Abstract
Pasteurella haemolytica A1 leukotoxin causes rapid (5 to 15 min) leakage of intracellular K+ and cell swelling and slower (15 to 60 min), Ca2+-dependent formation of large plasma membrane defects (congruent to 100 nm) and leakage of lactate dehydrogenase from bovine lymphoma cells (BL3 cells) (K. D. Clinkenbeard, D. A. Mosier, A. L. Timko, and A. W. Confer, Am. J. Vet. Res., in press). Incubation of BL3 cells in medium made hypertonic by inclusion of 75 mM sucrose blocked leukotoxin-induced cell swelling, formation of large plasma membrane defects, and leakage of lactate dehydrogenase but did not block leukotoxin-induced leakage of intracellular K+. Carbohydrates with molecular weights less than that of sucrose, e.g., mannitol, did not block leukotoxin-induced cell swelling of BL3 cells. Increasing the concentration of mannitol to twice that of sucrose still resulted in no protective effect. Assuming that leukotoxin acts as a transmembrane molecular sieve, then the functional transmembrane pore size formed by leukotoxin in BL3 cells is slightly less than the size of sucrose, i.e., 0.9 nm. Exposure of BL3 cells to leukotoxin for 15 or 45 min followed by the addition of hypertonic sucrose to the incubation medium reversed leukotoxin-induced cell swelling and prevented further leakage of lactate dehydrogenase. Leukotoxin-induced leakage of lactate dehydrogenase required both cell swelling and Ca2+-dependent processes. The Ca2+-dependent steps can occur before or concurrent with cell swelling.
Full text
PDF

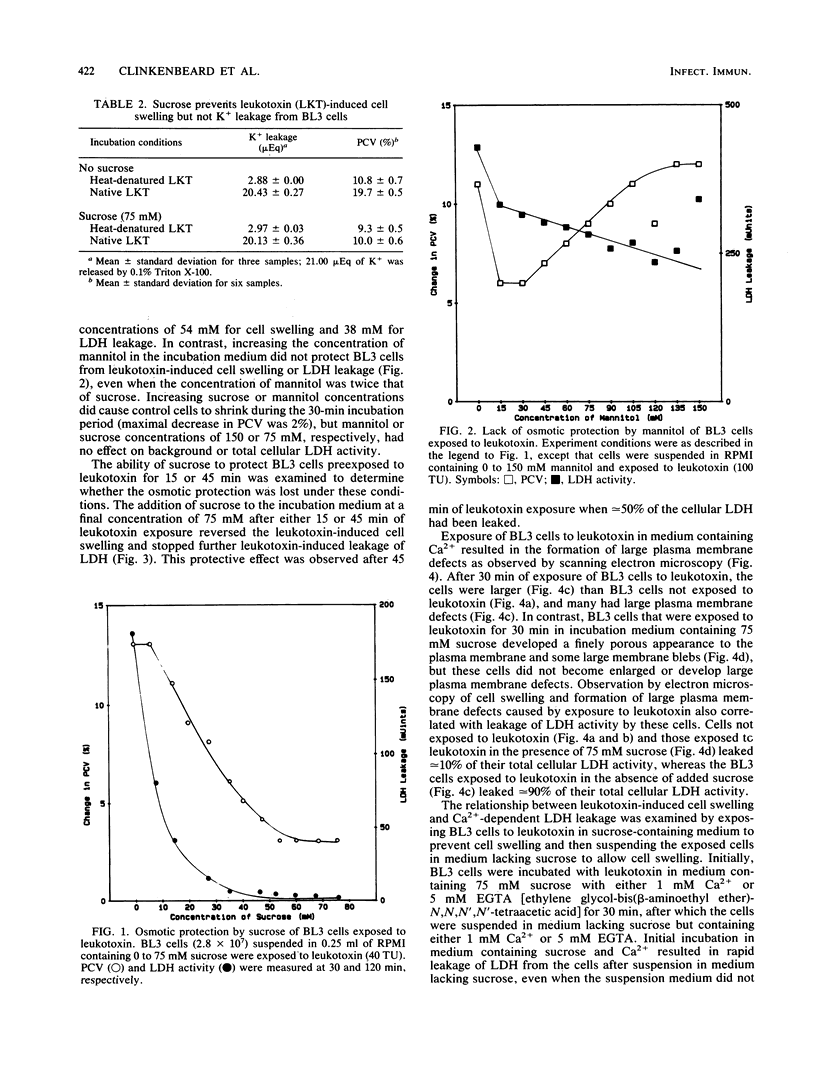
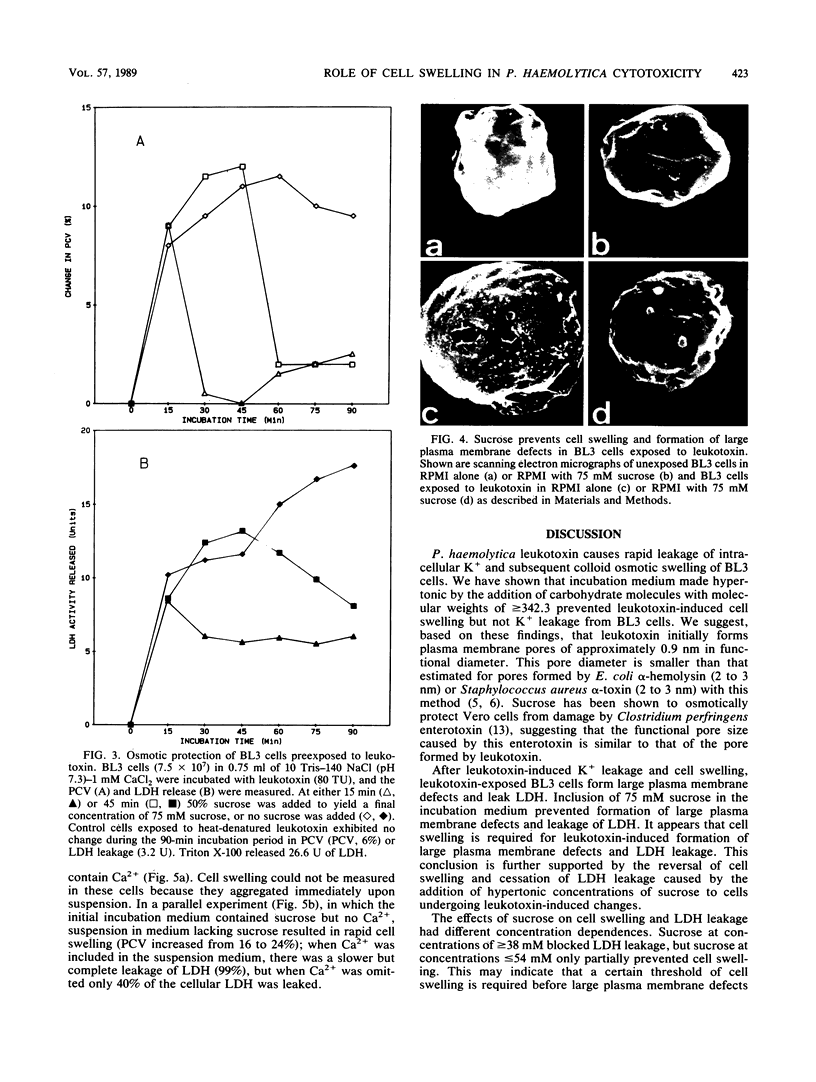
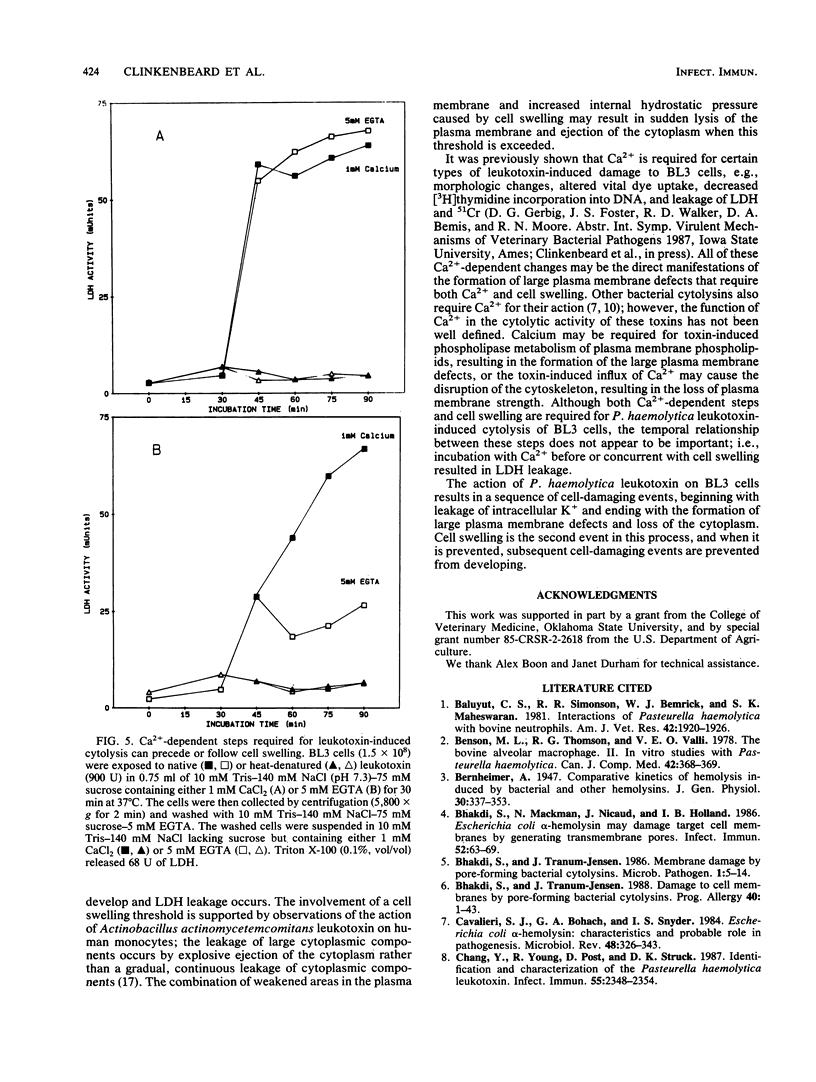

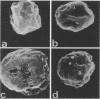
