Abstract
Pancreatic panniculitis is a rare type of disorder associated with pancreatic diseases. We describe here a case of 54-year-old man who was admitted to the Department of Dermatology with the diagnosis of erythema nodosum. The patient presented with a 9-month history of painful erythematous nodules on the extremities, joint pain and swelling, and weight loss. A highly elevated level of pancreatic lipase was found on the laboratory examinations. The biopsy specimens from the skin lesions showed subcutaneous fat necrosis. Abdominal computed tomography (CT) revealed a large mass with central necrosis in the body and tail of the pancreas. Distal pancreatectomy, splenectomy and partial transverse colectomy were successfully performed on day 17 of the hospitalization. The histopathologic findings supported the diagnosis of acinar cell carcinoma of the pancreas (ACCP). Postoperatively, the level of serum lipase returned to normal, and the skin lesions and joint manifestations gradually regressed. However, the swelling did not significantly resolve in the left knee. In view of the non-specific clinical presentation of this disease, clinicians should be alert and have a high index of suspicion for pancreatic panniculitis.
Keywords: Acinar cell carcinoma of pancreas, Erythema nodosum, Pancreatic panniculitis, Subcutaneous fat necrosis
INTRODUCTION
Pancreatic panniculitis is a rare entity that was first described by Chiari1 in 1883, and it is most frequently associated with pancreatic diseases. These patients most often present with painful, erythematous nodules on the lower extremities. The skin lesions frequently precede other clinical findings2. In a review of the literature, approximately 60% of the patients with pancreatic panniculitis had absent or mild abdominal symptoms3. Because of its rarity, the diagnosis of pancreatic panniculitis can easily be missed or significantly delayed. Most patients may be initially misdiagnosed as erythema nodosum and sent to a dermatologist and a rheumatologist4. The diagnosis of pancreatic panniculitis should be considered for patients with subcutaneous nodules and elevated levels of pancreatic enzymes. In view of the non-specific presentation, further investigations are required to obtain an accurate diagnosis. Herein, we describe one patient who presented with subcutaneous nodules and polyarthritis, and the diagnosis of pancreatic panniculitis was considered on the basis of extensive investigations.
CASE REPORT
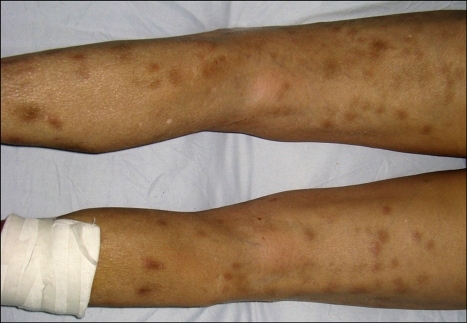
A 54-year-old man was admitted to the Department of Dermatology of West China Hospital with a 9-month history of painful erythematous nodules on the extremities, as well as painful and swelling of the ankle, knee, elbow, wrist and phalangeal joints. He also complained of anorexia and a weight loss of 10 kg within that time. Otherwise, the results of a review of the systems were normal. The physical examination revealed disseminated, ill-defined, tender, erythematous and violaceous nodules (1~4 cm in diameter) on the anterior aspects of the extremities. Some of the nodules were developing painless pigmentation (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Erythematous and violaceous nodules on the extremities.
