunt N. H., et al. 2010. Murine cerebral malaria: the whole story. Trends Parasitol. 26:272–274 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Idro R., et al. 2007. Burden, features, and outcome of neurological involvement in acute falciparum malaria in Kenyan children. JAMA 297:2232–2240 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Iorio M. V., et al. 2005. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 65:7065–7070 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Jerusalem C., et al. 1983. Comparative clinical and experimental study on the pathogenesis of cerebral malaria. Contrib. Microbiol. Immunol. 7:130–138 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Johnnidis J. B., et al. 2008. Regulation of progenitor cell proliferation and granulocyte function by microRNA-223. Nature 451:1125–1129 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Krek A., et al. 2005. Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nature Genetics 37:495–500 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Lackner P., et al. 2007. Apoptosis in experimental cerebral malaria: spatial profile of cleaved caspase-3 and ultrastructural alterations in different disease stages. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 33:560–571 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Langhorne J., Quin S. J., Sanni L. A. 2002. Mouse models of blood-stage malaria infections: immune responses and cytokines involved in protection and pathology. Chem. Immunol. 80:204–228 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Lewis B. P., Burge C. B., Bartel D. P. 2005. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120:15–20 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Lewis B. P., et al. 2003. Prediction of mammalian MicroRNA targets. Cell 115:787–798 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Li Q. J., et al. 2007. miR-181a is an intrinsic modulator of T cell sensitivity and selection. Cell 129:147–161 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Livak K. J., Schmittgen T. D. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔC(T) Method. Methods 25:402–408 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Lucas R., et al. 1997. Respective role of TNF receptors in the development of experimental cerebral malaria. J. Neuroimmunol. 72:143–148 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Ma N., Hunt N. H., Madigan M. C., Chan-Ling T. 1996. Correlation between enhanced vascular permeability, up-regulation of cellular adhesion molecules and monocyte adhesion to the endothelium in the retina during the development of fatal murine cerebral malaria. Am. J. Pathol. 149:1745–1762 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Maude R. J., et al. 2009. The eye in cerebral malaria: what can it teach us? Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 103:661–664 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Mitchell A. J., et al. 2005. Early cytokine production is associated with protection from murine cerebral malaria. Infect. Immun. 73:5645–5653 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Neill A. L., Hunt N. H. 1992. Pathology of fatal and resolving Plasmodium-berghei cerebral malaria in mice. Parasitology 105:165–175 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Newton K., et al. 1998. A dominant interfering mutant of FADD/MORT1 enhances deletion of autoreactive thymocytes and inhibits proliferation of mature T lymphocytes. EMBO J. 17:706–718 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. O'Hara S. P., et al. 2010. NFkappaB p50-CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta (C/EBPbeta)-mediated transcriptional repression of microRNA let-7i following microbial infection. J. Biol. Chem. 285:216–225 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. O'Meara W. P., et al. 2010. Changes in the burden of malaria in sub-Saharan Africa. Lancet Infect. Dis. 10:545–555 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Parekh S. B., et al. 2006. Brain metabolic markers reflect susceptibility status in cytokine gene knockout mice with murine cerebral malaria. Int. J. Parasitol. 36:1409–1418 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Penet M.-F., et al. 2005. Imaging experimental cerebral malaria in vivo: significant role of ischemic brain edema. J. Neurosci. 25:7352–7358 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Porta J., et al. 1993. Immunopathological changes in human cerebral malaria. Clin. Neuropathol. 12:142–146 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Pulkkinen K., et al. 2008. Hypoxia induces microRNA miR-210 in vitro and in vivo ephrin-A3 and neuronal pentraxin 1 are potentially regulated by miR-210. FEBS Lett. 582:2397–2401 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Rae C., et al. 2004. Brain gene expression, metabolism, and bioenergetics: interrelationships in murine models of cerebral and noncerebral malaria. FASEB J. 18:499–510 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Rodriguez A., et al. 2007. Requirement of bic/microRNA-155 for normal immune function. Science 316:608–611 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Sanni L. A., Fonseca L. F., Langhorne J. 2002. Mouse models for erythrocytic-stage malaria. Methods Mol. Med. 72:57–76 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Sanni L. A., et al. 1998. Dramatic changes in oxidative tryptophan metabolism along the kynurenine pathway in experimental cerebral and noncerebral malaria. Am. J. Pathol. 152:611–619 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Schofield L., Grau G. E. 2005. Immunological processes in malaria pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 5:722–735 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Suarez Y., et al. 2010. Cutting edge: TNF-induced microRNAs regulate TNF-induced expression of E-selectin and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 on human endothelial cells: feedback control of inflammation. J. Immunol. 184:21–25 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Tili E., et al. 2007. Modulation of miR-155 and miR-125b levels following lipopolysaccharide/TNF-alpha stimulation and their possible roles in regulating the response to endotoxin shock. J. Immunol. 179:5082–5089 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Togbe D., et al. 2007. Murine cerebral malaria development is independent of toll-like receptor signaling. Am. J. Pathol. 170:1640–1648 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Tourneur L., Chiocchia G. 2010. FADD: a regulator of life and death. Trends Immunol. 31:260–269 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Urbich C., Kuehbacher A., Dimmeler S. 2008. Role of microRNAs in vascular diseases, inflammation, and angiogenesis. Cardiovasc. Res. 79:581–588 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. van der Heyde H. C., et al. 2006. A unified hypothesis for the genesis of cerebral malaria: sequestration, inflammation and hemostasis leading to microcirculatory dysfunction. Trends Parasitol. 22:503–508 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. van Hensbroek M. B., et al. 1996. A trial of artemether or quinine in children with cerebral malaria. N. Engl. J. Med. 335:69–75 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. White N. J., et al. 2010. The murine cerebral malaria phenomenon. Trends Parasitol. 26:11–15 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Wiese L., Kurtzhals J. A. L., Penkowa M. 2006. Neuronal apoptosis, metallothionein expression and proinflammatory responses during cerebral malaria in mice. Exp. Neurol. 200:216–226 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Xiao B., et al. 2009. Induction of microRNA-155 during Helicobacter pylori infection and its negative regulatory role in the inflammatory response. J. Infect. Dis. 200:916–925 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Xiao C., et al. 2007. MiR-150 controls B cell differentiation by targeting the transcription factor c-Myb. Cell 131:146–159 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Xue X., Zhang Q., Huang Y., Feng L., Pan W. 2008. No miRNA were found in Plasmodium and the ones identified in erythrocytes could not be correlated with infection. Malar. J. 7:47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Zernecke A., et al. 2009. Delivery of microRNA-126 by apoptotic bodies induces CXCL12-dependent vascular protection. Sci. Signal. 2:ra81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Zhang J., et al. 1998. Fas-mediated apoptosis and activation-induced T-cell proliferation are defective in mice lacking FADD/Mort1. Nature 392:296–300 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]