Abstract
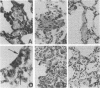
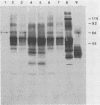
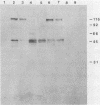
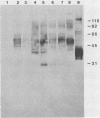
Outbreaks of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia occurred in colonies of nu/nu and scid/scid mice at four different institutions. The disease, which was characterized by chronic wasting and respiratory insufficiency, was more severe in older mice and in animals housed in cages with special protective tops. Histopathologic features included alveolar filling with the typical foamy honeycomb material and a mild, nonspecific host inflammatory response. Immunofluorescence and immunoblotting studies suggested the P. carinii isolate was of mouse rather than of rat or human origin, and the outbreaks could be related to each other by common vendor or source of breeding animals. Once P. carinii became established in a mouse colony, the organism tended to persist for long periods of time. The principal control measure was depopulation of the colony, although limited experience with the administration of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole was encouraging. Thus, outbreaks of pneumocystosis are a serious problem among colonies of immunodeficient mice, with important implications for the use of these animals in biomedical research. Data obtained by studying these outbreaks should enhance understanding of the pathogenesis of P. carinii pneumonia and be helpful in formulating improved methods of detection and control.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bosma G. C., Custer R. P., Bosma M. J. A severe combined immunodeficiency mutation in the mouse. Nature. 1983 Feb 10;301(5900):527–530. doi: 10.1038/301527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrow B. R., Watson A. D., Hartley W. J., Huxtable C. R. Pneumocystis pneumonia in the dog. J Comp Pathol. 1972 Oct;82(4):447–453. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(72)90044-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K., Good J. T., Shultz J. A. Latent Pneumocystis infection of rats, relapse, and chemotherapy. Lab Invest. 1966 Oct;15(10):1559–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuta T., Ueda K., Fujiwara K. Experimental Pneumocystis carinii infection in nude rats. Jpn J Exp Med. 1984 Apr;54(2):65–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuta T., Ueda K., Fujiwara K., Yamanouchi K. Cellular and humoral immune responses of mice subclinically infected with Pneumocystis carinii. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):544–548. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.544-548.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuta T., Ueda K. Intra- and inter-species transmission and antigenic difference of Pneumocystis carinii derived from rat and mouse. Jpn J Exp Med. 1987 Feb;57(1):11–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuta T., Ueda K., Kyuwa S., Fujiwara K. Effect of T-cell transfer on Pneumocystis carinii infection in nude mice. Jpn J Exp Med. 1984 Apr;54(2):57–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigliotti F., Stokes D. C., Cheatham A. B., Davis D. S., Hughes W. T. Development of murine monoclonal antibodies to Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):315–322. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves D. C., McNabb S. J., Ivey M. H., Worley M. A. Development and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Pneumocystis carinii. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):125–133. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.125-133.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves D. C., McNabb S. J., Worley M. A., Downs T. D., Ivey M. H. Analyses of rat Pneumocystis carinii antigens recognized by human and rat antibodies by using western immunoblotting. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):96–103. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.96-103.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendley J. O., Weller T. H. Activation and transmission in rats of infection with Pneumocystis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Sep;137(4):1401–1404. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Bartley D. L., Smith B. M. A natural source of infection due to pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1983 Mar;147(3):595–595. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.3.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Feldman S., Chaudhary S. C., Ossi M. J., Cox F., Sanyal S. K. Comparison of pentamidine isethionate and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in the treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. J Pediatr. 1978 Feb;92(2):285–291. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T. Limited effect of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole prophylaxis on Pneumocystis carinii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Sep;16(3):333–335. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.3.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., McNabb P. C., Makres T. D., Feldman S. Efficacy of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole in the prevention and treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Mar;5(3):289–293. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.3.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T. Natural mode of acquisition for de novo infection with Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jun;145(6):842–848. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.6.842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Rivera G. K., Schell M. J., Thornton D., Lott L. Successful intermittent chemoprophylaxis for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jun 25;316(26):1627–1632. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198706253162604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Smith B. L. Intermittent chemoprophylaxis for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Aug;24(2):300–301. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.2.