Abstract
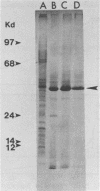
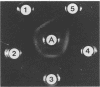
Corncobs, which are distinct morphological units formed by the ordered coaggregation of a filamentous microorganism and streptococci, can be made in vitro by using oral strains of Fusobacterium nucleatum and Streptococcus sanguis. Previous studies have shown that strains of F. nucleatum contain one of at least two different types of corncob receptor. The objective of this study was to isolate the receptor from F. nucleatum ATCC 10953 as the first step in the elucidation of the molecular basis of corncob formation. The cell envelope fraction from this bacterium was treated with trypsin, delipidated with chloroform-methanol, and subjected to ion-exchange chromatography. A single polypeptide (apparent Mr, 39,500), which was eluted from the column with 0.5 M sodium chloride and extracted with dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide to remove contaminating lipopolysaccharide, inhibited corncob formation between strain ATCC 10953 and S. sanguis CC5A. Similarly derived cell fractions from either F. nucleatum FDC 364 or Fusobacterium necrophorum failed to effect coaggregation in the inhibition assay. Amino acid analysis of the polypeptide showed a moderately hydrophobic character (polarity index, 41) and 11% basic residues. Antiserum made against the purified polypeptide agglutinated F. nucleatum ATCC 10953, neutralized the ability of this bacterium to form corncobs, and agglutinated whole cells of S. sanguis CC5A that were precoated with the receptor polypeptide. The identification and isolation of this receptor should greatly enhance our ability to define some of the complex intergeneric coaggregation mechanisms that are thought to occur in the human oral cavity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F. Lipids of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli: structure and metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):833–843. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.833-843.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Nikaido K. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of membrane proteins. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):616–623. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck E., Bremer E. Nucleotide sequence of the gene ompA coding the outer membrane protein II of Escherichia coli K-12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 11;8(13):3011–3027. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.13.3011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capaldi R. A., Vanderkooi G. The low polarity of many membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):930–932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R., Schmidmayr W., Krämer C., Chen-Schmeisser U., Henning U. Primary structure of major outer membrane protein II (ompA protein) of Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4592–4596. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta D. B., Arden B., Henning U. Major proteins of the Escherichia coli outer cell envelope membrane as bacteriophage receptors. J Bacteriol. 1977 Sep;131(3):821–829. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.3.821-829.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRienzo J. M., Rosan B. Isolation of a major cell envelope protein from Fusobacterium nucleatum. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):386–393. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.386-393.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hase S., Hofstad T., Rietschel E. T. Chemical structure of the lipid A component of lipopolysaccharides from Fusobacterium nucleatum. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):9–14. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.9-14.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch F. T. Correlation of amino-acid composition with certain characteristics of proteins. Nature. 1965 May 22;206(4986):777–779. doi: 10.1038/206777a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. J. A special relationship between spherical and filamentous microorganisms in mature human dental plaque. Arch Oral Biol. 1972 Mar;17(3):613–616. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(72)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelstrup J., Funder-Nielsen T. D. Aggregation of oral streptococci with Fusobacterium and Actinomyces. J Biol Buccale. 1974 Dec;2(4):347–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Andersen R. N. Multigeneric aggregations among oral bacteria: a network of independent cell-to-cell interactions. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):851–859. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.851-859.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristoffersen T., Hofstad T. Chemical composition of lipopolysaccharide endotoxins from human oral fusobacteria. Arch Oral Biol. 1970 Oct;15(10):909–916. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(70)90087-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancy P., Jr, Dirienzo J. M., Appelbaum B., Rosan B., Holt S. C. Corncob formation between Fusobacterium nucleatum and Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):303–309. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.303-309.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore L. V., Moore W. E., Cato E. P., Smibert R. M., Burmeister J. A., Best A. M., Ranney R. R. Bacteriology of human gingivitis. J Dent Res. 1987 May;66(5):989–995. doi: 10.1177/00220345870660052401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouton C., Reynolds H. S., Genco R. J. Characterization of tufted streptococci isolated from the "corn cob" configuration of human dental plaque. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):235–245. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.235-245.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouton C., Reynolds H., Genco R. J. Combined micromanipulation, culture and immunofluorescent techniques for isolation of the coccal organisms comprising the "corn cob" configuration of human dental plaque. J Biol Buccale. 1977 Dec;5(4):321–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. A., Kern D. G., Winkler J. R. Identification of a galactose-binding lectin on Fusobacterium nucleatum FN-2. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1314–1319. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1314-1319.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritz H. L. Microbial population shifts in developing human dental plaque. Arch Oral Biol. 1967 Dec;12(12):1561–1568. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(67)90190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savitt E. D., Socransky S. S. Distribution of certain subgingival microbial species in selected periodontal conditions. J Periodontal Res. 1984 Mar;19(2):111–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1984.tb00800.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada H., Ogawa T., Yoshimura F., Otsuka K., Kokeguchi S., Kato K., Umemoto T., Kotani S. Immunobiological activities of a porin fraction isolated from Fusobacterium nucleatum ATCC 10953. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):855–863. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.855-863.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takazoe I., Matsukubo T., Katow T. Experimental formation of "corn cob" in vitro. J Dent Res. 1978 Feb;57(2):384–387. doi: 10.1177/00220345780570024101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasstrand E. N., Hofstad T., Endresen C., Jensen H. B. Demonstration of lanthionine as a natural constituent of the peptidoglycan of Fusobacterium nucleatum. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):775–780. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.775-780.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Palenstein Helderman W. H. Total viable count and differential count of vibrio (campylobacter) sputorum, fusobacterium nucleatum, selenomonas sputigena, bacteroides ochraceus and veillonella in the inflamed and non inflamed human gingival crevice. J Periodontal Res. 1975 Nov;10(5):294–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1975.tb00037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]