Abstract
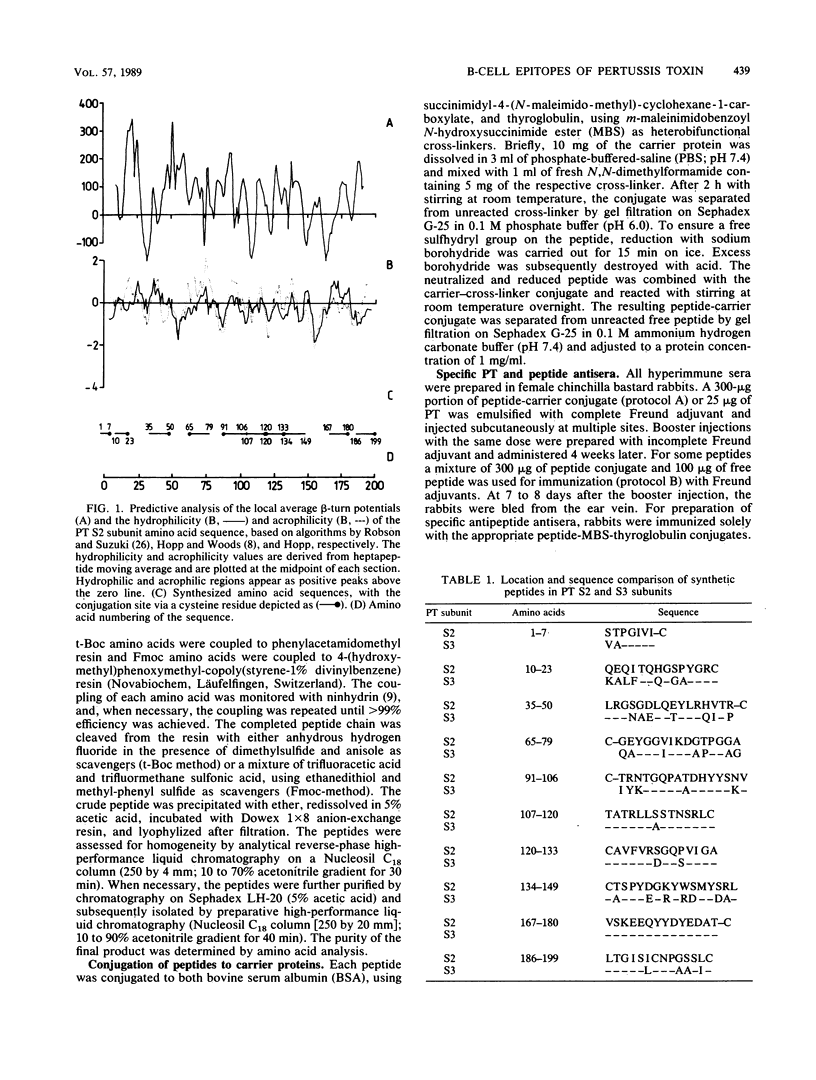
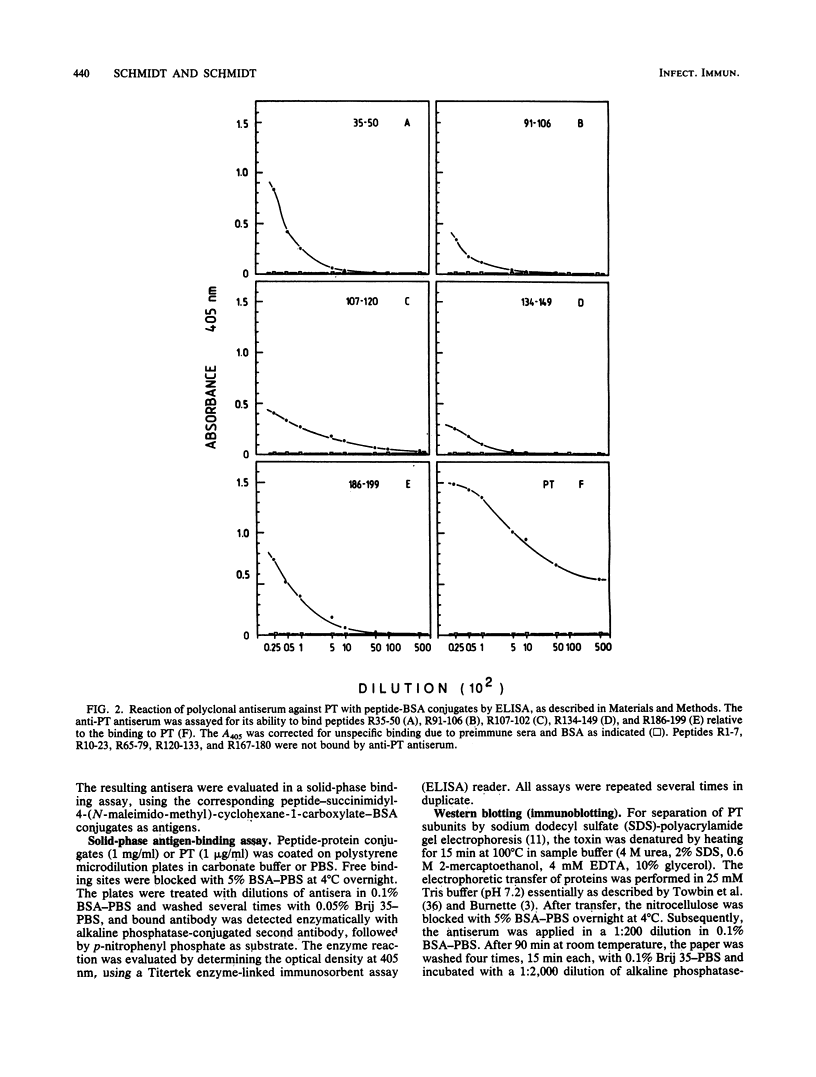
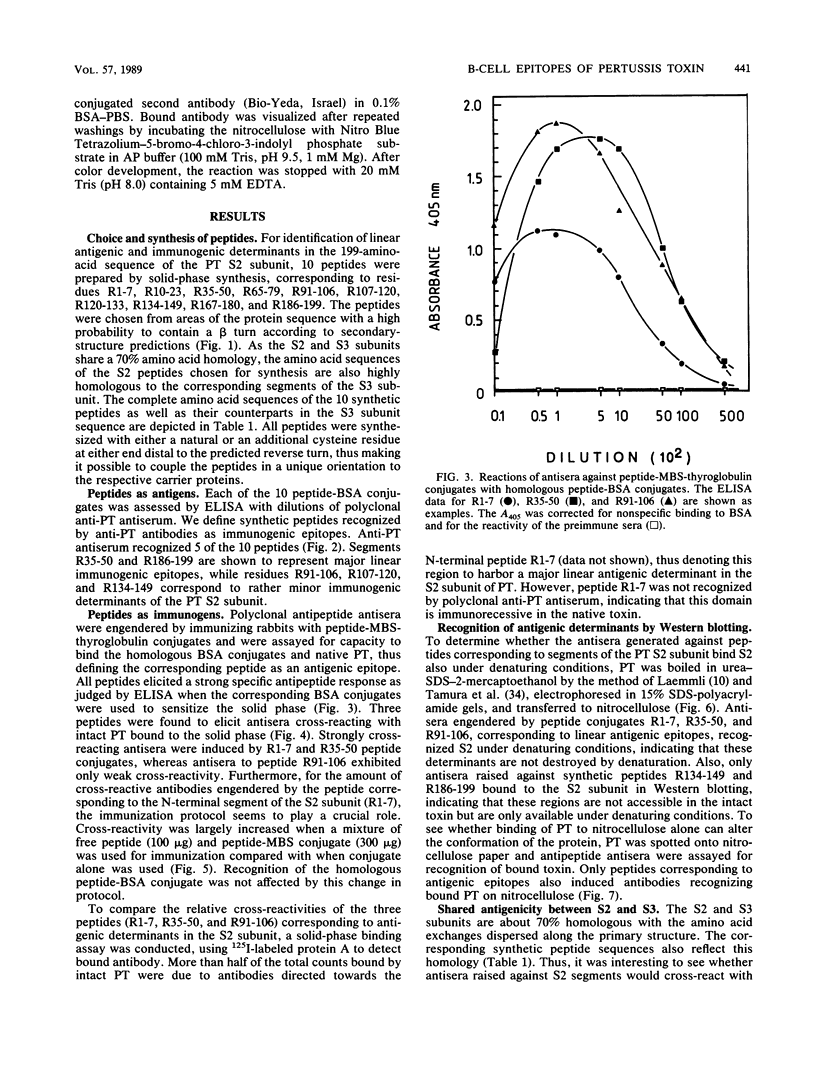
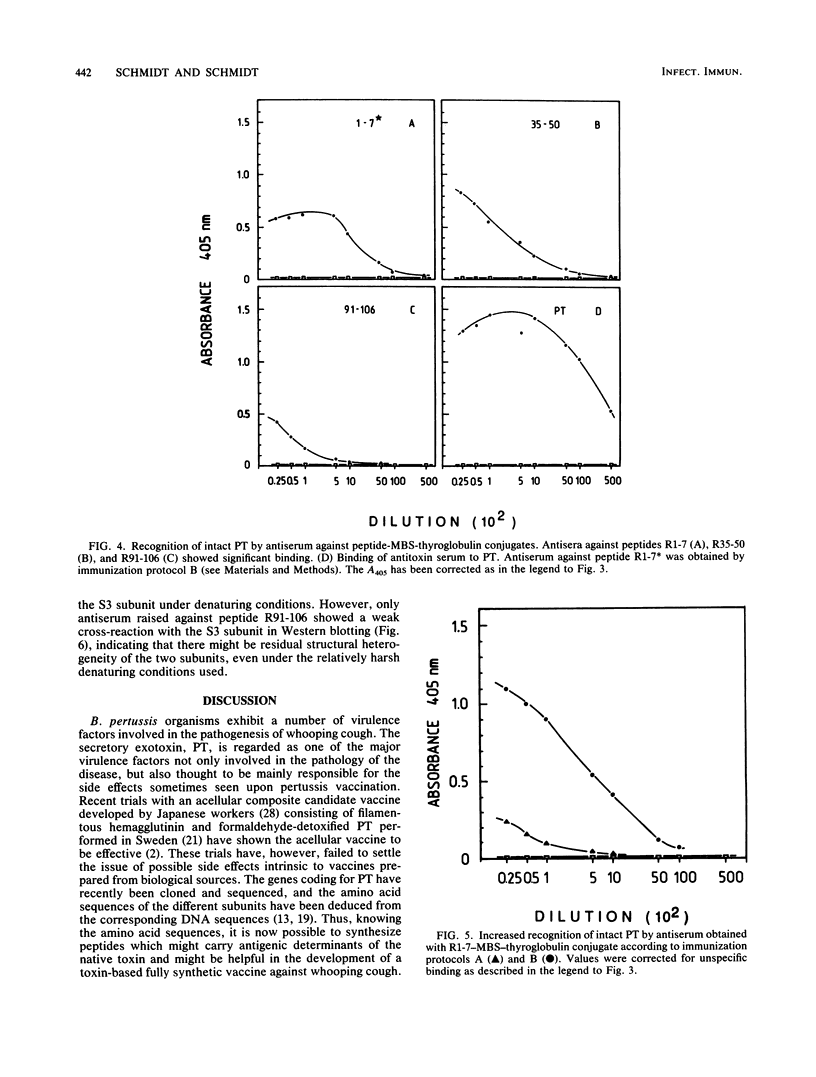
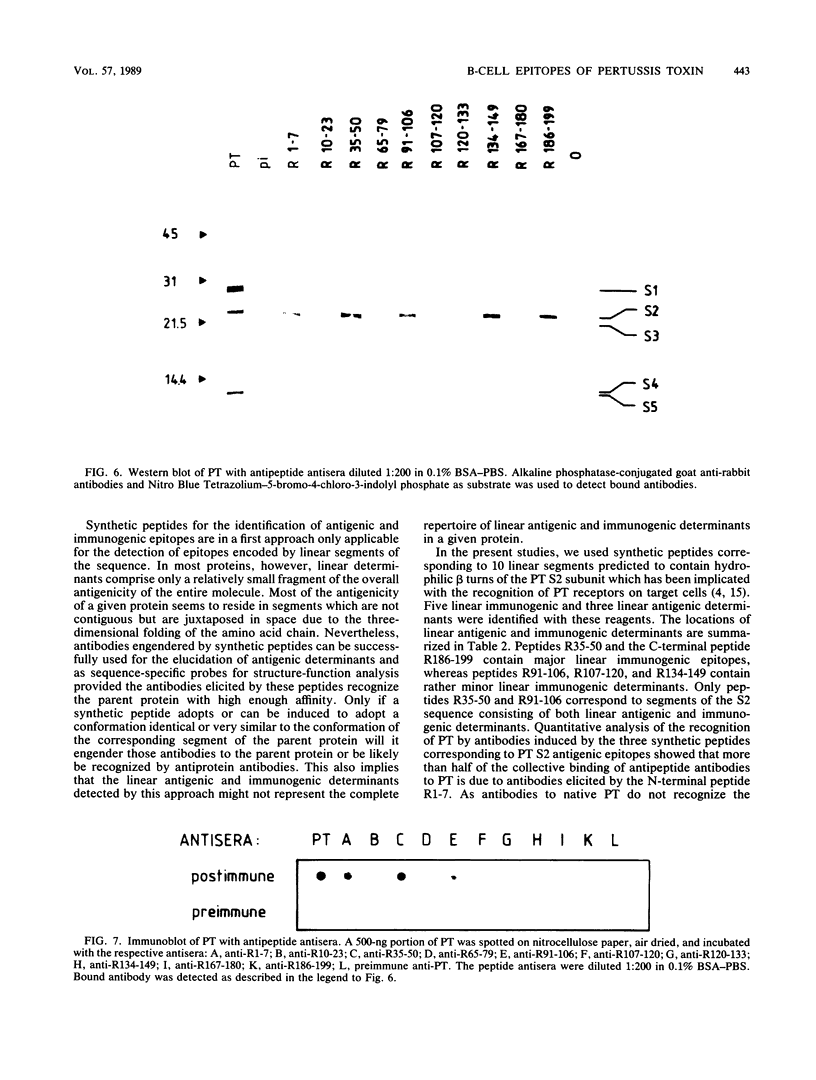
The linear immunogenic and antigenic structure of the S2 subunit of pertussis toxin was investigated with synthetic peptides corresponding to regions of the protein sequence predicted to contain surface-exposed hydrophilic beta turns. Five peptides as peptide-bovine serum albumin conjugates were recognized by anti-pertussis toxin antiserum and were thus designated "immunogenic epitopes." Two prominent immunogenic epitopes were specified by peptides corresponding to sequences spanning R107-120 and R186-199, whereas peptides corresponding to residues R35-50 and R91-106 were only bound in low titer. Three peptides as thyroglobulin conjugates elicited antisera in rabbits that bound intact pertussis toxin by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunoblot. These peptides were designated "antigenic epitopes." The most prominent antigenic determinant was localized to the N-terminal end of the S2 sequence encompassing residue R1-7. Peptides R35-50 and R91-106 represented two minor antigenic epitopes. Antisera to two additional peptides corresponding to residues R134-149 and R186-199 recognized the S2 subunit only by Western blotting (immunoblotting). Only antiserum raised against peptide R91-106 also recognized the S3 subunit by Western blotting, indicating a marked antigenic and probably also structural difference between the two highly homologous subunits.