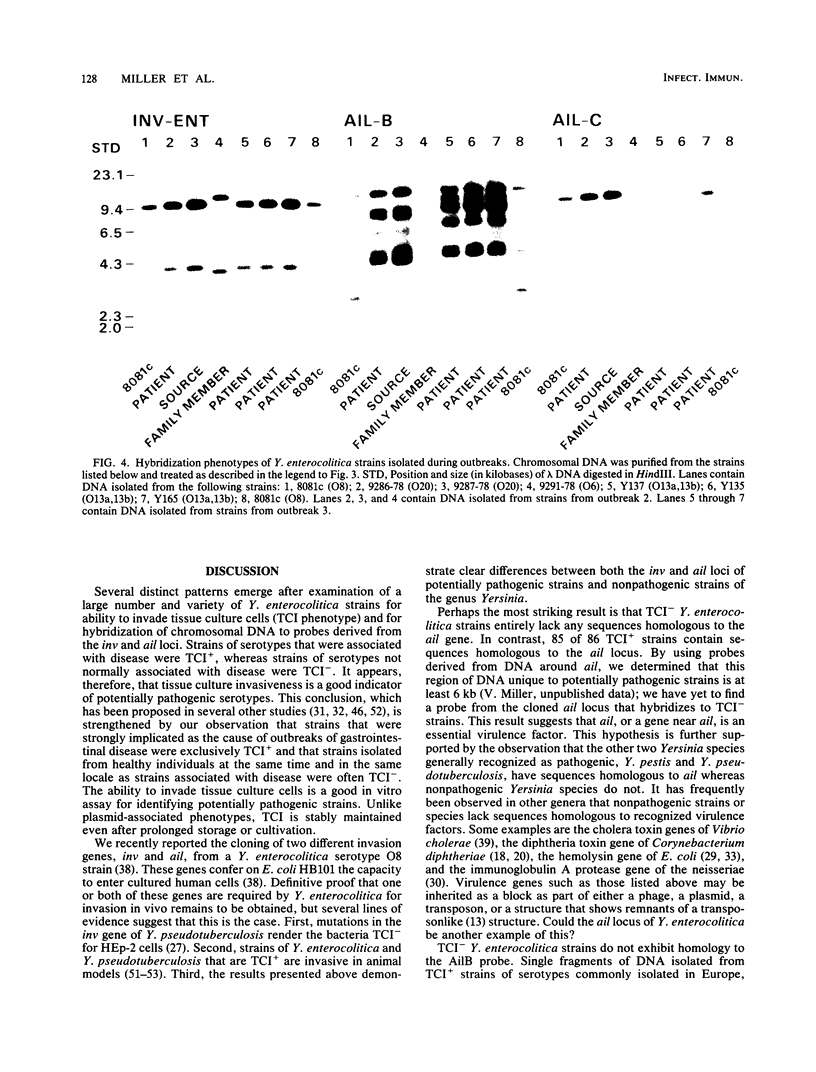
Abstract
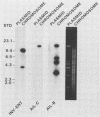
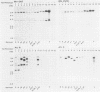
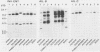
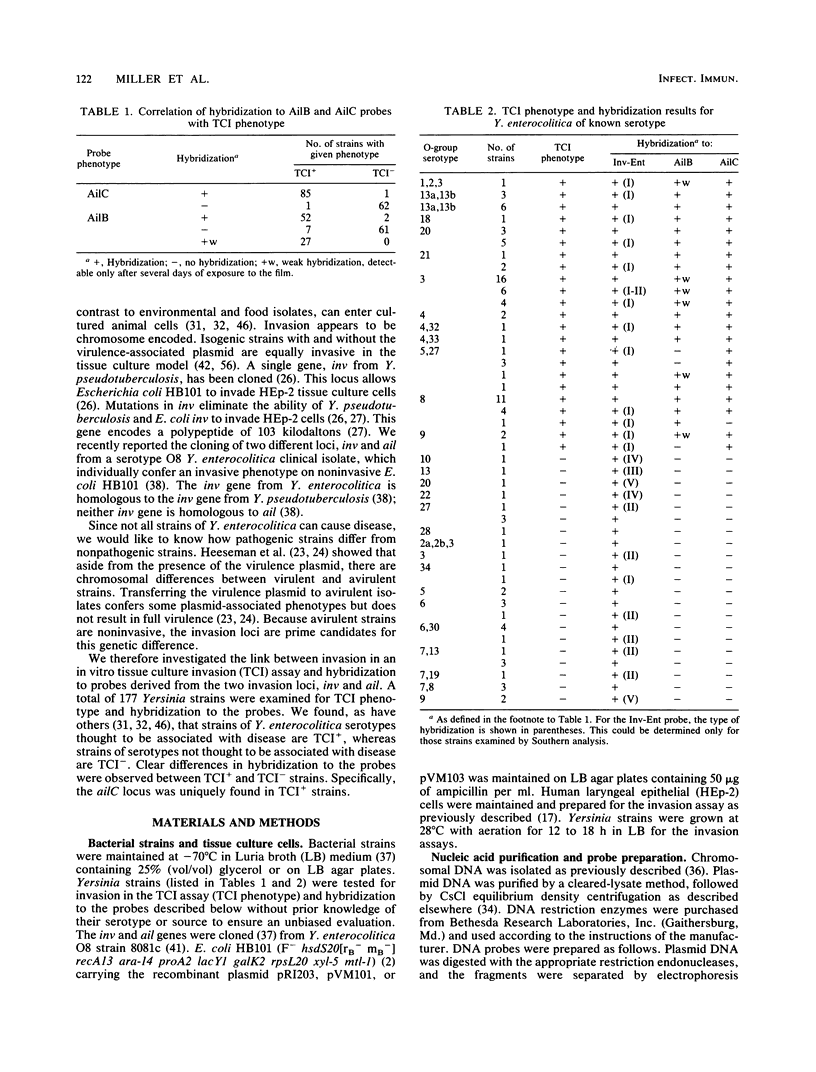
Yersinia enterocolitica is a heterogeneous group of organisms with more than 50 serotypes and several biotypes. Only a few of these serotypes cause gastrointestinal disease in otherwise healthy hosts; these serotypes are the pathogenic serotypes. Although Y. enterocolitica requires a high-molecular-weight plasmid to cause disease, chromosome-encoded determinants are required for the full expression of virulence. The ability of Yersinia spp. to invade eucaryotic cells is thought to be a virulence factor, because nonpathogenic serotypes are noninvasive in animals and in tissue culture cell models. Current evidence indicates that invasion ability is chromosome encoded. We recently reported cloning two loci, inv and ail, from Y. enterocolitica O8 strain 8081c that allow Escherichia coli to invade tissue culture cells. We investigated the link between invasion in an in vitro tissue culture invasion (TCI) model and hybridization to probes derived from the two invasion loci, inv and ail. We examined 177 Yersinia strains. Strains of serotypes and species associated with disease were TCI+, whereas strains of serotypes and species not associated with disease were TCI-. Only TCI+ strains had DNA homologous to probes derived from ail. All strains (TCI+ and TCI-) had DNA homologous to probes derived from inv, but there were certain restriction fragment-linked polymorphisms that were associated primarily with TCI+ strains. These observations held true for strains epidemiologically associated with disease. Both the inv and ail loci were found to be clearly located on the chromosome. No other genera, including other invasive organisms, had DNA homologous to inv or ail. These data support the hypothesis that the ail locus encodes a Y. enterocolitica invasion factor that may be involved in pathogenesis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. M., Farmer J. J., 3rd New bacteriophage typing system for Yersinia enterocolitica, Yersinia kristensenii, Yersinia frederiksenii, and Yersinia intermedia: correlation with serotyping, biotyping, and antibiotic susceptibility. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Mar;15(3):491–502. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.3.491-502.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakour R., Balligand G., Laroche Y., Cornelis G., Wauters G. A simple adult-mouse test for tissue invasiveness in Yersinia enterocolitica strains of low experimental virulence. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Apr;19(2):237–246. doi: 10.1099/00222615-19-2-237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black R. E., Jackson R. J., Tsai T., Medvesky M., Shayegani M., Feeley J. C., MacLeod K. I., Wakelee A. M. Epidemic Yersinia enterocolitica infection due to contaminated chocolate milk. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jan 12;298(2):76–79. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197801122980204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottone E. J. Yersinia enterocolitica: a panoramic view of a charismatic microorganism. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1977;5(2):211–241. doi: 10.3109/10408417709102312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford W. D., Noce P. S., Gutman L. T. Pathologic features of enteric infection with Yersinia enterocolitica. Arch Pathol. 1974 Jul;98(1):17–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Norlander L., Wolf-Watz H. Temperature-inducible outer membrane protein of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Yersinia enterocolitica is associated with the virulence plasmid. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):506–512. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.506-512.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calos M. P., Miller J. H. Transposable elements. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):579–595. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90305-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G., Laroche Y., Balligand G., Sory M. P., Wauters G. Yersinia enterocolitica, a primary model for bacterial invasiveness. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):64–87. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devenish J. A., Schiemann D. A. HeLa cell infection by Yersinia enterocolitica: evidence for lack of intracellular multiplication and development of a new procedure for quantitative expression of infectivity. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):48–55. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.48-55.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enteric infections due to Campylobacter, Yersinia, Salmonella, and Shigella. WHO Scientific Working Group. Bull World Health Organ. 1980;58(4):519–537. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEMAN V. J. Studies on the virulence of bacteriophage-infected strains of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Bacteriol. 1951 Jun;61(6):675–688. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.6.675-688.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Wells J. G., Tsai T. F., Puhr N. D. Detection of enterotoxigenic and invasive strains of Yersinia enterocolitica. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1979;5:329–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROMAN N. B. Evidence for the induced nature of the change from nontoxigenicity to toxigenicity in Corynebacterium diphtheriae as a result of exposure to specific bacteriophage. J Bacteriol. 1953 Aug;66(2):184–191. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.2.184-191.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T. Plasmid associated with pathogenicity and calcium dependency of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):682–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.682-685.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock G. E., Schaedler R. W., MacDonald T. T. Yersinia enterocolitica infection in resistant and susceptible strains of mice. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):26–31. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.26-31.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl D. L., Dykhuizen D. E. The population genetics of Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:31–68. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heesemann J., Algermissen B., Laufs R. Genetically manipulated virulence of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):105–110. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.105-110.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heesemann J., Laufs R. Construction of a mobilizable Yersinia enterocolitica virulence plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):761–767. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.761-767.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. E., Payne W. L., Aulisio C. C. Detection and enumeration of virulent Yersinia enterocolitica in food by DNA colony hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Sep;46(3):636–641. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.3.636-641.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Falkow S. A single genetic locus encoded by Yersinia pseudotuberculosis permits invasion of cultured animal cells by Escherichia coli K-12. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):262–264. doi: 10.1038/317262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Voorhis D. L., Falkow S. Identification of invasin: a protein that allows enteric bacteria to penetrate cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):769–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90335-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandolo K., Wauters G. Pyrazinamidase activity in Yersinia enterocolitica and related organisms. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;21(6):980–982. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.6.980-982.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp S., Hacker J., Jarchau T., Goebel W. Large, unstable inserts in the chromosome affect virulence properties of uropathogenic Escherichia coli O6 strain 536. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):22–30. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.22-30.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koomey J. M., Falkow S. Nucleotide sequence homology between the immunoglobulin A1 protease genes of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):101–107. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.101-107.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., McGrath P. P., Carter P. H., Eide E. L. The ability of some Yersinia enterocolitica strains to invade HeLa cells. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Dec;23(12):1714–1722. doi: 10.1139/m77-247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H. Testing for the recovery of Yersinia enterocolitica in foods and their ability to invade HeLa cells. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1979;5:228–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low D., David V., Lark D., Schoolnik G., Falkow S. Gene clusters governing the production of hemolysin and mannose-resistant hemagglutination are closely linked in Escherichia coli serotype O4 and O6 isolates from urinary tract infections. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):353–358. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.353-358.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J. Duplication and amplification of toxin genes in Vibrio cholerae. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
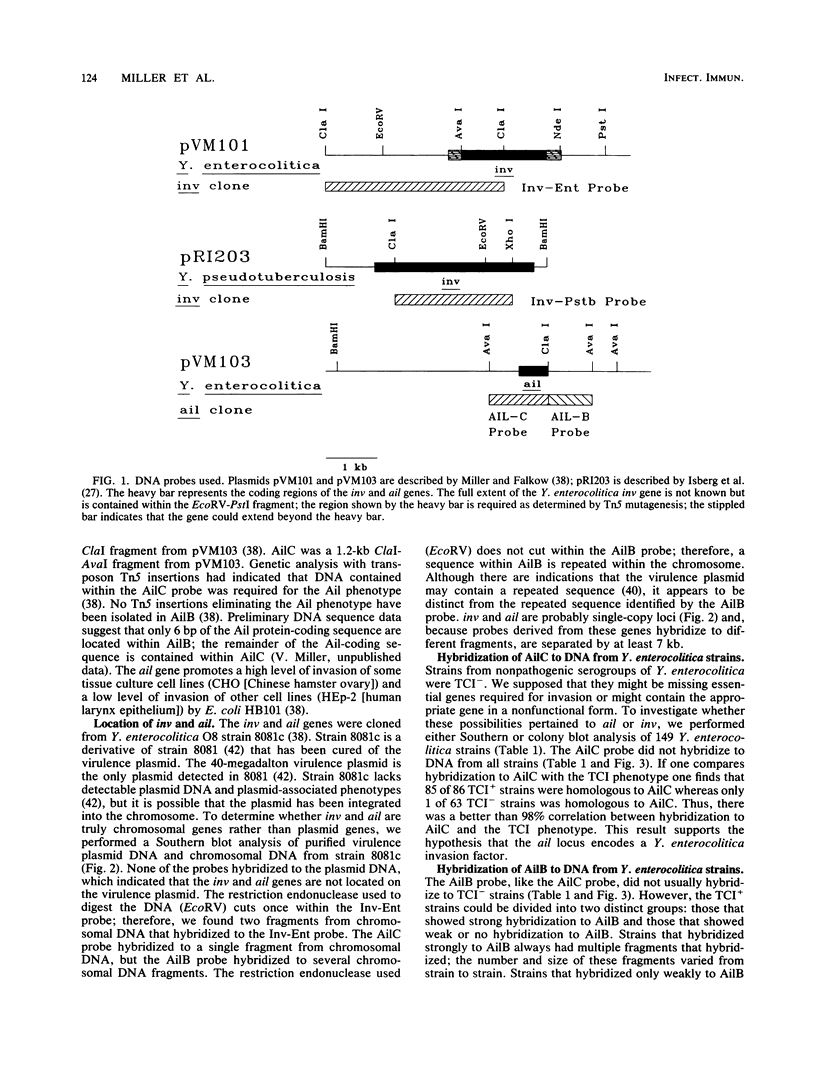
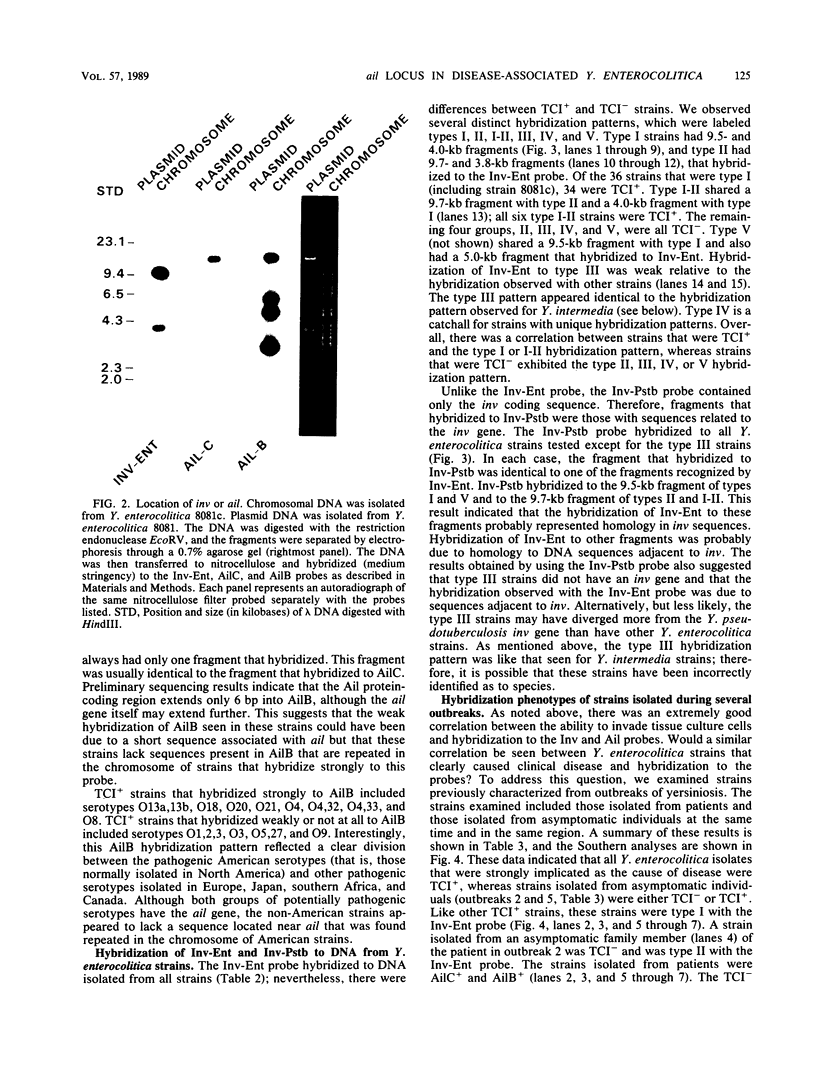
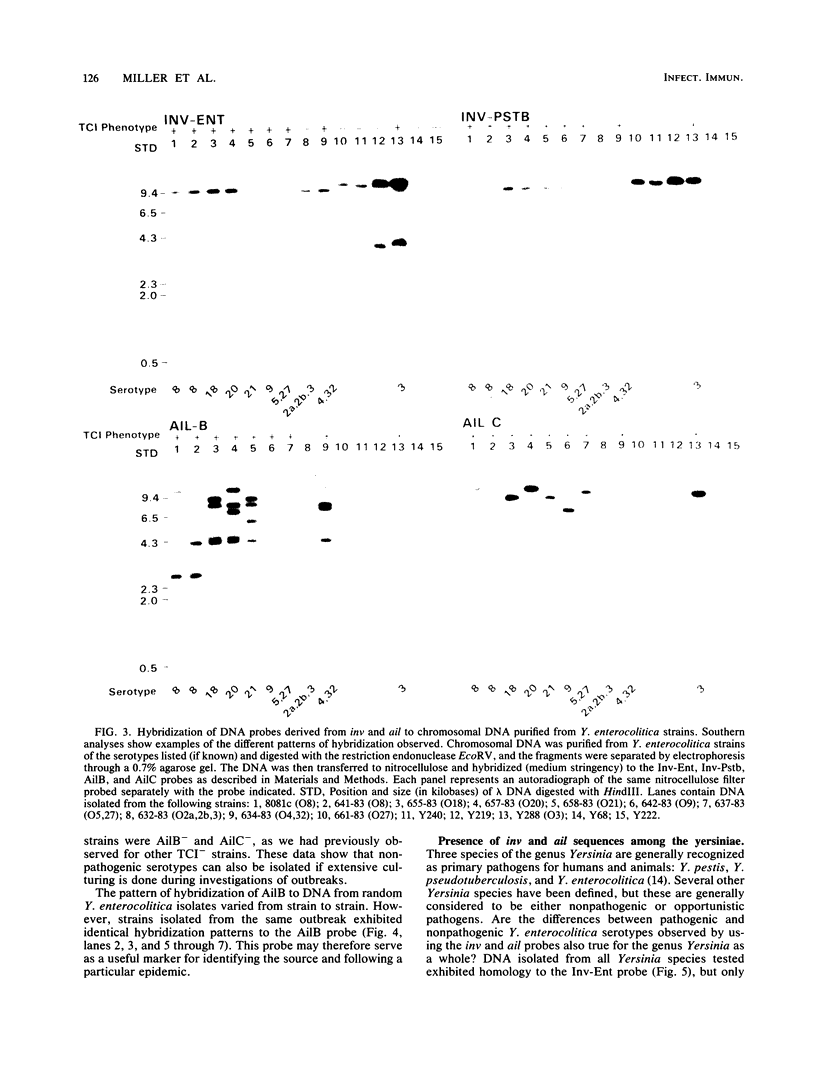
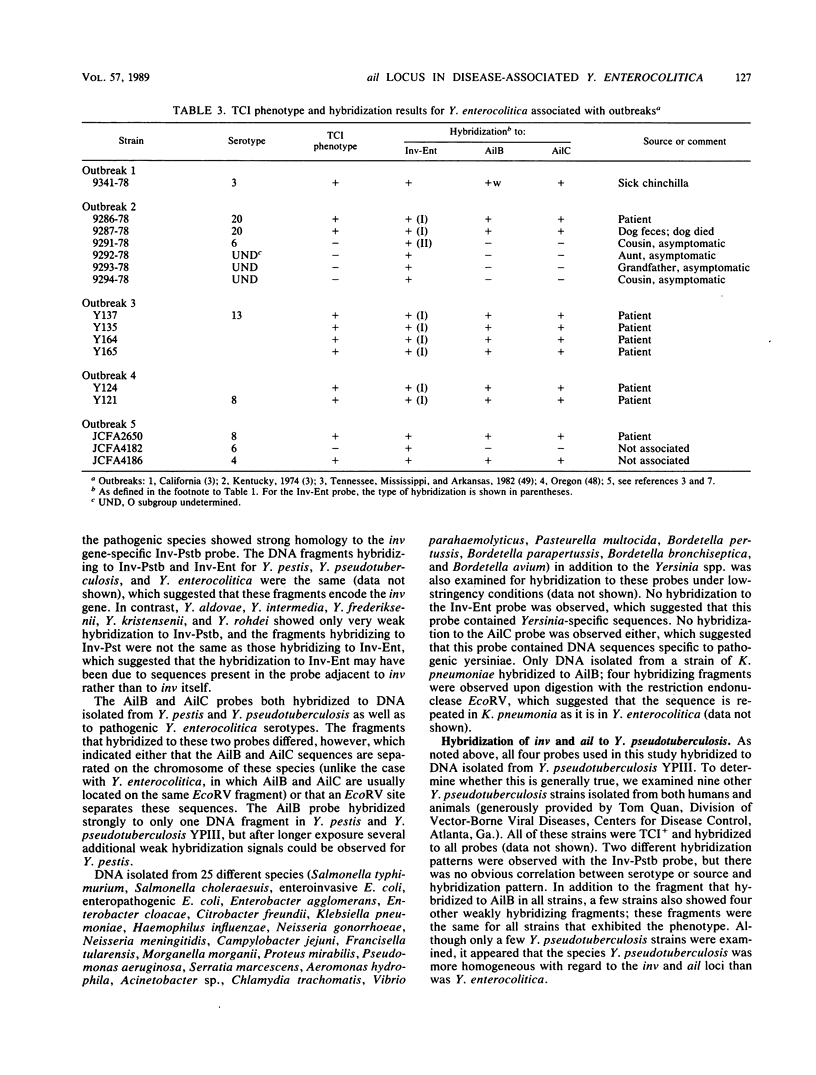
- Miller V. L., Falkow S. Evidence for two genetic loci in Yersinia enterocolitica that can promote invasion of epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1242–1248. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1242-1248.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. Synthesis of cholera toxin is positively regulated at the transcriptional level by toxR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3471–3475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Falkow S. Virulence-associated plasmids from Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pestis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Dec;148(3):877–883. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.3.877-883.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Martinez R. J. Role of a plasmid in the pathogenicity of Yersinia species. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;118:29–51. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70586-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids and plasmid-associated determinants of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.775-782.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prpic J. K., Robins-Browne R. M., Davey R. B. Differentiation between virulent and avirulent Yersinia enterocolitica isolates by using Congo red agar. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):486–490. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.486-490.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M., Tzipori S., Gonis G., Hayes J., Withers M., Prpic J. K. The pathogenesis of Yersinia enterocolitica infection in gnotobiotic piglets. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Jun;19(3):297–308. doi: 10.1099/00222615-19-3-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiemann D. A., Devenish J. A. Relationship of HeLa cell infectivity to biochemical, serological, and virulence characteristics of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):497–506. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.497-506.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiemann D. A., Devenish J. A. Virulence of Yersinia enterocolitica determined by lethality in Mongolian gerbils and by the Serény test. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):500–506. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.500-506.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacket C. O., Ballard J., Harris N., Allard J., Nolan C., Quan T., Cohen M. L. An outbreak of Yersinia enterocolitica infections caused by contaminated tofu (soybean curd). Am J Epidemiol. 1985 May;121(5):705–711. doi: 10.1093/aje/121.5.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacket C. O., Narain J. P., Sattin R., Lofgren J. P., Konigsberg C., Jr, Rendtorff R. C., Rausa A., Davis B. R., Cohen M. L. A multistate outbreak of infections caused by Yersinia enterocolitica transmitted by pasteurized milk. JAMA. 1984 Jan 27;251(4):483–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A. Electron microscope studies of experimental Salmonella infection. I. Penetration into the intestinal epithelium by Salmonella typhimurium. Am J Pathol. 