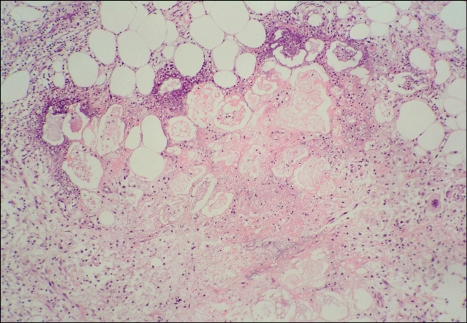
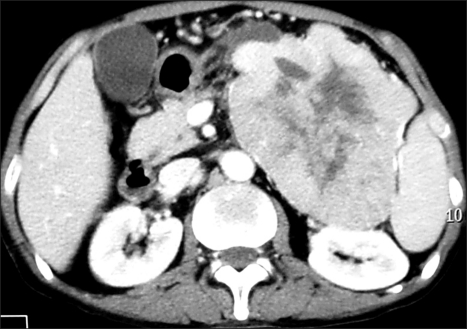
The initial laboratory values revealed a white blood cell count of 8.68×109/L (74.4% neutrophils), a hemoglobin level of 10.9 g/dL, a platelet count of 425×109/L and an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 41.0 mm/h. The liver profile showed normal levels of aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase and bilirubin. The plain film X-rays showed osteoporosis in both hands and the left knee. Based on the clinical manifestations and abnormal findings, the initial diagnosis of erythema nodosum was made. Symptomatic treatment, including Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F and hydrocortisone, brought no significant relief of his disease. New skin lesions then appeared on the patient's back. Further investigations revealed a highly elevated serum lipase level of 9,018 U/L (normal: 13~60 U/L), whereas the serum amylase value was normal. The level of tumor marker CA12-5 was 86.63 U/ml (normal: <35 U/ml), whereas the CA19-9 level was normal. A biopsy specimen of a nodule at the right lower leg showed focal fat necrosis, including ghost-like adipocytes with basophilic deposits, surrounded by an inflammatory infiltrate composed of neutrophils, lymphocytes, macrophages and multinucleated giant cells (Fig. 2). The contrast enhanced spiral CT scan of the abdomen showed a large mass (12.7×9.7 cm) in the body and tail of the pancreas, and the mass showed central necrosis (Fig. 3). Thus, the revised diagnosis of pancreatic panniculitis was made.
Fig. 2.
The skin biopsy showing pancreatic panniculitis with colliquative necrosis of adipocytes, ghost-like cells, an inflammatory infiltration and lipid-laden, foamy histiocytes (H&E, ×200).
Fig. 3.
Computed tomography scan showed a large mass with central necrosis in the body and tail of the pancreas.
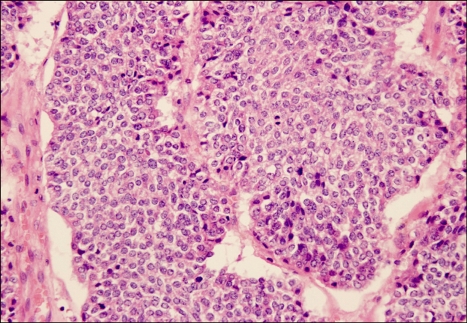
The patient was subsequently referred to the Hepatobiliopancreatic Surgical Department. Because of the poor nutritional status, the patient was treated with parenteral nutrition and high-dose intravenous octreotide (1.2 mg/day). Fortunately, the octreotide therapy was effective. The value of the serum lipase decreased to 2,999 U/L 3 days later. No new skin lesions appeared, the arthralgia improved as well. On day 17 of hospitalization, the patient and his relatives consented to laparotomy. The operation revealed a huge firm mass (approximately 11×11×10 cm) with central necrosis originating from the body and tail of the pancreas, and it had invaded the transverse colon. There was no evidence of metastasis in the lymph nodes, liver and other organs. Distal pancreatectomy, splenectomy and partial transverse colectomy were successfully performed. Histological examination of the resected specimen revealed an acinar cell carcinoma of the pancreas (ACCP) (Fig. 4). The incisional margin, spleen and all the resected lymph nodes were free of tumor.
Fig. 4.
The histological section of the pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma shows the acinar structure and a solid pattern with uniform nuclei (H&E, ×400).
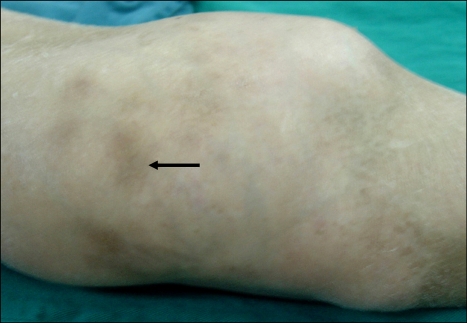
The patient then made an uneventful recovery. The serum lipase fell to 22 U/L on the 3rd day following surgery. On the follow up at two months, he had an increased appetite and had gained 5 kg in weight. The skin lesions regressed with subcutaneous pigmentation. All of the joint manifestations disappeared, except for those at the left knee (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5.
On the follow up at two months, the skin lesions regressed with subcutaneous pigmentation on the swollen left knee (arrows).