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aktories K., Jakobs K. H., Robbel L. Further contributions to an improved pertussis vaccine: I. Molecular mechanisms of pertussis toxin. Behring Inst Mitt. 1984 Nov;(76):106–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capiau C., Petre J., Van Damme J., Puype M., Vandekerckhove J. Protein-chemical analysis of pertussis toxin reveals homology between the subunits S2 and S3, between S1 and the A chains of enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli and identifies S2 as the haptoglobin-binding subunit. FEBS Lett. 1986 Aug 18;204(2):336–340. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80839-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):577–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser E., Colescott R. L., Bossinger C. D., Cook P. I. Color test for detection of free terminal amino groups in the solid-phase synthesis of peptides. Anal Biochem. 1970 Apr;34(2):595–598. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locht C., Barstad P. A., Coligan J. E., Mayer L., Munoz J. J., Smith S. G., Keith J. M. Molecular cloning of pertussis toxin genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 25;14(8):3251–3261. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.8.3251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locht C., Keith J. M. Pertussis toxin gene: nucleotide sequence and genetic organization. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1258–1264. doi: 10.1126/science.3704651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montecucco C., Tomasi M., Schiavo G., Rappuoli R. Hydrophobic photolabelling of pertussis toxin subunits interacting with lipids. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 6;194(2):301–304. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller A. S., Leeuwenburg J., Pratt D. S. Pertussis: epidemiology and control. Bull World Health Organ. 1986;64(2):321–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz J. J., Peacock M. G., Hadlow W. J. Anaphylaxis or so-called encephalopathy in mice sensitized to an antigen with the aid of pertussigen (pertussis toxin). Infect Immun. 1987 Apr;55(4):1004–1008. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.4.1004-1008.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia A., Perugini M., Franzini C., Casagli M. C., Borri M. G., Antoni G., Almoni M., Neri P., Ratti G., Rappuoli R. Cloning and sequencing of the pertussis toxin genes: operon structure and gene duplication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4631–4635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda M., Cowell J. L., Burstyn D. G., Manclark C. R. Protective activities of the filamentous hemagglutinin and the lymphocytosis-promoting factor of Bordetella pertussis in mice. J Infect Dis. 1984 Dec;150(6):823–833. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.6.823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman M., Furman B. L., Wardlaw A. C. Bordetella pertussis respiratory tract infection in the mouse: pathophysiological responses. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jul;142(1):56–66. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.1.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman M. Pertussis toxin: the cause of the harmful effects and prolonged immunity of whooping cough. A hypothesis. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 May-Jun;1(3):401–412. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.3.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman M. The concept of pertussis as a toxin-mediated disease. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1984 Sep-Oct;3(5):467–486. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198409000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A., Irons L. I., Ashworth L. A. Pertussis vaccine: present status and future prospects. Vaccine. 1985 Mar;3(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(85)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson B., Suzuki E. Conformational properties of amino acid residues in globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1976 Nov 5;107(3):327–356. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Sato Y. Bordetella pertussis infection in mice: correlation of specific antibodies against two antigens, pertussis toxin, and filamentous hemagglutinin with mouse protectivity in an intracerebral or aerosol challenge system. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):415–421. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.415-421.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman L., Sriram S., Adelman N. E., Zamvil S., McDevitt H. O., Urich H. Murine model for pertussis vaccine encephalopathy: linkage to H-2. Nature. 1982 Oct 21;299(5885):738–740. doi: 10.1038/299738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman L., Weiss A., Adelman N., Lim M., Zuniga R., Oehlert J., Hewlett E., Falkow S. Pertussis toxin is required for pertussis vaccine encephalopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8733–8736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura M., Nogimori K., Murai S., Yajima M., Ito K., Katada T., Ui M., Ishii S. Subunit structure of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, in conformity with the A-B model. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5516–5522. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura M., Nogimori K., Yajima M., Ase K., Ui M. A role of the B-oligomer moiety of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, in development of the biological effects on intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6756–6761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L. Virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:661–686. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.003305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





