Abstract
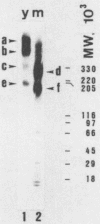
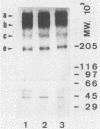
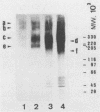
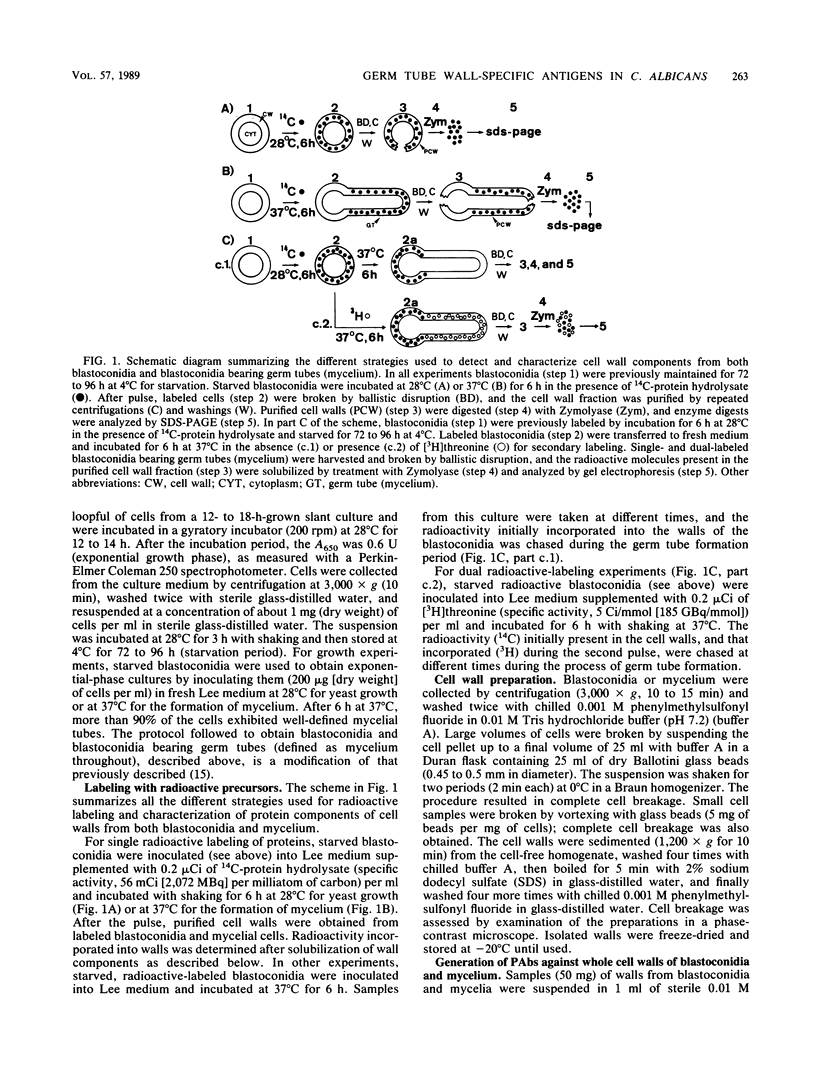
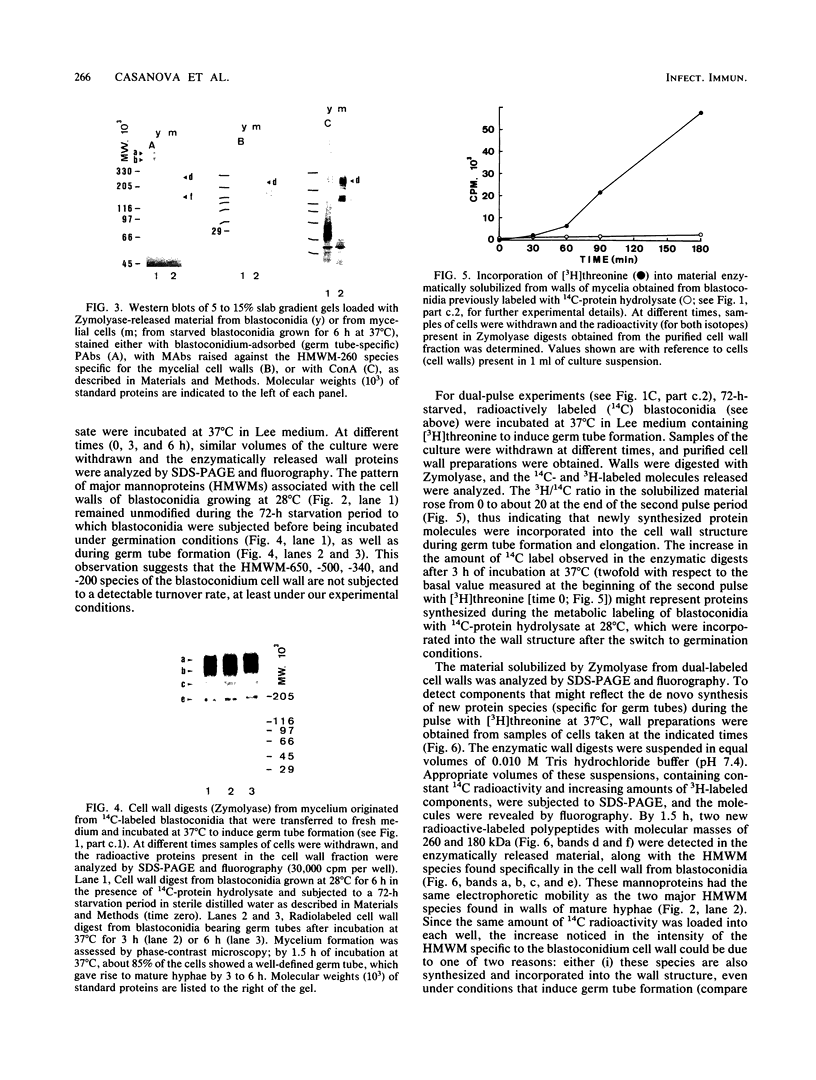
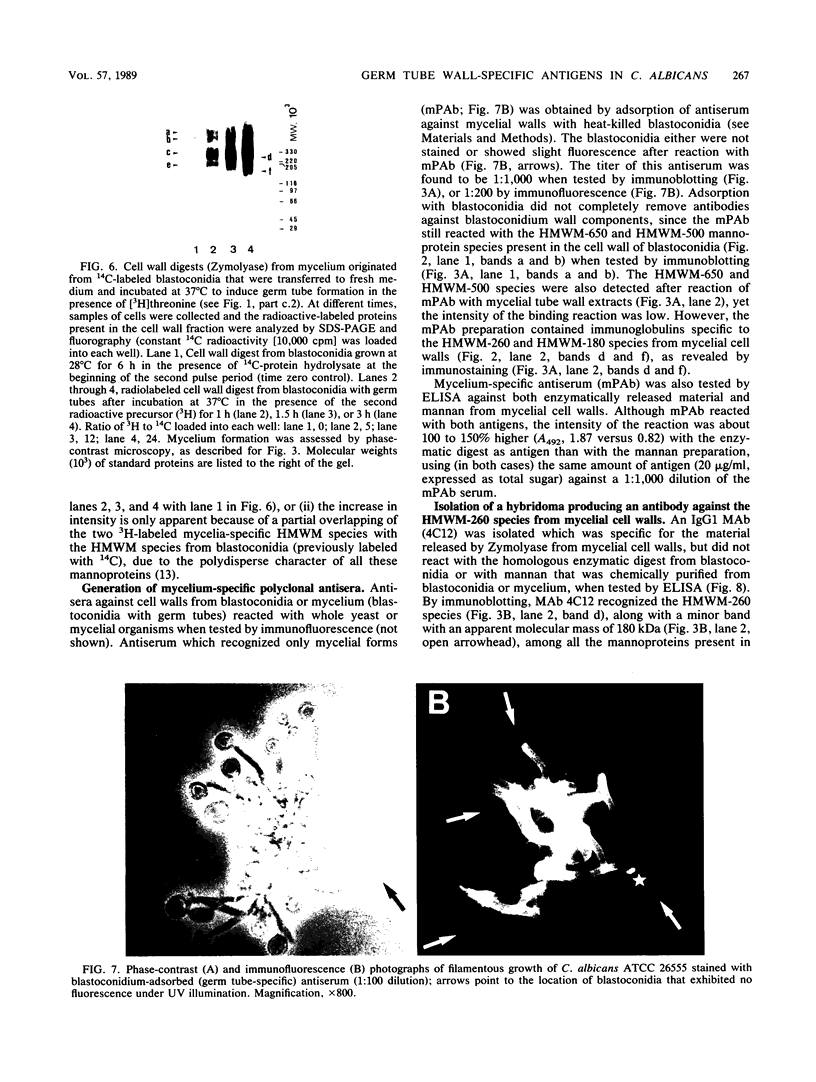
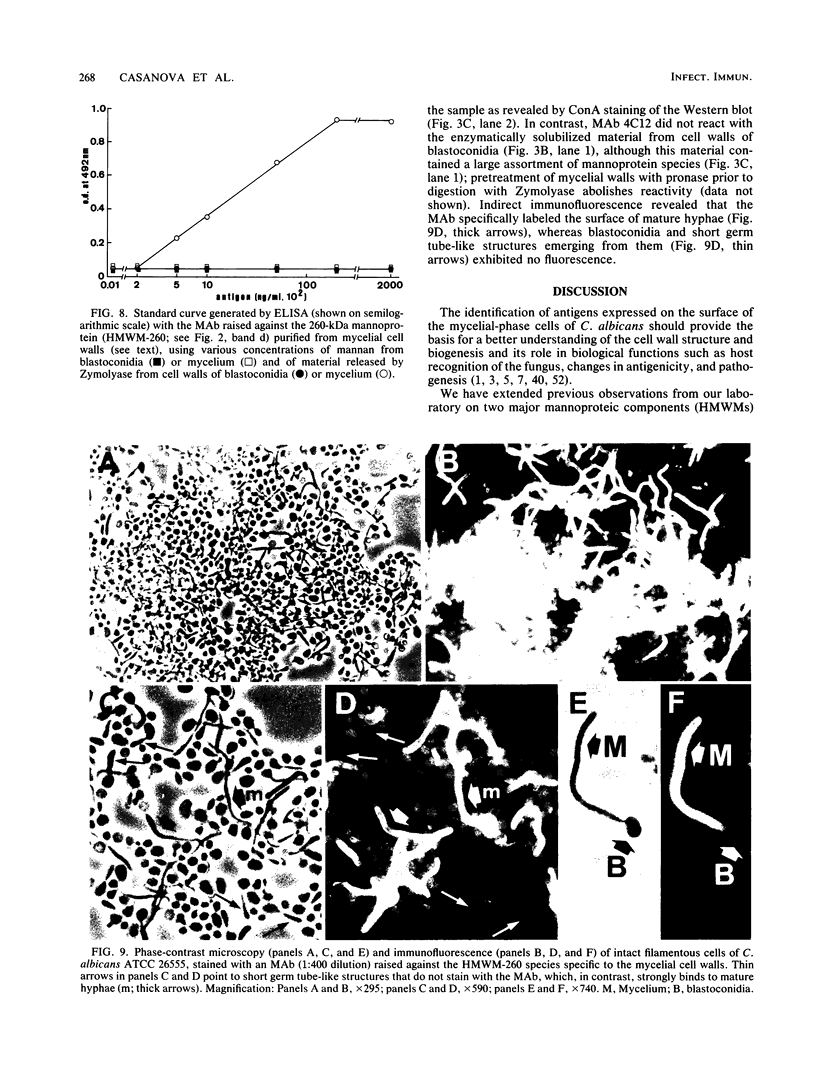
Walls of the two cellular forms (blastoconidia and mycelia) of Candida albicans ATCC 26555 were obtained from cells metabolically labeled (6-h pulse) with 14C-protein hydrolysate and [3H]threonine. Walls were purified by thorough washings with buffered and sodium dodecyl sulfate solutions and digested with Zymolyase 20T. The enzymatic treatment released four major high-molecular-weight mannoproteins (HMWM), with apparent molecular masses of 650, 500, 340, and 200 kilodaltons (HMWM-650, HMWM-500, HMWM-340, and HMWM-200, respectively), from yeast cells, whereas two high-molecular-mass mannoproteins (HMWM-260 and HMWM-180) were solubilized from mycelial cells. Some additional minor low-molecular-weight species were also detected in the enzymatic digests of walls from both types of cell. Single and dual pulse-chase experiments indicated that the HMWM-260 and HMWM-180 species reflect de novo synthesis of new proteins specific for the mycelia and do not represent a topological rearrangement of blastoconidium wall components. Monoclonal antibodies were raised against the HMWM-260 species (quantitatively the predominant component in the mycelial walls), and polyclonal rabbit antibodies were obtained against yeast or mycelial cell walls. Anti-mycelial cell wall polyclonal antibodies were adsorbed to whole killed blastoconidia to remove antibodies against common blastoconidium and mycelial wall antigens. Titration by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay revealed that the monoclonal antibodies could recognize an epitope of the protein moiety of the HMWM-260 mannoprotein. Immunoblotting and immunofluorescence techniques using these monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies confirmed that the HMWM-260 and HMWM-180 species are specific components of the envelope of the mycelial cell walls.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brawner D. L., Cutler J. E. Ultrastructural and biochemical studies of two dynamically expressed cell surface determinants on Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):327–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.327-336.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawner D. L., Cutler J. E. Variability in expression of a cell surface determinant on Candida albicans as evidenced by an agglutinating monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):966–972. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.966-972.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawner D. L., Cutler J. E. Variability in expression of cell surface antigens of Candida albicans during morphogenesis. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):337–343. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.337-343.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassone A., Kerridge D., Gale E. F. Ultrastructural changes in the cell wall of Candida albicans following cessation of growth and their possible relationship to the development of polyene resistance. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Feb;110(2):339–349. doi: 10.1099/00221287-110-2-339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centeno A., Davis C. P., Cohen M. S., Warren M. M. Modulation of Candida albicans attachment to human epithelial cells by bacteria and carbohydrates. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1354–1360. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1354-1360.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaffin W. L., Skudlarek J., Morrow K. J. Variable expression of a surface determinant during proliferation of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):302–309. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.302-309.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins-Lech C., Kalbfleisch J. H., Franson T. R., Sohnle P. G. Inhibition by sugars of Candida albicans adherence to human buccal mucosal cells and corneocytes in vitro. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):831–834. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.831-834.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Critchley I. A., Douglas L. J. Isolation and partial characterization of an adhesin from Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Mar;133(3):629–636. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-3-629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Critchley I. A., Douglas L. J. Role of glycosides as epithelial cell receptors for Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Mar;133(3):637–643. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-3-637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dippold W. G., Lloyd K. O., Li L. T., Ikeda H., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. Cell surface antigens of human malignant melanoma: definition of six antigenic systems with mouse monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6114–6118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elorza M. V., Marcilla A., Sentandreu R. Wall mannoproteins of the yeast and mycelial cells of Candida albicans: nature of the glycosidic bonds and polydispersity of their mannan moieties. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Aug;134(8):2393–2403. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-8-2393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elorza M. V., Murgui A., Sentandreu R. Dimorphism in Candida albicans: contribution of mannoproteins to the architecture of yeast and mycelial cell walls. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Sep;131(9):2209–2216. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-9-2209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elorza M. V., Rico H., Gozalbo D., Sentandreu R. Cell wall composition and protoplast regeneration in Candida albicans. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1983 Nov;49(4-5):457–469. doi: 10.1007/BF00399324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. G., Richardson M. D., Odds F. C., Holland K. T. Relevance of antigenicity of Candida albicans growth phases to diagnosis of systemic candidiasis. Br Med J. 1973 Oct 13;4(5884):86–87. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5884.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R. Identification of concanavalin A-binding proteins after sodium dodecyl sulfate--gel electrophoresis and protein blotting. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jun;123(1):143–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90634-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood V., Poulain D., Fortier B., Evans G., Vernes A. A monoclonal antibody to a cell wall component of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):222–227. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.222-227.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood V., Warnock D. W. New developments in the diagnosis of opportunistic fungal infection. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Aug;5(4):379–388. doi: 10.1007/BF02075691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. M. Quantitation of antibody against cell wall mannan and a major cytoplasmic antigen of Candida in rabbits, mice, and humans. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):78–89. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.78-89.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura L. H., Pearsall N. N. Adherence of Candida albicans to human buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):64–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.64-68.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura L. H., Pearsall N. N. Relationship between germination of Candida albicans and increased adherence to human buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):464–468. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.464-468.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., King R. D. Characterization of Candida albicans adherence to human vaginal epithelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1024–1030. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1024-1030.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. L., Buckley H. R., Campbell C. C. An amino acid liquid synthetic medium for the development of mycelial and yeast forms of Candida Albicans. Sabouraudia. 1975 Jul;13(2):148–153. doi: 10.1080/00362177585190271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer N., Segal E., Barr-Nea L. In vitro and in vivo adherence of Candida albicans to mucosal surfaces. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1983 Sep-Oct;134B(2):293–306. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(83)80042-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning-Zweerink M., Maloney C. S., Mitchell T. G., Weston H. Immunoblot analyses of Candida albicans-associated antigens and antibodies in human sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jan;23(1):46–52. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.1.46-52.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning M., Mitchell T. G. Strain variation and morphogenesis of yeast- and mycelial-phase Candida albicans in low-sulfate, synthetic medium. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):714–719. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.714-719.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Costerton J. W. The ultrastructure of Candida albicans infections. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Nov;27(11):1156–1164. doi: 10.1139/m81-181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millette C. F., Scott B. K. Identification of spermatogenic cell plasma membrane glycoproteins by two-dimensional electrophoresis and lectin blotting. J Cell Sci. 1984 Jan;65:233–248. doi: 10.1242/jcs.65.1.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyakawa Y., Kagaya K., Fukazawa Y., Soe G. Production and characterization of agglutinating monoclonal antibodies against predominant antigenic factors for Candida albicans. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 May;23(5):881–886. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.5.881-886.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastor F. I., Herrero E., Sentandreu R. Metabolism of Saccharomyces cerevisiae envelope mannoproteins. Arch Microbiol. 1982 Aug;132(2):144–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00508720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponton J., Jones J. M. Analysis of cell wall extracts of Candida albicans by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and Western blot techniques. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):565–572. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.565-572.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulain D., Hopwood V., Vernes A. Antigenic variability of Candida albicans. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1985;12(3):223–270. doi: 10.3109/10408418509104430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandin R. L., Rogers A. L., Patterson R. J., Beneke E. S. Evidence for mannose-mediated adherence of Candida albicans to human buccal cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):79–85. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.79-85.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherwitz C. Ultrastructure of human cutaneous candidosis. J Invest Dermatol. 1982 Mar;78(3):200–205. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12506451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal E., Lehrer N., Ofek I. Adherence of Candida albicans to human vaginal epithelial cells: inhibition by amino sugars. Exp Cell Biol. 1982;50(1):13–17. doi: 10.1159/000163121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal E., Soroka A., Lehrer N. Attachment of Candida to mammalian tissues--clinical and experimental studies. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1984 Jul;257(2):257–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smail E. H., Jones J. M. Demonstration and solubilization of antigens expressed primarily on the surfaces of Candida albicans germ tubes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):74–81. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.74-81.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel J. D., Muller G., Buckley H. R. Critical role of germ tube formation in the pathogenesis of candidal vaginitis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jun;44(3):576–580. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.3.576-580.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel J. D., Myers P. G., Kaye D., Levison M. E. Adherence of Candida albicans to human vaginal and buccal epithelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jan;143(1):76–82. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.1.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundstrom P. M., Kenny G. E. Characterization of antigens specific to the surface of germ tubes of Candida albicans by immunofluorescence. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):850–855. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.850-855.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundstrom P. M., Kenny G. E. Enzymatic release of germ tube-specific antigens from cell walls of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):609–614. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.609-614.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundstrom P. M., Nichols E. J., Kenny G. E. Antigenic differences between mannoproteins of germ tubes and blastospores of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):616–620. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.616-620.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundstrom P. M., Tam M. R., Nichols E. J., Kenny G. E. Antigenic differences in the surface mannoproteins of Candida albicans as revealed by monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):601–606. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.601-606.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syverson R. E., Buckley H. R., Campbell C. C. Cytoplasmic antigens unique to the mycelial or yeast phase of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):1184–1188. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.1184-1188.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]