Abstract
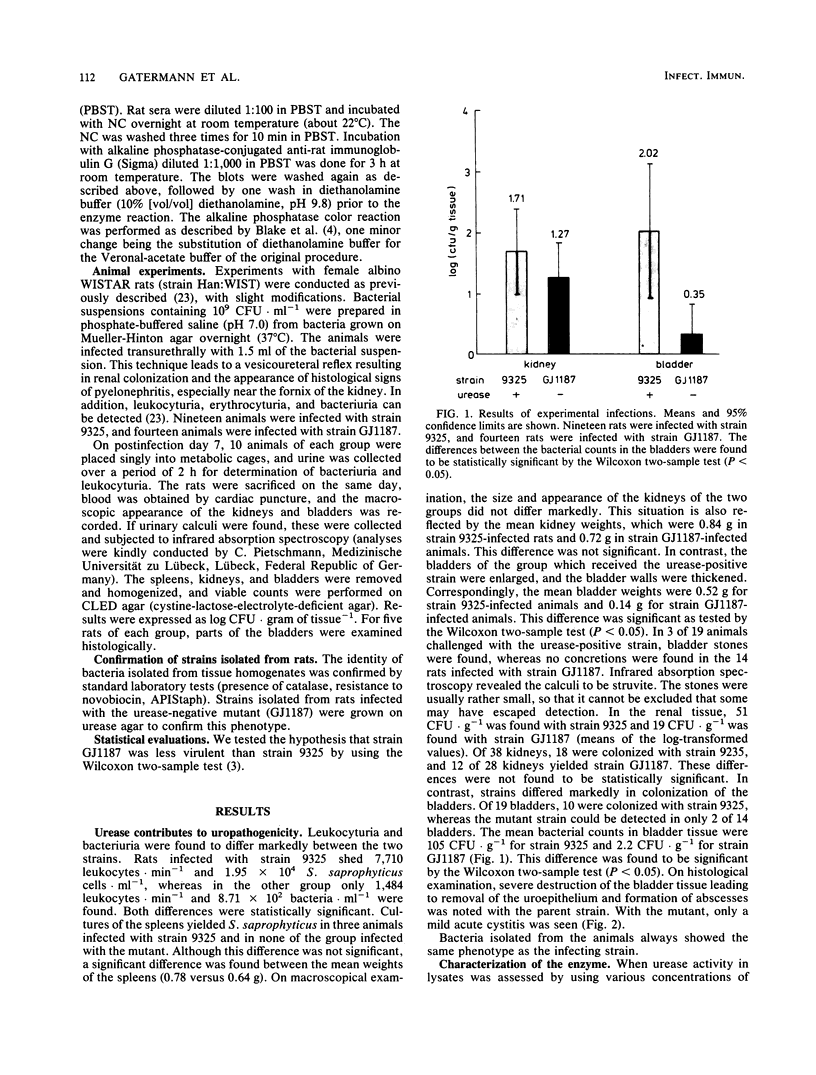
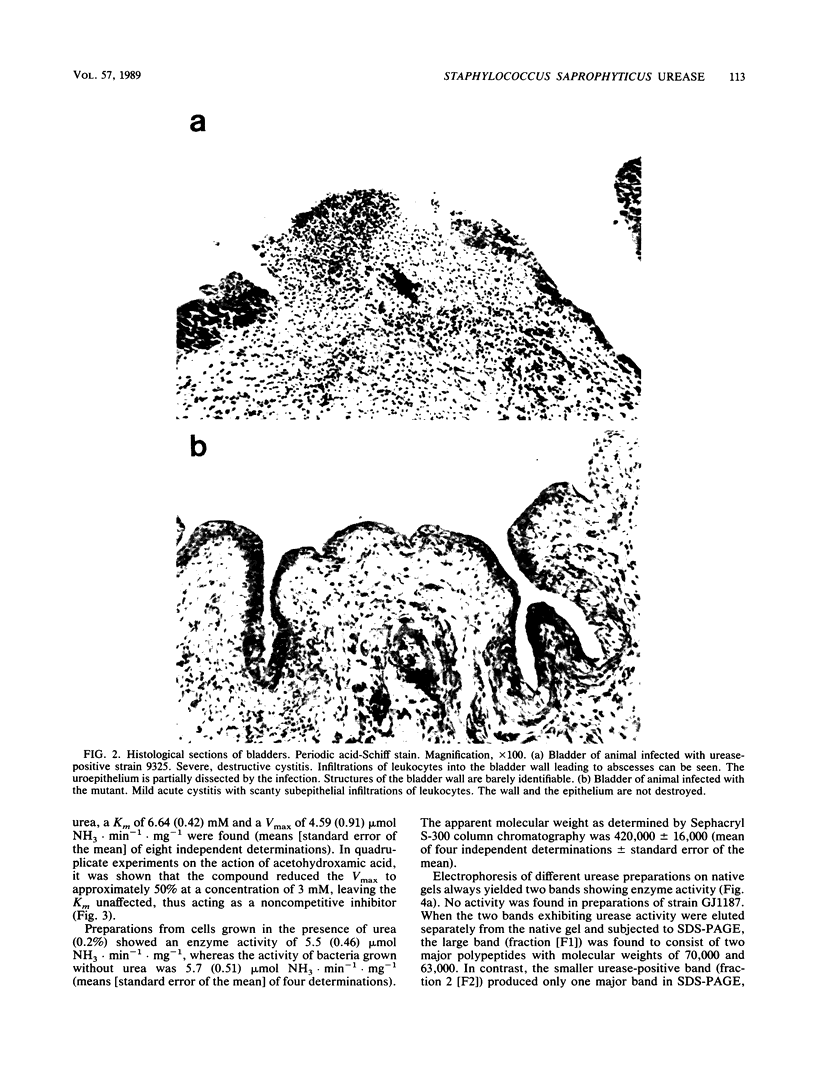
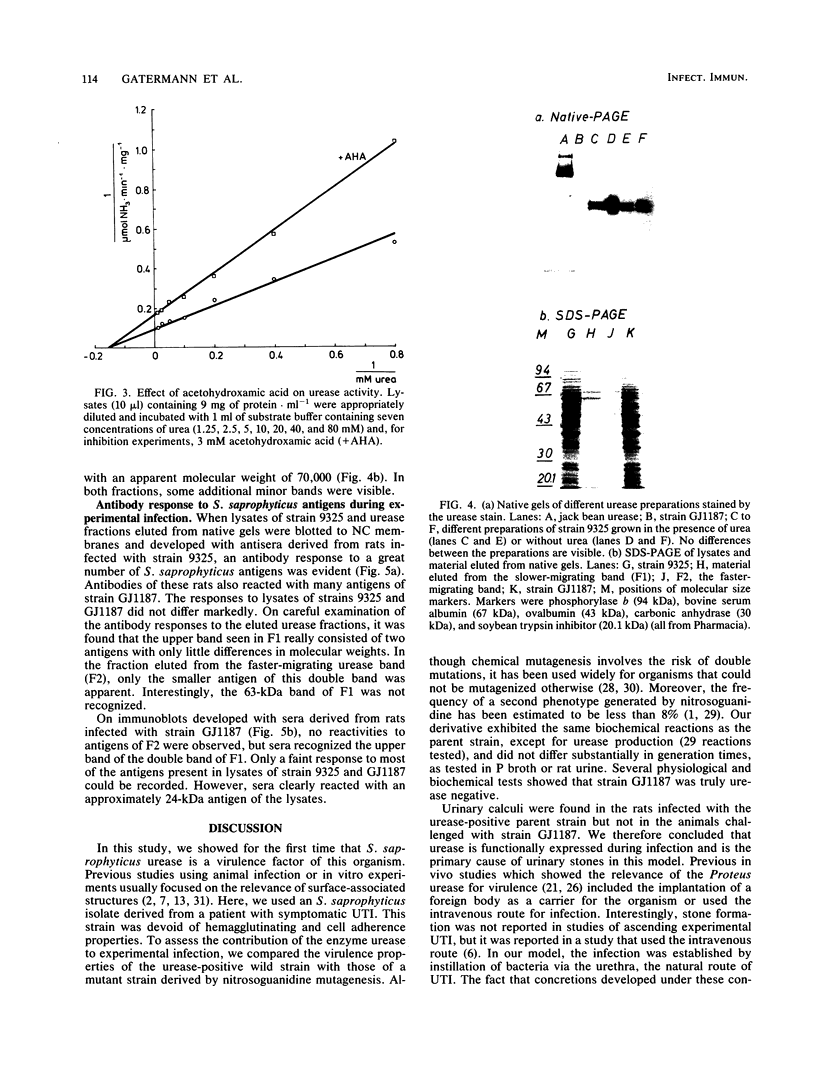
We studied the biochemical properties of the urease of Staphylococcus saprophyticus and the possible role of the urease in experimental urinary tract infections. For this purpose, the nonhemagglutinating and nonadherent strain 9325, which was isolated from a case of symptomatic urinary tract infection, was used. The urease was shown to have a Km of 6.64 mM urea and a Vmax of 4.59 mumol NH3.min-1.mg-1. The enzyme was inhibited by acetohydroxamic acid in a noncompetitive manner. By means of Sephacryl S-300 column chromatography, we determined a mean molecular weight (+/- standard error of the mean) of 420,000 +/- 16,000. To assess the contribution of S. saprophyticus urease to uropathogenicity, a urease-negative mutant was constructed by nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis. In the rat model of ascending unobstructed urinary tract infection, higher numbers of CFU.gram of tissue-1 and more-severe lesions were detected with the parent strain. Moreover, bladder stones were found in animals infected with the urease-positive strain only. Interestingly, the difference in mean bacterial counts of the bladders was found to be significant by the Wilcoxon two-sample test (P less than 0.05), whereas that between the kidney bacterial counts was not. Immunoblot studies revealed a faint antibody response in rats infected with the mutant strain, although bacteria could still be detected in the kidneys after 7 days. Sera of animals challenged with the parent strain reacted strongly with many antigens of S. saprophyticus. Our data indicate that urease is a major factor for invasiveness of S. saprophyticus, especially in the tissue of the bladder, whereas persistence in the urinary tract and nephropathogenicity of this organism are governed by factors other than urease.
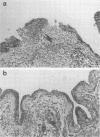
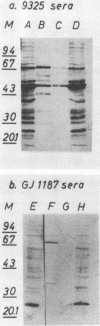