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. K., Foy J. M., Cushion M. T., Stanforth D., Linke M. J., Hendrix H. L., Walzer P. D. Comparison of histologic and quantitative techniques in evaluation of therapy for experimental Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):197–201. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Gill V., Swan J. C., Ognibene F., Shelhamer J., Parrillo J. E., Masur H. Prospective evaluation of a monoclonal antibody in diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Lancet. 1986 Jul 5;2(8497):1–3. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92555-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Halpern J. L., Swan J. C., Moss J., Parrillo J. E., Masur H. Identification of antigens and antibodies specific for Pneumocystis carinii. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 15;140(6):2023–2031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. H., Bolinger C. D., Bartlett M. S., Kohler R. B., Wilde C. E., 3rd, Smith J. W. Production of monoclonal antibody against Pneumocystis carinii by using a hybrid of rat spleen and mouse myeloma cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):505–508. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.505-508.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto Y., Amagai T., Yamada M., Imanishi J., Yoshida Y. Production of a monoclonal antibody with specificity for the pellicle of Pneumocystis carinii by hybridoma. Parasitol Res. 1987;73(3):228–233. doi: 10.1007/BF00578509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milder J. E., Walzer P. D., Coonrod J. D., Rutledge M. E. Comparison of histological and immunological techniques for detection of Pneumocystis carinii in rat bronchial lavage fluid. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):409–417. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.409-417.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. Pneumocystis carinii and Toxoplasma gondii infections in patients with AIDS. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Nov-Dec;8(6):1001–1011. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.6.1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minielly J. A., Mills S. D., Holley K. E. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Can Med Assoc J. 1969 May 10;100(18):846–854. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHELDON W. H. Experimental pulmonary Pneumocystis carinii infection in rabbits. J Exp Med. 1959 Jul 1;110(1):147–160. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes D. C., Gigliotti F., Rehg J. E., Snellgrove R. L., Hughes W. T. Experimental Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the ferret. Br J Exp Pathol. 1987 Apr;68(2):267–276. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda K., Goto Y., Yamazaki S., Fujiwara K. Chronic fatal pneumocystosis in nude mice. Jpn J Exp Med. 1977 Dec;47(6):475–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D. Diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):629–632. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Linke M. J. A comparison of the antigenic characteristics of rat and human Pneumocystis carinii by immunoblotting. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2257–2265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Perl D. P., Krogstad D. J., Rawson P. G., Schultz M. G. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the United States. Epidemiologic, diagnostic, and clinical features. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Jan;80(1):83–93. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-1-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Powell R. D., Jr, Yoneda K. Experimental Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in different strains of cortisonized mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):939–947. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.939-947.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Powell R. D., Jr, Yoneda K., Rutledge M. E., Milder J. E. Growth characteristics and pathogenesis of experimental Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):928–937. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.928-937.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Rutledge M. E. Comparison of rat, mouse, and human Pneumocystis carinii by immunofluorescence. J Infect Dis. 1980 Sep;142(3):449–449. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.3.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Rutledge M. E. Humoral immunity in experimental Pneumocystis carinii infection. I. Serum and bronchial lavage fluid antibody responses in rats. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Jun;97(6):820–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Rutledge M. E. Serum antibody responses to Pneumocystis carinii among different strains of normal and athymic mice. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):620–626. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.620-626.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Rutledge M. E., Yoneda K., Stahr B. J. Pneumocystis carinii: new separation method from lung tissue. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Jun;47(3):356–368. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90088-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Schnelle V., Armstrong D., Rosen P. P. Nude mouse: a new experimental model for Pneumocystis carinii infection. Science. 1977 Jul 8;197(4299):177–179. doi: 10.1126/science.301657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Stanforth D., Linke M. J., Cushion M. T. Pneumocystis carinii: immunoblotting and immunofluorescent analyses of serum antibodies during experimental rat infection and recovery. Exp Parasitol. 1987 Jun;63(3):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(87)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir E. C., Brownstein D. G., Barthold S. W. Spontaneous wasting disease in nude mice associated with Pneumocystis carinii infection. Lab Anim Sci. 1986 Apr;36(2):140–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida Y., Yamada M., Shiota T., Ikai T., Takeuchi S., Ogino K. Provocation experiment: Pneumocystis carinii in several kinds of animals. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1981;250(1-2):206–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]