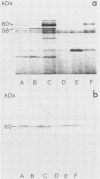
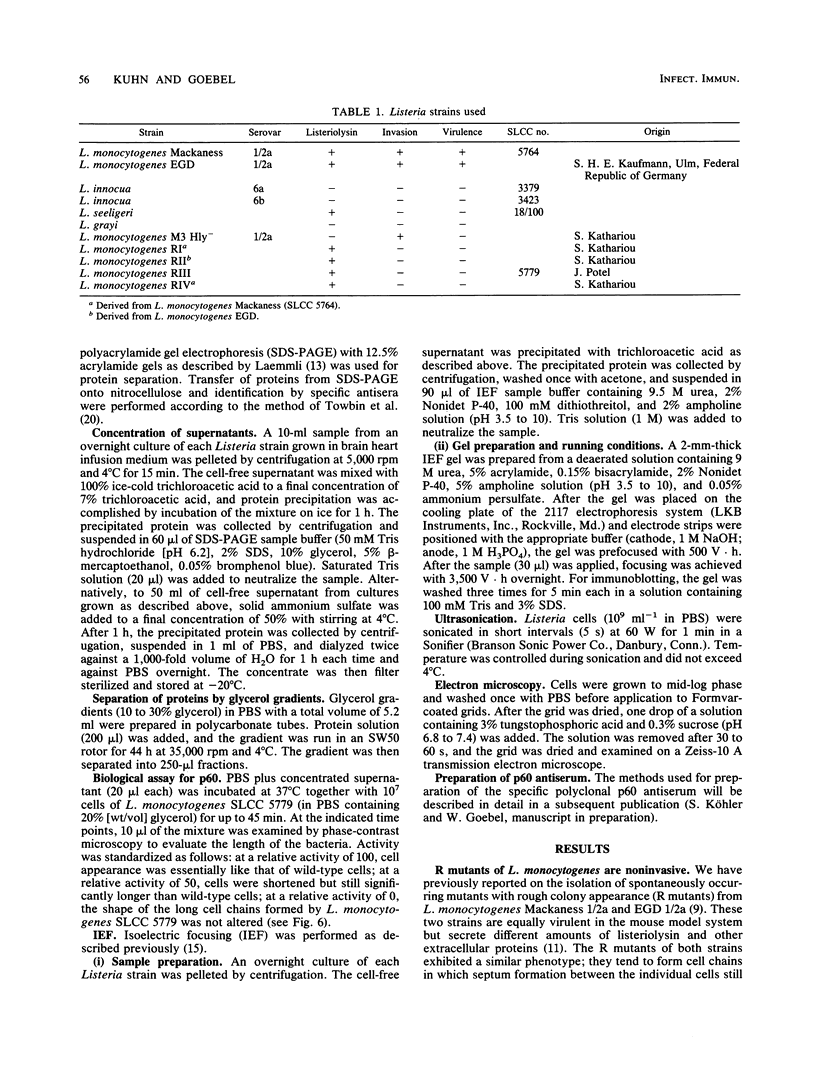
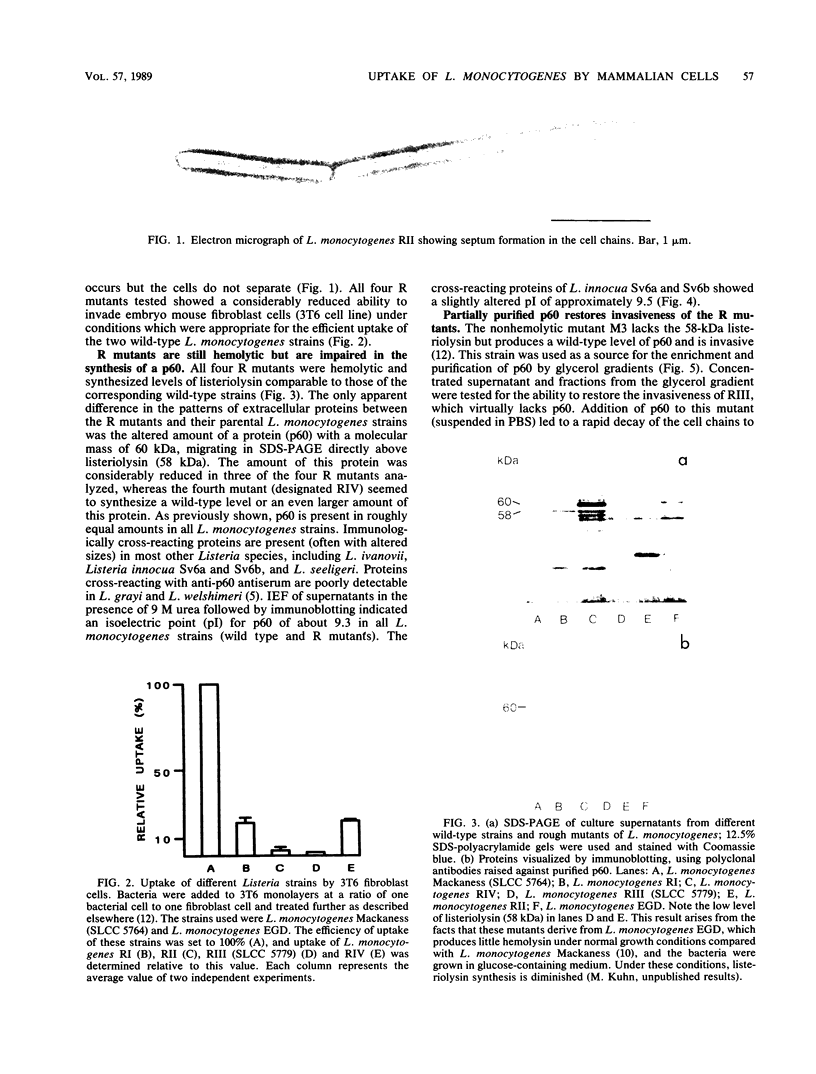
Abstract
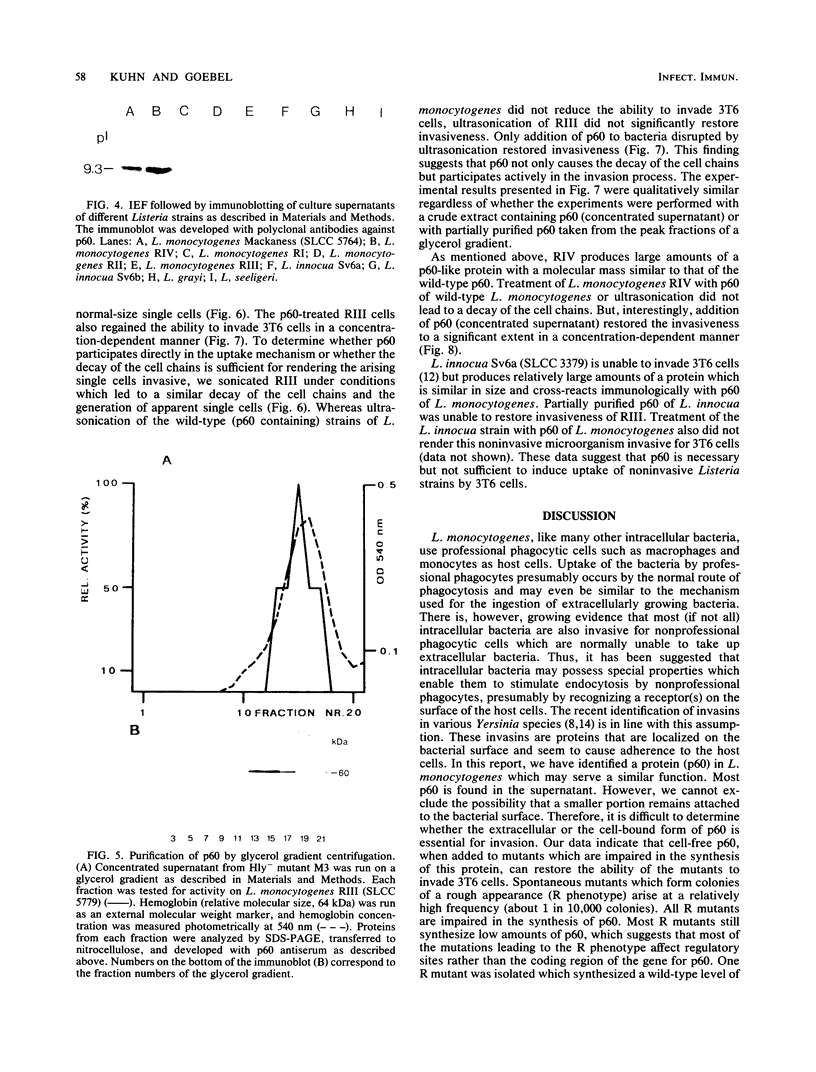
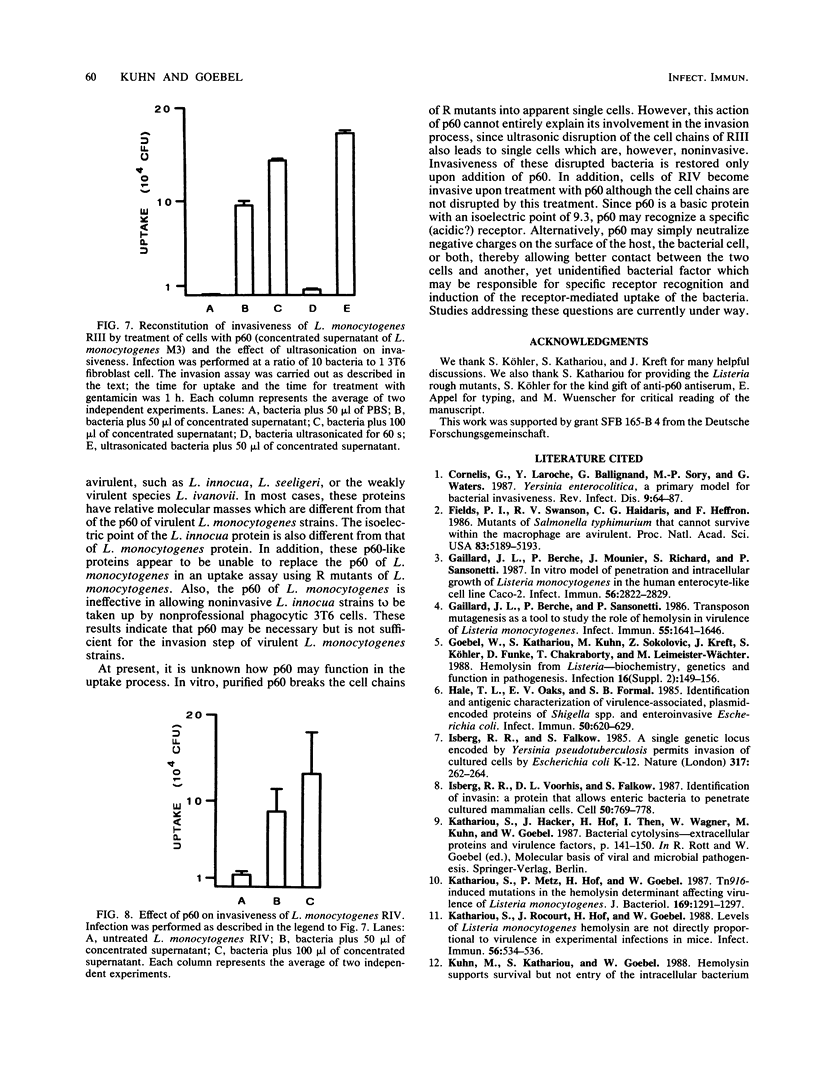
Mutants of Listeria monocytogenes were recently isolated which are impaired in the synthesis of a major extracellular protein (p60). As shown in this investigation, the p60 mutants have lost the capability of invading nonprofessional phagocytic 3T6 mouse fibroblast cells. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of supernatant proteins of these mutants indicated that no other extracellular protein was altered in these mutants. The p60 mutants formed long cell chains which disaggregated to normal-sized single bacteria upon treatment with partially purified p60. These disaggregated bacterial cells were able to invade 3T6 cells. Physical disruption of the cell chains by ultrasonication produced similar single cells which were, however, noninvasive. Treatment of these ultrasonicated mutant cells with wild-type p60 restored their ability to invade 3T6 cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cornelis G., Laroche Y., Balligand G., Sory M. P., Wauters G. Yersinia enterocolitica, a primary model for bacterial invasiveness. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):64–87. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields P. I., Swanson R. V., Haidaris C. G., Heffron F. Mutants of Salmonella typhimurium that cannot survive within the macrophage are avirulent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5189–5193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Mounier J., Richard S., Sansonetti P. In vitro model of penetration and intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes in the human enterocyte-like cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2822–2829. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2822-2829.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geoffroy C., Gaillard J. L., Alouf J. E., Berche P. Purification, characterization, and toxicity of the sulfhydryl-activated hemolysin listeriolysin O from Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1641–1646. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1641-1646.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Oaks E. V., Formal S. B. Identification and antigenic characterization of virulence-associated, plasmid-coded proteins of Shigella spp. and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):620–629. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.620-629.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Falkow S. A single genetic locus encoded by Yersinia pseudotuberculosis permits invasion of cultured animal cells by Escherichia coli K-12. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):262–264. doi: 10.1038/317262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Voorhis D. L., Falkow S. Identification of invasin: a protein that allows enteric bacteria to penetrate cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):769–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90335-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kathariou S., Metz P., Hof H., Goebel W. Tn916-induced mutations in the hemolysin determinant affecting virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1291–1297. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1291-1297.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kathariou S., Rocourt J., Hof H., Goebel W. Levels of Listeria monocytogenes hemolysin are not directly proportional to virulence in experimental infections of mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):534–536. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.534-536.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn M., Kathariou S., Goebel W. Hemolysin supports survival but not entry of the intracellular bacterium Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):79–82. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.79-82.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Falkow S. Evidence for two genetic loci in Yersinia enterocolitica that can promote invasion of epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1242–1248. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1242-1248.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen N. Y., Chrambach A. Stabilzation of pH gradients formed by ampholine. Anal Biochem. 1977 Sep;82(1):226–235. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocourt J., Alonso J. M., Seeliger H. P. Virulence comparée des cinq groupes génomiques de Listeria monocytogenes (sensu lato). Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1983 May-Jun;134A(3):359–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeliger H. P., Schrettenbrunner A., Pongratz G., Hof H. Zur Sonderstellung stark hämolysierender Stämme der Gattung Listeria. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1982 Jun;252(2):176–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]