DISCUSSION
Pancreatic panniculitis is a rare type of disease that appears in approximately 2~3% of all patients with pancreatic diseases5. It is associated with acute6 or chronic pancreatitis7, pancreas divisum8, pancreatic pseudocyst9 and pancreatic carcinoma10. Clinically, patients with pancreatic panniculitis most often present with disseminated, ill-defined, tender, erythematous and violaceous nodules in the decubitus areas and lower extremities2. These nodules may spontaneously ulcerate and drain an oily brown, sterile, viscous substance11.
Joint pain and swelling is another common symptom. Dahl et al.2 found that six of eleven patients with pancreatic panniculitis showed arthropathy or arthritis. The elbows, ankles, knees and small joints are usually involved and this involvement is similar to the distribution of skin lesions. The arthropathy or arthritis is not correlated with primary synovitis, but it is caused by periarticular fat necrosis3. This hypothesis is supported on the basis that the arthrocentesis yields a sterile, creamy substance that contains amylase, lipase and free fatty acid12. It is believed that arthropathy or arthritis is associated with a poor prognosis, as in our patient. Although the tumor was resected and the serum lipase level returned to baseline, the left knee remained swollen3.
The less common findings include eosinophilia, serositis, abdominal fat necrosis, mesenteric thrombosis and bone marrow fat necrosis13. The radiological findings of the tubular bones of the extremities usually show multiple osteolytic lesions, and a diffuse increase of tracer uptake is also present on skeletal scintigraphy. The findings are the characteristic of bone marrow fat necrosis rather than primary or metastatic bone tumor. Thus, osteolytic lesions should not prevent tumor resection if no clear evidence of distant metastasis is detected4.
The clinical appearance of pancreatic panniculitis is nonspecific and it mimics erythema nodosum, rheumatoid nodule, panniculitis-like subcutaneous lymphomas and α1-antitrypsin deficiency panniculitis14. Therefore, the diagnosis usually requires further investigations. Conventional radiological imaging of the pancreas and the involved joints, detailed laboratory examinations such as assessing the pancreatic enzymes and tumoral markers and a biopsy of the skin lesions should be obligatory.
Biopsy specimens from the mature lesions of pancreatic panniculitis show pathognomonic histopathology findings of liquefactive fat necrosis. Anucleated adipocytes with a thickened shadowy wall and granular basophilic cytoplasm, and these are called 'ghost-like' cells, can be seen in the affected fat lobules. Surrounding the foci of fat necrosis is an inflammatory infiltrate consisting of neutrophils, lymphocytes, macrophages and multinucleated giant cells6. These histologic changes are not static. The early lesions show septal panniculitis. This is characterized by a lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate within the fibrous septa dividing the subcutaneous fat into lobules. The later lesions show granulomatous panniculitis, which probably represents organization of subcutaneous fat necrosis. The diagnosis of pancreatic panniculitis should not be too rigid because the histologic character of an individual case changes during its evolution15.
The pathogenesis of pancreatic panniculitis is not clear, but the release of pancreatic enzymes such as trypsin, amylase, lipase and phospholipase may play a synergetic role in lipolysis. It is speculated that trypsin and phospholipase may erode the blood vessel endothelium and increase the vasopermeability, thereby allowing lipase to enter into the subcutaneous fat and hydrolyze triglycerides to form free fatty acids6. However, most cases of pancreatitis have high levels of serum amylase and/or lipase without subcutaneous fat necrosis. Furthermore, in an earlier study a case of pancreatic panniculitis with normal levels of amylase and lipase has been described2, and Zellman16 demonstrated the relationship between immunologic processes and subcutaneous fat necrosis in 1996. Hence, it is suggested that multiple factors may be involved in an episode of fat necrosis.
Here we described a case of pancreatic panniculitis associated with ACCP, which accounts for only 1~2% of all exocrine pancreatic neoplasms10. ACCP is a kind of functional exocrine tumor that is characterized by an increased level of serum lipase leading to paraneoplastic syndrome. There are no specific signs and symptoms in early stage of ACCP, and it tends to be large (mean size: 10 cm in diameter), locally invasive and metastatic, and especially to the liver at the time of diagnosis5. In our case abdominal symptoms were absent, leading to a misdiagnosis. The delay of 9 months for the diagnosis and treatment worsened the prognosis of this condition. Rarely, other types of pancreatic carcinoma are associated with panniculitis, including islet cell carcinoma17, neuroendocrine carcinoma4,18 and acinar cell cystadenocarcinoma5.
