Abstract
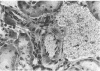
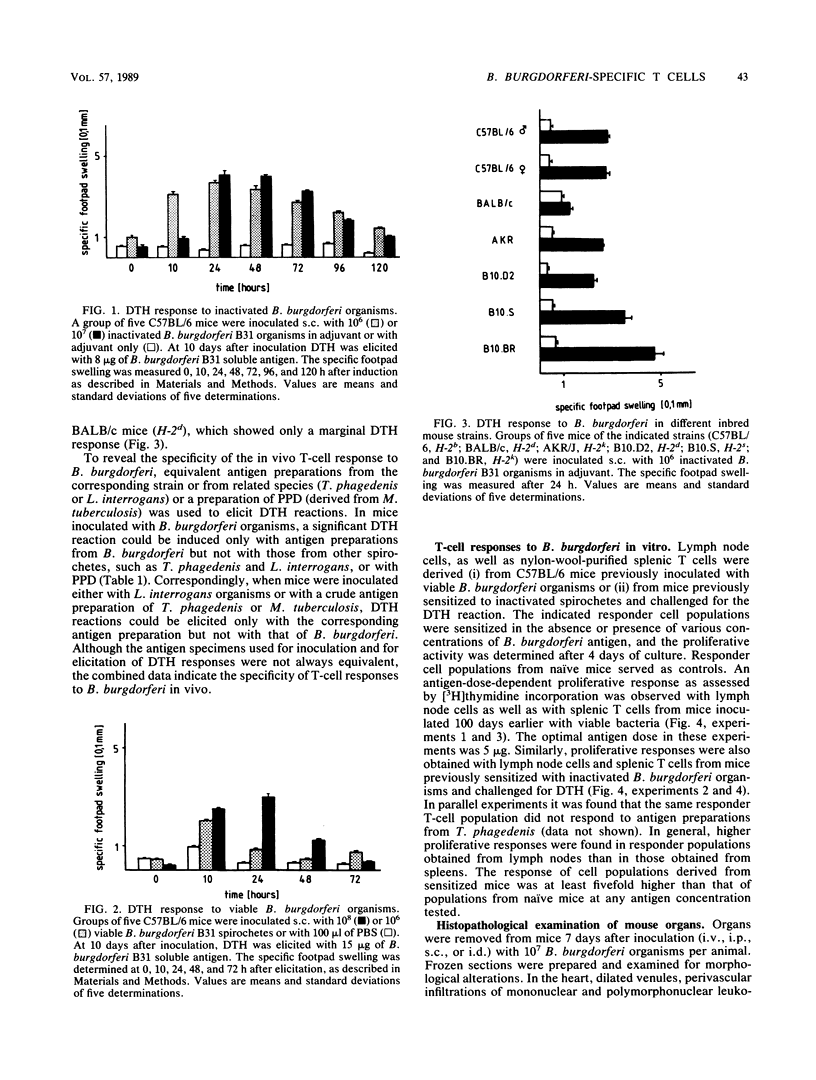
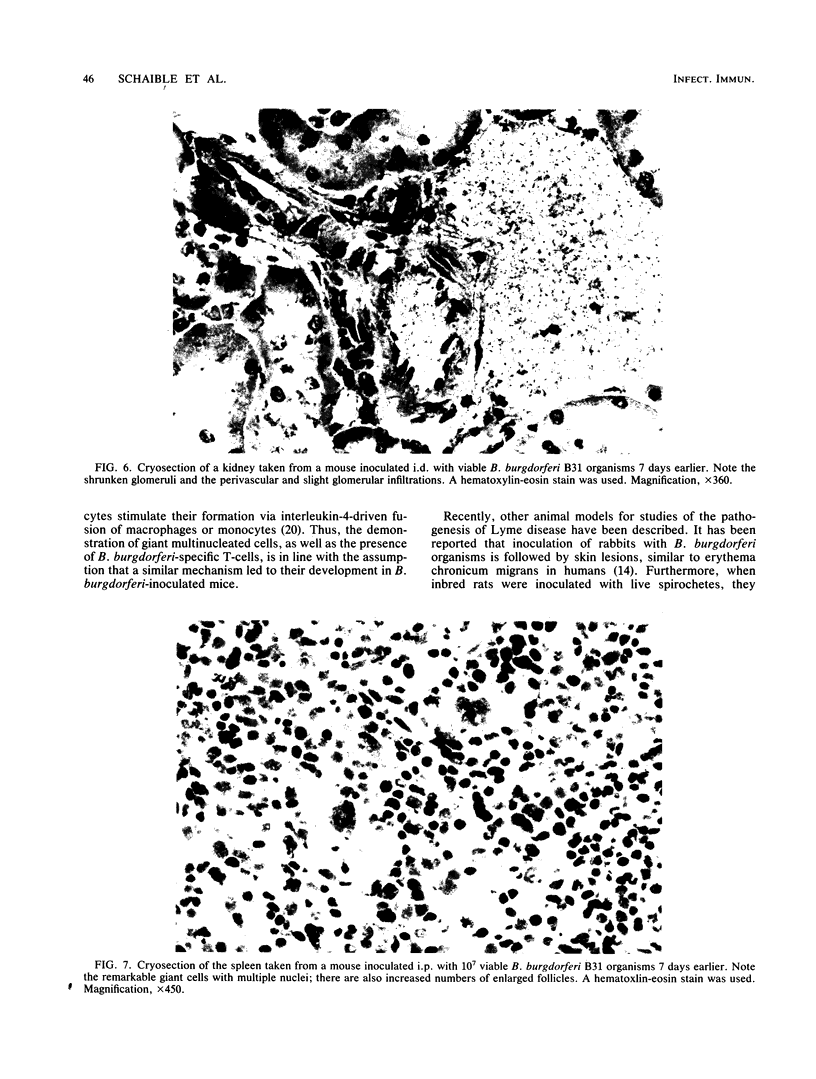
Antigen-specific T-cell responses and histopathological changes were studied in mice experimentally inoculated with Borrelia burgdorferi B31. Inbred mice with different H-2 haplotypes and/or different genetic backgrounds were inoculated with B. burgdorferi organisms and tested for antigen-specific T-cell responses in vivo (delayed-type hypersensitivity [DTH]) and in vitro (T-cell proliferation). Comparable DTH responses were found after inoculation with either inactivated (in the presence of adjuvants) or viable microorganisms in all mouse strains, except BALB/c, irrespective of the H-2 haplotype (b, d, k, or s) tested and the sex of the animals. Moreover, in mice presensitized to B. burgdorferi, DTH responses could be induced only with antigen preparations derived from the corresponding strain but not with those obtained from either related spirochetes such as Treponema phagedenis and Leptospira interrogans or unrelated bacteria such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis. T cells isolated from lymph nodes or spleens of mice previously sensitized to B. burgdorferi but not those from naïve mice could be induced for antigen-specific proliferation in vitro, as revealed by [3H]thymidine incorporation. Histopathological examination of mice inoculated with viable B. burgdorferi organisms revealed significant perivascular infiltrates consisting mainly of mononuclear and a few polymorphonuclear leukocytes in different organs (brain, heart, lungs, liver, and kidneys) and the appearance of giant multinucleated cells within the spleen similar to those found in human skin specimens of patients suffering from cutaneous manifestations of Lyme disease. Our findings suggest that mice are a suitable animal model with which to study the immune response to B. burgdorferi and the pathogenesis of Lyme disease.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann R., Gollmer E., Rehse-Küpper B. Progressive Borrelien-Enzephalomyelitis. Chronische Manifestation der Erythema-chronicum-migrans-Krankheit am Nervensystem. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1985 Jun 28;110(26):1039–1042. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1068956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Moody K. D., Terwilliger G. A., Duray P. H., Jacoby R. O., Steere A. C. Experimental Lyme arthritis in rats infected with Borrelia burgdorferi. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):842–846. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W. The enlarging spectrum of tick-borne spirochetoses: R. R. Parker Memorial Address. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Nov-Dec;8(6):932–940. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.6.932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess E. C., Amundson T. E., Davis J. P., Kaslow R. A., Edelman R. Experimental inoculation of Peromyscus spp. with Borrelia burgdorferi: evidence of contact transmission. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Mar;35(2):355–359. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft J. E., Fischer D. K., Shimamoto G. T., Steere A. C. Antigens of Borrelia burgdorferi recognized during Lyme disease. Appearance of a new immunoglobulin M response and expansion of the immunoglobulin G response late in the illness. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):934–939. doi: 10.1172/JCI112683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue J. G., Piesman J., Spielman A. Reservoir competence of white-footed mice for Lyme disease spirochetes. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 Jan;36(1):92–96. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.36.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duray P. H., Johnson R. C. The histopathology of experimentally infected hamsters with the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1986 Feb;181(2):263–269. doi: 10.3181/00379727-181-42251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn H., Kaufmann S. H., Miller T. E., Mackaness G. B. Peritoneal exudate T lymphocytes with specificity to sheep red blood cells. I. Production and characterization as to function and phenotype. Immunology. 1979 Apr;36(4):691–698. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Marek N., Kodner C. Infection of Syrian hamsters with Lyme disease spirochetes. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1099–1101. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1099-1101.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr Current concepts: immunology. Monocytes and macrophages. N Engl J Med. 1988 Mar 24;318(12):747–752. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198803243181205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblatt A. N., Steere A. C., Brownstein D. G. Experimental Lyme disease in rabbits: spirochetes found in erythema migrans and blood. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):220–223. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.220-223.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krampitz H. E., Bark S. Zur Epidemiologie der Ixodes-Borreliose in Süddeutschland. Immun Infekt. 1987 Jul;15(4):141–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. F., Wilson M. L., Spielman A. Mice as reservoirs of the Lyme disease spirochete. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 Mar;34(2):355–360. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Anderson J. F., Johnson R. C. Cross-reactivity in serological tests for Lyme disease and other spirochetal infections. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):183–188. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McInnes A., Rennick D. M. Interleukin 4 induces cultured monocytes/macrophages to form giant multinucleated cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):598–611. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffat C. M., Sigal L. H., Steere A. C., Freeman D. H., Dwyer J. M. Cellular immune findings in Lyme disease. Correlation with serum IgM and disease activity. Am J Med. 1984 Oct;77(4):625–632. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90352-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Májský A., Bojar M., Jirous J. Lyme disease and HLA-DR antigens. Tissue Antigens. 1987 Oct;30(4):188–189. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1987.tb01619.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfister H. W., Einhäupl K., Preac-Mursic V., Wilske B., Schierz G. The spirochetal etiology of lymphocytic meningoradiculitis of Bannwarth (Bannwarth's syndrome). J Neurol. 1984;231(3):141–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00313682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W. Antigenic changes of Borrelia burgdorferi as a result of in vitro cultivation. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):852–853. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.852-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W., Garon C. F. Changes in infectivity and plasmid profile of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, as a result of in vitro cultivation. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1831–1836. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1831-1836.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal L. H., Moffat C. M., Steere A. C., Dwyer J. M. Cellular immune findings in Lyme disease. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):595–598. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Batsford W. P., Weinberg M., Alexander J., Berger H. J., Wolfson S., Malawista S. E. Lyme carditis: cardiac abnormalities of Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jul;93(1):8–16. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-1-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Gibofsky A., Patarroyo M. E., Winchester R. J., Hardin J. A., Malawista S. E. Chronic Lyme arthritis. Clinical and immunogenetic differentiation from rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Jun;90(6):896–901. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-6-896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E., Newman J. H., Spieler P. N., Bartenhagen N. H. Antibiotic therapy in Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jul;93(1):1–8. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Schoen R. T., Taylor E. The clinical evolution of Lyme arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Nov;107(5):725–731. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-5-725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steurer J., Bansky G., Greminger P., Siegenthaler W. Acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans und Lymesche Erkrankung. Internist (Berl) 1987 Oct;28(10):693–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]