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baluyut C. S., Simonson R. R., Bemrick W. J., Maheswaran S. K. Interaction of Pasteurella haemolytica with bovine neutrophils: identification and partial characterization of a cytotoxin. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Nov;42(11):1920–1926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson M. L., Thomson R. G., Valli V. E. The bovine alveolar macrophage. II. In vitro studies with Pasteurella haemolytica. Can J Comp Med. 1978 Jul;42(3):368–369. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Mackman N., Nicaud J. M., Holland I. B. Escherichia coli hemolysin may damage target cell membranes by generating transmembrane pores. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):63–69. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.63-69.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Damage to cell membranes by pore-forming bacterial cytolysins. Prog Allergy. 1988;40:1–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Membrane damage by pore-forming bacterial cytolysins. Microb Pathog. 1986 Feb;1(1):5–14. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90027-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLIER J. R., BROWN W. W., Jr, CHOW T. L. Microbiologic investigations of natural epizootics of shipping fever of cattle. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1962 Apr 15;140:807–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri S. J., Bohach G. A., Snyder I. S. Escherichia coli alpha-hemolysin: characteristics and probable role in pathogenicity. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Dec;48(4):326–343. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.4.326-343.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. F., Young R., Post D., Struck D. K. Identification and characterization of the Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2348–2354. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2348-2354.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiguchi Y., Uemura T., Kozaki S., Sakaguchi G. Effects of Ca2+ and other cations on the action of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Oct 31;889(1):65–71. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo R. Y., Strathdee C. A., Shewen P. E. Nucleotide sequence of the leukotoxin genes of Pasteurella haemolytica A1. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):1987–1996. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.1987-1996.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor R. D., 2nd, Tobias C. A. Molecular sieving of red cell membranes during gradual osmotic hemolysis. J Membr Biol. 1972 Dec 29;10(3):345–356. doi: 10.1007/BF01867865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClane B. A., McDonel J. L. Protective effects of osmotic stabilizers on morphological and permeability alterations induced in Vero cells by Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Mar 6;641(2):401–409. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90496-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. A., Lessley B. A., Confer A. W., Antone S. M., Gentry M. J. Chromatographic separation and characterization of Pasteurella haemolytica cytotoxin. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Oct;47(10):2233–2241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathdee C. A., Lo R. Y. Extensive homology between the leukotoxin of Pasteurella haemolytica A1 and the alpha-hemolysin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3233–3236. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3233-3236.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taichman N. S., Dean R. T., Sanderson C. J. Biochemical and morphological characterization of the killing of human monocytes by a leukotoxin derived from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):258–268. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.258-268.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]