Abstract
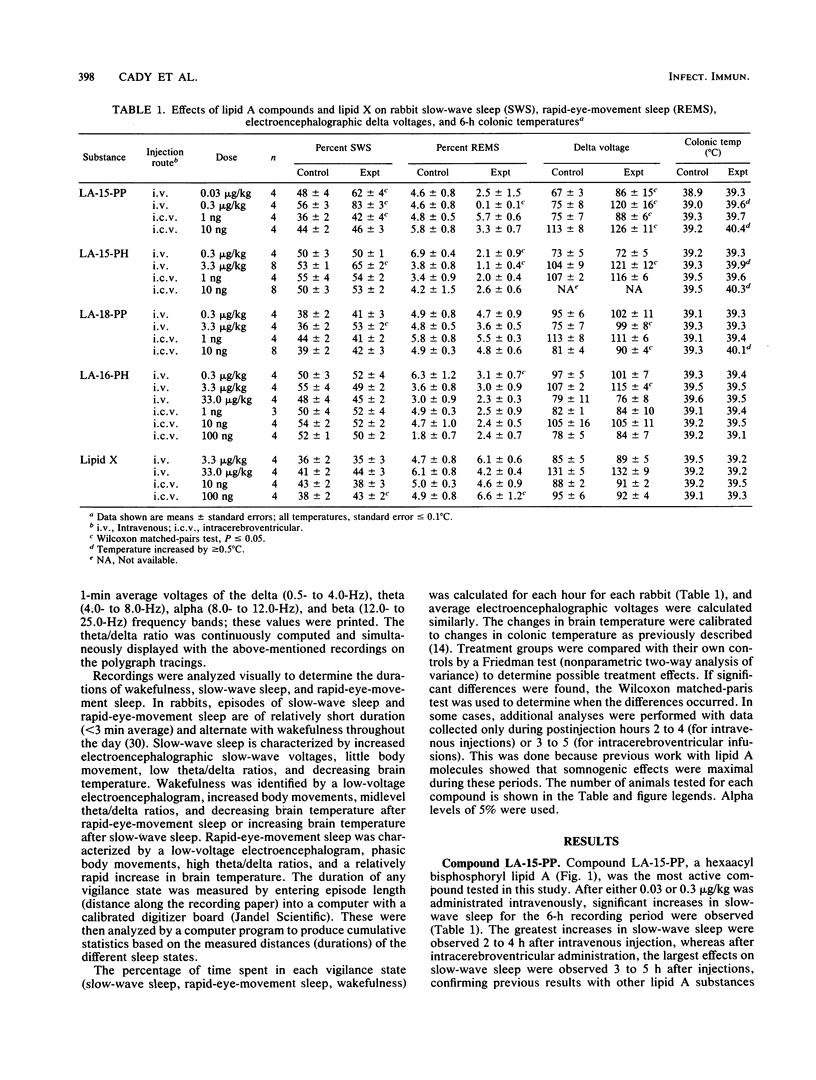
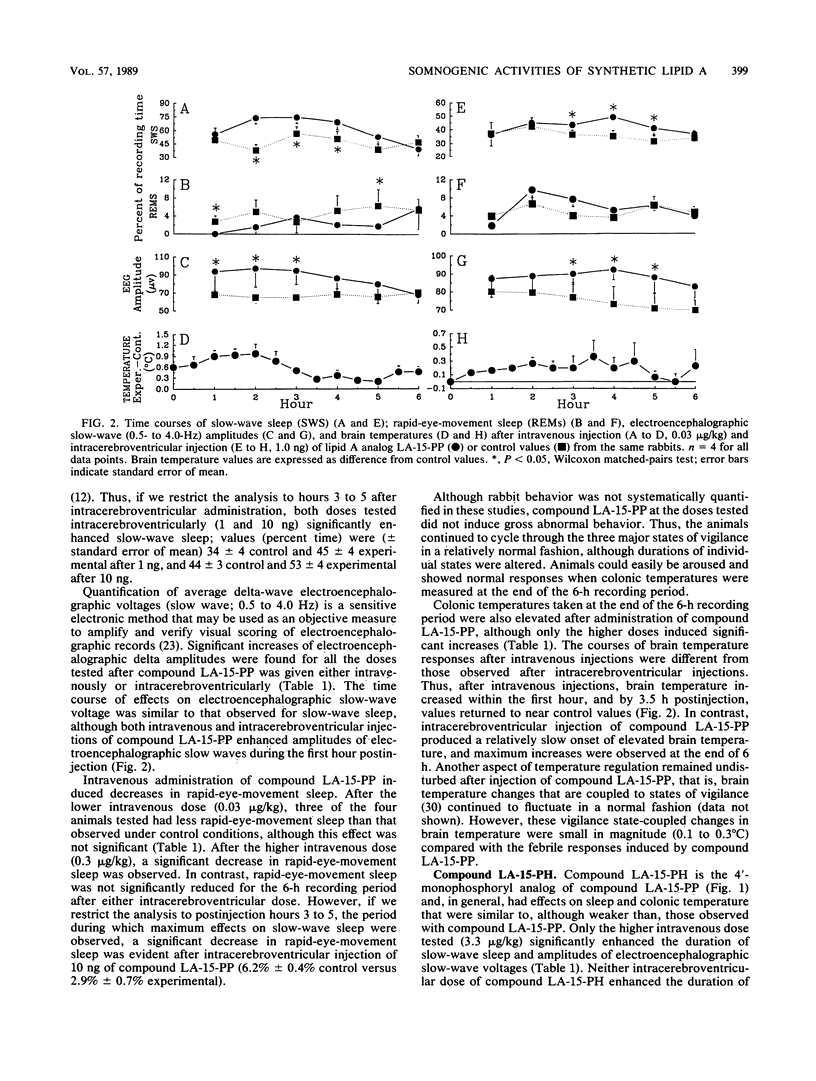
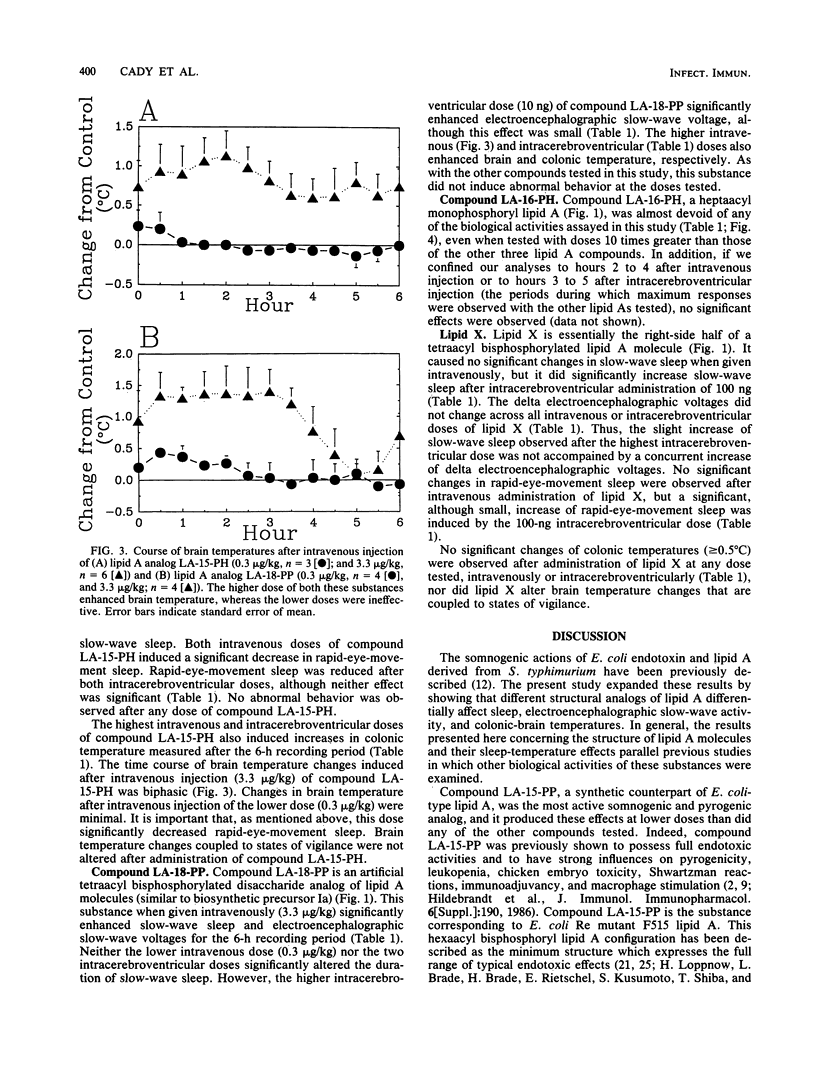
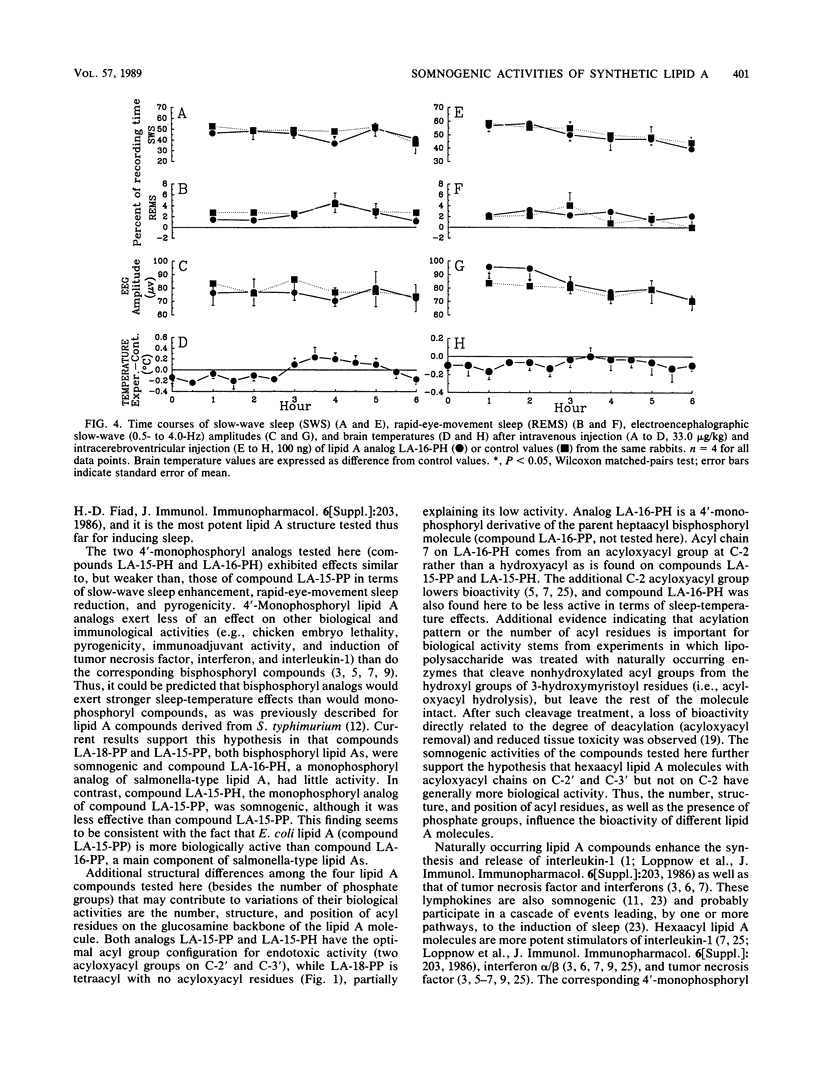
Bacterial infections and various immune response modifiers, including endotoxin and its lipid A moiety, alter sleep duration. The purpose of this study is to amplify our understanding of lipid A structure-somnogenic-pyrogenic activity relationships. Four synthetic disaccharide analogs of lipid A (LA-15-PP, LA-15-PH, LA-16-PH, and LA-18-PP) and a biosynthetic monosaccharide analog of lipid A (lipid X) were tested in rabbits for their effects on slow-wave sleep, rapid-eye-movement sleep, electroencephalographic slow-wave (0.5- to 4.0-Hz) amplitudes, and brain-colonic temperatures. Substances were injected intravenously and intracerebroventricularly. Compound LA-15-PP was the most potent; it significantly increased slow-wave sleep, delta electroencephalographic amplitudes, and brain-colonic temperatures while reducing rapid-eye-movement sleep. Compound LA-15-PH (monophosphoryl analog of LA-15-PP) induced effects similar to those of LA-15-PP, although the responses were weaker. Compound LA-18-PP induced increases in slow-wave sleep and delta amplitudes only after high doses, whereas compound LA-16-PH was devoid of these activities at the doses tested. Intracerebroventricular, but not intravenous, injections of lipid X induced small but significant increases in both slow-wave sleep and rapid-eye-movement sleep without affecting delta amplitudes or brain-colonic temperatures. These data suggest that the somnogenic actions of these lipid A analogs depend on the acylation or phosphorylation pattern and backbone structures of the molecules. Their soporific activities parallel their relative behaviors in other biological assays.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jan-Feb;6(1):51–95. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Rietschel E. T., Westphal O., Brade H., Brade L., Freudenberg M., Schade U., Imoto M., Yoshimura H. Synthetic and natural Escherichia coli free lipid A express identical endotoxic activities. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Apr 1;148(1):1–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma J. Y., Matsuura M., Kanegasaki S., Kawakubo Y., Kojima Y., Shibukawa N., Kumazawa Y., Yamamoto A., Tanamoto K., Yasuda T. Structural requirements of lipid A responsible for the functions: a study with chemically synthesized lipid A and its analogues. J Biochem. 1985 Aug;98(2):395–406. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanegasaki S., Tanamoto K., Yasuda T., Homma J. Y., Matsuura M., Nakatsuka M., Kumazawa Y., Yamamoto A., Shiba T., Kusumoto S. Structure-activity relationship of lipid A: comparison of biological activities of natural and synthetic lipid A's with different fatty acid compositions. J Biochem. 1986 Apr;99(4):1203–1210. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotani S., Takada H., Takahashi I., Ogawa T., Tsujimoto M., Shimauchi H., Ikeda T., Okamura H., Tamura T., Harada K. Immunobiological activities of synthetic lipid A analogs with low endotoxicity. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):673–682. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.673-682.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotani S., Takada H., Takahashi I., Tsujimoto M., Ogawa T., Ikeda T., Harada K., Okamura H., Tamura T., Tanaka S. Low endotoxic activities of synthetic Salmonella-type lipid A with an additional acyloxyacyl group on the 2-amino group of beta (1-6) glucosamine disaccharide 1,4'-bisphosphate. Infect Immun. 1986 Jun;52(3):872–884. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.3.872-884.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotani S., Takada H., Tsujimoto M., Ogawa T., Harada K., Mori Y., Kawasaki A., Tanaka A., Nagao S., Tanaka S. Immunobiologically active lipid A analogs synthesized according to a revised structural model of natural lipid A. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):293–296. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.293-296.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotani S., Takada H., Tsujimoto M., Ogawa T., Takahashi I., Ikeda T., Otsuka K., Shimauchi H., Kasai N., Mashimo J. Synthetic lipid A with endotoxic and related biological activities comparable to those of a natural lipid A from an Escherichia coli re-mutant. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):225–237. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.225-237.