1967 Jan;50(1):109–136. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T. Studies on the pathogenicity of Yersinia enterocolitica. I. Experimental infection in rabbits. Microbiol Immunol. 1977;21(7):341–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T. Studies on the pathogenicity of Yersinia enterocolitica. II. Interaction with cultured cells in vitro. Microbiol Immunol. 1977;21(7):365–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1977.tb00301.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T. Studies on the pathogenicity of Yersinia enterocolitica. III. Comparative studies between Y. enterocolitica and Y. pseudotuberculosis. Microbiol Immunol. 1977;21(9):505–516. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1977.tb00316.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Bromirska J., Mäki M. Enhancement of invasiveness of Yersinia enterocolitica and Escherichia coli in HEp-2 cells by centrifugation. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):834–836. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.834-836.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Nurmi T., Mäki M., Skurnik M., Sundqvist C., Granfors K., Grönroos P. Plasmids in Yersinia enterocolitica serotypes O:3 and O:9: correlation with epithelial cell adherence in vitro. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):870–876. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.870-876.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M., Ingbar S. H., Winblad S., Kasper D. L. Demonstration of a saturable binding site for thyrotropin in Yersinia enterocolitica. Science. 1983 Mar 18;219(4590):1331–1333. doi: 10.1126/science.6298936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink D. L., Feeley J. C., Wells J. G., Vanderzant C., Vickery J. C., Roof W. D., O'Donovan G. A. Plasmid-mediated tissue invasiveness in Yersinia enterocolitica. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):224–226. doi: 10.1038/283224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]