Treatment of pancreatic panniculitis should be directed at the underlying pancreatic diseases. The somatostatin analogue octreotide, which inhibits secretion of pancreatic enzymes, can be useful to resolve the skin lesions and arthropathy19. However, Preiss and his collegues18 demonstrated it was ineffective in an 88-year-old man with neuroendocrine carcinoma and whose somatostatin receptor scintigraphy was negative. It has also been demonstrated that corticosteroid, non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs, and immunosuppressants could effectively not control the symptoms5,11. In patients with pancreatic carcinoma, the resection of pancreatic tumor should be performed as soon as possible, and if this is not successful, then treatment with combination chemotherapeutics may be administered.
In conclusion, we present a rare example of pancreatic panniculitis in a patient with ACCP. The clinical appearance was nonspecific and this case was a diagnostic challenge. Therefore, clinicians should be alert to the association between ACCP and pancreatic panniculitis and conduct appropriate investigations.
References
- 1.Chiari H. Über die Sogenannte Fettnekrose. Prager Med Wochenschr. 1883;8:285–286. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Dahl PR, Su WP, Cullimore KC, Dicken CH. Pancreatic panniculitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;33:413–417. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(95)91385-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Narváez J, Bianchi MM, Santo P, de la Fuente D, Ríos-Rodriguez V, Bolao F, et al. Pancreatitis, panniculitis, and polyarthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2010;39:417–423. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2008.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Berkovic D, Hallermann C. Carcinoma of the pancreas with neuroendocrine differentiation and nodular panniculitis. Onkologie. 2003;26:473–476. doi: 10.1159/000072982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Beltraminelli HS, Buechner SA, Häusermann P. Pancreatic panniculitis in a patient with an acinar cell cystadenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Dermatology. 2004;208:265–267. doi: 10.1159/000077316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Suwattee P, Cham PM, Pope E, Ho N. Pancreatic panniculitis in a 4-year-old child with nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:659–660. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.2007.00561.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mourad FH, Hannoush HM, Bahlawan M, Uthman I, Uthman S. Panniculitis and arthritis as the presenting manifestation of chronic pancreatitis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2001;32:259–261. doi: 10.1097/00004836-200103000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Haber RM, Assaad DM. Panniculitis associated with a pancreas divisum. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;14:331–334. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(86)70037-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.López A, García Estañ J, Marras C, Castaño M, Rojas MJ, Garre C, et al. Pancreatitis associated with pleural-mediastinal pseudocyst, panniculitis and polyarthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 1998;17:335–339. doi: 10.1007/BF01451017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Antoine M, Khitrik-Palchuk M, Saif MW. Long-term survival in a patient with acinar cell carcinoma of pancreas. A case report and review of literature. JOP. 2007;8:783–789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jovanović M, Golušin Z, Petrović A, Vučković N, Brkić S, Sotirović-Seničar S, et al. Lobular panniculitis: a manifestation of pancreatic tumor with fatal outcome. Arch Oncol. 2005;13:153–155. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chi ZC, Ma SZ. Rheumatologic manifestations of hepatic diseases. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2003;2:32–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.García-Romero D, Vanaclocha F. Pancreatic panniculitis. Dermatol Clin. 2008;26:465–470. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2008.05.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Requena L. Normal subcutaneous fat, necrosis of adipocytes and classification of the panniculitides. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2007;26:66–70. doi: 10.1016/j.sder.2007.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ball NJ, Adams SP, Marx LH, Enta T. Possible origin of pancreatic fat necrosis as a septal panniculitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;34:362–364. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(07)80009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zellman GL. Pancreatic panniculitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35:282–283. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(96)90359-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lewis CT, 3rd, Tschen JA, Klima M. Subcutaneous fat necrosis associated with pancreatic islet cell carcinoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1991;13:52–56. doi: 10.1097/00000372-199102000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Preiss JC, Faiss S, Loddenkemper C, Zeitz M, Duchmann R. Pancreatic panniculitis in an 88-year-old man with neuroendocrine carcinoma. Digestion. 2002;66:193–196. doi: 10.1159/000066758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Durden FM, Variyam E, Chren MM. Fat necrosis with features of erythema nodosum in a patient with metastatic pancreatic carcinoma. Int J Dermatol. 1996;35:39–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4362.1996.tb01614.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]