Abstract
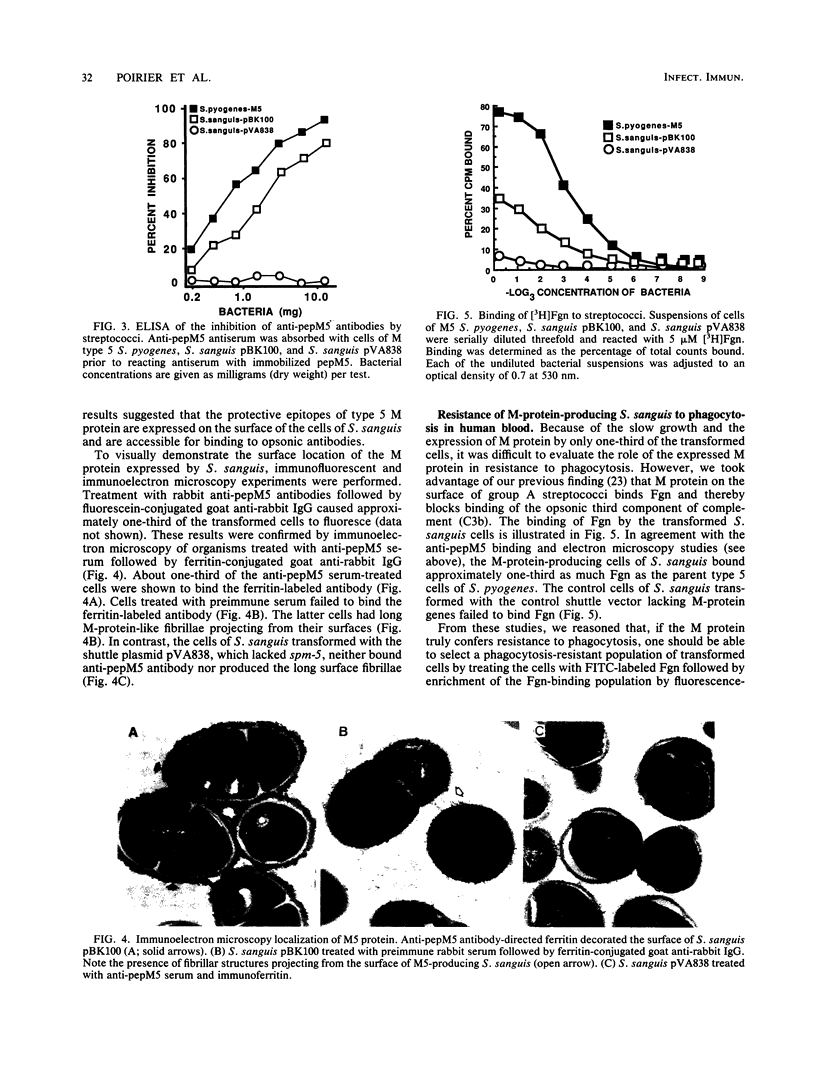
The biological properties of Streptococcus pyogenes M protein cloned and expressed in S. sanguis were investigated. The spm-5 gene previously cloned into Escherichia coli was subcloned into the E. coli-S. sanguis shuttle plasmid pVA838 to produce a newly constructed plasmid, pBK100. Cells of S. sanguis transformed with pBK100 expressed 53-, 55-, and 58-kilodalton polypeptides reacting with type 5 M protein antiserum in immunoblots. The M protein was expressed on the surface of S. sanguis cells as shown by the capacity of the intact cells to (i) inhibit the reactivity of anti-type 5 antibodies with purified M protein as demonstrated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; (ii) inhibit the opsonization by M5 antisera of type 5 S. pyogenes; (iii) express M-protein-like fibrils on the surface of the organisms that react with M5 antisera as revealed by immunoelectron microscopy; (iv) bind plasma fibrinogen and, as a consequence, resist phagocytosis by human blood neutrophils; and (v) be rendered susceptible to phagocytosis by opsonic M5 antisera. These results provide additional evidence that streptococcal M proteins bind host proteins as a ploy to evade host defense mechanisms.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beachey E. H., Campbell G. L., Ofek I. Peptic digestion of streptococcal M protein. II. Extraction of M antigen from group A streptococci with pepsin. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):891–896. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.891-896.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Ofek I. Epithelial cell binding of group A streptococci by lipoteichoic acid on fimbriae denuded of M protein. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):759–771. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Stollerman G. H., Johnson R. H., Ofek I., Bisno A. L. Human immune response to immunization with a structurally defined polypeptide fragment of streptococcal M protein. J Exp Med. 1979 Oct 1;150(4):862–877. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.4.862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horstmann R. D., Sievertsen H. J., Knobloch J., Fischetti V. A. Antiphagocytic activity of streptococcal M protein: selective binding of complement control protein factor H. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1657–1661. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks-Weis J., Kim Y., Cleary P. P. Restricted deposition of C3 on M+ group A streptococci: correlation with resistance to phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1897–1902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe M. A., Poirier T. P., Beachey E. H., Timmis K. N. Cloning and genetic analysis of serotype 5 M protein determinant of group A streptococci: evidence for multiple copies of the M5 determinant in the Streptococcus pyogenes genome. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):190–197. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.190-197.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe M., Timmis K. N. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the streptolysin O determinant from Streptococcus pyogenes: characterization of the cloned streptolysin O determinant and demonstration of the absence of substantial homology with determinants of other thiol-activated toxins. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):804–810. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.804-810.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Current knowledge of type-specific M antigens of group A streptococci. J Immunol. 1962 Sep;89:307–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBoeuf R. D., Raja R. H., Fuller G. M., Weigel P. H. Human fibrinogen specifically binds hyaluronic acid. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12586–12592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Tobian J. A., Jones K. R., Evans R. P., Clewell D. B. A cloning vector able to replicate in Escherichia coli and Streptococcus sanguis. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):345–353. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier T. P., Kehoe M. A., Beachey E. H. Protective immunity evoked by oral administration of attenuated aroA Salmonella typhimurium expressing cloned streptococcal M protein. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):25–32. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier T. P., Kehoe M. A., Dale J. B., Timmis K. N., Beachey E. H. Expression of protective and cardiac tissue cross-reactive epitopes of type 5 streptococcal M protein in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):198–203. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.198-203.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. R., Fischetti V. A. Expression of streptococcal M protein in Escherichia coli. Science. 1983 Aug 19;221(4612):758–760. doi: 10.1126/science.6192499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. R., Guenthner P. C., Malone L. M., Fischetti V. A. Conversion of an M- group A streptococcus to M+ by transfer of a plasmid containing an M6 gene. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1641–1651. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyer J. M., Kang A. H., Beachey E. H. Primary structural similarities between types 5 and 24 M proteins of Streptococcus pyogenes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 29;92(2):546–553. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90368-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spanier J. G., Jones S. J., Cleary P. Small DNA deletions creating avirulence in Streptococcus pyogenes. Science. 1984 Aug 31;225(4665):935–938. doi: 10.1126/science.6089334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitnack E., Beachey E. H. Inhibition of complement-mediated opsonization and phagocytosis of Streptococcus pyogenes by D fragments of fibrinogen and fibrin bound to cell surface M protein. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):1983–1997. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitnack E., Bisno A. L., Beachey E. H. Hyaluronate capsule prevents attachment of group A streptococci to mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):985–991. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.985-991.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