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida R. J., Jorgensen J. H. Comparison of adherence and urine growth rate properties of Staphylococcus saprophyticus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;3(6):542–545. doi: 10.1007/BF02013615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUDE A. I., SIEMIENSKI J. Role of bacterial urease in experimental pyelonephritis. J Bacteriol. 1960 Aug;80:171–179. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.2.171-179.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colleen S., Hovelius B., Wieslander A., Mårdh P. A. Surface properties of Staphylococcus saprophyticus and Staphylococcus epidermidis as studied by adherence tests and two-polymer, aqueous phase systems. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Dec;87(6):321–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1979.tb02446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colleen S., Luttropp W., Mårdh P. A., Ripa T. The microbial flora of the urogenital tract in women with symptoms of recurrent urinary tract infection. The non-influence of methenaminehippurate treatment on the idigenous flora. Invest Urol. 1978 Mar;15(5):367–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon N. E., Hinds J. A., Fihelly A. K., Gazzola C., Winzor D. J., Blakeley R. L., Zerner B. Jack bean urease (EC 3.5.1.5). IV. The molecular size and the mechanism of inhibition by hydroxamic acids. Spectrophotometric titration of enzymes with reversible inhibitors. Can J Biochem. 1980 Dec;58(12):1323–1334. doi: 10.1139/o80-180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golledge C. L. Staphylococcus saprophyticus bacteremia. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):215–215. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith D. P., Musher D. M., Itin C. Urease. The primary cause of infection-induced urinary stones. Invest Urol. 1976 Mar;13(5):346–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heesemann J., Keller C., Morawa R., Schmidt N., Siemens H. J., Laufs R. Plasmids of human strains of Yersinia enterocolitica: molecular relatedness and possible importance for pathogenesis. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jan;147(1):107–115. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.1.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovelius B., Colleen S., Mårdh P. A. Urinary tract infections in men caused by Staphylococcus saprophyticus. Scand J Infect Dis. 1984;16(1):37–41. doi: 10.3109/00365548409068407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovelius B., Mårdh P. A., Bygren P. Urinary tract infections caused by Staphylococcus saprophyticus: recurrences and complications. J Urol. 1979 Nov;122(5):645–647. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)56541-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovelius B., Mårdh P. A. Haemagglutination by Staphylococcus saprophyticus and other staphylococcal species. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Feb;87B(1):45–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1979.tb02401.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. D., Mobley H. L. Genetic and biochemical diversity of ureases of Proteus, Providencia, and Morganella species isolated from urinary tract infection. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2198–2203. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2198-2203.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Carpenter R. J., Phillips L. E., Faro S. Pyelonephritis and sepsis due to Staphylococcus saprophyticus. J Infect Dis. 1987 May;155(5):1079–1080. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.5.1079-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLaren D. M. The significance of urease in proteus pyelonephritis: a histological and biochemical study. J Pathol. 1969 Jan;97(1):43–49. doi: 10.1002/path.1710970107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marre R., Hacker J., Henkel W., Goebel W. Contribution of cloned virulence factors from uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains to nephropathogenicity in an experimental rat pyelonephritis model. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):761–767. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.761-767.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley H. L., Jones B. D., Jerse A. E. Cloning of urease gene sequences from Providencia stuartii. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):161–169. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.161-169.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley H. L., Jones B. D., Penner J. L. Urease activity of Proteus penneri. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Dec;25(12):2302–2305. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.12.2302-2305.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M., Griffith D. P., Yawn D., Rossen R. D. Role of urease in pyelonephritis resulting from urinary tract infection with Proteus. J Infect Dis. 1975 Feb;131(2):177–181. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.2.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstein I. J., Hamilton-Miller J. M., Brumfitt W. Role of urease in the formation of infection stones: comparison of ureases from different sources. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):32–37. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.32-37.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandström G., Löfgren S., Tärnvik A. A capsule-deficient mutant of Francisella tularensis LVS exhibits enhanced sensitivity to killing by serum but diminished sensitivity to killing by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1194–1202. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1194-1202.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. O., Beckwith J. R. Mutagens which cause deletions in Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1969 Feb;61(2):371–376. doi: 10.1093/genetics/61.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svanborg-Edén C., Hagberg L., Hull R., Hull S., Magnusson K. E., Ohman L. Bacterial virulence versus host resistance in the urinary tracts of mice. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1224–1232. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1224-1232.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teti G., Chiofalo M. S., Tomasello F., Fava C., Mastroeni P. Mediation of Staphylococcus saprophyticus adherence to uroepithelial cells by lipoteichoic acid. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):839–842. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.839-842.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallmark G., Arremark I., Telander B. Staphylococcus saprophyticus: a frequent cause of acute urinary tract infection among female outpatients. J Infect Dis. 1978 Dec;138(6):791–797. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.6.791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. J., Rodman J. S., Peterson C. M. A randomized double-blind study of acetohydroxamic acid in struvite nephrolithiasis. N Engl J Med. 1984 Sep 20;311(12):760–764. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198409203111203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]