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. M., Bacsik J., García-Arrarás J. Sleep-promoting material from human urine and its relation to factor S from brain. Am J Physiol. 1980 Feb;238(2):E116–E123. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.238.2.E116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. M., Dinarello C. A., Shoham S., Davenne D., Walter J., Kubillus S. Interferon alpha-2 enhances slow-wave sleep in rabbits. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1987;9(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(87)90107-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. M., Kubillus S., Shoham S., Davenne D. Enhancement of slow-wave sleep by endotoxin and lipid A. Am J Physiol. 1986 Sep;251(3 Pt 2):R591–R597. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1986.251.3.R591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. M., Pappenheimer J. R., Karnovsky M. L. Sleep-promoting effects of muramyl peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):6102–6106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. M., Pappenheimer J. R., Karnovsky M. L. The composition of sleep-promoting factor isolated from human urine. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1664–1669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. M., Rosenthal R. S., Martin S. A., Walter J., Davenne D., Shoham S., Kubillus S. L., Biemann K. Bacterial peptidoglycans as modulators of sleep. I. Anhydro forms of muramyl peptides enhance somnogenic potency. Brain Res. 1987 Feb 17;403(2):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90062-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mashburn T. A., Jr, Llanos J., Hunter W. S., Ahokas R. A., Blatteis C. M. Differential acute-phase responses in febrile and cold- and heat-exposed rabbits. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Oct;402(2):157–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00583328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen Z., Karnovsky M. L. Qualitative detection of muramic acid in normal mammalian tissues. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):937–941. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.937-941.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoham S., Davenne D., Cady A. B., Dinarello C. A., Krueger J. M. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1 enhance slow-wave sleep. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jul;253(1 Pt 2):R142–R149. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1987.253.1.R142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi I., Kotani S., Takada H., Shiba T., Kusumoto S. Structural requirements of endotoxic lipopolysaccharides and bacterial cell walls in induction of interleukin-1. Blood Purif. 1988;6(3):188–206. doi: 10.1159/000169545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi I., Kotani S., Takada H., Tsujimoto M., Ogawa T., Shiba T., Kusumoto S., Yamamoto M., Hasegawa A., Kiso M. Requirement of a properly acylated beta(1-6)-D-glucosamine disaccharide bisphosphate structure for efficient manifestation of full endotoxic and associated bioactivities of lipid A. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):57–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.57-68.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama K., Qureshi N., Ribi E., Cantrell J. L. Separation and characterization of toxic and nontoxic forms of lipid A. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jul-Aug;6(4):439–443. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.4.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanamoto K., Zähringer U., McKenzie G. R., Galanos C., Rietschel E. T., Lüderitz O., Kusumoto S., Shiba T. Biological activities of synthetic lipid A analogs: pyrogenicity, lethal toxicity, anticomplement activity, and induction of gelation of Limulus amoebocyte lysate. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):421–426. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.421-426.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toth L. A., Krueger J. M. Alteration of sleep in rabbits by Staphylococcus aureus infection. Infect Immun. 1988 Jul;56(7):1785–1791. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.7.1785-1791.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen M. W., Gray G. R. Processing of Bacillus subtilis peptidoglycan by a mouse macrophage cell line. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):476–483. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.476-483.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



